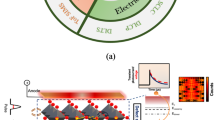
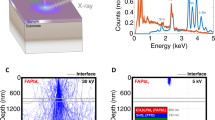
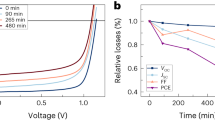
Abstract
Metal halide perovskite solar cells have considerable potential for next-generation solar power production. However, if not controlled, the migration of mobile ions can hamper the stability of perovskite solar cells. Intensive research efforts have devised methods of suppressing ion migration and degradation in perovskite materials, resulting in solar cells that are stable over thousands of hours during accelerated ageing testing. Here, we review the chemical origins of ion migration, its effect on material and device performance and stability, and strategies to mitigate its impact. Ion migration originates in the soft lattice of the halide perovskite framework and its low defect-formation energy, but there are many different strategies to reduce its effects, from compositional engineering of materials and device architecture changes to additives and strain engineering. The field has made great progress in understanding the origin and properties of mobile ions in halide perovskites and has improved operational stability beyond expectations. Nonetheless, there are still ample opportunities to further improve the long-term durability of perovskite solar cells, either by reducing ion migration or its effect on solar cell efficiency.

This is a preview of subscription content, access via your institution
Access options
Access Nature and 54 other Nature Portfolio journals
Get Nature+, our best-value online-access subscription
$32.99 / 30 days
cancel any time
Subscribe to this journal
Receive 12 digital issues and online access to articles
$119.00 per year
only $9.92 per issue
Buy this article
- Purchase on SpringerLink
- Instant access to the full article PDF.
USD 39.95
Prices may be subject to local taxes which are calculated during checkout




Similar content being viewed by others
References
Photovoltaic Research — best research-cell efficiency chart. National Laboratory of the Rockies https://www.nrel.gov/pv/cell-efficiency (2025).
Ahangharnejhad, R. H. et al. Impact of lifetime on the levelized cost of electricity from perovskite single junction and tandem solar cells. Sustain. Energy Fuels 6, 2718–2726 (2022).
Bag, M. et al. Kinetics of ion transport in perovskite active layers and its implications for active layer stability. J. Am. Chem. Soc. 137, 13130–13137 (2015).
Lang, F. et al. Radiation hardness and self-healing of perovskite solar cells. Adv. Mater. 28, 8726–8731 (2016).
Xiao, Z. & Huang, J. Energy-efficient hybrid perovskite memristors and synaptic devices. Adv. Electron. Mater. 2, 1600100 (2016).
Thiesbrummel, J. et al. Ion-induced field screening as a dominant factor in perovskite solar cell operational stability. Nat. Energy 9, 664–676 (2024). This study shows that performance degradation in perovskite solar cells is dominated by mobile-ion-induced losses at the early timescales.
Duan, L. et al. Stability challenges for the commercialization of perovskite–silicon tandem solar cells. Nat. Rev. Mater. 8, 261–281 (2023).
Mizusaki, J., Arai, K. & Fueki, K. Ionic conduction of the perovskite-type halides. Solid State Ion. 11, 203–211 (1983).
Tress, W. Metal halide perovskites as mixed electronic–ionic conductors: challenges and opportunities—from hysteresis to memristivity. J. Phys. Chem. Lett. 8, 3106–3114 (2017).
Walsh, A. & Stranks, S. D. Taking control of ion transport in halide perovskite solar cells. ACS Energy Lett. 3, 1983–1990 (2018).
Senocrate, A. & Maier, J. Solid state ionics of hybrid halide perovskites. J. Am. Chem. Soc. 141, 8382–8396 (2019).
Futscher, M. H. & Milić, J. V. Mixed conductivity of hybrid halide perovskites: emerging opportunities and challenges. Front. Energy Res. 9, 629074 (2021).
Munro, L. J. & Wales, D. J. Defect migration in crystalline silicon. Phys. Rev. B 59, 3969–3980 (1999).
Steirer, K. X. et al. Defect tolerance in methylammonium lead triiodide perovskite. ACS Energy Lett. 1, 360–366 (2016).
Hoke, E. T. et al. Reversible photo-induced trap formation in mixed-halide hybrid perovskites for photovoltaics. Chem. Sci. 6, 613–617 (2015).
deQuilettes, D. W. et al. Photo-induced halide redistribution in organic–inorganic perovskite films. Nat. Commun. 7, 11683 (2016).
Sun, Q. et al. Role of microstructure in oxygen induced photodegradation of methylammonium lead triiodide perovskite films. Adv. Energy Mater. 7, 1700977 (2017).
Eames, C. et al. Ionic transport in hybrid lead iodide perovskite solar cells. Nat. Commun. 6, 7497 (2015). Early work on the mechanisms of ionic transport and deriving Ea values for ionic migration in metal halide perovskites.
Yang, T. Y., Gregori, G., Pellet, N., Grätzel, M. & Maier, J. The significance of ion conduction in a hybrid organic-inorganic lead-iodide-based perovskite photosensitizer. Angew. Chem. Int. Ed. 54, 7905–7910 (2015).
Azpiroz, J. M., Mosconi, E., Bisquert, J. & Angelis, F. D. Defect migration in methylammonium lead iodide and its role in perovskite solar cell operation. Energy Environ. Sci. 8, 2118–2127 (2015).
Tyagi, V., Pols, M., Brocks, G. & Tao, S. Tracing ion migration in halide perovskites with machine learned force fields. J. Phys. Chem. Lett. 16, 5153–5159 (2025).
