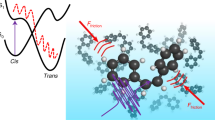
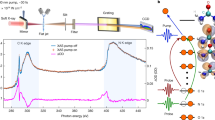
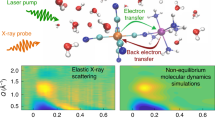
Abstract
Ultrafast X-ray spectroscopy provides access to molecular dynamics with unprecedented time resolution, element specificity and site selectivity. These unique properties are optimally suited for investigating intramolecular and intermolecular interactions of molecular species in the liquid phase. This Review summarizes experimental breakthroughs, such as water photolysis and proton transfer on femtosecond and attosecond time scales, dynamics of solvated electrons, charge-transfer processes in metal complexes, multiscale dynamics in haem proteins, proton-transfer dynamics in prebiotic systems and liquid-phase extreme-ultraviolet high-harmonic spectroscopy. An important novelty for ultrafast liquid-phase spectroscopy is the availability of high-brightness ultrafast short-wavelength sources that allowed access to the water window (from 200 eV to 550 eV) and thus to the K-edges of the key elements of organic and biological chemistry: C, N and O. Not only does this Review present experimental examples that demonstrate the unique capabilities of ultrafast short-wavelength spectroscopy in liquids, but it also highlights the broad range of spectroscopic methodologies already applied in this field.

This is a preview of subscription content, access via your institution
Access options
Access Nature and 54 other Nature Portfolio journals
Get Nature+, our best-value online-access subscription
$32.99 / 30 days
cancel any time
Subscribe to this journal
Receive 12 digital issues and online access to articles
$119.00 per year
only $9.92 per issue
Buy this article
- Purchase on SpringerLink
- Instant access to the full article PDF.
USD 39.95
Prices may be subject to local taxes which are calculated during checkout






Similar content being viewed by others
References
Maiuri, M., Garavelli, M. & Cerullo, G. Ultrafast spectroscopy: State of the art and open challenges. J. Am. Chem. Soc. 142, 3–15 (2020).
Baltuška, A., Emde, M. F., Pshenichnikov, M. S. & Wiersma, D. A. Early-time dynamics of the photoexcited hydrated electron. J. Phys. Chem. A 103, 10065–10082 (1999).
Fresch, E. et al. Two-dimensional electronic spectroscopy. Nat. Rev. Methods Primers 3, 84 (2023).
Engel, G. S. et al. Evidence for wavelike energy transfer through quantum coherence in photosynthetic systems. Nature 446, 782–786 (2007).
Brixner, T. et al. Two-dimensional spectroscopy of electronic couplings in photosynthesis. Nature 434, 625–628 (2005).
Jonas, D. M. Two-dimensional femtosecond spectroscopy. Annu. Rev. Phys. Chem. 54, 425–463 (2003).
Kraus, P. M., Zürch, M., Cushing, S. K., Neumark, D. M. & Leone, S. R. The ultrafast X-ray spectroscopic revolution in chemical dynamics. Nat. Rev. Chem. 2, 82–94 (2018).
Siegbahn, H. & Siegbahn, K. ESCA applied to liquids. J. Electron Spectros. Relat. Phenomena 2, 319–325 (1973).
Siegbahn, H., Svensson, S. & Lundholm, M. A new method for ESCA studies of liquid-phase samples. J. Electron Spectros. Relat. Phenomena 24, 205–213 (1981).
Siegbahn, H. Electron spectroscopy for chemical analysis of liquids and solutions. J. Phys. Chem. 89, 897–909 (1985).
Lundholm, M., Siegbahn, H., Holmberg, S. & Arbam, M. Core electron spectroscopy of water solutions. J. Electron Spectros. Relat. Phenomena 40, 163–180 (1986).
Faubel, M., Steiner, B. & Toennies, J. P. Photoelectron spectroscopy of liquid water, some alcohols, and pure nonane in free micro jets. J. Chem. Phys. 106, 9013–9031 (1997).
Fransson, T. et al. X-ray and electron spectroscopy of water. Chem. Rev. 116, 7551–7569 (2016).
Smith, J. W. & Saykally, R. J. Soft X-ray absorption spectroscopy of liquids and solutions. Chem. Rev. 117, 13909–13934 (2017).
