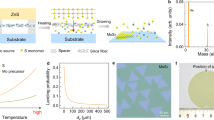
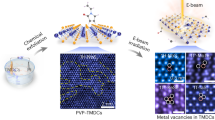
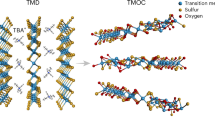
Abstract
Two-dimensional transition metal dichalcogenides (TMDCs) are highly anisotropic, layered semiconductors, with the general formula ME2 (M = metal, E = sulfur, selenium or tellurium). Much current research in this field focusses on TMDCs for catalysis and energy applications; they are also attracting great interest for next-generation transistor and optoelectronic devices. The latter high-tech applications place stringent requirements on the stoichiometry, crystallinity, morphology and electronic properties of monolayer and few-layer materials. As a solution-based process, wherein the material grows specifically on the electrode surface, electrodeposition offers great promise as a readily scalable, area-selective growth process. This Review explores the state-of-the-art for TMDC electrodeposition, highlighting how the choice of precursor (or precursors), solvent and electrode designs, with novel ‘device-ready’ electrode geometries, influence their morphologies and properties, thus enabling the direct growth of ultrathin, highly anisotropic 2D TMDCs and much scope for future advances.

This is a preview of subscription content, access via your institution
Access options
Access Nature and 54 other Nature Portfolio journals
Get Nature+, our best-value online-access subscription
$32.99 / 30 days
cancel any time
Subscribe to this journal
Receive 12 digital issues and online access to articles
$119.00 per year
only $9.92 per issue
Buy this article
- Purchase on SpringerLink
- Instant access to the full article PDF.
USD 39.95
Prices may be subject to local taxes which are calculated during checkout







Similar content being viewed by others
References
Chowdhury, T., Sadler, E. C. & Kempa, T. J. Progress and prospects in transition-metal dichalcogenide research beyond 2D. Chem. Rev. 120, 12563–12591 (2020).
Manzeli, S., Ovchinnikov, D., Pasquier, D., Yazyev, O. V. & Kis, A. 2D transition metal dichalcogenides. Nat. Rev. Mater. 2, 17033 (2017).
Yin, X. et al. Recent developments in 2D transition metal dichalcogenides: phase transition and applications of the (quasi-)metallic phases. Chem. Soc. Rev. 50, 10087–10115 (2021).
Choi, W. et al. Recent development of two-dimensional transition metal dichalcogenides and their applications. Mater. Today 20, 116–130 (2017).
Chhowalla, M. et al. The chemistry of two-dimensional layered transition metal dichalcogenide nanosheets. Nat. Chem. 5, 263–375 (2013).
Wang, Q. H., Kalantar-Zadeh, K., Kis, A., Coleman, J. N. & Strano, M. S. Electronics and optoelectronics of two-dimensional transition metal dichalcogenides. Nat. Nanotechnol. 7, 699–712 (2012).
Wu, F. et al. Vertical MoS2 transistors with sub-1-nm gate lengths. Nature 603, 259–264 (2022).
Lin, Z. et al. Solution-processable 2D semiconductors for high-performance large-area electronics. Nature 562, 254–258 (2018).
Xia, F., Wang, H., Xiao, D., Dubey, M. & Ramasubramaniam, A. Two-dimensional material nanophotonics. Nat. Photonics 8, 899–907 (2014).
Massicotte, M. et al. Picosecond photoresponse in van der Waals heterostructures. Nat. Nanotechnol. 11, 42–46 (2016).
Yu, W. J. et al. Highly efficient gate-tunable photocurrent generation in vertical heterostructures of layered materials. Nat. Nanotechnol. 8, 952–958 (2013).
Barua, S., Dutta, H. S., Gogoi, S., Devi, R. & Khan, R. Nanostructured MoS2-based advanced biosensors: a review. ACS Appl. Nano Mater. 1, 2–25 (2018).
Voiry, D., Yang, J. & Chhowalla, M. Recent strategies for improving the catalytic activity of 2D TMD nanosheets toward the hydrogen evolution reaction. Adv. Mater. 28, 6197–6206 (2016).
Yin, J. et al. Optimized metal chalcogenides for boosting water splitting. Adv. Sci. 7, 1903070 (2020).
Lei, Z., Zhan, J., Tang, L., Zhang, Y. & Wan, Y. Recent development of metallic (1T) phase of molybdenum disulfide for energy conversion and storage. Adv. Energy Mater. 8, 1703482 (2018).
Ma, Q. et al. 2D materials for all-solid-state lithium batteries. Adv. Mater. 34, 2108079 (2022).
