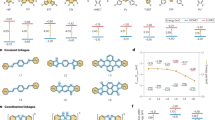
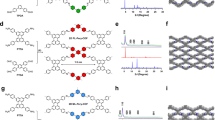
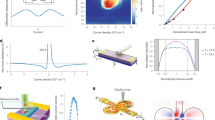
Abstract
Two-dimensional framework materials (2DFMs) have emerged as a transformative class of synthetic organic 2D crystal materials, in which molecular building blocks and/or metal nodes are linked through covalent or coordination bonds to form layered networks stabilized by π–π interactions. Their modular design allows atomic-level control over electronic configurations, enabling novel quantum phenomena and tunable functionalities. Over the past decade, strategic exploitation of intralayer π-extended conjugation and interlayer electronic coupling has revolutionized charge transport engineering in 2DFMs, driving advancements in (opto-)electronics, energy storage and quantum materials. In this Review, we provide a coherent overview of structural design strategies, charge transport mechanisms and cutting-edge characterization methodologies for electrically conductive 2DFMs. We emphasize recent progress elucidating key factors governing charge transport properties and intricate structure–property relationships. Finally, we discuss promising directions for advancing this rapidly evolving field that bridges atomic precision with solid-state physics, offering unprecedented opportunities to design electronic materials from the bottom up.
This is a preview of subscription content, access via your institution
Access options
Access Nature and 54 other Nature Portfolio journals
Get Nature+, our best-value online-access subscription
$32.99 / 30 days
cancel any time
Subscribe to this journal
Receive 12 digital issues and online access to articles
$119.00 per year
only $9.92 per issue
Buy this article
- Purchase on SpringerLink
- Instant access to the full article PDF.
USD 39.95
Prices may be subject to local taxes which are calculated during checkout







Similar content being viewed by others
References
Fan, H. et al. MOF-in-COF molecular sieving membrane for selective hydrogen separation. Nat. Commun. 12, 38 (2021).
Peng, Y. et al. Metal-organic framework nanosheets as building blocks for molecular sieving membranes. Science 346, 1356–1359 (2014).
Wu, W. et al. Accurate stacking engineering of MOF nanosheets as membranes for precise H2 sieving. Nat. Commun. 15, 10730 (2024).
Fan, H. et al. Covalent organic framework-covalent organic framework bilayer membranes for highly selective gas separation. J. Am. Chem. Soc. 140, 10094–10098 (2018).
Ying, Y. et al. Ultrathin two-dimensional membranes assembled by ionic covalent organic nanosheets with reduced apertures for gas separation. J. Am. Chem. Soc. 142, 4472–4480 (2020).
Peng, Y., Li, Y., Ban, Y. & Yang, W. Two-dimensional metal-organic framework nanosheets for membrane-based gas separation. Angew. Chem. Int. Ed. 56, 9757–9761 (2017).
Clough, A. J., Yoo, J. W., Mecklenburg, M. H. & Marinescu, S. C. Two-dimensional metal-organic surfaces for efficient hydrogen evolution from water. J. Am. Chem. Soc. 137, 118–121 (2015).
Huang, Y. et al. Growth of Au nanoparticles on 2D metalloporphyrinic metal-organic framework nanosheets used as biomimetic catalysts for cascade reactions. Adv. Mater. 29, 1700102 (2017).
Lin, S. et al. Covalent organic frameworks comprising cobalt porphyrins for catalytic CO2 reduction in water. Science 349, 1208–1213 (2015).
Wang, X. et al. Homochiral 2D porous covalent organic frameworks for heterogeneous asymmetric catalysis. J. Am. Chem. Soc. 138, 12332–12335 (2016).
Xu, H., Gao, J. & Jiang, D. Stable, crystalline, porous, covalent organic frameworks as a platform for chiral organocatalysts. Nat. Chem. 7, 905–912 (2015).
Chen, R. et al. Rational design of isostructural 2D porphyrin-based covalent organic frameworks for tunable photocatalytic hydrogen evolution. Nat. Commun. 12, 1354 (2021).
Zhang, W. et al. Reconstructed covalent organic frameworks. Nature 604, 72–79 (2022).
Liu, R. et al. Linkage-engineered donor-acceptor covalent organic frameworks for optimal photosynthesis of hydrogen peroxide from water and air. Nat. Catal. 7, 195–206 (2024).
Wang, X. et al. Sulfone-containing covalent organic frameworks for photocatalytic hydrogen evolution from water. Nat. Chem. 10, 1180–1189 (2018).