Rehr, J. & Albers, R. Theoretical approaches to X-ray absorption fine structure. Rev. Mod. Phys. 72, 621–654 (2000).
van Bokhoven, J. A. & Lamberti, C. (eds) X-Ray Absorption and X-Ray Emission Spectroscopy: Theory and Applications (Wiley, 2016).
Evans, J. X-ray Absorption Spectroscopy for the Chemical and Materials Sciences (Wiley, 2018).
Wang, M., Árnadóttir, L., Xu, Z. J. & Feng, Z. In situ X-ray absorption spectroscopy studies of nanoscale electrocatalysts. Nanomicro Lett. 11, 47 (2019).
Bressler, C. et al. Femtosecond XANES study of the light-induced spin crossover dynamics in an iron(II) complex. Science 323, 489–492 (2009).
Huse, N. et al. Femtosecond soft X-ray spectroscopy of solvated transition-metal complexes: deciphering the interplay of electronic and structural dynamics. J. Phys. Chem. Lett. 2, 880–884 (2011).
Emma, P. et al. First lasing and operation of an ångstrom-wavelength free-electron laser. Nat. Photon. 4, 641–647 (2010).
Ackermann, W. et al. Operation of a free-electron laser from the extreme ultraviolet to the water window. Nat. Photon. 1, 336–342 (2007).
Allaria, E. et al. Highly coherent and stable pulses from the FERMI seeded free-electron laser in the extreme ultraviolet. Nat. Photon. 6, 699–704 (2012).
Chapman, H. N. et al. Femtosecond diffractive imaging with a soft-X-ray free-electron laser. Nat. Phys. 2, 839–843 (2006).
Ishikawa, T. et al. A compact X-ray free-electron laser emitting in the sub-ångström region. Nat. Photon. 6, 540–544 (2012).
Wabnitz, H. et al. Multiple ionization of atom clusters by intense soft X-rays from a free-electron laser. Nature 420, 482–485 (2002).
Huang, Z. & Kim, K.-J. Review of X-ray free-electron laser theory. Phys. Rev. Accel. Beams 10, 034801 (2007).
Boutet, S. & Yabashi, M. in X-Ray Free Electron Lasers (eds Boutet, S. et al.) 1–21 (Springer, 2018).
Ekeberg, T. et al. Observation of a single protein by ultrafast X-ray diffraction. Light Sci. Appl. 13, 15 (2024).
Tamasaku, K. et al. Nonlinear spectroscopy with X-ray two-photon absorption in metallic copper. Phys. Rev. Lett. 121, 083901 (2018).
Foglia, L. et al. First evidence of purely extreme-ultraviolet four-wave mixing. Phys. Rev. Lett. 120, 263901 (2018).
Bencivenga, F. et al. Nanoscale transient gratings excited and probed by extreme ultraviolet femtosecond pulses. Sci. Adv. 5, eaaw5805 (2019).
Rouxel, J. R. et al. Hard X-ray transient grating spectroscopy on bismuth germanate. Nat. Photon. 15, 499–503 (2021).
Beye, M. Transient gratings with X-rays. Nat. Photon. 15, 490–492 (2021).
Duris, J. et al. Tunable isolated attosecond X-ray pulses with gigawatt peak power from a free-electron laser. Nat. Photon. 14, 30–36 (2020).
Li, S. et al. Attosecond coherent electron motion in Auger-Meitner decay. Science 375, 285–290 (2022).
Li, S. et al. Attosecond-pump attosecond-probe X-ray spectroscopy of liquid water. Science 383, 1118–1122 (2024).
Bermúdes Macias, I. J. et al. Study of temporal, spectral, arrival time and energy fluctuations of SASE FEL pulses. Opt. Express 29, 10491–10508 (2021).
Gaumnitz, T. et al. Streaking of 43-attosecond soft-X-ray pulses generated by a passively CEP-stable mid-infrared driver. Opt. Express 25, 27506–27518 (2017).
Géneaux, R., Chang, H.-T., Schwartzberg, A. M. & Marroux, H. J. B. Source noise suppression in attosecond transient absorption spectroscopy by edge-pixel referencing. Opt. Express 29, 951–960 (2021).
Popmintchev, T. et al. Bright coherent ultrahigh harmonics in the keV X-ray regime from mid-infrared femtosecond lasers. Science 336, 1287–1291 (2012).
