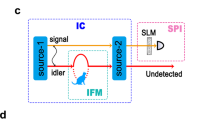
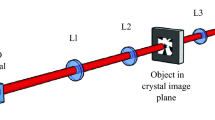
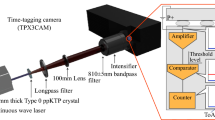
Abstract
Modern imaging technologies are widely based on classical principles of light or electromagnetic wave propagation. They can be remarkably sophisticated, with recent successes ranging from single-molecule microscopy to imaging far-distant galaxies. However, new imaging technologies based on quantum principles are gradually emerging. They can either surpass classical approaches or provide novel imaging capabilities that would not otherwise be possible. Here we provide an overview of the most recently developed quantum imaging systems, highlighting the nonclassical properties of sources, such as bright squeezed light, entangled photons and single-photon emitters that enable their functionality. We outline potential upcoming trends and the associated challenges, all driven by a central enquiry, which is to understand whether quantum light can make visible the invisible.
This is a preview of subscription content, access via your institution
Access options
Access Nature and 54 other Nature Portfolio journals
Get Nature+, our best-value online-access subscription
$32.99 / 30 days
cancel any time
Subscribe to this journal
Receive 12 print issues and online access
$259.00 per year
only $21.58 per issue
Buy this article
- Purchase on SpringerLink
- Instant access to the full article PDF.
USD 39.95
Prices may be subject to local taxes which are calculated during checkout




Similar content being viewed by others
References
Lupo, C. & Pirandola, S. Ultimate precision bound of quantum and subwavelength imaging. Phys. Rev. Lett. 117, 190802 (2016).
Giovannetti, V., Lloyd, S. & Maccone, L. Advances in quantum metrology. Nat. Photon. 5, 222–229 (2011).
Casacio, C. A. et al. Quantum-enhanced nonlinear microscopy. Nature 594, 201–206 (2021).
Tenne, R. et al. Super-resolution enhancement by quantum image scanning microscopy. Nat. Photon. 13, 116–122 (2019).
Kviatkovsky, I., Chrzanowski, H. M., Avery, E. G., Bartolomaeus, H. & Ramelow, S. Microscopy with undetected photons in the mid-infrared. Sci. Adv. 6, eabd0264 (2020).
Lloyd, S. Enhanced sensitivity of photodetection via quantum illumination. Science 321, 1463–1465 (2008).
Boto, A. N. et al. Quantum interferometric optical lithography: exploiting entanglement to beat the diffraction limit. Phys. Rev. Lett. 85, 2733–2736 (2000).
Crawford, J. et al. Towards quantum telescopes: demonstration of a two-photon interferometer for precision astrometry. Opt. Express 31, 44246–44258 (2023).
Kolobov, M. I. Quantum Imaging (Springer, 2007).
Genovese, M. Real applications of quantum imaging. J. Opt. 18, 073002 (2016).
Moreau, P.-A., Toninelli, E., Gregory, T. & Padgett, M. J. Imaging with quantum states of light. Nat. Rev. Phys. 1, 367–380 (2019).
Gatti, A., Brambilla, E. & Lugiato, L. Quantum imaging. Prog. Opt. 51, 251–348 (2008).
Gilaberte Basset, M. et al. Perspectives for applications of quantum imaging. Laser Photon. Rev. 13, 1900097 (2019).
Magaña-Loaiza, O. S. & Boyd, R. W. Quantum imaging and information. Rep. Prog. Phys. 82, 124401 (2019).
Shih, Y. Quantum imaging. IEEE J. Select. Top. Quantum Electron. 13, 1016–1030 (2007).
Lubin, G., Oron, D., Rossman, U., Tenne, R. & Yallapragada, V. J. Photon correlations in spectroscopy and microscopy. ACS Photonics 9, 2891–2904 (2022).
Moodley, C. & Forbes, A. Advances in quantum imaging with machine intelligence. Laser Photon. Rev. https://doi.org/10.1002/lpor.202300939 (2024).
Cramér, H. Mathematical Methods of Statistics Vol. 43 (Princeton Univ. Press, 1999).