Zheng, L. et al. Covalent organic framework membrane reactor for boosting catalytic performance. Nat. Commun. 15, 6837 (2024).
Spitler, E. L. & Dichtel, W. R. Lewis acid-catalysed formation of two-dimensional phthalocyanine covalent organic frameworks. Nat. Chem. 2, 672–677 (2010).
Zhou, T. et al. PEG-stabilized coaxial stacking of two-dimensional covalent organic frameworks for enhanced photocatalytic hydrogen evolution. Nat. Commun. 12, 3934 (2021).
Jin, E. et al. A nanographene-based two-dimensional covalent organic framework as a stable and efficient photocatalyst. Angew. Chem. Int. Ed. 61, e202114059 (2022).
Huang, X. et al. Metal-phthalocyanine-based two-dimensional conjugated metal-organic frameworks for electrochemical glycerol oxidation reaction. Angew. Chem. Int. Ed. 64, e202416178 (2025).
Liu, J. et al. Tricycloquinazoline-based 2D conductive metal-organic frameworks as promising electrocatalysts for CO2 reduction. Angew. Chem. Int. Ed. 60, 14473–14479 (2021).
Jin, E. et al. 2D sp2 carbon-conjugated covalent organic frameworks for photocatalytic hydrogen production from water. Chem 5, 1632–1647 (2019).
Li, C. et al. Tunable catalytic vertex wall chemistry in metal-free covalent organic frameworks for enhanced oxygen reduction. Angew. Chem. Int. Ed. 64, e202500336 (2025).
You, P.-Y. et al. Reversible modulation of interlayer stacking in 2D copper-organic frameworks for tailoring porosity and photocatalytic activity. Nat. Commun. 15, 194 (2024).
Feng, D. et al. Robust and conductive two-dimensional metal-organic frameworks with exceptionally high volumetric and areal capacitance. Nat. Energy 3, 30–36 (2018).
Xu, S. et al. A nitrogen-rich 2D sp2-carbon-linked conjugated polymer framework as a high-performance cathode for lithium-ion batteries. Angew. Chem. Int. Ed. 58, 849–853 (2019).
Bi, S. et al. Molecular understanding of charge storage and charging dynamics in supercapacitors with MOF electrodes and ionic liquid electrolytes. Nat. Mater. 19, 552–558 (2020).
Nam, K. W. et al. Conductive 2D metal-organic framework for high-performance cathodes in aqueous rechargeable zinc batteries. Nat. Commun. 10, 4948 (2019).
Sporrer, L. et al. Skeletal nitrogen functionalization of isostructural 2D conjugated MOFs for enhancement of the dual-ion storage capacity. Angew. Chem. Int. Ed. 64, e202418390 (2024).
Wang, M. et al. Phthalocyanine-based 2D conjugated metal-organic framework nanosheets for high-performance micro-supercapacitors. Adv. Funct. Mater. 30, 2002664 (2020).
Lu, Y. et al. sp-Carbon incorporated conductive metal-organic framework as photocathode for photoelectrochemical hydrogen generation. Angew. Chem. Int. Ed. 61, e202208163 (2022).
Zhong, H. et al. Synergistic electroreduction of carbon dioxide to carbon monoxide on bimetallic layered conjugated metal-organic frameworks. Nat. Commun. 11, 1409 (2020).
Park, J. et al. Stabilization of hexaaminobenzene in a 2D conductive metal–organic framework for high power sodium storage. J. Am. Chem. Soc. 140, 10315–10323 (2018).
DeBlase, C. R., Silberstein, K. E., Truong, T.-T., Abruña, H. D. & Dichtel, W. R. β-Ketoenamine-linked covalent organic frameworks capable of pseudocapacitive energy storage. J. Am. Chem. Soc. 135, 16821–16824 (2013).
Yang, Z. et al. Arylamine-linked 2D covalent organic frameworks for efficient pseudocapacitive energy storage. Angew. Chem. Int. Ed. 60, 20754–20759 (2021).
Sun, Z. et al. Two-dimensional fused π-conjugated multi-activity covalent organic framework as high-performance cathode for lithium-ion batteries. Nano Energy 129, 110073 (2024).
Zhang, H. et al. Charge and mass transport mechanisms in two-dimensional covalent organic frameworks (2D COFs) for electrochemical energy storage devices. Energy Environ. Sci. 16, 889–951 (2023).