Domanski, K. et al. Not all that glitters is gold: metal-migration-induced degradation in perovskite solar cells. ACS Nano 10, 6306–6314 (2016). Early evidence of degradation caused by migration from the metal electrodes.
Futscher, M. H. et al. Quantification of ion migration in CH3NH3PbI3 perovskite solar cells by transient capacitance measurements. Mater. Horiz. 6, 1497–1503 (2019).
Clark, C. P. et al. Formation of stable metal halide perovskite/perovskite heterojunctions. ACS Energy Lett. 5, 3443–3451 (2020).
Meloni, S. et al. Ionic polarization-induced current–voltage hysteresis in CH3NH3PbX3 perovskite solar cells. Nat. Commun. 7, 10334 (2016).
Senocrate, A. et al. The nature of ion conduction in methylammonium lead iodide: a multimethod approach. Angew. Chem. Int. Ed. 56, 7755–7759 (2017). Complementary methods enable pinpointing of the dominant ionic conductivity of iodine vacancies (and the limited contribution of MA).
Senocrate, A. et al. Charge carrier chemistry in methylammonium lead iodide. Solid State Ion. 321, 69–74 (2018).
Pols, M., Brouwers, V., Calero, S. & Tao, S. How fast do defects migrate in halide perovskites: insights from on-the-fly machine-learned force fields. Chem. Commun. 59, 4660–4663 (2023).
Zhou, Y. et al. How photogenerated I2 induces I-rich phase formation in lead mixed halide perovskites. Adv. Mater. 36, 2305567 (2024).
Xue, H., Vicent-Luna, J. M., Tao, S. & Brocks, G. Compound defects in halide perovskites: a first-principles study of CsPbI3. J. Phys. Chem. C 127, 1189–1197 (2023).
Kim, G. Y. et al. Large tunable photoeffect on ion conduction in halide perovskites and implications for photodecomposition. Nat. Mater. 17, 445–449 (2018).
Brennan, M. C., Ruth, A., Kamat, P. V. & Kuno, M. Photoinduced anion segregation in mixed halide perovskites. Trends Chem. 2, 282–301 (2020).
Seitz, M. et al. Halide mixing inhibits exciton transport in two-dimensional perovskites despite phase purity. ACS Energy Lett. 7, 358–365 (2022).
Rolston, N. et al. Mechanical integrity of solution-processed perovskite solar cells. Extreme Mech. Lett. 9, 353–358 (2016).
Rolston, N. et al. Effect of cation composition on the mechanical stability of perovskite solar cells. Adv. Energy Mater. 8, 1702116 (2018).
Liu, D. et al. Strain analysis and engineering in halide perovskite photovoltaics. Nat. Mater. 20, 1337–1346 (2021).
Muscarella, L. A. & Ehrler, B. The influence of strain on phase stability in mixed-halide perovskites. Joule 6, 2016–2031 (2022).
Xue, D. J. et al. Regulating strain in perovskite thin films through charge-transport layers. Nat. Commun. 11, 1514 (2020).
Muscarella, L. A. et al. Lattice compression increases the activation barrier for phase segregation in mixed-halide perovskites. ACS Energy Lett. 5, 3152–3158 (2020).
Boyd, C. C., Cheacharoen, R., Leijtens, T. & McGehee, M. D. Understanding degradation mechanisms and improving stability of perovskite photovoltaics. Chem. Rev. 119, 3418–3451 (2019).
Batatia, I. et al. A foundation model for atomistic materials chemistry. J. Chem. Phys. 163, 184110 (2025).
Ahlawat, P. et al. Atomistic mechanism of the nucleation of methylammonium lead iodide perovskite from solution. Chem. Mater. 32, 529–536 (2020).
Bolhuis, P. G. & Swenson, D. W. H. Transition path sampling as Markov chain Monte Carlo of trajectories: recent algorithms, software, applications, and future outlook. Adv. Theory Simul. 4, 2000237 (2021).
Lu, H. et al. Vapor-assisted deposition of highly efficient, stable black-phase FAPbI3 perovskite solar cells. Science 370, eabb8985 (2020).
Schmidt, M. C., Alvarez, A. O., de Boer, J. J., van de Ven, L. J. M. & Ehrler, B. Consistent interpretation of time- and frequency-domain traces of ion migration in perovskite semiconductors. ACS Energy Lett. 9, 5850–5858 (2024).
Futscher, M. H., Gangishetty, M. K., Congreve, D. N. & Ehrler, B. Quantifying mobile ions in perovskite-based devices with temperature-dependent capacitance measurements: frequency versus time domain. J. Chem. Phys. 152, 044202 (2020).
Luo, Y. et al. Direct observation of halide migration and its effect on the photoluminescence of methylammonium lead bromide perovskite single crystals. Adv. Mater. 29, 1703451 (2017).
Klein-Kedem, N., Cahen, D. & Hodes, G. Effects of light and electron beam irradiation on halide perovskites and their solar cells. Acc. Chem. Res. 49, 347–354 (2016).
Vidon, G. et al. The impact of X-ray radiation on chemical and optical properties of triple-cation lead halide perovskite: from the surface to the bulk. Adv. Funct. Mater. 33, 2304730 (2023).
Wieghold, S., Bieber, A. S., Mardani, M., Siegrist, T. & Nienhaus, L. Understanding the effect of light and temperature on the optical properties and stability of mixed-ion halide perovskites. J. Mater. Chem. C 8, 9714–9723 (2020).