Rao, C. R. in Mathematical Proceedings of the Cambridge Philosophical Society Vol. 43, 280–283 (Cambridge Univ. Press, 1947).
Caves, C. M. Quantum-mechanical noise in an interferometer. Phys. Rev. D 23, 1693–1708 (1981).
Helstrom, C. W. Quantum detection and estimation theory. J. Stat. Phys. 1, 231–252 (1969).
Braunstein, S. L. & Caves, C. M. Statistical distance and the geometry of quantum states. Phys. Rev. Lett. 72, 3439–3443 (1994).
Pezze, L., Smerzi, A., Oberthaler, M. K., Schmied, R. & Treutlein, P. Quantum metrology with nonclassical states of atomic ensembles. Rev. Mod. Phys. 90, 035005 (2018).
Fabre, C. & Treps, N. Modes and states in quantum optics. Rev. Mod. Phys. 92, 035005 (2020).
Gessner, M., Treps, N. & Fabre, C. Estimation of a parameter encoded in the modal structure of a light beam: a quantum theory. Optica 10, 996–999 (2023).
Gessner, M., Fabre, C. & Treps, N. Superresolution limits from measurement crosstalk. Phys. Rev. Lett. 125, 100501 (2020).
Pinel, O. et al. Ultimate sensitivity of precision measurements with intense gaussian quantum light: a multimodal approach. Phys. Rev. A 85, 010101 (2012).
Treps, N. et al. A quantum laser pointer. Science 301, 940–943 (2003).
Tsang, M., Nair, R. & Lu, X.-M. Quantum theory of superresolution for two incoherent optical point sources. Phys. Rev. X 6, 031033 (2016).
Boucher, P., Fabre, C., Labroille, G. & Treps, N. Spatial optical mode demultiplexing as a practical tool for optimal transverse distance estimation. Optica 7, 1621–1626 (2020).
Santamaria, L., Pallotti, D., de Cumis, M. S., Dequal, D. & Lupo, C. Spatial-mode demultiplexing for enhanced intensity and distance measurement. Opt. Express 31, 33930–33944 (2023).
Rouvière, C. et al. Ultra-sensitive separation estimation of optical sources. Optica 11, 166–170 (2024).
Ansari, V. et al. Achieving the ultimate quantum timing resolution. PRX Quantum 2, 010301 (2021).
Tan, X.-J. et al. Quantum-inspired superresolution for incoherent imaging. Optica 10, 1189–1194 (2023).
Bowen, W. P., Schnabel, R., Treps, N., Bachor, H. & Lam, P. K. Recovery of continuous wave squeezing at low frequencies. J. Opt. B Quantum Semiclass. Opt. 4, 421–424 (2002).
McCormick, C., Boyer, V., Arimondo, E. & Lett, P. Strong relative intensity squeezing by four-wave mixing in rubidium vapor. Opt. Lett. 32, 178–180 (2007).
Harry, G. M. et al. Advanced LIGO: the next generation of gravitational wave detectors. Class. Quantum Grav. 27, 084006 (2010).
Dwyer, S. E., Mansell, G. L. & McCuller, L. Squeezing in gravitational wave detectors. Galaxies 10, 46 (2022).
Taylor, M. A. & Bowen, W. P. Quantum metrology and its application in biology. Phys. Rep. 615, 1–59 (2016).
Vahlbruch, H., Mehmet, M., Danzmann, K. & Schnabel, R. Detection of 15-dB squeezed states of light and their application for the absolute calibration of photoelectric quantum efficiency. Phys. Rev. Lett. 117, 110801 (2016).
Lawrie, B. J., Lett, P. D., Marino, A. M. & Pooser, R. C. Quantum sensing with squeezed light. ACS Photonics 6, 1307–1318 (2019).
Taylor, M. A. et al. Biological measurement beyond the quantum limit. Nat. Photon. 7, 229–233 (2013).
Taylor, M. A. et al. Subdiffraction-limited quantum imaging within a living cell. Phys. Rev. X 4, 011017 (2014).
Pooser, R. et al. Truncated nonlinear interferometry for quantum-enhanced atomic force microscopy. Phys. Rev. Lett. 124, 230504 (2020).