Corkum, P. B. Plasma perspective on strong field multiphoton ionization. Phys. Rev. Lett. 71, 1994 (1993).
Midorikawa, K. Progress on table-top isolated attosecond light sources. Nat. Photon. 16, 267–278 (2022).
Shan, B. & Chang, Z. Dramatic extension of the high-order harmonic cutoff by using a long-wavelength driving field. Phys. Rev. A 65, 011804 (2001).
Colosimo, P. et al. Scaling strong-field interactions towards the classical limit. Nat. Phys. 4, 386–389 (2008).
Vozzi, C. et al. Millijoule-level phase-stabilized few-optical-cycle infrared parametric source. Opt. Lett. 32, 2957–2959 (2007).
Takahashi, E. J., Kanai, T., Ishikawa, K. L., Nabekawa, Y. & Midorikawa, K. Coherent water window x ray by phase-matched high-order harmonic generation in neutral media. Phys. Rev. Lett. 101, 253901 (2008).
Ishii, N. et al. Carrier-envelope phase-dependent high harmonic generation in the water window using few-cycle infrared pulses. Nat. Commun. 5, 3331 (2014).
Cousin, S. L. et al. High-flux table-top soft X-ray source driven by sub-2-cycle, CEP stable, 1.85-μm 1-kHz pulses for carbon K-edge spectroscopy. Opt. Lett. 39, 5383–5386 (2014).
Johnson, A. S. et al. Measurement of sulfur L2,3 and carbon K edge XANES in a polythiophene film using a high harmonic supercontinuum. Struct. Dyn. 3, 062603 (2016).
Schmidt, B. E. et al. CEP stable 1.6 cycle laser pulses at 1.8 μm. Opt. Express 19, 6858–6864 (2011).
Stein, G. J. et al. Water-window soft X-ray high-harmonic generation up to the nitrogen K-edge driven by a kHz, 2.1 μm OPCPA source. J. Phys. B 49, 155601 (2016).
Austin, D. R. et al. Spatio-temporal characterization of intense few-cycle 2 μm pulses. Opt. Express 24, 24786–24798 (2016).
Fan, G. et al. Hollow-core-waveguide compression of multi-millijoule CEP-stable 3.2 μm pulses. Optica 3, 1308–1311 (2016).
Teichmann, S. M., Silva, F., Cousin, S. L., Hemmer, M. & Biegert, J. 0.5-keV soft X-ray attosecond continua. Nat. Commun. 7, 11493 (2016).
Silva, F., Teichmann, S. M., Cousin, S. L., Hemmer, M. & Biegert, J. Spatiotemporal isolation of attosecond soft X-ray pulses in the water window. Nat. Commun. 6, 6611 (2015).
Tate, J. et al. Scaling of wave-packet dynamics in an intense midinfrared field. Phys. Rev. Lett. 98, 013901 (2007).
Driever, S. et al. Tunable 1.6–2 μm near infrared few-cycle pulse generation by filamentation. Appl. Phys. Lett. 102, 191119 (2013).
Shiner, A. D. et al. Wavelength scaling of high harmonic generation efficiency. Phys. Rev. Lett. 103, 073902 (2009).
Pertot, Y. et al. Time-resolved X-ray absorption spectroscopy with a water window high-harmonic source. Science 355, 264–267 (2017).
Baltuska, A. et al. Attosecond control of electronic processes by intense light fields. Nature 421, 611–615 (2003).
Saito, N., Ishii, N., Kanai, T., Watanabe, S. & Itatani, J. Attosecond streaking measurement of extreme ultraviolet pulses using a long-wavelength electric field. Sci. Rep. 6, 35594 (2016).
Cousin, S. L. et al. Attosecond streaking in the water window: a new regime of attosecond pulse characterization. Phys. Rev. X 7, 041030 (2017).
Keathley, P. D., Bhardwaj, S., Moses, J., Laurent, G. & Kärtner, F. X. Volkov transform generalized projection algorithm for attosecond pulse characterization. New J. Phys. 18, 073009 (2016).
Gebhardt, M. et al. Bright, high-repetition-rate water window soft X-ray source enabled by nonlinear pulse self-compression in an antiresonant hollow-core fibre. Light Sci. Appl. 10, 36 (2021).
Pupeikis, J. et al. Water window soft X-ray source enabled by a 25 W few-cycle 2.2 μm OPCPA at 100 kHz. Optica 7, 168–171 (2020).
