Abstract
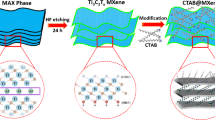
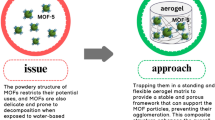
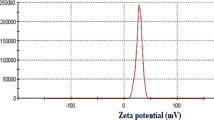
Ultralight, water-stable adsorbents that deliver both dye removal and sustained antibacterial activity are increasingly sought for decentralized water purification. We report a scalable strategy to integrate Ti₃C₂Tₓ MXene with chitosan (CS) into three-dimensional, compressible aerogels (MCA) that couple high adsorption capacity for the anionic azo dyes methyl orange (MO) and Eriochrome Black T (EBT) with strong, reusable suppression of Escherichia coli and Enterococcus faecalis. At an optimal 12 wt% MXene loading (MCA@12), the aerogel exhibited ultralow density (~0.027 g cm⁻³), high elastic recoverability, seven-fold higher BET surface area than CS-only aerogels, and remarkable long-term aqueous stability (≥2160 h). In batch adsorption, MCA@12 achieved a maximum MO capacity of ~523 mg g⁻¹ (Langmuir fit) and retained ~89% capacity over five cycles. Adsorption was faster under mildly acidic conditions due to enhanced protonation of chitosan’s amine groups and electrostatic attraction with anionic dyes. Under continuous-flow filtration, MCA@12 sustained ~92% bacterial clearance and ~93% MO removal, maintaining performance over six reuse cycles. These findings outline a clear design strategy where low MXene content embedded in a chitosan-rich, biodegradable matrix yields a mechanically robust, water-stable, and multifunctional aerogel—a cost-effective and modular platform for practical water purification.

Similar content being viewed by others
Data availability
The authors declare that the data supporting the findings of this study are available within the paper and its Supplementary Information files.
References
Mumbi, A. W. & Watanabe, T. Cost estimations of water pollution for the adoption of suitable water treatment technology. Sustainability 14, 649 (2022).
Lin, L., Yang, H. & Xu, X. Effects of water pollution on human health and disease heterogeneity: a review. Front. Environ. Sci. 10, 1–16 (2022).
Tortajada, C. Contributions of recycled wastewater to clean water and sanitation sustainable development goals. npj Clean Water 3, 22 (2020).
Asranudin et al. Adsorption and biodegradation of the azo dye methyl orange using Ralstonia pickettii immobilized in polyvinyl alcohol (PVA)–alginate–hectorite beads (BHec-RP). RSC Adv. 14, 18277–18290 (2024).
Baena-Baldiris, D., Montes-Robledo, A. & Baldiris-Avila, R. Franconibacter sp., 1MS: a new strain in decolorization and degradation of azo dyes Ponceau S Red and Methyl Orange. ACS Omega 5, 28146–28157 (2020).
Ahmed, M. et al. Recent developments in hazardous pollutants removal from wastewater and water reuse within a circular economy. npj Clean Water, 5 https://doi.org/10.1038/s41545-022-00154-5 (2022).
Tanure, N. R. M. et al. Removal of a model reactive azo dye from aqueous solution by a bioadsorbent in batch and fixed-bed column modes: application of the developed technology to a textile wastewater. Water Resour. Ind. 32, 100261 https://doi.org/10.1016/j.wri.2024.100261 (2024).
Chauhan, P. S. et al. Combined advanced oxidation dye-wastewater treatment plant: design and development with data-driven predictive performance modeling. npj Clean. Water 7, 15 (2024).
Good, C. R., White, A., Brandao, J. & Jackson, S. Endotoxin, a novel biomarker for the rapid risk assessment of faecal contamination of coastal and transitional waters. J. Water Health 22, 1044–1052 (2024).
Alhabeb, M. et al. Guidelines for synthesis and processing of two-dimensional titanium carbide (Ti3C2Tx MXene). Chem. Mater. 29, 7633–7644 (2017).
Oyehan, T. A. et al. MXenes: synthesis, properties, and applications for sustainable energy and environment. Appl. Mater. Today 35, 101993 (2023).
Sun, P. F. et al. Interlayered forward osmosis membranes with Ti3C2Tx MXene and carbon nanotubes for enhanced municipal wastewater concentration. Environ. Sci. Technol. 55, 13219–13230 (2021).
Lukatskaya, M. R. et al. Cation intercalation and high volumetric capacitance of two-dimensional titanium carbide. Science 341, 1502–1505 (2013).
Rosenkranz, A., Righi, M. C., Sumant, A. V., Anasori, B. & Mochalin, V. N. Perspectives of 2D MXene Tribology. Adv. Mater. 35, 2207757 (2023).