Ruan, S. et al. Light induced degradation in mixed-halide perovskites. J. Mater. Chem. C 7, 9326–9334 (2019).
Sharma, R. et al. Effect of air exposure on electron-beam-induced degradation of perovskite films. ACS Nanosci. Au 3, 230–240 (2023).
von Hauff, E. Impedance spectroscopy for emerging photovoltaics. J. Phys. Chem. C 123, 11329–11346 (2019).
Heath, J. T., Cohen, J. D. & Shafarman, W. N. Bulk and metastable defects in CuIn1−xGaxSe2 thin films using drive-level capacitance profiling. J. Appl. Phys. 95, 1000–1010 (2004).
Ravishankar, S., Unold, T. & Kirchartz, T. Comment on ‘Resolving spatial and energetic distributions of trap states in metal halide perovskite solar cells’. Science 371, eabd8014 (2021). Publication that highlights the limits of capacitance-based methods to determine charged defect density.
Guerrero, A., Bisquert, J. & Garcia-Belmonte, G. Impedance spectroscopy of metal halide perovskite solar cells from the perspective of equivalent circuits. Chem. Rev. 121, 14430–14484 (2021).
Alvarez, A. O., Ravishankar, S. & Fabregat-Santiago, F. Combining modulated techniques for the analysis of photosensitive devices. Small Methods 5, e2100661 (2021).
Pockett, A. et al. Characterization of planar lead halide perovskite solar cells by impedance spectroscopy, open-circuit photovoltage decay, and intensity-modulated photovoltage/photocurrent spectroscopy. J. Phys. Chem. C 119, 3456–3465 (2015).
Futscher, M. H. & Deibel, C. Defect spectroscopy in halide perovskites is dominated by ionic rather than electronic defects. ACS Energy Lett. 7, 140 (2022).
Lang, D. V. Deep-level transient spectroscopy: a new method to characterize traps in semiconductors. J. Appl. Phys. 45, 3023–3032 (1974).
Heiser, T. & Weber, E. R. Transient ion-drift-induced capacitance signals in semiconductors. Phys. Rev. B 58, 3893 (1998).
Reichert, S. et al. Probing the ionic defect landscape in halide perovskite solar cells. Nat. Commun. 11, 6098 (2020).
Reichert, S. et al. Ionic-defect distribution revealed by improved evaluation of deep-level transient spectroscopy on perovskite solar cells. Phys. Rev. Appl. 13, 034018 (2020).
Tammireddy, S. et al. Temperature dependent ionic conductivity and properties of iodine related defects in metal halide perovskites. ACS Energy Lett. 7, 310–319 (2022).
Barboni, D. & De Souza, R. A. The thermodynamics and kinetics of iodine vacancies in the hybrid perovskite methylammonium lead iodide. Energy Environ. Sci. 11, 3266–3274 (2018).
Schmidt, M. C., Gutierrez-Partida, E., Stolterfoht, M. & Ehrler, B. Impact of mobile ions on transient capacitance measurements of perovskite solar cells. PRX Energy 2, 043011 (2023).
Tammireddy, S. et al. Hysteresis and its correlation to ionic defects in perovskite solar cells. J. Phys. Chem. Lett. 15, 1363–1372 (2024).
Leupold, N., Seibel, A. L., Moos, R. & Panzer, F. Electrical conductivity of halide perovskites follows expectations from classical defect chemistry. Eur. J. Inorg. Chem. 2021, 2882–2889 (2021).
Dieterich, W., Dürr, O., Pendzig, P., Bunde, A. & Nitzan, A. Percolation concepts in solid state ionics. Phys. A Stat. Mech. Appl. 266, 229–237 (1999).
Kodur, M. et al. X-ray microscopy of halide perovskites: techniques, applications, and prospects. Adv. Energy Mater. 10, 1903170 (2020).
Ran, J. et al. Electron-beam-related studies of halide perovskites: challenges and opportunities. Adv. Energy Mater. 10, 1903191 (2020).
Szostak, R. et al. In situ and operando characterizations of metal halide perovskite and solar cells: insights from lab-sized devices to upscaling processes. Chem. Rev. 123, 3160–3236 (2023).
Aristidou, N. et al. Fast oxygen diffusion and iodide defects mediate oxygen-induced degradation of perovskite solar cells. Nat. Commun. 8, 15218 (2017).
Jeangros, Q. et al. In situ TEM analysis of organic–inorganic metal-halide perovskite solar cells under electrical bias. Nano Lett. 16, 7013–7018 (2016).
Xiao, C. et al. Operando characterizations of light-induced junction evolution in perovskite solar cells. ACS Appl. Mater. Interfaces 15, 20909–20916 (2023).
Zohar, A. et al. In operando, photovoltaic, and microscopic evaluation of recombination centers in halide perovskite-based solar cells. ACS Appl. Mater. Interfaces 14, 34171–34179 (2022).
Jung, H. J. et al. Stability of halide perovskite solar cell devices: in situ observation of oxygen diffusion under biasing. Adv. Mater. 30, 1802769 (2018).
Jariwala, S. et al. Dimethylammonium addition to halide perovskite precursor increases vertical and lateral heterogeneity. ACS Energy Lett. 7, 204–210 (2022).
Emelianov, N. A. et al. Direct nanoscale visualization of the electric-field-induced aging dynamics of MAPbI3 thin films. Materials 16, 4277 (2023).
Tennyson, E. M. et al. Correlated electrical and chemical nanoscale properties in potassium-passivated, triple-cation perovskite solar cells. Adv. Mater. Interfaces 7, 2000515 (2020).