Dowran, M., Kumar, A., Lawrie, B. J., Pooser, R. C. & Marino, A. M. Quantum-enhanced plasmonic sensing. Optica 5, 628–633 (2018).
Pooser, R. C. & Lawrie, B. Plasmonic trace sensing below the photon shot noise limit. ACS Photonics 3, 8–13 (2016).
de Andrade, R. B. et al. Quantum-enhanced continuous-wave stimulated Raman scattering spectroscopy. Optica 7, 470–475 (2020).
Xu, Z. et al. Stimulated Raman scattering spectroscopy with quantum-enhanced balanced detection. Opt. Express 30, 18589–18598 (2022).
Xu, Z. et al. Quantum-enhanced stimulated Raman scattering microscopy in a high-power regime. Opt. Lett. 47, 5829–5832 (2022).
Xu, Z. et al. Dual-polarization quantum-enhanced stimulated Raman scattering microscopy. Appl. Phys. Lett 123, 024006 (2023).
Li, T., Li, F., Liu, X., Yakovlev, V. V. & Agarwal, G. S. Quantum-enhanced stimulated brillouin scattering spectroscopy and imaging. Optica 9, 959–964 (2022).
Cheng, J.-X. & Xie, X. S. Vibrational spectroscopic imaging of living systems: an emerging platform for biology and medicine. Science 350, aaa8870 (2015).
Camp Jr, C. H. & Cicerone, M. T. Chemically sensitive bioimaging with coherent Raman scattering. Nat. Photon. 9, 295–305 (2015).
Fu, Y., Wang, H., Shi, R. & Cheng, J.-X. Characterization of photodamage in coherent anti-Stokes Raman scattering microscopy. Opt. Express 14, 3942–3951 (2006).
Burnham, D. C. & Weinberg, D. L. Observation of simultaneity in parametric production of optical photon pairs. Phys. Rev. Lett. 25, 84–87 (1970).
Brida, G., Genovese, M. & Ruo Berchera, I. Experimental realization of sub-shot-noise quantum imaging. Nat. Photon. 4, 227–230 (2010).
Samantaray, N., Ruo-Berchera, I., Meda, A. & Genovese, M. Realization of the first sub-shot-noise wide field microscope. Light Sci. Appl. 6, e17005 (2017).
Ortolano, G. et al. Quantum enhanced non-interferometric quantitative phase imaging. Light Sci. Appl. 12, 171 (2023).
Madonini, F., Severini, F., Zappa, F. & Villa, F. Single photon avalanche diode arrays for quantum imaging and microscopy. Adv. Quantum Technol. 4, 2100005 (2021).
Vidyapin, V., Zhang, Y., England, D. & Sussman, B. Characterisation of a single photon event camera for quantum imaging. Sci. Rep. 13, 1009 (2023).
Giovannetti, V., Lloyd, S., Maccone, L. & Shapiro, J. H. Sub-Rayleigh-diffraction-bound quantum imaging. Phys. Rev. A 79, 013827 (2009).
Reichert, M., Defienne, H. & Fleischer, J. W. Massively parallel coincidence counting of high-dimensional entangled states. Sci. Rep. 8, 7925 (2018).
Toninelli, E. et al. Resolution-enhanced quantum imaging by centroid estimation of biphotons. Optica 6, 347–353 (2019).
He, Z., Zhang, Y., Tong, X., Li, L. & Wang, L. V. Quantum microscopy of cells at the Heisenberg limit. Nat. Commun. 14, 2441 (2023).
D’Angelo, M., Chekhova, M. V. & Shih, Y. Two-photon diffraction and quantum lithography. Phys. Rev. Lett. 87, 013602 (2001).
Unternährer, M., Bessire, B., Gasparini, L., Perenzoni, M. & Stefanov, A. Super-resolution quantum imaging at the Heisenberg limit. Optica 5, 1150–1154 (2018).
Ono, T., Okamoto, R. & Takeuchi, S. An entanglement-enhanced microscope. Nat. Commun. 4, 2426 (2013).