Gu, Q. et al. Constructing chiral covalent-organic frameworks for circularly polarized light detection. Adv. Mater. 36, 2306414 (2024).
Tang, X. et al. Construction of chiral covalent organic frameworks through a linker decomposition chiral induction strategy for circularly polarized light detection. Angew. Chem. Int. Ed. 64, e202413675 (2025).
Zhang, Q. et al. The transfer dehydrogenation method enables a family of high crystalline benzimidazole-linked Cu (II)-phthalocyanine-based covalent organic frameworks films. Angew. Chem. Int. Ed. 63, e202319027 (2024).
Yu, F. et al. Photostimulus-responsive large-area two-dimensional covalent organic framework films. Angew. Chem. Int. Ed. 58, 16101–16104 (2019).
Wan, S., Guo, J., Kim, J., Ihee, H. & Jiang, D. A belt-shaped, blue luminescent, and semiconducting covalent organic framework. Angew. Chem. Int. Ed. 47, 8826–8830 (2008).
Wan, S., Guo, J., Kim, J., Ihee, H. & Jiang, D. A photoconductive covalent organic framework: self-condensed arene cubes composed of eclipsed 2D polypyrene sheets for photocurrent generation. Angew. Chem. Int. Ed. 48, 5439–5442 (2009).
Feng, X. et al. High-rate charge-carrier transport in porphyrin covalent organic frameworks: switching from hole to electron to ambipolar conduction. Angew. Chem. Int. Ed. 51, 2618–2622 (2012).
Sahabudeen, H. et al. Wafer-sized multifunctional polyimine-based two-dimensional conjugated polymers with high mechanical stiffness. Nat. Commun. 7, 13461 (2016).
Zhou, D., Tan, X., Wu, H., Tian, L. & Li, M. Synthesis of C−C bonded two-dimensional conjugated covalent organic framework films by Suzuki polymerization on a liquid-liquid interface. Angew. Chem. Int. Ed. 58, 1376–1381 (2019).
Wang, R. et al. Highly conductive covalent-organic framework films. Small 20, 2306634 (2024).
Li, C. et al. Two-dimensional conjugated polymer synthesized by interfacial Suzuki reaction: towards electronic device applications. Angew. Chem. Int. Ed. 59, 9403–9407 (2020).
Ding, X. et al. An n-channel two-dimensional covalent organic framework. J. Am. Chem. Soc. 133, 14510–14513 (2011).
Bag, S. et al. Covalent organic framework thin-film photodetectors from solution-processable porous nanospheres. J. Am. Chem. Soc. 145, 1649–1659 (2023).
Arora, H. et al. Demonstration of a broadband photodetector based on a two-dimensional metal-organic framework. Adv. Mater. 32, 1907063 (2020).
Liu, C.-K. et al. 2D metal-organic framework Cu3(HHTT)2 films for broadband photodetectors from ultraviolet to mid-infrared. Adv. Mater. 34, 2204140 (2022).
Song, J. et al. Large-area fabrication of hexaazatrinaphthylene-based 2D metal-organic framework films for flexible photodetectors and optoelectronic synapses. Adv. Sci. 11, 2305551 (2024).
Song, J. et al. 2D metal-organic frameworks for ultraflexible electrochemical transistors with high transconductance and fast response speeds. Sci. Adv. 9, eadd9627 (2023).
Liu, Y. et al. Face-to-face growth of wafer-scale 2D semiconducting MOF films on dielectric substrates. Adv. Mater. 33, 2007741 (2021).
Wu, G.-D. et al. MOF nanosheet reconstructed two-dimensional bionic nanochannel for protonic field-effect transistors. Angew. Chem. Int. Ed. 60, 9931–9935 (2021).
Xian, Z. et al. 2D ferroelectric metal-organic frameworks for ultralow power field effect transistors. Adv. Funct. Mater. 35, 2409388 (2025).
Wu, G., Huang, J., Zang, Y., He, J. & Xu, G. Porous field-effect transistors based on a semiconductive metal-organic framework. J. Am. Chem. Soc. 139, 1360–1363 (2017).
Wang, B. Luo, Y., Liu, B. & Duan, G. Field-effect transistor based on an in situ grown metal-organic framework film as a liquid-gated sensing device. ACS Appl. Mater. Interfaces 11, 35935–35940 (2019).
Shi, N. et al. Ultrathin metal-organic framework nanosheets as nano-floating-gate for high performance transistor memory device. Adv. Funct. Mater. 32, 2110784 (2022).
