Abstract
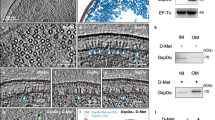
Secretin is a large outer-membrane channel found in secretion systems of Gram-negative bacteria, facilitating the last step for transfer of proteins into the extracellular environment. In the type II secretion system, a lipoprotein called pilotin is essential to bind and target its corresponding secretin to the outer membrane. However, there is only limited structural information available about the interaction and assembly of the pilotin–secretin complex. Here we report the first near-atomic-resolution structure of a full-length Vibrio-type pilotin–secretin (AspS–GspD) complex from enterotoxigenic Escherichia coli by cryo-electron microscopy, which reveals the detailed assembly mode of the full-length pilotin–secretin complex. The AspS subunits attach to the secretin channel surface with a 15:15 stoichiometric ratio to GspD subunits, and insert their amino terminus into the outer membrane. The AspS subunits interact with all three secondary structural elements of the S domain of GspD, including strong interaction with the carboxy-terminal α-helix and weak interactions with another two elements, an α-helix and a loop. These structural and biochemical details provide a deeper insight to pilotin–secretin interaction and their assembly mode.
This is a preview of subscription content, access via your institution
Access options
Access Nature and 54 other Nature Portfolio journals
Get Nature+, our best-value online-access subscription
$32.99 / 30 days
cancel any time
Subscribe to this journal
Receive 12 digital issues and online access to articles
$119.00 per year
only $9.92 per issue
Buy this article
- Purchase on SpringerLink
- Instant access to the full article PDF.
USD 39.95
Prices may be subject to local taxes which are calculated during checkout




Similar content being viewed by others
References
Costa, T. R. et al. Secretion systems in Gram-negative bacteria: structural and mechanistic insights. Nat. Rev. Microbiol. 13, 343–359 (2015).
Korotkov, K. V., Sandkvist, M. & Hol, W. G. The type II secretion system: biogenesis, molecular architecture and mechanism. Nat. Rev. Microbiol. 10, 336–351 (2012).
Yan, Z., Yin, M., Xu, D., Zhu, Y. & Li, X. Structural insights into the secretin translocation channel in the type II secretion system. Nat. Struct. Mol. Biol. 24, 177–183 (2017).
Filloux, A. The underlying mechanisms of type II protein secretion. Biochim Biophys. Acta 1694, 163–790 (2004).
Peabody, C. R. et al. Type II protein secretion and its relationship to bacterial type IV pili and archaeal flagella. Microbiology 149, 3051–3072 (2003).
Thanassi, D. G. & Hultgren, S. J. Multiple pathways allow protein secretion across the bacterial outer membrane. Curr. Opin. Cell Biol. 12, 420–430 (2000).
Viarre, V. et al. HxcQ liposecretin is self-piloted to the outer membrane by its N-terminal lipid anchor. J. Biol. Chem. 284, 33815–33823 (2009).
Bose, N. & Taylor, R. K. Identification of a TcpC-TcpQ outer membrane complex involved in the biogenesis of the toxin-coregulated pilus of Vibrio cholerae. J. Bacteriol. 187, 2225–2232 (2005).
Schmidt, S. A. et al. Structure-function analysis of BfpB, a secretin-like protein encoded by the bundle-forming-pilus operon of enteropathogenic Escherichia coli . J. Bacteriol. 183, 4848–4859 (2001).
Hu, N. T., Hung, M. N., Liao, C. T. & Lin, M. H. Subcellular location of XpsD, a protein required for extracellular protein secretion by Xanthomonas campestris pv. campestris. Microbiology 141(Pt 6), 1395–1406 (1995).
Korotkov, K. V., Gonen, T. & Hol, W. G. Secretins: dynamic channels for protein transport across membranes. Trends Biochem. Sci. 36, 433–443 (2011).
Strozen, T. G., Li, G. & Howard, S. P. YghG (GspSβ) is a novel pilot protein required for localization of the GspSβ type II secretion system secretin of enterotoxigenic Escherichia coli. Infect. Immun. 80, 2608–2622 (2012).