Wang, Z. et al. Unveiling highly ambient-stable multilayered 1T-MoS2 towards all-solid-state flexible supercapacitors. J. Mater. Chem. A 7, 19152–19160 (2019).
Acerce, M., Voiry, D. & Chhowalla, M. Metallic 1T phase MoS2 nanosheets as supercapacitor electrode materials. Nat. Nanotechnol. 10, 313–318 (2015).
Nazif, K. N. et al. High-specific-power flexible transition metal dichalcogenide solar cells. Nat. Commun. 12, 7034 (2021).
Pang, H. et al. Realizing N-type SnTe thermoelectrics with competitive performance through suppressing Sn vacancies. J. Am. Chem. Soc. 143, 8538–8542 (2021).
Sethi, V. et al. Tungsten dichalcogenide WS2xSe2−2x films via single source precursor low-pressure CVD and their (thermo-)electric properties. J. Mater. Chem. A 11, 9635–9645 (2023).
Raza, A. et al. Advances in liquid-phase and intercalation exfoliations of transition metal dichalcogenides to produce 2D framework. Adv. Mater. Interfaces 8, 2002205 (2021).
Zhang, Q., Mei, L., Cao, X., Tang, Y. & Zeng, Z. Intercalation and exfoliation chemistries of transition metal dichalcogenides. J. Mater. Chem. A 8, 15417–15444 (2020).
Busch, R. T. et al. Exfoliation procedure-dependent optical properties of solution deposited MoS2 films. npj 2D Mater. Appl. 7, 12 (2023).
Wang, J. et al. Controlled growth of atomically thin transition metal dichalcogenides via chemical vapor deposition method. Mater. Today Adv. 8, 100098 (2020).
Hoang, A. T., Qu, K., Chen, Z. & Ahn, J.-H. Large-area synthesis of transition metal dichalcogenides via CVD and solution-based approaches and their device applications. Nanoscale 13, 615–633 (2021).
Li, H., Li, Y., Aljarb, A., Shi, Y. & Li, L.-J. Epitaxial growth of two-dimensional layered transition-metal dichalcogenides: growth mechanism, controllability, and scalability. Chem. Rev. 118, 6134–6150 (2018).
Mattinen, M., Leskelä, M. & Ritala, M. Atomic layer deposition of 2D metal dichalcogenides for electronics, catalysis, energy storage, and beyond. Adv. Mater. Interfaces 8, 2001677 (2021).
Cho, A.-H. et al. Stepwise growth of crystalline MoS2 in atomic layer deposition. J. Mater. Chem. C 10, 7031–7038 (2022).
Singh, D. K. & Gupta, G. van der Waals epitaxy of transition metal dichalcogenides via molecular beam epitaxy: looking back and moving forward. Mater. Adv. 3, 6142–6156 (2022).
Choudhury, T. H., Zhang, X., Al Balushi, Z. Y., Chubarov, M. & Redwing, J. M. Epitaxial growth of two-dimensional layered transition metal dichalcogenides. Ann. Rev. Mater. Res. 20, 155–177 (2020).
Li, J. et al. Synthesis of ultrathin metallic MTe2 (M = V, Nb, Ta) single-crystalline nanoplates. Adv. Mater. 30, 1801043 (2018).
Gong, Y. et al. Two-step growth of two-dimensional WSe2/MoSe2 heterostructures. Nano Lett. 15, 6135–6141 (2015).
Li, M. Y. et al. Epitaxial growth of a monolayer WSe2-MoS2 lateral p-n junction with an atomically sharp interface. Science 349, 524–528 (2015).
Zhou, J. et al. Morphology engineering in monolayer MoS2-WS2 lateral heterostructures. Adv. Funct. Mater. 28, 1801568 (2018).
Giri, A., Park, G. & Jeong, U. Layer-structured anisotropic metal chalcogenides: recent advances in synthesis, modulation, and applications. Chem. Rev. 123, 3329–3442 (2023). This article provides a detailed review of the various processes typically used to grow 2D TMDCs and the modulation of the films for various applications.
Zhou, H., Zhang, C., Gao, A., Shi, E. & Guo, Y. Patterned growth of two-dimensional atomic layer semiconductors. Chem. Commun. 60, 943–955 (2024). This work sets out the current state-of-the-art for patterning 2D semiconductors on the nanoscale.
Balasubramanyam, S. et al. Area-selective atomic layer deposition of two-dimensional WS2 nanolayers. ACS Mater. Lett. 2, 511–518 (2020).
Parsons, G. N. & Clark, R. D. Area-selective deposition: fundamentals, applications, and future outlook. Chem. Mater. 32, 4920–4953 (2020). This article provides a review of area-selective deposition of 2D materials, with a particular focus on CVD and ALD techniques.