Israel, Y., Rosen, S. & Silberberg, Y. Supersensitive polarization microscopy using NOON states of light. Phys. Rev. Lett. 112, 103604 (2014).
Camphausen, R. et al. A quantum-enhanced wide-field phase imager. Sci. Adv. 7, eabj2155 (2021).
Defienne, H. et al. Pixel super-resolution with spatially entangled photons. Nat. Commun. 13, 3566 (2022).
Devaux, F., Mosset, A., Moreau, P.-A. & Lantz, E. Imaging spatiotemporal Hong-Ou-Mandel interference of biphoton states of extremely high Schmidt number. Phys. Rev. X 10, 031031 (2020).
Ndagano, B. et al. Quantum microscopy based on Hong–Ou–Mandel interference. Nat. Photon. 16, 384–389 (2022).
Lyons, A. et al. Attosecond-resolution Hong-Ou-Mandel interferometry. Sci. Adv. 4, eaap9416 (2018).
Lopaeva, E. et al. Experimental realization of quantum illumination. Phys. Rev. Lett. 110, 153603 (2013).
Defienne, H., Reichert, M., Fleischer, J. W. & Faccio, D. Quantum image distillation. Sci. Adv. 5, eaax0307 (2019).
Gregory, T., Moreau, P.-A., Toninelli, E. & Padgett, M. J. Imaging through noise with quantum illumination. Sci. Adv. 6, eaay2652 (2020).
Zhao, J. et al. Light detection and ranging with entangled photons. Opt. Express 30, 3675–3683 (2022).
England, D. G., Balaji, B. & Sussman, B. J. Quantum-enhanced standoff detection using correlated photon pairs. Phys. Rev. A 99, 023828 (2019).
Liu, H., Qin, C., Papangelakis, G., Iu, M. L. & Helmy, A. S. Compact all-fiber quantum-inspired LiDAR with over 100-dB noise rejection and single photon sensitivity. Nat. Commun. 14, 5344 (2023).
Zhang, Y. et al. Quantum imaging of biological organisms through spatial and polarization entanglement. Sci. Adv. 10, eadk1495 (2024).
Pittman, T. B., Shih, Y., Strekalov, D. & Sergienko, A. V. Optical imaging by means of two-photon quantum entanglement. Phys. Rev. A 52, R3429–R3432 (1995).
Devaux, F., Mosset, A., Bassignot, F. & Lantz, E. Quantum holography with biphotons of high schmidt number. Phys. Rev. A 99, 033854 (2019).
Defienne, H., Ndagano, B., Lyons, A. & Faccio, D. Polarization entanglement-enabled quantum holography. Nat. Phys. 17, 591–597 (2021).
Zhang, Y., England, D. & Sussman, B. Snapshot hyperspectral imaging with quantum correlated photons. Opt. Express 31, 2282–2291 (2023).
Hodgson, H., Zhang, Y., England, D. & Sussman, B. Reconfigurable phase contrast microscopy with correlated photon pairs. Appl. Phys. Lett 122, 034001 (2023).
Cameron, P. et al. Adaptive optical imaging with entangled photons. Science 383, 1142–1148 (2024).
Aspden, R. S. et al. Photon-sparse microscopy: visible light imaging using infrared illumination. Optica 2, 1049–1052 (2015).
Bornman, N. et al. Ghost imaging using entanglement-swapped photons. npj Quantum Inf. 5, 63 (2019).
Lemos, G. B. et al. Quantum imaging with undetected photons. Nature 512, 409–412 (2014).
Somaschi, N. et al. Near-optimal single-photon sources in the solid state. Nat. Photon. 10, 340–345 (2016).
Wang, L., Zou, X. & Mandel, L. Observation of induced coherence in two-photon downconversion. JOSA B 8, 978–980 (1991).
Cardoso, A. C. et al. Classical imaging with undetected light. Phys. Rev. A 97, 033827 (2018).
Lemos, G. B., Lahiri, M., Ramelow, S., Lapkiewicz, R. & Plick, W. N. Quantum imaging and metrology with undetected photons: tutorial. JOSA B 39, 2200–2228 (2022).