Szostak, R. et al. Nanoscale mapping of chemical composition in organic-inorganic hybrid perovskite films. Sci. Adv. 5, eaaw6619 (2019).
Xie, Q. & Xu, X. G. What do different modes of AFM-IR mean for measuring soft matter surfaces? Langmuir 39, 17593–17599 (2023).
Gross, E. Challenges and opportunities in IR nanospectroscopy measurements of energy materials. Nano Res. 12, 2200–2210 (2019).
Ledinský, M. et al. Raman spectroscopy of organic–inorganic halide perovskites. J. Phys. Chem. Lett. 6, 401–406 (2015).
Franssen, W. M. J. & Kentgens, A. P. M. Solid–state NMR of hybrid halide perovskites. Solid State Nucl. Magn. Reson. 100, 36–44 (2019).
Weber, S. A. L. et al. How the formation of interfacial charge causes hysteresis in perovskite solar cells. Energy Environ. Sci. 11, 2404–2413 (2018).
Usiobo, O. J. et al. Nanoscale mass-spectrometry imaging of grain boundaries in perovskite semiconductors. J. Phys. Chem. C 124, 23230–23236 (2020).
Harvey, S. P. et al. Probing perovskite inhomogeneity beyond the surface: TOF-SIMS analysis of halide perovskite photovoltaic devices. ACS Appl. Mater. Interfaces 10, 28541–28552 (2018).
Akriti et al. Anion diffusion in two-dimensional halide perovskites. APL Mater. 10, 040903 (2022).
Song, K. et al. Atomic-resolution imaging of halide perovskites using electron microscopy. Adv. Energy Mater. 10, 1904006 (2020).
Rothmann, M. U. et al. Atomic-scale microstructure of metal halide perovskite. Science 370, eabb5940 (2020).
Dang, Z. et al. In situ transmission electron microscopy study of electron beam-induced transformations in colloidal cesium lead halide perovskite nanocrystals. ACS Nano 11, 2124–2132 (2017).
Kumar, S., Houben, L., Rechav, K. & Cahen, D. Halide perovskite dynamics at work: large cations at 2D-on-3D interfaces are mobile. Proc. Natl Acad. Sci. 119, e2114740119 (2022).
Kim, T. et al. Mapping the pathways of photo-induced ion migration in organic-inorganic hybrid halide perovskites. Nat. Commun. 14, 1846 (2023).
Peng, S. et al. Kinetics and mechanism of light-induced phase separation in a mixed-halide perovskite. Matter 6, 2052–2065 (2023).
Peña-Camargo, F. et al. Revealing the doping density in perovskite solar cells and its impact on device performance. Appl. Phys. Rev. 9, 021409 (2022).
Würfel, P. Physics of Solar Cells: From Basic Principles to Advanced Concepts 2nd edn (Wiley-VCH, 2009).
Tress, W., Leo, K. & Riede, M. Influence of hole-transport layers and donor materials on open-circuit voltage and shape of I–V curves of organic solar cells. Adv. Funct. Mater. 21, 2140–2149 (2011).
Calado, P. et al. Evidence for ion migration in hybrid perovskite solar cells with minimal hysteresis. Nat. Commun. 7, 13831 (2016). An important paper showing that the absence of hysteresis in a perovskite solar cell does not mean there are no mobile ions in the device.
Tessler, N. & Vaynzof, Y. Insights from device modeling of perovskite solar cells. ACS Energy Lett. 5, 1260–1270 (2020).
Le Corre, V. M. et al. Quantification of efficiency losses due to mobile ions in perovskite solar cells via fast hysteresis measurements. Sol. RRL 6, 2100772 (2022).
Thiesbrummel, J. et al. Universal current losses in perovskite solar cells due to mobile ions. Adv. Energy Mater. 11, 2101447 (2021).
Ginting, R. T. et al. Degradation mechanism of planar-perovskite solar cells: correlating evolution of iodine distribution and photocurrent hysteresis. J. Mater. Chem. A 5, 4527–4534 (2017).
Domanski, K. et al. Migration of cations induces reversible performance losses over day/night cycling in perovskite solar cells. Energy Environ. Sci. 10, 604–613 (2017).
Tress, W. et al. Understanding the rate-dependent J–V hysteresis, slow time component, and aging in CH3NH3PbI3 perovskite solar cells: the role of a compensated electric field. Energy Environ. Sci. 8, 995–1004 (2015). This study provides strong suggestion for a link between ion migration and device ageing.
Torre Cachafeiro, M. A. et al. Ion migration in mesoscopic perovskite solar cells: effects on electroluminescence, open circuit voltage, and photovoltaic quantum efficiency. Adv. Energy Mater. 15, 2403850 (2025).
Zhao, Y. et al. Mobile-ion-induced degradation of organic hole-selective layers in perovskite solar cells. J. Phys. Chem. C 121, 14517–14523 (2017).
Kim, S. et al. Relationship between ion migration and interfacial degradation of CH3NH3PbI3 perovskite solar cells under thermal conditions. Sci. Rep. 7, 1200 (2017).
Guerrero, A. et al. Interfacial degradation of planar lead halide perovskite solar cells. ACS Nano 10, 218–224 (2016).
Besleaga, C. et al. Iodine migration and degradation of perovskite solar cells enhanced by metallic electrodes. J. Phys. Chem. Lett. 7, 5168–5175 (2016).
Li, J., Dong, Q., Li, N. & Wang, L. Direct evidence of ion diffusion for the silver-electrode-induced thermal degradation of inverted perovskite solar cells. Adv. Energy Mater. 7, 1602922 (2017).