Keneshbekova, A. et al. MXene/carbon nanocomposites for water treatment. Membranes 14 https://doi.org/10.3390/membranes14090184 (2024).
Ding, L. et al. A Two-dimensional lamellar membrane: MXene nanosheet stacks. Angew. Chem., Int. Ed. 56, 1825–1829 (2017).
Ding, L. et al. Effective ion sieving with Ti3C2Tx MXene membranes for production of drinking water from seawater. Nat. Sustain. 3, 296 (2020).
Byun, S. et al. Photothermal-assisted cleaning and reusability of MXene-MWCNT membranes for efficient oil–water separation. npj Clean. Water 8, 54 (2025).
Wang, J. et al. A regularly channeled lamellar membrane for unparalleled water and organics permeation. Angew. Chem. Int. Ed. Engl. 57, 6814–6818 (2018).
Guzel Kaya, G., Aznar, E., Deveci, H. & Martinez-Manez, R. Aerogels as promising materials for antibacterial applications: a mini-review. Biomater. Sci. 9, 7034–7048 (2021).
Su, H. et al. Biobased amphoteric aerogel with core-shell structure for the hierarchically efficient adsorption of anionic and cationic dyes. J. Hazard. Mater. 480, 136235 (2024).
Krishna Kumar, A. S. et al. Heavy metal and organic dye removal via a hybrid porous hexagonal boron nitride-based magnetic aerogel. npj Clean Water 5 https://doi.org/10.1038/s41545-022-00175-0 (2022).
Yang, J., Shojaei, S. & Shojaei, S. Removal of drug and dye from aqueous solutions by graphene oxide: adsorption studies and chemometrics methods. npj Clean. Water 5, 5 (2022).
Zhang, Y. et al. Three-dimensional MXene-based functional materials for water treatment: preparation, functional tailoring, and applications. Ind. Eng. Chem. Res. 62, 7297–7335 (2023).
Qiao, J. et al. Dual cross-linked magnetic Mxene aerogel with high strength and durability enables multifunctionality. Adv. Funct. Mater. 34 https://doi.org/10.1002/adfm.202401687 (2024).
Zhang, X., Liu, X., Dong, S., Yang, J. & Liu, Y. Template-free synthesized 3D macroporous MXene with superior performance for supercapacitors. Appl. Mater. Today 16, 315–321 (2019).
Bian, R. et al. Ultralight MXene-based aerogels with high electromagnetic interference shielding performance. J. Mater. Chem. C. 7, 474–478 (2019).
Gutiérrez, M. C., Ferrer, M. L. & del Monte, F. Ice-templated materials: sophisticated structures exhibiting enhanced functionalities obtained after unidirectional freezing and ice-segregation-induced self-assembly. Chem. Mater. 20, 634–648 (2008).
Yang, C. et al. 3D Printed template-assisted assembly of additive-free Ti3C2Tx MXene microlattices with customized structures toward high areal capacitance. ACS Nano 16, 2699–2710 (2022).
Tetik, H. et al. 3D printed MXene Aerogels with truly 3D macrostructure and highly engineered microstructure for enhanced electrical and electrochemical performance. Adv. Mater. 34, 2104980 (2022).
Xiong, Y. et al. A 3D titanate aerogel with cellulose as the adsorption-aggregator for highly efficient water purification. J. Mater. Chem. A 5, 5813–5819 (2017).
Li, L., Zhang, M., Zhang, X. & Zhang, Z. New Ti3 C2 aerogel as promising negative electrode materials for asymmetric supercapacitors. J. Power Sour. 364, 234–241 (2017).
Chen, S. et al. Multifunctional super-hydrophilic Mxene/biomass composite aerogel evaporator for efficient solar-driven desalination and wastewater treatment. Small 20, 2400603 (2024).
Li, W. et al. Synchronization of Ti3C2 MXene/Fe3+ with sodium persulfate for the degradation of reactive dyes. npj Clean. Water 7, 34 (2024).
Shu, D. et al. Enhanced degradation and recycling of reactive dye wastewater using cobalt loaded MXene catalysts. npj Clean. Water 7, 88 (2024).
Ghidiu, M., Lukatskaya, M. R., Zhao, M.-Q., Gogotsi, Y. & Barsoum, M. W. Conductive two-dimensional titanium carbide ‘clay’ with high volumetric capacitance. Nature 516, 78–81 (2014).
Huang, L., Ding, L., Caro, J., & Wang, H. MXene-based membranes for drinking water production. Angew. Chem. Int. Ed. 62 https://doi.org/10.1002/anie.202311138 (2023).