Ni, X., Huang, H. & Brédas, J.-L. Emergence of a two-dimensional topological Dirac semimetal phase in a phthalocyanine-based covalent organic framework. Chem. Mater. 34, 3178–3184 (2022).
Hsu, C.-H., Huang, Z.-Q., Macam, G. M., Chuang, F.-C. & Huang, L. Prediction of two-dimensional organic topological insulator in metal-DCB lattices. Appl. Phys. Lett. 113, 233301 (2018).
Gao, Z. A. et al. Synthesis and characterization of a single-layer conjugated metal–organic structure featuring a non-trivial topological gap. Nanoscale 11, 878–881 (2019).
Gao, Z. A. et al. Design and synthesis of a single-layer ferromagnetic metal-organic framework with topological nontrivial gaps. J. Phys. Chem. C 124, 27017–27023 (2020).
Jiang, W., Zhang, S., Wang, Z., Liu, F. & Low, T. Topological band engineering of Lieb lattice in phthalocyanine-based metal-organic frameworks. Nano Lett. 20, 1959–1966 (2020).
López-Cabrelles, J. et al. Chemical design and magnetic ordering in thin layers of 2D metal-organic frameworks (MOFs). J. Am. Chem. Soc. 143, 18502–18510 (2021).
Wang, Z. F., Liu, Z. & Liu, F. Quantum anomalous Hall effect in 2D organic topological insulators. Phys. Rev. Lett. 110, 196801 (2013).
Un, H.-I., et al. Controlling film formation and host-guest interactions to enhance the thermoelectric properties of nickel-nitrogen-based 2D conjugated coordination polymers. Adv. Mater. 36, 2312325 (2024).
Evans, A. M. et al. Thermally conductive ultra-low-k dielectric layers based on two-dimensional covalent organic frameworks. Nat. Mater. 20, 1142–1148 (2021).
Sun, L. et al. A microporous and naturally nanostructured thermoelectric metal-organic framework with ultralow thermal conductivity. Joule 1, 168–177 (2017).
Erickson, K. J. et al. Thin film thermoelectric metal-organic framework with high Seebeck coefficient and low thermal conductivity. Adv. Mater. 27, 3453–3459 (2015).
Zhou, T. et al. Atomistic design of two-dimensional covalent organic frameworks with high thermoelectric performance. J. Mater. Chem. A 11, 15821–15832 (2023).
Kulkarni, R. et al. Real-time optical and electronic sensing with a β-amino enone linked, triazine-containing 2D covalent organic framework. Nat. Commun. 10, 3228 (2019).
Evans, A. M. et al. High-sensitivity acoustic molecular sensors based on large-area, spray-coated 2D covalent organic frameworks. Adv. Mater. 32, 2004205 (2020).
Ye, W. et al. Halide perovskite glues activate two-dimensional covalent organic framework crystallites for selective NO2 sensing. Nat. Commun. 14, 2133 (2023).
Yao, M.-S. et al. Van der Waals heterostructured MOF-on-MOF thin films: cascading functionality to realize advanced chemiresistive sensing. Angew. Chem. Int. Ed. 58, 14915–14919 (2019).
Campbell, M. G., Liu, S. F., Swager, T. M. & Dincă, M. Chemiresistive sensor arrays from conductive 2D metal-organic frameworks. J. Am. Chem. Soc. 137, 13780–13783 (2015).
Dong, J. et al. Ultrathin two-dimensional porous organic nanosheets with molecular rotors for chemical sensing. Nat. Commun. 8, 1142 (2017).
Zhang, M. et al. Two-dimensional metal-organic framework with wide channels and responsive turn-on fluorescence for the chemical sensing of volatile organic compounds. J. Am. Chem. Soc. 136, 7241–7244 (2014).
Meng, Z., Stolz, R. M. & Mirica, K. A. Two-dimensional chemiresistive covalent organic framework with high intrinsic conductivity. J. Am. Chem. Soc. 141, 11929–11937 (2019).
Smith, M. K. & Mirica, K. A. Self-organized frameworks on textiles (SOFT): conductive fabrics for simultaneous sensing, capture, and filtration of gases. J. Am. Chem. Soc. 139, 16759–16767 (2017).
Meng, Z., Aykanat, A. & Mirica, K. A. Welding metallophthalocyanines into bimetallic molecular meshes for ultrasensitive, low-power chemiresistive detection of gases. J. Am. Chem. Soc. 141, 2046–2053 (2019).