Zhang, T. et al. Profiling the organic cation-dependent degradation of organolead halide perovskite solar cells. J. Mater. Chem. A 5, 1103–1111 (2017).
Zhao, L. et al. Redox chemistry dominates the degradation and decomposition of metal halide perovskite optoelectronic devices. ACS Energy Lett. 1, 595–602 (2016).
Mosconi, E., Azpiroz, J. M. & De Angelis, F. Ab initio molecular dynamics simulations of methylammonium lead iodide perovskite degradation by water. Chem. Mater. 27, 4885–4892 (2015).
Ke, J. C.-R. et al. In situ investigation of degradation at organometal halide perovskite surfaces by X-ray photoelectron spectroscopy at realistic water vapour pressure. Chem. Commun. 53, 5231–5234 (2017).
Hu, S. et al. Formation and stabilization of metastable halide perovskite phases for photovoltaics. Cell Rep. Phys. Sci. 5, 101825 (2024).
Zhang, X., Turiansky, M. E., Shen, J.-X. & Van de Walle, C. G. Defect tolerance in halide perovskites: a first-principles perspective. J. Appl. Phys. 131, 090901 (2022).
Datta, K. et al. Effect of light-induced halide segregation on the performance of mixed-halide perovskite solar cells. ACS Appl. Energy Mater. 4, 6650–6658 (2021).
Nie, W. et al. Light-activated photocurrent degradation and self-healing in perovskite solar cells. Nat. Commun. 7, 11574 (2016).
Yuan, H. et al. Degradation of methylammonium lead iodide perovskite structures through light and electron beam driven ion migration. J. Phys. Chem. Lett. 7, 561–566 (2016).
Kim, G. Y., Senocrate, A., Wang, Y., Moia, D. & Maier, J. Photo-effect on ion transport in mixed cation and halide perovskites and implications for photo-demixing. Angew. Chem. Int. Ed. 60, 820–826 (2020).
DuBose, J. T. & Kamat, P. V. TiO2-assisted halide ion segregation in mixed halide perovskite films. J. Am. Chem. Soc. 142, 5362–5370 (2020).
Apergi, S., Koch, C., Brocks, G., Olthof, S. & Tao, S. Decomposition of organic perovskite precursors on MoO3: role of halogen and surface defects. ACS Appl. Mater. Interfaces 14, 34208–34219 (2022).
Jacobs, D. A. et al. Lateral ion migration accelerates degradation in halide perovskite devices. Energy Environ. Sci. 15, 5324–5339 (2022).
Koopmans, M., Corre, V. & Koster, L. SIMsalabim: an open-source drift-diffusion simulator for semiconductor devices. J. Open Source Softw. 7, 3727 (2022).
Liu, J. et al. Correlations between electrochemical ion migration and anomalous device behaviors in perovskite solar cells. ACS Energy Lett. 6, 1003–1014 (2021).
Cave, J. M. et al. Deducing transport properties of mobile vacancies from perovskite solar cell characteristics. J. Appl. Phys. 128, 184501 (2020).
Clarke, W. et al. IonMonger 2.0: software for free, fast and versatile simulation of current, voltage and impedance response of planar perovskite solar cells. J. Comput. Electron. 22, 364–382 (2023).
Zhang, J. et al. Precise control of process parameters for > 23% efficiency perovskite solar cells in ambient air using an automated device acceleration platform. Energy Environ. Sci. 17, 5490–5499 (2024).
Hart, L. J. F. et al. More is different: mobile ions improve the design tolerances of perovskite solar cells. Energy Environ. Sci. 17, 7107–7118 (2024). This study shows that mobile ions can also have positive effects, for example by improving design tolerances.
Zhu, H. et al. Long-term operating stability in perovskite photovoltaics. Nat. Rev. Mater. 8, 569–586 (2023).
Tong, C.-J., Li, L., Liu, L.-M. & Prezhdo, O. V. Synergy between ion migration and charge carrier recombination in metal-halide perovskites. J. Am. Chem. Soc. 142, 3060–3068 (2020).
Saliba, M., Stolterfoht, M., Wolff, C. M., Neher, D. & Abate, A. Measuring aging stability of perovskite solar cells. Joule 2, 1019–1024 (2018).
Shin, S. & Shin, H. Aging of perovskite solar cells: a mini review. Mater. Today Energy 37, 101381 (2023).
Zhao, X. et al. Accelerated aging of all-inorganic, interface-stabilized perovskite solar cells. Science 377, 307–310 (2022).
Pockett, A. et al. Microseconds, milliseconds and seconds: deconvoluting the dynamic behaviour of planar perovskite solar cells. Phys. Chem. Chem. Phys. 19, 5959–5970 (2017).
Ehrler, B. & Hutter, E. M. Routes toward long-term stability of mixed-halide perovskites. Matter 2, 800–802 (2020).
Ferdani, D. W. et al. Partial cation substitution reduces iodide ion transport in lead iodide perovskite solar cells. Energy Environ. Sci. 12, 2264–2272 (2019).
Lin, Y. et al. Suppressed ion migration in low-dimensional perovskites. ACS Energy Lett. 2, 1571–1572 (2017).
Huang, Z. et al. Suppressed ion migration in reduced-dimensional perovskites improves operating stability. ACS Energy Lett. 4, 1521–1527 (2019).