Meskher, H. et al. Recent advances in applications of MXenes for desalination, water purification and as an antibacterial: a review. Environ. Sci. Nano 12, 1012–1036 (2025).
Zaed, M. A., Tan, K. H., Saidur, R., Abdullah, N. & Pandey, A. K. Invited viewpoint: pathways to low-cost MXene synthesis. J. Mater. Sci. 59, 7575–7594 (2024).
Zaed, M. A. et al. Cost analysis of MXene for low-cost production, and pinpointing of its economic footprint. Open Ceram. 17, 100526 (2024).
Karthikeyan, P. et al. Effective removal of Cr(VI) and methyl orange from the aqueous environment using two-dimensional (2D) Ti3C2Tx MXene nanosheets. Ceram. Int. 47, 3692–3698 (2021).
Song, G. et al. Adsorption of anionic dyes from aqueous solutions by a novel CTAB/MXene/carbon nanotube composite: characterization, experiments, and theoretical analysis. Appl. Surf. Sci. 661, 160036 https://doi.org/10.1016/j.apsusc.2024.160036 (2024).
Najibikhah, P. & Rahbar-Kelishami, A. Preparation of cationic surfactant modified two-dimensional (2D) multi-layered Ti3C2Tx MXene for methyl orange removal from aqueous solution: kinetic, equilibrium, and adsorption mechanisms. Chemosphere 350, 141058 (2024).
Riofrio, A., Alcivar, T. & Baykara, H. Environmental and economic viability of chitosan production in Guayas-Ecuador: a robust investment and life cycle analysis. ACS Omega 6, 23038–23051 (2021).
Huang, P. et al. Dye-mediated interactions in chitosan-based polyelectrolyte/organoclay hybrids for enhanced adsorption of industrial dyes. ACS Appl. Mater. Interfaces 11, 11961–11969 (2019).
Abo Elsoud, M. M., & El Kady, E. M. Current trends in fungal biosynthesis of chitin and chitosan. Bull. Natl. Res. Cent. 43 https://doi.org/10.1186/s42269-019-0105-y (2019).
Jin, W., Nan, J., Chen, M., Song, L. & Wu, F. Superior performance of novel chitosan-based flocculants in decolorization of anionic dyes: responses of flocculation performance to flocculant molecular structures and hydrophobicity and flocculation mechanism. J. Hazard. Mater. 452, 131273 (2023).
Yadav, H., Malviya, R., & Kaushik, N. Chitosan in biomedicine: a comprehensive review of recent developments. Carbohydr. Polym. Tech. 8 https://doi.org/10.1016/j.carpta.2024.100551 (2024).
Korniienko, V. et al. Antibacterial potential and biocompatibility of chitosan/polycaprolactone nanofibrous membranes incorporated with silver nanoparticles. Polymers 16 https://doi.org/10.3390/polym16121729 (2024).
Zafar, S., Nayak, V., Mahapatra, S. N. & Lochab, B. Benzoxazine-sulfur-chitosan based freestanding beads: synthesis, characterization, stability, and removal of mercury and oil. Sep. Purif. Technol. 320, 124063 (2023).
Roas-Escalona, N., Becquart, F., Delair, T. & Dutertre, F. Chitosan-based hydrogels: influence of crosslinking strategy on rheological properties. Carbohydr. Polym. 341, 122329 (2024).
Shekhirev, M., Shuck, C. E., Sarycheva, A., & Gogotsi, Y. Characterization of MXenes at every step, from their precursors to single flakes and assembled films. Prog. Mater. Sci. 120 https://doi.org/10.1016/j.pmatsci.2020.100757 (2021).
Sarycheva, A. et al. Two-dimensional titanium carbide (Mxene) as surface-enhanced raman scattering substrate. J. Phys. Chem. C. 121, 19983 (2017).
Hu, T. et al. Vibrational properties of Ti3C2 and Ti3C2T2 (T = O, F, OH) monosheets by first-principles calculations: a comparative study. Phys. Chem. Chem. Phys. 17, 9997–10003 (2015).
Choudhury, S. et al. A surface modified laser-induced graphene based flexible biosensor for multiplexed sweat analysis. J. Mater. Chem. B 13, 274–287 (2025).
Zhang, J. et al. Applications of X-ray-based characterization in MXene research. Small Methods 7, e2201527 (2023).
Gartner, C. et al. Interplay between structure and dynamics in chitosan films investigated with solid-state NMR, dynamic mechanical analysis, and X-ray diffraction. Biomacromolecules 12, 1380–1386 (2011).