Schlesinger, T. E., Rajeshwar, K. & de Tacconi, N. R. in Modern Electroplating Ch. 14 (eds Schlesinger, M. & Paunovic, M.) 383–411 (Wiley, 2010).
Lincot, D. Electrodeposition of semiconductors. Thin Solid Films 487, 40–48 (2005).
Bouroushian, M. Electrochemistry of Metal Chalcogenides (ed. Scholtz, F.) (Springer, 2010).
Osaka, T. Electrodeposition of highly functional thin films for magnetic recording devices of the next century. Electrochim. Acta 45, 3311–3321 (2000).
Andricacos, P. C., Uzoh, C., Dukovic, J. O., Horkans, J. & Deligianni, H. Damascene copper electroplating for chip interconnections. IBM J. Res. Dev. 42, 568–574 (1998).
Paunovic, M. & Schlesinger, M. (eds) Fundamentals of Electrochemical Deposition 2nd edn (Wiley, 2006). This book provides a very useful introduction to the principles of electrodeposition.
Black, A. W. & Bartlett, P. N. Selection and characterisation of weakly coordinating solvents for semiconductor electrodeposition. Phys. Chem. Chem. Phys. 24, 8093–8103 (2022).
Cook, D. A. et al. Tellurium electrodeposition from tellurium(II) and tellurium(IV) chloride salts in dichloromethane. Electrochim. Acta 456, 142456 (2023).
Bartlett, P. N., Cummings, C. Y., Levason, W., Pugh, D. & Reid, G. Halometallate complexes of germanium(II) and (IV): probing the role of cation, oxidation state and halide on the structural and electrochemical properties. Chem. Eur. J. 2, 5019–5027 (2014).
Aliyev, A. S., Elrouby, M. & Cafarova, S. F. Electrochemical synthesis of molybdenum sulfide semiconductor. Mater. Sci. Semicond. Process. 32, 31–39 (2015).
Zhang, L., Wu, L., Li, J. & Lei, J. Electrodeposition of amorphous molybdenum sulfide thin film for electrochemical hydrogen evolution reaction. BMC Chem. 13, 88 (2019).
Mohapatra, S., Das, H. T., Tripathy, B. C. & Das, N. Recent developments in electrodeposition of transition metal chalcogenides-based electrode materials for advance supercapacitor applications: a review. Chem. Rec. 24, e202300220 (2024).
Zhang, Z. et al. All-in-one two-dimensional retinomorphic hardware device for motion detection and recognition. Nat. Nanotechnol. 17, 27–32 (2022).
Shin, G. H., Park, C., Lee, K. J., Jin, H. J. & Choi, S. Y. Ultrasensitive phototransistor based on WSe2–MoS2 van der Waals heterojunction. Nano Lett. 20, 5741–5748 (2020).
Huang, R. et al. Towards a 3D GST phase change memory with integrated selector by non-aqueous electrodeposition. Faraday Disc 213, 339–355 (2019).
Szymczak, J. et al. Electrodeposition of stoichiometric bismuth telluride Bi2Te3 using a piperidinium ionic liquid binary mixture. Electrochim. Acta 137, 586594 (2014).
Hansen, B. B. et al. Deep eutectic solvents: a review of fundamentals and applications. Chem. Rev. 121, 1232–1285 (2021).
Sargar, A. M., Patil, N. S., Mane, S. R., Gawale, S. N. & Bhosale, P. N. Optostructural and electrical studies on electrodeposited Indium doped ZrS2 thin films. J. Alloys Compd 474, 14–17 (2009).
Hankare, P. P. et al. Effect of annealing on properties of ZrSe2 thin films. J. Cryst. Growth 294, 254–259 (2006).
Sargar, A. M., Patil, N. S., Mane, S. R., Gawale, S. N. & Bhosale, P. N. Electrochemical synthesis and characterisation of ZrSe2 thin films. Int. J. Electrochem. Sci. 4, 887–894 (2009).
Rakkini, A. P. V. & Mohanraj, K. Influence of pH of the electrolyte on the formation and properties of electrodeposited ZrSe2 thin films. Inorg. Nano Met. Chem. 52, 570–575 (2022).
Manyepedza, T., Courtney, J. M., Snowden, A., Jones, C. R. & Rees, N. V. Impact electrochemistry of MoS2: electrocatalysis and hydrogen generation at low overpotentials. J. Phys. Chem. C 126, 17942–17951 (2022).
Teli, A. M. et al. Electrodeposited crumpled MoS2 nanoflakes for asymmetric supercapacitor. Ceram. Mater. 48, 29002–29010 (2022).