Ko, M. et al. Employing conductive metal-organic frameworks for voltammetric detection of neurochemicals. J. Am. Chem. Soc. 142, 11717–11733 (2020).
Mirica, K. A., Weis, J. G., Schnorr, J. M., Esser, B. & Swager, T. M. Mechanical drawing of gas sensors on paper. Angew. Chem. Int. Ed. 51, 10740–10745 (2012).
Mendecki, L., Ko, M., Zhang, X., Meng, Z. & Mirica, K. A. Porous scaffolds for electrochemically controlled reversible capture and release of ethylene. J. Am. Chem. Soc. 139, 17229–17232 (2017).
Aykanat, A., Meng, Z., Stolz, R. M., Morrell, C. T. & Mirica, K. A. Bimetallic two-dimensional metal-organic frameworks for the chemiresistive detection of carbon monoxide. Angew. Chem. Int. Ed. 61, e202113665 (2022).
Campbell, M. G., Sheberla, D., Liu, S. F., Swager, T. M. & Dincă, M. Cu3(hexaiminotriphenylene)2: an electrically conductive 2D metal-organic framework for chemiresistive sensing. Angew. Chem. Int. Ed. 54, 4349–4352 (2015).
Shustova, N. B., Cozzolino, A. F., Reineke, S., Baldo, M. & Dincă, M. Selective turn-on ammonia sensing enabled by high-temperature fluorescence in metal-organic frameworks with open metal sites. J. Am. Chem. Soc. 135, 13326–13329 (2013).
Stassen, I., Dou, J.-H., Hendon, C. & Dincă, M. Chemiresistive sensing of ambient CO2 by an autogenously hydrated Cu3(hexaiminobenzene)2 framework. ACS Cent. Sci. 5, 1425–1431 (2019).
Jiao, J. et al. A trimming-π strategy for constructing functional conductive metal–organic frameworks using metalloporphyrazine units. Angew. Chem. Int. Ed. 64, e202502066 (2025).
Mitra, S. et al. Targeted drug delivery in covalent organic nanosheets (CONs) via sequential postsynthetic modification. J. Am. Chem. Soc. 139, 4513–4520 (2017).
Mal, A. et al. Supramolecular surface charge regulation in ionic covalent organic nanosheets: reversible exfoliation and controlled bacterial growth. Angew. Chem. Int. Ed. 59, 8713–8719 (2020).
Mal, A. et al. Supramolecular reassembly of self-exfoliated ionic covalent organic nanosheets for label-free detection of double-stranded DNA. Angew. Chem. Int. Ed. 57, 8443–8447 (2018).
Zhang, L. et al. Covalent organic frameworks as favorable constructs for photodynamic therapy. Angew. Chem. Int. Ed. 58, 14213–14218 (2019).
Mi, Z. et al. Stable radical cation-containing covalent organic frameworks exhibiting remarkable structure-enhanced photothermal conversion. J. Am. Chem. Soc. 141, 14433–14442 (2019).
Peng, Y. et al. Ultrathin two-dimensional covalent organic framework nanosheets: preparation and application in highly sensitive and selective DNA detection. J. Am. Chem. Soc. 139, 8698–8704 (2017).
Das, G. et al. Covalent organic nanosheets for bioimaging. Chem. Sci. 9, 8382–8387 (2018).
Sun, Q., Aguila, B., Lan, P. C. & Ma, S. Tuning pore heterogeneity in covalent organic frameworks for enhanced enzyme accessibility and resistance against denaturants. Adv. Mater. 31, 1900008 (2019).
Ji, W. et al. Synthesis of a covalent organic framework with hetero-environmental pores and its medicine co-delivery application. Nat. Commun. 14, 6049 (2023).
Esrafili, A. et al. Crystallinity of covalent organic frameworks controls immune responses. Nat. Commun. 15, 9739 (2024).
Wei, J. et al. Efficient selective removal of uremic toxin precursor by olefin-linked covalent organic frameworks for nephropathy treatment. Nat. Commun. 14, 2805 (2023).
Bhunia, S., Jaiswal, M. K., Singh, K. A., Deo, K. A. & Gaharwar, A. K. 2D covalent organic framework direct osteogenic differentiation of stem cells. Adv. Healthc. Mater. 11, 2101737 (2022).
Yang, B., Yao, H., Yang, J., Chen, C. & Shi, J. Construction of a two-dimensional artificial antioxidase for nanocatalytic rheumatoid arthritis treatment. Nat. Commun. 13, 1988 (2022).