Futscher, M. H., Gangishetty, M. K., Congreve, D. N. & Ehrler, B. Manganese doping stabilizes perovskite light-emitting diodes by reducing ion migration. ACS Appl. Electron. Mater. 2, 1522–1528 (2020).
García-Rodríguez, R., Ferdani, D., Pering, S., Baker, P. J. & Cameron, P. J. Influence of bromide content on iodide migration in inverted MAPb(I1−xBrx)3 perovskite solar cells. J. Mater. Chem. A 7, 22604–22614 (2019).
Lin, C., Li, S., Zhang, W., Shao, C. & Yang, Z. Effect of bromine substitution on the ion migration and optical absorption in MAPbI3 perovskite solar cells: the first-principles study. ACS Appl. Energy Mater. 1, 1374–1380 (2018).
Dey, K. et al. Substitution of lead with tin suppresses ionic transport in halide perovskite optoelectronics. Energy Environ. Sci. 17, 760–769 (2024).
Kang, Y. et al. Stability-enhanced perovskite heterointerfaces and solar cells via strongly anchored and sterically hindered ligands. Nano Energy 120, 109178 (2024).
Zhao, Y. et al. Suppressing ion migration in metal halide perovskite via interstitial doping with a trace amount of multivalent cations. Nat. Mater. 21, 1396–1402 (2022).
Jiang, Q. et al. Surface passivation of perovskite film for efficient solar cells. Nat. Photon. 13, 460–466 (2019).
Pering, S. R. & Cameron, P. J. The effect of multiple ion substitutions on halide ion migration in perovskite solar cells. Mater. Adv. 3, 7918–7924 (2022).
Li, Z. et al. Inhibiting ion migration by guanidinium cation doping for efficient perovskite solar cells with enhanced operational stability. Sol. RRL 6, 2200003 (2022).
Minussi, F. B., da Silva, R. M. J. & Araújo, E. B. Differing effects of mixed a-site composition on the properties of hybrid lead iodide perovskites. J. Phys. Chem. C 127, 8814–8824 (2023).
Mahapatra, A. et al. Elucidation of the role of guanidinium incorporation in single-crystalline MAPbI3 perovskite on ion migration and activation energy. Phys. Chem. Chem. Phys. 22, 11467–11473 (2020).
Nandi, P. et al. Stabilizing mixed halide lead perovskites against photoinduced phase segregation by A-site cation alloying. ACS Energy Lett. 6, 837–847 (2021).
Ruiz Preciado, M. A. et al. Supramolecular modulation of hybrid perovskite solar cells via bifunctional halogen bonding revealed by two-dimensional 19F solid-state NMR spectroscopy. J. Am. Chem. Soc. 142, 1645–1654 (2020).
Luo, W., AlSabeh, G. & Milić, J. V. in Photochemistry, Vol. 50 (eds Crespi, S. & Protti, S.) 346–370 (The Royal Society of Chemistry, 2022).
Ferdowsi, P. et al. Host–guest complexation in wide bandgap perovskite solar cells. Sol. RRL 8, 2300655 (2024).
Ghasemi, M. et al. Dual-ion-diffusion induced degradation in lead-free Cs2AgBiBr6 double perovskite solar cells. Adv. Funct. Mater. 30, 2002342 (2020).
Bhawna, Roy, M., Kaur, A., Alam, A. & Aslam, M. BiOBr surface-functionalized halide double-perovskite films for slow ion migration and improved stability. ACS Appl. Mater. Interfaces 15, 18473–18481 (2023).
Lan, C., Zhao, S., Luo, J. & Fan, P. First-principles study of anion diffusion in lead-free halide double perovskites. Phys. Chem. Chem. Phys. 20, 24339–24344 (2018).
Cho, J., DuBose, J. T., Le, A. N. T. & Kamat, P. V. Suppressed halide ion migration in 2D lead halide perovskites. ACS Mater. Lett. 2, 565–570 (2020).
Mathew, P., Cho, J. & Kamat, P. V. Ramifications of ion migration in 2D lead halide perovskites. ACS Energy Lett. 9, 1103–1114 (2024).
deQuilettes, D. W. et al. Photoluminescence lifetimes exceeding 8 μs and quantum yields exceeding 30% in hybrid perovskite thin films by ligand passivation. ACS Energy Lett. 1, 438–444 (2016).
You, S. et al. Bifunctional hole-shuttle molecule for improved interfacial energy level alignment and defect passivation in perovskite solar cells. Nat. Energy 8, 515–525 (2023).
Lin, Y.-H. et al. Bandgap-universal passivation enables stable perovskite solar cells with low photovoltage loss. Science 384, 767–775 (2024).
Fu, L. et al. Defect passivation strategies in perovskites for an enhanced photovoltaic performance. Energy Environ. Sci. 13, 4017–4056 (2020).
Zhang, Z. et al. Rationalization of passivation strategies toward high-performance perovskite solar cells. Chem. Soc. Rev. 52, 163–195 (2023).
Xu, J. et al. Anion optimization for bifunctional surface passivation in perovskite solar cells. Nat. Mater. 22, 1507–1514 (2023).
Zhang, H., Nazeeruddin, M. K. & Choy, W. C. H. Perovskite photovoltaics: the significant role of ligands in film formation, passivation, and stability. Adv. Mater. 31, 1805702 (2019).
Milić, J. V. Supramolecular engineering of hybrid materials in photovoltaics and beyond. Chimia 76, 784–791 (2022).
Pothoof, J., Westbrook, R. J. E., Giridharagopal, R., Breshears, M. D. & Ginger, D. S. Surface passivation suppresses local ion motion in halide perovskites. J. Phys. Chem. Lett. 14, 6092–6098 (2023).