Strange, L. E. et al. Electrodeposited transition metal dichalcogenides for use in hydrogen evolution electrocatalysts. J. Electrochem. Soc. 169, 026510 (2022).
Soram, B. S., Dai, J. Y., Thangjam, I. S., Kim, N. H. & Lee, J. H. One-step electrodeposited MoS2@Ni-mesh electrode for flexible and transparent asymmetric solid-state supercapacitors. J. Mater. Chem. A 8, 24040–24052 (2020).
Mabayoje, O. et al. Electrodeposition of MoSx hydrogen evolution catalysts from sulfur-rich precursors. ACS Appl. Mater. Interfaces 11, 32879–32886 (2019).
Li, C.-D., Wang, W.-W., Jin, M., Shen, Y. & Xu, J.-J. Friction property of MoS2 coatings deposited on the chemical-etched surface of Al–Si alloy cylinder liner. J. Tribol. 140, 041302 (2018).
Quy, V. H. V. et al. Electrodeposited MoS2 as electrocatalytic counter electrode for quantum dot- and dye-sensitized solar cells. Electrochim. Acta 260, 716–725 (2018).
Erfanifan, S. et al. Tunable bandgap and spin-orbit coupling by composition control of MoS2 and MoOx (x = 2 and 3) thin film compounds. Mater. Des. 122, 220–225 (2017).
Anand, T. J. S., Sanjeeviraja, C. & Jayachandran, M. Preparation of layered semiconductor (MoSe2) by electrosynthesis. Vacuum 60, 431–435 (2001).
Ponomarev, E. A., Neumann-Spallart, M., Hodes, G. & Lévy-Clément, C. Electrochemical deposition of MoS2 thin films by reduction of tetrathiomolybdate. Thin Solid Films 280, 86–89 (1996).
Poorahong, S., Izquierdo, R. & Siaj, M. An efficient porous molybdenum diselenide catalyst for electrochemical hydrogen generation. J. Mater. Chem. A 5, 20993–21001 (2017).
Kowalik, R. et al. Electrochemical deposition of Mo-Se thin films. ECS Trans. 64, 23 (2015).
Dukstiene, N., Kazancev, K., Prosycevas, I. & Guobiene, A. Electrodeposition of Mo-Se thin films from a sulfamatic electrolyte. J. Solid State Electrochem. 8, 330–336 (2004).
Kim, E.-K. et al. Epitaxial electrodeposition of single crystal MoTe2 nanorods and Li+ storage feasibility. J. Electroanal. Chem. 878, 114672 (2020).
Myung, N. et al. Electrosynthesis of MoTe2 thin films: a combined voltammetry-electrochemical quartz crystal microgravimetry study of mechanistic aspects. J. Electrochem. Soc. 167, 116510 (2020).
Zhou, Y. et al. MoTe2 nanodendrites based on Mo doped reduced graphene oxide/polyimide composite film for electrocatalytic hydrogen evolution in neutral solution. Electrochim. Acta 229, 121–128 (2017).
Veeralingam, S., Durai, L. & Badhulika, S. Facile fabrication of P(electrodeposition)/N(solvothermal) 2D-WS2-homojunction based high performance photo responsive, strain modulated piezo-phototronic diode. ChemNanoMat 5, 1521–1530 (2019).
Devadasan, J. J., Sanjeeviraja, C. & Jayachandran, M. Electrodeposition of p-WS2 thin film and characterisation. J. Cryst. Growth 226, 67–72 (2001).
Delphine, S. M., Jayachandran, M. & Sanjeeviraja, C. Pulsed electrodeposition and characterisation of tungsten diselenide thin films. Mater. Chem. Phys. 81, 78–83 (2003).
Devadasan, J. J., Sanjeeviraja, C. & Jayachandran, M. Electrosynthesis and characterisation of n-WSe2 thin films. Mater. Chem. Phys. 77, 397–401 (2003).
Peng, Z. et al. Controllable (h k 1) preferred orientation of Sb2S3 thin films fabricated by pulse electrodeposition. Sol. Energy Mater. Sol. Cells 253, 112208 (2003).
García, R. G. A. et al. Phase pure CuSbS2 thin films by heat treatment of electrodeposited Sb2S3/Cu layers. J. Solid State Electrochem. 24, 185–194 (2020).
Garcia, R. G. A., Avendaño, C. A. M., Pal, M., Delgado, F. P. & Mathews, N. R. Antimony sulfide (Sb2S3) thin films by pulse electrodeposition: effect of thermal treatment on structural, optical and electrical properties. Mater. Sci. Semicond. Proc. 44, 91–100 (2016).
Subramanium, S. et al. High-energy ion induced physical and surface modifications in antimony sulphide thin films. Curr. Appl. Phys. 10, 1112–1116 (2010).