Xue, B. et al. Fully stabilized multi-TW optical waveform synthesizer: toward gigawatt isolated attosecond pulses. Sci. Adv. 6, eaay2802 (2020).
Schmidt, B. E. et al. Compression of 1.8 μm laser pulses to sub two optical cycles with bulk material. Appl. Phys. Lett. 96, 121109 (2010).
Schmidt, C. et al. High-order harmonic source spanning up to the oxygen K-edge based on filamentation pulse compression. Opt. Express 26, 11834–11842 (2018).
Garratt, D. et al. Direct observation of ultrafast exciton localization in an organic semiconductor with soft X-ray transient absorption spectroscopy. Nat. Commun. 13, 3414 (2022).
Miller, K. D. Jr. Distribution of spray from impinging liquid jets. J. Appl. Phys. 31, 1132–1133 (1960).
Hasson, D. & Peck, R. E. Thickness distribution in a sheet formed by impinging jets. AIChE J. 10, 752–754 (1964).
Eggers, J. & Villermaux, E. Physics of liquid jets. Rep. Prog. Phys. 71, 036601 (2008).
Ekimova, M., Quevedo, W., Faubel, M., Wernet, P. & Nibbering, E. T. J. A liquid flatjet system for solution phase soft-X-ray spectroscopy. Struct. Dyn. 2, 054301 (2015).
Nagasaka, M., Yuzawa, H. & Kosugi, N. Intermolecular interactions of pyridine in liquid phase and aqueous solution studied by soft X-ray absorption spectroscopy. Z. Phys. Chem. 232, 705–722 (2018).
Fondell, M. et al. Time-resolved soft X-ray absorption spectroscopy in transmission mode on liquids at MHz repetition rates. Struct. Dyn. 4, 054902 (2017).
Luu, T. T. et al. Extreme–ultraviolet high–harmonic generation in liquids. Nat. Commun. 9, 3723 (2018).
Yin, Z., Luu, T. T. & Wörner, H. J. Few-cycle high-harmonic generation in liquids: in-operando thickness measurement of flat microjets. J. Phys. Photonics 2, 044007 (2020).
Chang, Y.-P., Yin, Z., Balciunas, T., Wörner, H. J. & Wolf, J.-P. Temperature measurements of liquid flat jets in vacuum. Struct. Dyn. 9, 014901 (2022).
Galinis, G. et al. Micrometer-thickness liquid sheet jets flowing in vacuum. Rev. Sci. Instrum. 88, 083117 (2017).
Koralek, J. D. et al. Generation and characterization of ultrathin free-flowing liquid sheets. Nat. Commun. 9, 1353 (2018).
Loh, Z. H. et al. Quantum state-resolved probing of strong-field-ionized xenon atoms using femtosecond high-order harmonic transient absorption spectroscopy. Phys. Rev. Lett. 98, 143601 (2007).
Schultze, M. et al. Attosecond band-gap dynamics in silicon. Science 346, 1348–1352 (2014).
Smith, A. D. et al. Femtosecond soft-X-ray absorption spectroscopy of liquids with a water-window high-harmonic source. J. Phys. Chem. Lett. 11, 1981–1988 (2020).
Yin, Z. et al. Femtosecond proton transfer in urea solutions probed by X-ray spectroscopy. Nature 619, 749–754 (2023).
Loh, Z.-H. et al. Observation of the fastest chemical processes in the radiolysis of water. Science 367, 179–182 (2020).
Wernet, P. et al. Orbital-specific mapping of the ligand exchange dynamics of Fe(CO)5 in solution. Nature 520, 78–81 (2015).
Engel, N. et al. Light-induced relaxation dynamics of the ferricyanide ion revisited by ultrafast XUV photoelectron spectroscopy. Phys. Chem. Chem. Phys. 19, 14248–14255 (2017).
Ojeda, J., Arrell, C. A., Longetti, L., Chergui, M. & Helbing, J. Charge-transfer and impulsive electronic-to-vibrational energy conversion in ferricyanide: ultrafast photoelectron and transient infrared studies. Phys. Chem. Chem. Phys. 19, 17052–17062 (2017).
Nishitani, J., Yamamoto, Y.-i, West, C. W., Karashima, S. & Suzuki, T. Binding energy of solvated electrons and retrieval of true UV photoelectron spectra of liquids. Sci. Adv. 5, eaww6896 (2019).