Koo, J., Burrows, L. L. & Howell, P. L. Decoding the roles of pilotins and accessory proteins in secretin escort services. FEMS Microbiol. Lett. 328, 1–12 (2012).
Collin, S., Guilvout, I., Nickerson, N. N. & Pugsley, A. P. Sorting of an integral outer membrane protein via the lipoprotein-specific Lol pathway and a dedicated lipoprotein pilotin. Mol. Microbiol. 80, 655–665 (2011).
Dunstan, R. A. et al. Assembly of the type II secretion system such as found in Vibrio cholerae depends on the novel Pilotin AspS. PLoS Pathog. 9, e1003117 (2013).
Gu, S., Rehman, S., Wang, X., Shevchik, V. E. & Pickersgill, R. W. Structural and functional insights into the pilotin-secretin complex of the type II secretion system. PLoS Pathog. 8, e1002531 (2012).
Nickerson, N. N. et al. Outer membrane targeting of secretin PulD protein relies on disordered domain recognition by a dedicated chaperone. J. Biol. Chem. 286, 38833–38843 (2011).
Tosi, T. et al. Pilotin-secretin recognition in the type II secretion system of Klebsiella oxytoca. Mol. Microbiol. 82, 1422–1432 (2011).
Rehman, S., Gu, S., Shevchik, V. E. & Pickersgill, R. W. Anatomy of secretin binding to the Dickeya dadantii type II secretion system pilotin. Acta Crystallogr D. Biol. Crystallogr 69, 1381–1386 (2013).
Okon, M. et al. Structural characterization of the type-III pilot-secretin complex from Shigella flexneri. Structure 16, 1544–1554 (2008).
Worrall, L. J. et al. Near-atomic-resolution cryo-EM analysis of the Salmonella T3S injectisome basal body. Nature 540, 597–601 (2016).
Das, D. et al. Crystal structure of a putative quorum sensing-regulated protein (PA3611) from the Pseudomonas-specific DUF4146 family. Proteins 82, 1086–1092 (2014).
Scheich, C., Kummel, D., Soumailakakis, D., Heinemann, U. & Bussow, K. Vectors for co-expression of an unrestricted number of proteins. Nucleic Acids Res. 35, e43 (2007).
Rueden, C. T. et al. ImageJ2: ImageJ for the next generation of scientific image data. BMC Bioinform. 18, 529 (2017).
Li, X., Zheng, S., Agard, D. A. & Cheng, Y. Asynchronous data acquisition and on-the-fly analysis of dose fractionated cryoEM images by UCSFImage. J. Struct. Biol. 192, 174–178 (2015).
Li, X. et al. Electron counting and beam-induced motion correction enable near-atomic-resolution single-particle cryo-EM. Nat. Methods 10, 584–590 (2013).
Mindell, J. A. & Grigorieff, N. Accurate determination of local defocus and specimen tilt in electron microscopy. J. Struct. Biol. 142, 334–347 (2003).
Scheres, S. H. Semi-automated selection of cryo-EM particles in RELION-1.3. J. Struct. Biol. 189, 114–122 (2015).
Scheres, S. H. RELION: implementation of a Bayesian approach to cryo-EM structure determination. J. Struct. Biol. 180, 519–530 (2012).
Scheres, S. H. Classification of structural heterogeneity by maximum-likelihood methods. Methods Enzymol. 482, 295–320 (2010).
Kucukelbir, A., Sigworth, F. J. & Tagare, H. D. Quantifying the local resolution of cryo-EM density maps. Nat. Methods 11, 63–65 (2014).
Shaikh, T. R. et al. SPIDER image processing for single-particle reconstruction of biological macromolecules from electron micrographs. Nat. Protoc. 3, 1941–1974 (2008).
Zheng, S. Q. et al. MotionCor2: anisotropic correction of beam-induced motion for improved cryo-electron microscopy. Nat. Methods 14, 331–332 (2017).