Yesugade, N. S., Lokhande, C. D. & Bhosale, C. H. Structural and optical properties of electrodeposited Bi2S3, Sb2S3 and As2S3 thin films. Thin Solid Films 263, 145–149 (1995).
Majidzade, V. A., Javadova, S. P., Jafarova, S. F., Aliyev, A. S. & Tagiyev, D. B. Electrochemical deposition of Sb2S3 thin films. Russ. J. Appl. Chem. 95, 1627–1633 (2022).
Majidzade, V. A., Aliyev, A. S., Guliyev, P. H. & Babanly, D. M. Electrodeposition of the Sb2Se3 thin films on various substrates from the tartaric electrolyte. J. Electrochem. Sci. Eng. 10, 1–9 (2020).
Majidzade, V. A., Aliyev, A. S., Qasimogli, I., Quliyev, P. H. & Tagiyev, D. B. Electrical properties of electrochemically grown thin Sb2Se3 semiconductor films. Inorg. Mater. 55, 979–983 (2019).
MacLeod, D., Parker, A. J. & Singh, P. Electrochemistry of copper in aqueous acetonitrile. J. Soln. Chem. 10, 757–774 (1981).
Asif, O., Azadian, F. & Rastogi, A. C. Titanium disulphide (TiS2) dichalcogenide thin films as inorganic hole transport layer for perovskite solar cells synthesized from ionic liquid electrodeposition. MRS Adv. 5, 3555–3564 (2020).
Murugesan, S. et al. Room temperature electrodeposition of molybdenum sulfide for catalytic and photoluminescence applications. ACS Nano 7, 8199–8205 (2013).
Hayyan, M., Mjalli, F. S., Hashim, M. A., AlNashef, I. M. & Mei, T. X. Investigating the electrochemical windows of ionic liquids. J. Indust. Eng. Chem. 19, 106–112 (2013).
Tiago, G. A. O., Matias, I. A. S., Ribeiro, A. P. C. & Martins, L. M. D. R. S. Application of ionic liquids in electrochemistry — recent advances. Molecules 25, 5812 (2020).
Sedev, R. Surface tension, interfacial tension and contact angles of ionic liquids. Curr. Opin. Coll. Interface Sci. 16, 310–316 (2011).
Kamlet, M. J., Abboud, J. L. M., Abraham, M. H. & Taft, R. W. Linear solvation energy relationships. 23. A comprehensive collection of the solvatochromic parameters, p*, a, and ß, and some methods for simplifying the generalized solvatochromic equation. J. Org. Chem. 48, 2877–2887 (1983). This work sets out the parameters used to describe solvents and is a useful resource that brings together the numerical values for a range of different solvents.
Bartlett, P. N. et al. A versatile precursor system for supercritical fluid electrodeposition of main-group materials. Chem. Eur. J. 22, 302–309 (2016).
Fan, L. & Suni, I. I. Electrodeposition and capacitance measurements of WS2 thin films. J. Electrochem. Soc. 164, D681–D686 (2017).
Bartlett, P. N. et al. Non-aqueous electrodeposition of functional semiconducting metal chalcogenides: Ge2Sb2Te5 phase change memory. Mater. Horiz. 2, 420–426 (2015). This work describes a method for the electrodeposition of GeSbTe thin films and nanostructures from a CH2Cl2 electrolyte using compatible multi-source precursors.
Kissling, G. P. et al. Electrodeposition of a functional solid state memory material: germanium antimony telluride from a non-aqueous plating bath. J. Electrochem. Soc. 165, D557–D567 (2018).
Bartlett, P. N. et al. Non-aqueous electrodeposition of p-block metals and metalloids from halometallate salts. RSC Adv. 3, 15645–15654 (2013).
Lodge, A. W. et al. Electrodeposition of tin nanowires from a dichloromethane based electrolyte. RSC Adv. 8, 24013–24020 (2018).
Bartlett, P. N. et al. Haloplumbate salts as reagents for the non-aqueous electrodeposition of lead. RSC Adv. 6, 73323–72330 (2016).
Cook, D. A. et al. Cathodic stripping of elemental Te in dichloromethane. Electrochim. Acta 465, 142997 (2023).
Evans, D. H. One-electron and two-electron transfers in electrochemistry and homogeneous solution reaction. Chem. Rev. 108, 2113–2144 (2008).
Cicvaric, K. et al. Thermoelectric properties of bismuth telluride thin films electrodeposited from a nonaqueous solution. ACS Omega 5, 14679–14688 (2020).
Jaafer, A. H. et al. Flexible memristor devices using hybrid polymer/electrodeposited GeSbTe nanoscale thin films. ACS Appl. Nano Mater. 5, 17711–17720 (2022).