Svoboda, V. et al. Real-time observation of water radiolysis and hydrated electron formation induced by extreme-ultraviolet pulses. Sci. Adv. 6, eaaz0385 (2020).
Wang, C. et al. Different timescales during ultrafast stilbene isomerization in the gas and liquid phases revealed using time-resolved photoelectron spectroscopy. Nat. Chem. 14, 1126–1132 (2022).
Yamamoto, S. & Matsuda, I. Time-resolved photoelectron spectroscopies using synchrotron radiation: past, present, and future. J. Phys. Soc. Jpn 82, 021003 (2013).
Jordan, I. et al. Attosecond spectroscopy of liquid water. Science 369, 974–979 (2020).
Gong, X. et al. Attosecond spectroscopy of size-resolved water clusters. Nature 609, 507–511 (2022).
Kjellsson, L. et al. Resonant inelastic X-ray scattering reveals hidden local transitions of the aqueous OH radical. Phys. Rev. Lett. 124, 236001 (2020).
Garrett, B. C. et al. Role of water in electron-initiated processes and radical chemistry: issues and scientific advances. Chem. Rev. 105, 355–390 (2004).
Lu, L. et al. The “hole” story in ionized water from the perspective of Ehrenfest dynamics. J. Phys. Chem. Lett. 11, 9946–9951 (2020).
Xu, H. et al. Recent progress in metal–organic complexes for optoelectronic applications. Chem. Soc. Rev. 43, 3259–3302 (2014).
Frauenfelder, H., McMahon, B. H. & Fenimore, P. Myoglobin: the hydrogen atom of biology and a paradigm of complexity. Proc. Natl Acad. Sci. USA 100, 8615–8617 (2003).
Parak, F. G. & Nienhaus, G. U. Myoglobin, a paradigm in the study of protein dynamics. ChemPhysChem 3, 249–254 (2002).
Kinschel, D. et al. Femtosecond X-ray emission study of the spin cross-over dynamics in haem proteins. Nat. Commun. 11, 4145 (2020).
Martin, J. L. et al. Femtosecond photolysis of CO-ligated protoheme and hemoproteins: appearance of deoxy species with a 350-fsec time constant. Proc. Natl Acad. Sci. USA 80, 173–177 (1983).
Ye, X. et al. Investigations of heme protein absorption line shapes, vibrational relaxation, and resonance Raman scattering on ultrafast time scales. J. Phys. Chem. A 107, 8156–8165 (2003).
Ferrante, C., Pontecorvo, E., Cerullo, G., Vos, M. H. & Scopigno, T. Direct observation of subpicosecond vibrational dynamics in photoexcited myoglobin. Nat. Chem. 8, 1137–1143 (2016).
Shelby, M. L. et al. Interplays of electron and nuclear motions along CO dissociation trajectory in myoglobin revealed by ultrafast X-rays and quantum dynamics calculations. Proc. Natl Acad. Sci. USA 118, e2018966118 (2021).
Ansari, A. et al. Protein states and protein quakes. Proc. Natl Acad. Sci. USA 82, 5000–5004 (1985).
Lee, Y. et al. Ultrafast coherent motion and helix rearrangement of homodimeric hemoglobin visualized with femtosecond X-ray solution scattering. Nat. Commun. 12, 3677 (2021).
Levantino, M. et al. Ultrafast myoglobin structural dynamics observed with an X-ray free-electron laser. Nat. Commun. 6, 6772 (2015).
Jay, R. M., Kunnus, K., Wernet, P. & Gaffney, K. J. Capturing atom-specific electronic structural dynamics of transition-metal complexes with ultrafast soft X-ray spectroscopy. Annu. Rev. Phys. Chem. 73, 187–208 (2022).
Kubin, M. et al. Soft X-ray absorption spectroscopy of metalloproteins and high-valent metal-complexes at room temperature using free-electron lasers. Struct. Dyn. 4, 054307 (2017).
Bergues, B., Ansari, Z., Hanstorp, D. & Kiyan, I. Y. Photodetachment in a strong laser field: an experimental test of Keldysh-like theories. Phys. Rev. A 75, 063415 (2007).
Sutra, P. & Igau, A. Emerging Earth-abundant (Fe, Co, Ni, Cu) molecular complexes for solar fuel catalysis. Curr. Opin. Green Sustain. Chem. 10, 60–67 (2018).