Wang, H. et al. Ion migration inhibition and defect passivation via sulfonate salt coordination for high-performance perovskite solar cells with enhanced phase stability. J. Mater. Chem. C 11, 13518–13525 (2023).
Chen, L. et al. Surface passivation of MAPbBr3 perovskite single crystals to suppress ion migration and enhance photoelectronic performance. ACS Appl. Mater. Interfaces 14, 10917–10926 (2022).
McGovern, L., Koschany, I., Grimaldi, G., Muscarella, L. A. & Ehrler, B. Grain size influences activation energy and migration pathways in MAPbBr3 perovskite solar cells. J. Phys. Chem. Lett. 12, 2423–2428 (2021).
Shan, W. & Saidi, W. A. Segregation of native defects to the grain boundaries in methylammonium lead iodide perovskite. J. Phys. Chem. Lett. 8, 5935–5942 (2017).
Hua, Y. et al. Suppressed ion migration for high-performance X-ray detectors based on atmosphere-controlled EFG-grown perovskite CsPbBr3 single crystals. Nat. Photonics 18, 870–877 (2024).
Li, C. & Chen, C. Single-crystal perovskite for solar cell applications. Small 20, 2402759 (2024).
Abdi-Jalebi, M. et al. Maximizing and stabilizing luminescence from halide perovskites with potassium passivation. Nature 555, 497–501 (2018).
Uddin, M. A. et al. Iodide manipulation using zinc additives for efficient perovskite solar minimodules. Nat. Commun. 15, 1355 (2024).
Chen, S., Xiao, X., Gu, H. & Huang, J. Iodine reduction for reproducible and high-performance perovskite solar cells and modules. Sci. Adv. 7, eabe8130 (2021).
Lu, X. et al. Dynamic reversible oxidation-reduction of iodide ions for operationally stable perovskite solar cells under ISOS-L-3 protocol. Adv. Mater. 36, 2400852 (2024).
Hutter, E. M. et al. Thermodynamic stabilization of mixed-halide perovskites against phase segregation. Cell Rep. Phys. Sci. 1, 100120 (2020).
Córdoba, M. & Taretto, K. Insight into the dependence of photovoltaic performance on interfacial energy alignment in solar cells with mobile ions. Sol. RRL 8, 2300742 (2024).
Courtier, N. E., Cave, J. M., Foster, J. M., Walker, A. B. & Richardson, G. How transport layer properties affect perovskite solar cell performance: insights from a coupled charge transport/ion migration model. Energy Environ. Sci. 12, 396–409 (2019).
Mozaffari, N. et al. Unraveling the role of energy band alignment and mobile ions on interfacial recombination in perovskite solar cells. Sol. RRL 6, 2101087 (2022).
Pallotta, R., Cavalli, S., Degani, M. & Grancini, G. Smart materials to empowering perovskite solar cells with self-healing capability. Small Struct. 5, 2300448 (2024).
Bowring, A. R., Bertoluzzi, L., O’Regan, B. C. & McGehee, M. D. Reverse bias behavior of halide perovskite solar cells. Adv. Energy Mater. 8, 1702365 (2018).
Sakhatskyi, K. et al. Assessing the drawbacks and benefits of ion migration in lead halide perovskites. ACS Energy Lett. 7, 3401–3414 (2022).
Xu, J. et al. Ion-migration inhibitor for Spiro-OMeTAD/perovskite contact toward stable perovskite solar cells. ACS Energy Lett. 9, 1073–1081 (2024).
Suo, J. et al. Multifunctional sulfonium-based treatment for perovskite solar cells with less than 1% efficiency loss over 4,500-h operational stability tests. Nat. Energy 9, 172–183 (2024).
Ren, G. et al. Organic iodides in efficient and stable perovskite solar cells: strong surface passivation and interaction. Energy Environ. Sci. 16, 565–573 (2023).
Grancini, G. et al. One-Year stable perovskite solar cells by 2D/3D interface engineering. Nat. Commun. 8, 15684 (2017).
Shen, Z. et al. Efficient and stable perovskite solar cells with regulated depletion region. Nat. Photon. 18, 450–457 (2024).
Yang, Y. et al. Inverted perovskite solar cells with over 2,000 h operational stability at 85 °C using fixed charge passivation. Nat. Energy 9, 37–46 (2024).
Kato, Y. et al. Silver iodide formation in methyl ammonium lead iodide perovskite solar cells with silver top electrodes. Adv. Mater. Interfaces 2, 1500195 (2015).
Jiang, C. et al. Double layer composite electrode strategy for efficient perovskite solar cells with excellent reverse-bias stability. Nano-Micro Lett. 15, 12 (2023).
Ehrler, B. DD parameters ion migration simulations. GitHub https://github.com/AMOLF-Hybrid-Solar-Cells/DD-parameters-ion-migration-simulations (2025).
Clarke, W., Cameron, P. & Richardson, G. Predicting long-term stability from short-term measurement: insights from modeling degradation in perovskite solar cells during voltage scans and impedance spectroscopy. J. Phys. Chem. Lett. 15, 11730–11736 (2024).
Zou, Y. & Holmes, R. J. Temperature-dependent bias poling and hysteresis in planar organo-metal halide perovskite photovoltaic cells. Adv. Energy Mater. 6, 1501994 (2016).
Bruno, A. et al. Temperature and electrical poling effects on ionic motion in MAPbI3 photovoltaic cells. Adv. Energy Mater. 7, 1700265 (2017).