Noori, Y. J. et al. Phase-change memory by GeSbTe electrodeposition in crossbar arrays. ACS Appl. Electron. Mater. 3, 3610–3618 (2021).
Liang, T. et al. A facile approach to enhance the hydrogen evolution reaction of electrodeposited MoS2 in acidic solutions. N. J. Chem. 46, 23344–23350 (2022).
Xue, J. et al. Enhanced photoelectrocatalytic hydrogen production performance of porous MoS2/PPy/ZnO film under visible light irradiation. Int. J. Hydr. Energy 46, 35219–35229 (2021).
Nisar, T., Balster, T. & Wagner, V. Mechanical transfer of electrochemically grown molybdenum sulfide layers to silicon wafer. J. Appl. Electrochem. 51, 1279–1286 (2021).
Aslan, E. & Patir, I. H. Catalysis of hydrogen evolution reaction by in situ electrodeposited amorphous molybdenum sulfide at soft interfaces. Mater. Today Energy 21, 100742 (2021).
Chakraborty, B., Maity, I., Chung, P., Ho, M. & Bhattacharyya, P. Understanding the highly selective methanol sensing mechanism of electrodeposited pristine MoS2 using first principle analysis. IEEE Sens. J. 21, 15 (2021).
Shit, S., Bolar, S., Murmu, N. C. & Kuila, T. Tailoring the bifunctional electrocatalytic activity of electrodeposited molybdenum sulfide/iron oxide heterostructure to achieve excellent overall water splitting. Chem. Eng. J. 417, 129333 (2021).
Levinas, R., Tsyntsaru, N. & Cesiulis, K. The characterisation of electrodeposited MoS2 thin films on a foam-based electrode for hydrogen evolution. Catalysts 10, 1182 (2020).
Chang, C.-Y. et al. Potential-reversal electrodeposited MoS2 thin film as an efficient electrocatalytic material for bifacial dye-sensitized solar cells. Sol. Energy 206, 163–170 (2020).
Yagati, A. K., Go, A., Vu, N. H. & Lee, M. H. A MoS2–Au nanoparticle-modified immunosensor for T3 biomarker detection in clinical serum samples. Electrochim. Acta 342, 136065 (2020).
Gurulakshmi, M. et al. Electrodeposited MoS2 counter electrode for flexible dye sensitized solar cell module with ionic liquid assisted photoelectrode. Sol. Energy 199, 447–452 (2020).
Lei, Y. et al. Synthesis of V-MoS2 layered alloys as stable Li-ion battery anodes. ACS Appl. Energy Mater. 2, 8625–8632 (2019).
Giang, H., Pali, M., Fan, L. & Suni, I. I. Impedance biosensing atop MoS2 thin films with Mo−S bond formation to antibody fragments created by disulphide bond reduction. Electroanalysis 31, 957–965 (2019).
Yang, L. et al. Efficient hydrogen evolution catalyzed by amorphous molybdenum sulfide/N-doped active carbon hybrid on carbon fiber paper. Int. J. Hydr. Energy 43, 15135–15143 (2018).
Amin, R., Hossain, M. A. & Yahya Zakaria, Y. Interfacial kinetics and ionic diffusivity of the electrodeposited MoS2 film. ACS Appl. Mater. Interfaces 10, 13509–13518 (2018).
Chia, X., Sutrisnoh, N. A. A. & Pumera, M. Tunable Pt–MoSx hybrid catalysts for hydrogen evolution. ACS Appl. Mater. Interfaces 10, 8702–8711 (2018).
Lamouchi, A., Assaker, I. B. & Chtourou, R. Effect of annealing temperature on the structural, optical, and electrical properties of MoS2 electrodeposited onto stainless steel mesh. J. Mater. Sci. 52, 4635–4646 (2017).
Falola, B. D., Wiltowski, T. & Suni, I. I. Electrodeposition of MoS2 for charge storage in electrochemical supercapacitors. J. Electrochem. Soc. 163, D568 (2016).
Ahn, H. S. & Bard, A. J. Electrochemical surface interrogation of a MoS2 hydrogen-evolving catalyst: in situ determination of the surface hydride coverage and the hydrogen evolution kinetics. J. Phys. Chem. Lett. 7, 2748–2752 (2016).
Ponomarev, E. A., Tenne, R., Katty, A. & Lévy-Clément, C. Highly oriented photoactive polycrystalline MoS2 layers obtained by van der Waals rheotaxy technique from electrochemically deposited thin films. Sol. Energy Mater. Sol. Cells 52, 125–133 (1998).