Miller, S. L. & Urey, H. C. Organic compound synthesis on the primitive earth. Science 130, 245–251 (1959).
Menor Salván, C. et al. Prebiotic origin of pre-RNA building blocks in a urea “warm little pond” scenario. ChemBioChem 21, 3504–3510 (2020).
Chang, Y.-P. et al. Electronic dynamics created at conical intersections and its dephasing in aqueous solution. Nat. Phys. 21, 137–145 (2025).
Orimo, N., Yamamoto, Y-i., Karashima, S., Boyer, A. & Suzuki, T. Ultrafast electronic relaxation in 6-methyluracil and 5-fluorouracil in isolated and aqueous conditions: substituent and solvent effects. J. Phys. Chem. Lett. 14, 2758–2763 (2023).
Miura, Y. et al. Formation of long-lived dark states during electronic relaxation of pyrimidine nucleobases studied using extreme ultraviolet time-resolved photoelectron spectroscopy. J. Am. Chem. Soc. 145, 3369–3381 (2023).
Heim, Z. N. & Neumark, D. M. Nonadiabatic dynamics studied by liquid-jet time-resolved photoelectron spectroscopy. Acc. Chem. Res. 55, 3652–3662 (2022).
Koga, M. et al. Extreme ultraviolet time-resolved photoelectron spectroscopy of adenine, adenosine and adenosine monophosphate in a liquid flat jet. Phys. Chem. Chem. Phys. 26, 13106–13117 (2024).
Ikonnikov, E. et al. Photoelectron spectroscopy of oppositely charged molecular switches in the aqueous phase: theory and experiment. J. Phys. Chem. Lett. 14, 6061–6070 (2023).
Hummert, J. et al. Femtosecond extreme ultraviolet photoelectron spectroscopy of organic molecules in aqueous solution. J. Phys. Chem. Lett. 9, 6649–6655 (2018).
Kanai, T., Minemoto, S. & Sakai, H. Quantum interference during high-order harmonic generation from aligned molecules. Nature 435, 470–474 (2005).
Baker, S. et al. Probing proton dynamics in molecules on an attosecond time scale. Science 312, 424 (2006).
Wörner, H. J., Niikura, H., Bertrand, J. B., Corkum, P. B. & Villeneuve, D. M. Observation of electronic structure minima in high-harmonic generation. Phys. Rev. Lett. 102, 103901 (2009).
Lein, M. Attosecond probing of vibrational dynamics with high-harmonic generation. Phys. Rev. Lett. 94, 053004 (2005).
Shafir, D. et al. Resolving the time when an electron exits a tunnelling barrier. Nature 485, 343–346 (2012).
Kraus, P. M. et al. Measurement and laser control of attosecond charge migration in ionized iodoacetylene. Science 350, 790–795 (2015).
Zhou, X. et al. Molecular recollision interferometry in high harmonic generation. Phys. Rev. Lett. 100, 073902–4 (2008).
Baykusheva, D. et al. Real-time probing of chirality during a chemical reaction. Proc. Natl Acad. Sci. USA 116, 23923–23929 (2019).
Mondal, A. et al. High-harmonic spectroscopy of low-energy electron-scattering dynamics in liquids. Nat. Phys. 19, 1813–1820 (2023).
Zhang, P., Perry, C., Luu, T. T., Matselyukh, D. & Wörner, H. J. Intermolecular Coulombic decay in liquid water. Phys. Rev. Lett. 128, 133001 (2022).
Gadeyne, T., Zhang, P., Schild, A. & Wörner, H. J. Low-energy electron distributions from the photoionization of liquid water: a sensitive test of electron mean free paths. Chem. Sci. 13, 1675–1692 (2022).
Frühling, U., Trinter, F., Karimi, F., Williams, J. & Jahnke, T. Time-resolved studies of interatomic Coulombic decay. J. Electron Spectros. Relat. Phenomena 204, 237–244 (2015).
Zhang, P. et al. Time-resolved multielectron coincidence spectroscopy of double Auger-Meitner decay following Xe 4d ionization. Phys. Rev. Lett. 132, 083201 (2024).
López-Tarifa, P. et al. Ultrafast damage following radiation-induced oxidation of uracil in aqueous solution. Angew. Chem. Int. Ed. 52, 3160–3163 (2013).