Ni, K. et al. Synergistic checkpoint-blockade and radiotherapy-radiodynamic therapy via an immunomodulatory nanoscale metal-organic framework. Nat. Biomed. Eng. 6, 144–156 (2022).
Li, J. et al. 2D MOF periodontitis photodynamic ion therapy. J. Am. Chem. Soc. 143, 15427–15439 (2021).
Huang, N., Zhai, L., Xu, H. & Jiang, D. Stable covalent organic frameworks for exceptional mercury removal from aqueous solutions. J. Am. Chem. Soc. 139, 2428–2434 (2017).
Benyettou, F. et al. Tunable wettability of a dual-faced covalent organic framework membrane for enhanced water filtration. J. Am. Chem. Soc. 146, 23537–23554 (2024).
Qin, C. et al. Twistedly hydrophobic basis with suitable aromatic metrics in covalent organic networks govern micropollutant decontamination. Nat. Commun. 14, 6740 (2023).
Akhzari, S., Raissi, H. & Ghahari, A. Architectural design of 2D covalent organic frameworks (COFs) for pharmaceutical pollutant removal. npj Clean Water 7, 31 (2024).
Lu, C., Clayville, B., Choi, J. Y. & Park, J. 2D metal-organic frameworks as an emerging platform with tunable electronic structures. Chem 9, 2757–2770 (2023).
Huang, X. et al. Superconductivity in a copper (II)-based coordination polymer with perfect kagome structure. Angew. Chem. Int. Ed. 57, 146 (2018).
Talin, A. A. et al. Tunable electrical conductivity in metal-organic framework thin-film devices. Science 343, 66–69 (2014).
Wang, M. et al. Exceptionally high charge mobility in phthalocyanine-based poly(benzimidazobenzophenanthroline)-ladder-type two-dimensional conjugated polymers. Nat. Mater. 22, 880–887 (2023).
Fu, S. et al. Unveiling high-mobility hot carriers in a two-dimensional conjugated coordination polymer. Nat. Mater. 24, 1457–1464 (2025).
Spies, L. et al. Spatiotemporal spectroscopy of fast excited-state diffusion in 2D covalent organic framework thin films. J. Am. Chem. Soc. 147, 1758–1766 (2025).
Pan, Z. et al. Atomic-precision non-van der Waals 2D structures: superconductivity in π–d conjugated coordination polymers. Nat. Commun. 15, 9342 (2024).
Takenaka, T. et al. Strongly correlated superconductivity in a copper-based metal-organic framework with a perfect kagome lattice. Sci. Adv. 7, eabf3996 (2021).
Lu, Y. et al. Rational construction of layered two-dimensional conjugated metal–organic frameworks with room-temperature quantum coherence. J. Am. Chem. Soc. 147, 8778–8784 (2025).
Zhao, M. et al. Two-dimensional metal-organic framework nanosheets: synthesis and applications. Chem. Soc. Rev. 47, 6267–6295 (2018).
Chakraborty, G., Park, I.-H., Medishetty, R. & Vittal, J. J. Two-dimensional metal-organic framework materials: synthesis, structures, properties and applications. Chem. Rev. 121, 3751–3891 (2021).
Liu, J., Xing, G. & Chen, L. 2D conjugated metal-organic frameworks: defined synthesis and tailor-made functions. Acc. Chem. Res. 57, 1032–1045 (2024).
Dong, R., Zhang, T. & Feng, X. Interface-assisted synthesis of 2D materials: trend and challenges. Chem. Rev. 118, 6189–6235 (2018).
Dang, S., Zhu, Q.-L. & Xu, Q. Nanomaterials derived from metal-organic frameworks. Nat. Rev. Mater. 3, 17075 (2017).
Li, Y., Chen, W., Xing, G., Jiang, D. & Chen, L. New synthetic strategies toward covalent organic frameworks. Chem. Soc. Rev. 49, 2852–2868 (2020).
Colson, J. W. & Dichtel, W. R. Rationally synthesized two-dimensional polymers. Nat. Chem. 5, 453–465 (2013).
Zhang, T., Zhang, G. & Chen, L. 2D conjugated covalent organic frameworks: defined synthesis and tailor-made functions. Acc. Chem. Res. 55, 795–808 (2022).
Qian, C. et al. Imine and imine-derived linkages in two-dimensional covalent organic frameworks. Nat. Rev. Chem. 6, 881–898 (2022).