Lahiri, M., Hochrainer, A., Lapkiewicz, R., Lemos, G. B. & Zeilinger, A. Nonclassicality of induced coherence without induced emission. Phys. Rev. A 100, 053839 (2019).
Wang, L., Zou, X. & Mandel, L. Induced coherence without induced emission. Phys. Rev. A 44, 4614–4622 (1991).
Shapiro, J. H., Venkatraman, D. & Wong, F. N. C. Classical imaging with undetected photons. Sci. Rep. 5, 10329 (2015).
Kolobov, M. I., Giese, E., Lemieux, S., Fickler, R. & Boyd, R. W. Controlling induced coherence for quantum imaging. J. Opt. 19, 054003 (2017).
Viswanathan, B., Lemos, G. B. & Lahiri, M. Position correlation enabled quantum imaging with undetected photons. Opt. Lett. 46, 3496–3499 (2021).
Fuenzalida, J. et al. Resolution of quantum imaging with undetected photons. Quantum 6, 646 (2022).
Basset, M. G. et al. Experimental analysis of image resolution of quantum imaging with undetected light through position correlations. Phys. Rev. A 108, 052610 (2023).
Santos, E. A., Pertsch, T., Setzpfandt, F. & Saravi, S. Subdiffraction quantum imaging with undetected photons. Phys. Rev. Lett. 128, 173601 (2022).
Kviatkovsky, I., Chrzanowski, H. M. & Ramelow, S. Mid-infrared microscopy via position correlations of undetected photons. Opt. Express 30, 5916–5925 (2022).
Kutas, M. et al. Terahertz quantum sensing. Sci. Adv. 6, eaaz8065 (2020).
Töpfer, S. et al. Quantum holography with undetected light. Sci. Adv. 8, eabl4301 (2022).
Vallés, A., Jiménez, G., Salazar-Serrano, L. J. & Torres, J. P. Optical sectioning in induced coherence tomography with frequency-entangled photons. Phys. Rev. A 97, 023824 (2018).
Paterova, A. V., Yang, H., An, C., Kalashnikov, D. A. & Krivitsky, L. A. Tunable optical coherence tomography in the infrared range using visible photons. Quantum Sci. Technol. 3, 025008 (2018).
Vanselow, A. et al. Frequency-domain optical coherence tomography with undetected mid-infrared photons. Optica 7, 1729–1736 (2020).
Machado, G. J., Frascella, G., Torres, J. P. & Chekhova, M. V. Optical coherence tomography with a nonlinear interferometer in the high parametric gain regime. Appl. Phys. Lett 117, 094002 (2020).
Kalashnikov, D. A., Paterova, A. V., Kulik, S. P. & Krivitsky, L. A. Infrared spectroscopy with visible light. Nat. Photon. 10, 98–101 (2016).
Paterova, A. V., Maniam, S. M., Yang, H., Grenci, G. & Krivitsky, L. A. Hyperspectral infrared microscopy with visible light. Sci. Adv. 6, eabd0460 (2020).
Kaufmann, P., Chrzanowski, H. M., Vanselow, A. & Ramelow, S. Mid-IR spectroscopy with NIR grating spectrometers. Opt. Express 30, 5926–5936 (2022).
Placke, M. et al. Fourier-transform mid-IR hyperspectral imaging with undetected photons. In CLEO: Applications and Technology, AM2N–4 (Optica Publishing Group, 2023).
Hashimoto, K., Horoshko, D. B. & Chekhova, M. V. Broadband spectroscopy and interferometry with undetected photons at strong parametric amplification. Adv. Quantum Technol. https://doi.org/10.1002/qute.202300299 (2023).
Lindner, C. et al. High-sensitivity quantum sensing with pump-enhanced spontaneous parametric down-conversion. APL Photonics 8, 051301 (2023).
Pearce, E. et al. Practical quantum imaging with undetected photons. Opt. Continuum 2, 2386–2397 (2023).
Thiel, C. et al. Quantum imaging with incoherent photons. Phys. Rev. Lett. 99, 133603 (2007).
Oppel, S., Büttner, T., Kok, P. & von Zanthier, J. Superresolving multiphoton interferences with independent light sources. Phys. Rev. Lett. 109, 233603 (2012).