Joy, S. & Periyasamy, G. Influence of explicit water molecules on the charge migration dynamics of peptidomimetics: a DFT study. Theor. Chem. Acc. 139, 92 (2020).
Li, J. et al. 53-attosecond X-ray pulses reach the carbon K-edge. Nat. Commun. 8, 186 (2017).
Goulielmakis, E. et al. Single-cycle nonlinear optics. Science 320, 1614–1617 (2008).
Sansone, G. et al. Isolated single-cycle attosecond pulses. Science 314, 443 (2006).
Hentschel, M. et al. Attosecond metrology. Nature 414, 509–513 (2001).
Hartmann, N. et al. Attosecond time–energy structure of X-ray free-electron laser pulses. Nat. Photon. 12, 215–220 (2018).
Yang, Y. et al. Strong-field coherent control of isolated attosecond pulse generation. Nat. Commun. 12, 6641 (2021).
Ossiander, M. et al. Attosecond correlation dynamics. Nat. Phys. 13, 280–285 (2017).
Mashiko, H. et al. Double optical gating of high-order harmonic generation with carrier-envelope phase stabilized lasers. Phys. Rev. Lett. 100, 103906 (2008).
Ferrari, F. et al. High-energy isolated attosecond pulses generated by above-saturation few-cycle fields. Nat. Photon. 4, 875–879 (2010).
Bergues, B. et al. Tabletop nonlinear optics in the 100-eV spectral region. Optica 5, 237–242 (2018).
Xue, B., Midorikawa, K. & Takahashi, E. J. Gigawatt-class, tabletop, isolated-attosecond-pulse light source. Optica 9, 360–363 (2022).
Feng, X. et al. Generation of isolated attosecond pulses with 20 to 28 femtosecond lasers. Phys. Rev. Lett. 103, 183901 (2009).
Sola, I. J. et al. Controlling attosecond electron dynamics by phase-stabilized polarization gating. Nat. Phys. 2, 319–322 (2006).
Takahashi, E. J., Lan, P., Muecke, O. D., Nabekawa, Y. & Midorikawa, K. Attosecond nonlinear optics using gigawatt-scale isolated attosecond pulses. Nat. Commun. 4, 2691 (2013).
Barillot, T. R. et al. Towards XUV pump-probe experiments in the femtosecond to sub-femtosecond regime: new measurement of the helium two-photon ionization cross-section. Chem. Phys. Lett. 683, 38–42 (2017).
Sekikawa, T., Kosuge, A., Kanai, T. & Watanabe, S. Nonlinear optics in the extreme ultraviolet. Nature 432, 605–608 (2004).
Acknowledgements
H.J.W. acknowledges funding from the European Research Council through a Starting Grant (307270-ATTOSCOPE) and a Consolidator Grant (772797-ATTOLIQ), the Swiss National Science Foundation (SNSF) through grants 200021_172946 and 200020_204928 and ETH Zürich. J.-P.W. acknowledges funding from the SNSF through grant 200021_204844. Both authors acknowledge funding through the NCCR-MUST, a funding instrument of the SNSF.
Author information
Authors and Affiliations
Contributions
The authors contributed equally to all aspects of the article.
Corresponding authors
Ethics declarations
Competing interests
The authors declare no competing interests.
Peer review
Peer review information
Nature Reviews Chemistry thanks the anonymous reviewers for their contribution to the peer review of this work.
Additional information
Publisher’s note Springer Nature remains neutral with regard to jurisdictional claims in published maps and institutional affiliations.
Related links
The Nobel Committee for Physics: Scientific Background to the Nobel Prize in Physics 2023: https://www.nobelprize.org/uploads/2023/10/advanced-physicsprize2023-2.pdf
Rights and permissions
Springer Nature or its licensor (e.g. a society or other partner) holds exclusive rights to this article under a publishing agreement with the author(s) or other rightsholder(s); author self-archiving of the accepted manuscript version of this article is solely governed by the terms of such publishing agreement and applicable law.
About this article
Cite this article
Wörner, H.J., Wolf, JP. Ultrafast spectroscopy of liquids using extreme-ultraviolet to soft-X-ray pulses. Nat Rev Chem 9, 185–199 (2025). https://doi.org/10.1038/s41570-025-00692-9
Accepted:
Published:
Version of record:
Issue date:
DOI: https://doi.org/10.1038/s41570-025-00692-9