Rosenthal, P. B. & Henderson, R. Optimal determination of particle orientation, absolute hand, and contrast loss in single-particle electron cryomicroscopy. J. Mol. Biol. 333, 721–745 (2003).
Arnold, K., Bordoli, L., Kopp, J. & Schwede, T. The SWISS-MODEL workspace: a web-based environment for protein structure homology modelling. Bioinformatics 22, 195–201 (2006).
Pettersen, E. F. et al. UCSF Chimera—a visualization system for exploratory research and analysis. J. Comput. Chem. 25, 1605–1612 (2004).
Emsley, P., Lohkamp, B., Scott, W. G. & Cowtan, K. Features and development of Coot. Acta Crystallogr. D. Biol. Crystallogr. 66, 486–501 (2010).
Korotkov, K. V., Pardon, E., Steyaert, J. & Hol, W. G. Crystal structure of the N-terminal domain of the secretin GspD from ETEC determined with the assistance of a nanobody. Structure 17, 255–265 (2009).
Adams, P. D. et al. PHENIX: a comprehensive Python-based system for macromolecular structure solution. Acta Crystallogr D Biol Crystallogr 66, (213–221 (2010).
Larkin, M. A. et al. Clustal W and Clustal X version 2.0. Bioinformatics 23, 2947–2948 (2007).
Gouet, P., Robert, X. & Courcelle, E. ESPript/ENDscript: Extracting and rendering sequence and 3D information from atomic structures of proteins. Nucleic Acids Res. 31, 3320–3323 (2003).
The PyMOL Molecular Graphics System v.1.8. (Schrödinger, LLC, 2015).
Acknowledgements
This work was supported by funds from The National Key Research and Development Program (2016YFA0501102 and 2016YFA0501902 to X.L.), National Natural Science Foundation of China (31570730 to X.L.), Advanced Innovation Center for Structural Biology (to X.L.), Tsinghua-Peking Joint Center for Life Sciences (to X.L.) and One-Thousand Talent Program by the State Council of China (to X.L.). We thank C. Lin for providing assistance with protein preparation. We thank Tsinghua University Branch of the China National Center for Protein Sciences Beijing for providing facility support in protein preparation, cryo-electron microscopy and computation. We are grateful to Tsinghua-Nikon imaging center and Tsinghua Imaging Core Facility for providing technical support and to Yanli Zhang for assistance with confocal microscopy and image processing.
Author information
Authors and Affiliations
Contributions
M.Y., Z.Y. and X.L. designed all experiments. M.Y. and Z.Y. performed all the cryo-electron microscopy and biochemistry experiments. All authors contributed to the data analysis, manuscript preparation and revision.
Corresponding author
Ethics declarations
Competing interests
The authors declare no competing interests.
Additional information
Publisher’s note: Springer Nature remains neutral with regard to jurisdictional claims in published maps and institutional affiliations.
Supplementary information
Supplementary Information
Supplementary Figures 1–7, Supplementary Table 1.
Rights and permissions
About this article
Cite this article
Yin, M., Yan, Z. & Li, X. Structural insight into the assembly of the type II secretion system pilotin–secretin complex from enterotoxigenic Escherichia coli. Nat Microbiol 3, 581–587 (2018). https://doi.org/10.1038/s41564-018-0148-0
Received:
Accepted:
Published:
Version of record:
Issue date:
DOI: https://doi.org/10.1038/s41564-018-0148-0
This article is cited by
-
pTripleTREP – A vector for tightly controlled expression and purification of virulence factors in Staphylococcus aureus
Microbial Cell Factories (2025)
-
Structural insights into the secretin complex of a type IVb pilus system
Nature Communications (2025)
-
Membrane translocation process revealed by in situ structures of type II secretion system secretins
Nature Communications (2023)
-
Assembly mechanism of a Tad secretion system secretin-pilotin complex
Nature Communications (2023)
-
Analysis of diverse eukaryotes suggests the existence of an ancestral mitochondrial apparatus derived from the bacterial type II secretion system
Nature Communications (2021)