Meggiolaro, D., Mosconi, E. & De Angelis, F. Formation of surface defects dominates ion migration in lead-halide perovskites. ACS Energy Lett. 4, 779–785 (2019).
Xue, H., Brocks, G. & Tao, S. Intrinsic defects in primary halide perovskites: A first-principles study of the thermodynamic trends. Phys. Rev. Mater. 6, 055402 (2022).
Moia, D. et al. Ionic-to-electronic current amplification in hybrid perovskite solar cells: ionically gated transistor-interface circuit model explains hysteresis and impedance of mixed conducting devices. Energy Environ. Sci. 12, 1296–1308 (2019).
Birkhold, S. T. et al. Direct observation and quantitative analysis of mobile Frenkel defects in metal halide perovskites using scanning Kelvin probe microscopy. J. Phys. Chem. C 122, 12633–12639 (2018).
Arber, A. N., Vikram, Mocanu, F. C. & Islam, M. S. Ion migration and dopant effects in the gamma-CsPbI3 perovskite photovoltaic material: Atomistic insights through ab initio and machine learning methods. Chem. Mater. 37, 4416–4424 (2025).
Almora, O., García-Batlle, M. & Garcia-Belmonte, G. Utilization of temperature-sweeping capacitive techniques to evaluate band gap defect densities in photovoltaic perovskites. J. Phys. Chem. Lett. 10, 3661–3669 (2019).
Wang, H., Guerrero, A., Bou, A., Al-Mayouf, A. M. & Bisquert, J. Kinetic and material properties of interfaces governing slow response and long timescale phenomena in perovskite solar cells. Energy Environ. Sci. 12, 2054–2079 (2019).
Bertoluzzi, L. et al. In situ measurement of electric-field screening in hysteresis-free PTAA/FA0.83Cs0.17Pb(I0.83Br0.17)3/C60 perovskite solar cells gives an ion mobility of ~3 × 10−7 cm2/(V s), 2 orders of magnitude faster than reported for metal-oxide-contacted perovskite cells with hysteresis. J. Am. Chem. Soc. 140, 12775–12784 (2018).
Almora, O., Guerrero, A. & Garcia-Belmonte, G. Ionic charging by local imbalance at interfaces in hybrid lead halide perovskites. Appl. Phys. Lett. 108, 043903 (2016).
De Souza, R. A., Kemp, D., Wolf, M. J. & Ramadan, A. H. H. Caution! Static supercell calculations of defect migration in higher symmetry ABX3 perovskite halides may be unreliable: a case study of methylammonium lead iodide. J. Phys. Chem. Lett. 13, 11363–11368 (2022).
McGovern, L., Futscher, M. H., Muscarella, L. A. & Ehrler, B. Understanding the stability of MAPbBr3 versus MAPbI3: suppression of methylammonium migration and reduction of halide migration. J. Phys. Chem. Lett. 11, 7127–7132 (2020).
Acknowledgements
The work of J.T., E.C.G. and B.E. is part of the Dutch Research Council and was performed at the AMOLF research institute. J.V.M. appreciates the support of the Swiss National Science Foundation via PRIMA project no. 193174 and European Research Council (ERC) under the European Union’s Horizon 2020 research and innovation programme for project no. 101114653. S.T. acknowledges funding from Vidi (Project VI.Vidi.213.091) from the Dutch Research Council (NWO). The work of W.T. received funding from the ERC programme under Grant Agreement no. 851676. C.D. thanks the Deutsche Forschungsgemeinschaft (DFG) for generous support within the framework of SPP 2196 project (PERFECT PVs). A.G. thanks Grant PID2022-141850OB-C21 funded by MICIU/AEI /10.13039/501100011033 and by ERDF/EU. The related work of M.S.I. received funding from the UK Engineering and Physical Sciences Research Council (EP/X038777/1; EP/X012263/1). The work of B.E. received funding from the ERC under Grant Agreement no. 947221. E.C.G. received funding from the ERC under Grant Agreement no. 101043783.
Author information
Authors and Affiliations
Contributions
Sections were primarily written by the authors specified as follows. The chemistry of ion migration in halide perovskites: J.V.M., M.S.I. and S.T. Measurement techniques and visualization of ion migration: C.D. and E.C.G. Effects of ion migration on solar cell performance: A.G., J.T., S.T. and T.K. Suppression of ion migration effects in materials and solar cell devices: A.G., M.S.I., P.C. and W.T. J.T. and B.E. integrated the different sections and coordinated the project. All authors contributed to editing and revision of the manuscript.
Corresponding author
Ethics declarations
Competing interests
The authors declare no competing interests.
Peer review
Peer review information
Nature Reviews Chemistry thanks Xiaopeng Zheng, Guoqing Tong and the other anonymous reviewer(s) for their contribution to the peer review of this work.
Additional information
Publisher’s note Springer Nature remains neutral with regard to jurisdictional claims in published maps and institutional affiliations.
Rights and permissions
Springer Nature or its licensor (e.g. a society or other partner) holds exclusive rights to this article under a publishing agreement with the author(s) or other rightsholder(s); author self-archiving of the accepted manuscript version of this article is solely governed by the terms of such publishing agreement and applicable law.
About this article
Cite this article
Thiesbrummel, J., Milić, J.V., Deibel, C. et al. Ion migration in perovskite solar cells. Nat Rev Chem (2026). https://doi.org/10.1038/s41570-025-00790-8
Accepted:
Published:
Version of record:
DOI: https://doi.org/10.1038/s41570-025-00790-8