Albu-Yaron, A., Lévy-Clément, C., Katty, A., Bastide, S. & Tenne, R. Influence of the electrochemical deposition parameters on the microstructure of MoS2 thin films. Thin Solid Films 361–362, 223–228 (2000).
Ponomarev, E. A., Albu‐Yaron, A., Tenne, R. & Lévy‐Clément, C. Electrochemical deposition of quantized particle MoS2 thin films. J. Electrochem. Soc. 144, L277 (1997).
Fan, L. & Suni, I. I. Polysulfide reduction and oxidation at MoS2, WS2 and Cu-doped MoS2 thin film electrodes. J. Electrochem. Soc. 166, A1471 (2019).
Novčić, K. A., Iffelsberger, C., Ng, S. & Pumera, M. Local electrochemical activity of transition metal dichalcogenides and their heterojunctions on 3D-printed nanocarbon surfaces. Nanoscale 13, 5324–5332 (2021).
Pu, Z., Liu, Q., Asiri, A. M., Obaid, A. Y. & Sun, X. One-step electrodeposition fabrication of graphene film-confined WS2 nanoparticles with enhanced electrochemical catalytic activity for hydrogen evolution. Electrochim. Acta 134, 8–12 (2014).
Redman, D. W., Rose, M. J. & Stevenson, K. J. Electrodeposition of amorphous molybdenum chalcogenides from ionic liquids and their activity for the hydrogen evolution reaction. Langmuir 33, 9354–9360 (2017).
Ng, S., Iffelsberger, C., Sofer, Z. & Pumera, M. Tunable room-temperature synthesis of ReS2 bicatalyst on 3D- and 2D-printed electrodes for photo- and electrochemical energy applications. Adv. Funct. Mater. 30, 1910193 (2020).
Wallace, A. G. et al. Anodic Sb2S3 electrodeposition from a single source precursor for resistive random-access memory devices. Electrochim. Acta 432, 141162 (2022).
Thomas, S. et al. Electrodeposition of MoS2 from dichloromethane. J. Electrochem. Soc. 167, 106511 (2020).
Thomas, S. et al. Tungsten disulfide thin films via electrodeposition from a single source precursor. Chem. Commun. 57, 10194–10197 (2021). This work describes the preparation and electrochemistry of a stoichiometric SSP for the electrodeposition of WS2 without the need for a proton source.
O’Neal, S. C. & Kolis, J. W. Convenient preparation and structures of selenometalates MoSe42−, WSe42−, and MoSe92− from polyselenide anions and metal carbonyls. J. Am. Chem. Soc. 110, 1971–1973 (1988).
Kim, J. et al. A facile synthetic route to tungsten diselenide using a new precursor containing a long alkyl chain cation for multifunctional electronic and optoelectronic applications. RSC Adv. 9, 6169–6176 (2019).
Klingelhöfer, P. & Müller, U. Thiochlorowolframate von wolfram(V) und -(VI). Die kristallstrukturen von PPh4[WSCl4] und (PPh4)2[WS2Cl4]·2CH2Cl2. Z. Anorg. Allg. Chem. 556, 70–78 (1988).
Greenacre, V. K. et al. Tungsten(VI) selenide tetrachloride, WSeCl4 — synthesis, properties, coordination complexes and application of [WSeCl4(SenBu2)] for CVD growth of WSe2 thin films. Dalton Trans. 51, 2400–2412 (2022).
Thomas, S. et. al. Electrodeposition of 2D layered tungsten diselenide thin films using a single source precursor. J. Mater. Chem. C https://doi.org/10.1039/D4TC02755H (2024).
Das, S. et al. A self-limiting electro-ablation technique for the top-down synthesis of large-area monolayer flakes of 2D materials. Sci. Rep. 6, 28195 (2016). This article describes a method for electropolishing multilayer (bulk) TMDC crystals to produce monolayers.
Wan, X. et al. Controlled electrochemical deposition of large-area MoS2 on graphene for high-responsivity photodetectors. Adv. Funct. Mater. 27, 1603998 (2017).
Noori, Y. J. et al. Large-area electrodeposition of few-layer MoS2 on graphene for 2D material heterostructures. ACS Appl. Mater. Interfaces 12, 49786–49794 (2020).
Noori, Y. J. et al. Electrodeposited WS2 monolayers on patterned graphene. 2D Mater. 9, 015025 (2022). This article describes a method for the electrochemical growth of ultrathin WS2 over graphene electrodes using a SSP and a CH2Cl2 electrolyte.
Abdelazim, N. et al. Lateral growth of MoS2 2D material semiconductors over an insulator via electrodeposition. Adv. Electron. Mater. 7, 2100419 (2021). This article describes the clean-room fabrication process for nano-band electrodes and their application for the electrochemical growth of 2D MoS2 over an insulating SiO2 surface.