Geng, K. et al. Covalent organic frameworks: design, synthesis, and functions. Chem. Rev. 120, 8814–8933 (2020).
Jin, Y., Hu, Y. & Zhang, W. Tessellated multiporous two-dimensional covalent organic frameworks. Nat. Rev. Chem. 1, 0056 (2017).
Wang, C. et al. 2D covalent organic frameworks: from synthetic strategies to advanced optical-electrical-magnetic functionalities. Adv. Mater. 34, 2102290 (2022).
Huang, N., Wang, P. & Jiang, D. Covalent organic frameworks: a materials platform for structural and functional designs. Nat. Rev. Mater. 1, 16068 (2016).
Tan, K. T. et al. Covalent organic frameworks. Nat. Rev. Methods Primers 3, 1 (2023).
Liu, R. et al. Covalent organic frameworks: an ideal platform for designing ordered materials and advanced applications. Chem. Soc. Rev. 50, 120–242 (2021).
Feng, X., Ding, X. & Jiang, D. Covalent organic frameworks. Chem. Soc. Rev. 41, 6010–6022 (2012).
Seki, S., Paitandi, R. P., Choi, W., Ghosh, S. & Tanaka, T. Electron transport over 2D molecular materials and assemblies. Acc. Chem. Res. 57, 2665–2677 (2024).
Liu, Q. et al. Two-dimensional covalent organic frameworks in organic electronics. Angew. Chem. Int. Ed. 64, e202502536 (2025).
Chen, G. et al. Recent advances in functional electronic devices enabled by two-dimensional covalent organic framework films. Mater. Chem. Front. 9, 1443–1458 (2025).
Rodríguez-San-Miguel, D., Montoro, C. & Zamora, F. Covalent organic framework nanosheets: preparation, properties and applications. Chem. Soc. Rev. 49, 2291–2302 (2020).
Wang, M., Dong, R. & Feng, X. Two-dimensional conjugated metal-organic frameworks (2D c-MOFs): chemistry and function for MOFtronics. Chem. Soc. Rev. 50, 2764–2793 (2021).
Sun, L., Campbell, M. G. & Dincă, M. Electrically conductive porous metal-organic frameworks. Angew. Chem. Int. Ed. 55, 3566–3579 (2016).
Xie, L. S., Skorupskii, G. & Dinca, M. Electrically conductive metal-organic frameworks. Chem. Rev. 120, 8536–8580 (2020).
Wang, Z., Wang, M., Heine, T. & Feng, X. Electronic and quantum properties of organic two-dimensional crystals. Nat. Rev. Mater. 10, 147–166 (2025).
Zhu, Y., Jiang, S., Jing, X. & Feng, X. Electrically conductive 2D covalent organic frameworks. Trends Chem. 4, 128–141 (2022).
Blätte, D., Ortmann, F. & Bein, T. Photons, excitons, and electrons in covalent organic frameworks. J. Am. Chem. Soc. 146, 32161–32205 (2024).
Keller, N. & Bein, T. Optoelectronic processes in covalent organic frameworks. Chem. Soc. Rev. 50, 1813–1845 (2021).
Huang, Z. & Geilhufe, R. M. Quantum metal-organic frameworks. Small Sci. 4, 2400161 (2024).
Rosen, A. S. et al. Machine learning the quantum-chemical properties of metal–organic frameworks for accelerated materials discovery. Matter 4, 1578–1597 (2021).
Jiang, W., Ni, X. & Liu, F. Exotic topological bands and quantum states in metal–organic and covalent–organic frameworks. Acc. Chem. Res. 54, 416–426 (2021).
Misumi, Y. et al. Quantum spin liquid state in a two-dimensional semiconductive metal–organic framework. J. Am. Chem. Soc. 142, 16513–16517 (2020).
Wu, M. et al. Conetronics in 2D metal-organic frameworks: double/half Dirac cones and quantum anomalous Hall effect. 2D Mater. 4, 015015 (2016).
Kohn, J. T., Li, H., Evans, A. M., Brédas, J.-L. & Grimme, S. Quantum chemistry insight into the multifaceted structural properties of two-dimensional covalent organic frameworks. Chem. Mater. 35, 2820–2826 (2023).
Lu, Y., Samorì, P. & Feng, X. Rational construction of two-dimensional conjugated metal–organic frameworks (2D c-MOFs) for electronics and beyond. Acc. Chem. Res. 57, 1985–1996 (2024).