Dertinger, T., Colyer, R., Iyer, G., Weiss, S. & Enderlein, J. Fast, background-free, 3D super-resolution optical fluctuation imaging (SOFI). Proc. Natl Acad. Sci. USA 106, 22287–22292 (2009).
Schwartz, O. et al. Superresolution microscopy with quantum emitters. Nano Lett. 13, 5832–5836 (2013).
Israel, Y., Tenne, R., Oron, D. & Silberberg, Y. Quantum correlation enhanced super-resolution localization microscopy enabled by a fibre bundle camera. Nat. Commun. 8, 14786 (2017).
Monticone, D. G. et al. Beating the Abbe diffraction limit in confocal microscopy via nonclassical photon statistics. Phys. Rev. Lett. 113, 143602 (2014).
Lubin, G. et al. Quantum correlation measurement with single photon avalanche diode arrays. Opt. Express 27, 32863–32882 (2019).
Sroda, A. et al. SOFISM: super-resolution optical fluctuation image scanning microscopy. Optica 7, 1308–1316 (2020).
Classen, A., von Zanthier, J., Scully, M. O. & Agarwal, G. S. Superresolution via structured illumination quantum correlation microscopy. Optica 4, 580–587 (2017).
Liu, P. Resolution enhancement in random illumination microscopy using photon correlations. Appl. Opt. 61, 2910–2914 (2022).
Field, J. J. et al. Superresolved multiphoton microscopy with spatial frequency-modulated imaging. Proc. Natl Acad. Sci. USA 113, 6605–6610 (2016).
Weston, K. D. et al. Measuring the number of independent emitters in single-molecule fluorescence images and trajectories using coincident photons. Anal. Chem. 74, 5342–5349 (2002).
Wayne, M. et al. A 500 × 500 dual-gate SPAD imager with 100% temporal aperture and 1-ns minimum gate length for flim and phasor imaging applications. IEEE Trans. Electron Devices 69, 2865–2872 (2022).
Resta, G. V. et al. Gigahertz detection rates and dynamic photon-number resolution with superconducting nanowire arrays. Nano Lett. 23, 6018–6026 (2023).
Rossman, U. et al. Rapid quantum image scanning microscopy by joint sparse reconstruction. Optica 6, 1290–1296 (2019).
Kudyshev, Z. A. et al. Machine learning assisted quantum super-resolution microscopy. Nat. Commun. 14, 4828 (2023).
Treps, N. et al. Surpassing the standard quantum limit for optical imaging using nonclassical multimode light. Phys. Rev. Lett. 88, 203601 (2002).
Paterova, A. V., Yang, H., Toa, Z. S. & Krivitsky, L. A. Quantum imaging for the semiconductor industry. Appl. Phys. Lett 117, 054004 (2020).
Gilaberte Basset, M. et al. Video-rate imaging with undetected photons. Laser Photon. Rev. 15, 2000327 (2021).
Courme, B. et al. Quantifying high-dimensional spatial entanglement with a single-photon-sensitive time-stamping camera. Opt. Lett. 48, 3439–3442 (2023).
Lounis, B., Bechtel, H., Gerion, D., Alivisatos, P. & Moerner, W. Photon antibunching in single CdSe/ZnS quantum dot fluorescence. Chem. Phys. Lett. 329, 399–404 (2000).
Kocher, C. A. & Commins, E. D. Polarization correlation of photons emitted in an atomic cascade. Phys. Rev. Lett. 18, 575–577 (1967).
Kimble, H. J., Dagenais, M. & Mandel, L. Photon antibunching in resonance fluorescence. Phys. Rev. Lett. 39, 691–695 (1977).
Slusher, R., Hollberg, L., Yurke, B., Mertz, J. & Valley, J. Observation of squeezed states generated by four-wave mixing in an optical cavity. Phys. Rev. Lett. 55, 2409–2412 (1985).
Xiao, M., Wu, L.-A. & Kimble, H. J. Precision measurement beyond the shot-noise limit. Phys. Rev. Lett. 59, 278–281 (1987).