Greenacre, V. K., Levason, W., Reid, G. & Smith, D. E. Coordination complexes and applications of transition metal sulfide and selenide halides. Coord. Chem. Rev. 424, 213512 (2020).
Black, A. W., Zhang, W., Noori, Y. J., Reid, G. & Bartlett, P. N. Temperature effects on the electrodeposition of semiconductors from a weakly coordinating solvent. J. Electroanal. Chem. 944, 117638 (2023).
Liang, X., Jayaraju, N., Thambidurai, C., Zhang, Q. & Stickney, J. L. Controlled electrochemical formation of GexSbyTez using atomic layer deposition (ALD). Chem. Mater. 23, 1742–1752 (2011).
Schwarzacher, W. & Lashmore, D. S. Giant magnetoresistance in electrodeposited films. IEEE Trans. Magn. 32, 3133–3153 (1996).
Jyoko, Y. & Schwarzacher, W. Characterization of electrodeposited magnetic Co/Pt multilayered nanostructures. Electrochim. Acta 47, 371–378 (2001).
Schlesinger, M. & Paunovic, M. (eds) Modern Electroplating (Wiley, 2010).
Reeves, S. J., Noori, Y. J., Zhang, W., Reid, G. & Bartlett, P. N. Chloroantimonate electrochemistry in dichloromethane. Electrochim. Acta 354, 136692 (2020).
Acknowledgements
The authors thank the Engineering and Physical Sciences Research Council (EPSRC), UK, for funding our work in this area, mainly through grants EP/V062689/1, EP/P025137/1 and EP/N035437/1.
Author information
Authors and Affiliations
Contributions
P.N.B. and G.R. conceived the idea and drafted the proposal. P.N.B., R.H., S.T. and G.R. wrote most of the content. Y.J.N., C.H.D.G., R.H., V.K.G. and S.T. prepared the graphic concepts. All of the authors edited and revised the manuscript.
Corresponding authors
Ethics declarations
Competing interests
The authors declare no competing interests.
Peer review
Peer review information
Nature Reviews Chemistry thanks Daniel Mandler, Andrew Mount, John Henry, Julie Macpherson and the other, anonymous, reviewer(s) for their contribution to the peer review of this work.
Additional information
Publisher’s note Springer Nature remains neutral with regard to jurisdictional claims in published maps and institutional affiliations.
Glossary
- Anisotropic growth
-
Growth strongly favoured in one or two specific directions; in the case of transition metal dichalcogenides, this is typically from the edges of the growing layer (to produce a 2D sheet).
- Area-selective growth
-
Growth of materials only on specific regions of a pre-patterned substrate.
- Brighteners
-
Chemical used in electrodeposition to increase the optical brightness of the deposited material.
- Counter electrode
-
The electrode used to complete the circuit in the electrochemical cell. It has to pass an equal but opposite current from that at the working electrode.
- Electrolyte
-
The solution used for the electrochemical experiment, usually comprising the solvent, precursor (or precursors) and a redox inactive cation–anion salt that dissociates in the solvent to form ions that carry the charge.
- iR drop
-
Difference between the applied potential and the potential at the working electrode owing to passage of current through solution, or other uncompensated resistance.
- Levellers
-
Chemical used in electrodeposition to increase the uniformity of the deposited material.
- Macroelectrodes
-
Electrode with diameter >0.1 mm.
- Microelectrodes
-
Electrode with diameter <50 μm.
- Nano-band electrodes
-
Electrode structure wherein the conducting surface is in the form of a line <100 nm deep, typically fabricated on a silicon substrate.
- Planar diffusion
-
Diffusion in 1D to or from the electrode surface.
- Radial diffusion
-
Diffusion in 2D or 3D to or from the electrode surface.
- Single-source precursors
-
(SSPs). Compounds that can be used for depositing the target transition metal dichalcogenide that contains pre-formed metal–chalcogen bonds.
Rights and permissions
Springer Nature or its licensor (e.g. a society or other partner) holds exclusive rights to this article under a publishing agreement with the author(s) or other rightsholder(s); author self-archiving of the accepted manuscript version of this article is solely governed by the terms of such publishing agreement and applicable law.
About this article
Cite this article
Bartlett, P.N., de Groot, C.H.K., Greenacre, V.K. et al. Molecular precursors for the electrodeposition of 2D-layered metal chalcogenides. Nat Rev Chem 9, 88–101 (2025). https://doi.org/10.1038/s41570-024-00671-6
Accepted:
Published:
Version of record:
Issue date:
DOI: https://doi.org/10.1038/s41570-024-00671-6