Ferrara, C. et al. The missing piece: the structure of the T3C2Tx Mxene and its behavior as negative electrode in sodium ion batteries. Nano Lett. 21, 8290–8297 (2021).
Carey, M. & Barsoum, M. W. MXene polymer nanocomposites: a review. Mater. Today Adv. 9, 100120 (2021).
Guibal, E. Interactions of metal ions with chitosan-based sorbents: a review. Sep. Purif. Technol. 38, 43–74 (2004).
Deshmukh, S., Ghosh, K., Pykal, M., Otyepka, M. & Pumera, M. Laser-induced Mxene-functionalized graphene nanoarchitectonics-based microsupercapacitor for health monitoring application. ACS Nano 17, 20537–20550 (2023).
Kauppinen, J. K., Moffatt, D. J., Mantsch, H. H. & Cameron, D. G. Fourier transforms in the computation of self-deconvoluted and first-order derivative spectra of overlapped band contours. Anal. Chem. 53, 1454–1457 (1981).
Kamysbayev, V. et al. Covalent surface modifications and superconductivity of two-dimensional metal carbide MXenes. Science 369, 979–983 (2020).
Olivieri, G. et al. Intermolecular hydrogen bonding and molecular orbital distortion in 4-hydroxycyanobenzene investigated by X-ray spectroscopy. J. Phys. Chem. C. 119, 121–129 (2015).
Pazniak, A. et al. Ti3C2Tx MXene characterization produced from SHS-ground Ti3AlC2. Mater. Des. 183, 108143 (2019).
Wang, X. Y. et al. Enhancing the chemical stability of Mxene through synergy of hydrogen bond and coordination bond in aqueous solution. Small Methods 7, 2201694 (2023).
Niranjan, R., Zafar, S., Lochab, B. & Priyadarshini, R. Synthesis and characterization of sulfur and sulfur-selenium nanoparticles loaded on reduced graphene oxide and their antibacterial activity against gram-positive pathogeathogens. Nanomaterials 12, 191 (2022).
Acknowledgements
This work was supported by Shiv Nadar Foundation and the Indian Council of Medical Research (ICMR) grant (35/10/2022-NANO/BMS). S.N.M., S.Z., J.K., and R.N. would like to acknowledge the instrumentation facility and fellowship from the Shiv Nadar (Institution of Eminence) University, Delhi-NCR, and ICMR-SRF, respectively. We thank Dr. Nisha Yadav for performing thermal analysis and GPC measurements.
Funding
Open access funding provided by Shiv Nadar University.
Author information
Authors and Affiliations
Contributions
S.N.M. prepared materials, performed characterization and interpretation, conducted data analysis, and contributed to drafting and editing the manuscript. S.Z. prepared materials, performed characterization and interpretation, and conducted data analysis. R.N. carried out antibacterial studies, processed experimental data, and assisted in preparing the manuscript section related to bacterial work. J.K. contributed to antibacterial studies, processed experimental data, and assisted in manuscript preparation. R.P. supervised antibacterial work and contributed to writing and reviewing that section. B.L. secured funding, conceived the research concept, designed the experimental protocol, supervised the overall work, and contributed to writing the manuscript.
Corresponding author
Ethics declarations
Competing interests
The authors declare no competing interests.
Additional information
Publisher’s note Springer Nature remains neutral with regard to jurisdictional claims in published maps and institutional affiliations.
Supplementary information
Rights and permissions
Open Access This article is licensed under a Creative Commons Attribution-NonCommercial-NoDerivatives 4.0 International License, which permits any non-commercial use, sharing, distribution and reproduction in any medium or format, as long as you give appropriate credit to the original author(s) and the source, provide a link to the Creative Commons licence, and indicate if you modified the licensed material. You do not have permission under this licence to share adapted material derived from this article or parts of it. The images or other third party material in this article are included in the article’s Creative Commons licence, unless indicated otherwise in a credit line to the material. If material is not included in the article’s Creative Commons licence and your intended use is not permitted by statutory regulation or exceeds the permitted use, you will need to obtain permission directly from the copyright holder. To view a copy of this licence, visit http://creativecommons.org/licenses/by-nc-nd/4.0/.
About this article
Cite this article
Mahapatra, S.N., Zafar, S., Niranjan, R. et al. Ultralight, mechanically robust, water stable MXene–chitosan aerogels for concurrent dye adsorption and antibacterial filtration at low MXene loading. npj Clean Water (2026). https://doi.org/10.1038/s41545-025-00551-6
Received:
Accepted:
Published:
DOI: https://doi.org/10.1038/s41545-025-00551-6