Kolobov, M. & Sokolov, I. Multimode squeezing, antibunching in space and noise-free optical images. Europhys. Lett. 15, 271 (1991).
Bennink, R. S., Bentley, S. J. & Boyd, R. W. ‘Two-photon’ coincidence imaging with a classical source. Phys. Rev. Lett. 89, 113601 (2002).
Valencia, A., Scarcelli, G., D’Angelo, M. & Shih, Y. Two-photon imaging with thermal light. Phys. Rev. Lett. 94, 063601 (2005).
Klyshko, D. Utilization of vacuum fluctuations as an optical brightness standard. Sov. J. Quantum Electron. 7, 591 (1977).
Hong, C. & Mandel, L. Experimental realization of a localized one-photon state. Phys. Rev. Lett. 56, 58–60 (1986).
Rarity, J., Tapster, P. & Jakeman, E. Observation of sub-poissonian light in parametric downconversion. Opt. Commun. 62, 201–206 (1987).
Laurat, J., Coudreau, T., Treps, N., Maître, A. & Fabre, C. Conditional preparation of a quantum state in the continuous variable regime: generation of a sub-Poissonian state from twin beams. Phys. Rev. Lett. 91, 213601 (2003).
Iskhakov, T. S. et al. Heralded source of bright multi-mode mesoscopic sub-Poissonian light. Opt. Lett. 41, 2149–2152 (2016).
Brambilla, E., Caspani, L., Jedrkiewicz, O., Lugiato, L. & Gatti, A. High-sensitivity imaging with multi-mode twin beams. Phys. Rev. A 77, 053807 (2008).
Acknowledgements
W.P.B. acknowledges support from the Air Force Office of Scientific Research under awards nos. FA9550-20-1-0391 and FA9550-22-1-0047, the Australian Research Council Centre of Excellence for Engineered Quantum Systems (EQUS, CE170100009) and the Australian Research Council Centre of Excellence in Quantum Biotechnology (QUBIC, CE230100021). H.D. acknowledges funding from an ERC Starting Grant (grant no. SQIMIC-101039375). G.B.L. acknowledges CAPES, CNPq and FAPERJ (JCNE, E-26/201.438/2021) from the John Templeton Foundation (grant no. 62424). S.R. acknowledges funding by the Federal Ministry of Education and Research (BMBF) under projects nos. 13N16384, 13N15402 and 13N15944, as well as by the Einstein Foundation Berlin (EJF-2021-681). D.F. is supported by the Royal Academy of Engineering through the Chairs in Emerging Technologies programme and the UKRI Frontier Research scheme.
Author information
Authors and Affiliations
Contributions
All authors contributed to writing the Review.
Corresponding author
Ethics declarations
Competing interests
The authors declare no competing interests.
Peer review
Peer review information
Nature Photonics thanks Markus Gräfe and the other, anonymous, reviewer(s) for their contribution to the peer review of this work.
Additional information
Publisher’s note Springer Nature remains neutral with regard to jurisdictional claims in published maps and institutional affiliations.
Rights and permissions
Springer Nature or its licensor (e.g. a society or other partner) holds exclusive rights to this article under a publishing agreement with the author(s) or other rightsholder(s); author self-archiving of the accepted manuscript version of this article is solely governed by the terms of such publishing agreement and applicable law.
About this article
Cite this article
Defienne, H., Bowen, W.P., Chekhova, M. et al. Advances in quantum imaging. Nat. Photon. 18, 1024–1036 (2024). https://doi.org/10.1038/s41566-024-01516-w
Received:
Accepted:
Published:
Version of record:
Issue date:
DOI: https://doi.org/10.1038/s41566-024-01516-w
This article is cited by
-
Quantum imaging using spatially entangled photon pairs from a nonlinear metasurface
eLight (2025)
-
From pixels to camera: scaling superconducting nanowire single-photon detectors for imaging at the quantum-limit
Nano Convergence (2025)
-
Structured light meets machine intelligence
eLight (2025)
-
Twisting entangled photons on a chip
Nature Photonics (2025)
-
Quantum imaging with ultra-thin metasurfaces
Light: Science & Applications (2025)