Nicks, J., Sasitharan, K., Prasad, R. R. R., Ashworth, D. J. & Foster, J. A. Metal–organic framework nanosheets: programmable 2D materials for catalysis, sensing, electronics, and separation applications. Adv. Funct. Mater. 31, 2103723 (2021).
Zheng, Y., Sun, F.-Z., Han, X., Xu, J. & Bu, X.-H. Recent progress in 2D metal-organic frameworks for optical applications. Adv. Opt. Mater. 8, 2000110 (2020).
Ren, X. et al. Two-dimensional MOF and COF nanosheets for next-generation optoelectronic applications. Coord. Chem. Rev. 435, 213781 (2021).
Li, X., Yadav, P. & Loh, K. P. Function-oriented synthesis of two-dimensional (2D) covalent organic frameworks–from 3D solids to 2D sheets. Chem. Soc. Rev. 49, 4835–4866 (2020).
Valentini, C., Montes-García, V., Pakulski, D., Samorì, P. & Ciesielski, A. Covalent organic frameworks and 2D materials hybrids: synthesis strategies, properties enhancements, and future directions. Small 21, 2410544 (2025).
Guo, Q. et al. Structural codes of organic electrode materials for rechargeable multivalent metal batteries. Chem. Soc. Rev. 54, 4035–4086 (2025).
Wang, H. et al. Covalent organic framework photocatalysts: structures and applications. Chem. Soc. Rev. 49, 4135–4165 (2020).
Khalil, I. E., Das, P. & Thomas, A. Two-dimensional covalent organic frameworks: structural insights across different length scales and their impact on photocatalytic efficiency. Acc. Chem. Res. 57, 3138–3150 (2024).
Lin, L. et al. Rational design and synthesis of two-dimensional conjugated metal-organic polymers for electrocatalysis applications. Chem 8, 1822–1854 (2022).
Wan, S. et al. Covalent organic frameworks with high charge carrier mobility. Chem. Mater. 23, 4094–4097 (2011).
Tries, A. et al. Experimental observation of strong exciton effects in graphene nanoribbons. Nano Lett. 20, 2993–3002 (2020).
Handa, T. et al. Spontaneous exciton dissociation in transition metal dichalcogenide monolayers. Sci. Adv. 10, eadj4060 (2024).
Saha, M. N. On a physical theory of stellar spectra. Proc. R. Soc. Lond. A 99, 135–153 (1921).
Wang, M. et al. High-mobility semiconducting two-dimensional conjugated covalent organic frameworks with p-type doping. J. Am. Chem. Soc. 142, 21622–21627 (2020).
Huang, X. et al. Semiconducting conjugated coordination polymer with high charge mobility enabled by “4+ 2” phenyl ligands. J. Am. Chem. Soc. 145, 2430–2438 (2023).
Fu, G. -e, Yang, H., Zhao, W., Samorì, P. & Zhang, T. 2D conjugated polymer thin films for organic electronics: opportunities and challenges. Adv. Mater. 36, 2311541 (2024).
Fu, S. et al. Outstanding charge mobility by band transport in two-dimensional semiconducting covalent organic frameworks. J. Am. Chem. Soc. 144, 7489–7496 (2022).
Dong, R. et al. High-mobility band-like charge transport in a semiconducting two-dimensional metal-organic framework. Nat. Mater. 17, 1027–1032 (2018).
Liu, Y. et al. A thiophene backbone enables two-dimensional poly(arylene vinylene)s with high charge carrier mobility. Angew. Chem. Int. Ed. 62, e202305978 (2023).
Ghosh, S. et al. Band-like transport of charge carriers in oriented two-dimensional conjugated covalent organic frameworks. Chem. Mater. 34, 736–745 (2022).
Wang, S. et al. A fully conjugated 3D covalent organic framework exhibiting band-like transport with ultrahigh electron mobility. Angew. Chem. Int. Ed. 60, 9321–9325 (2021).
Giannini, S. & Blumberger, J. Charge transport in organic semiconductors: the perspective from nonadiabatic molecular dynamics. Acc. Chem. Res. 55, 819–830 (2022).
Troisi, A. Charge transport in high mobility molecular semiconductors: classical models and new theories. Chem. Soc. Rev. 40, 2347–2358 (2011).
Kim, S.-W. et al. Hexaazatriphenylene-based two-dimensional conductive covalent organic framework with anisotropic charge transfer. Angew. Chem. Int. Ed. 62, e202310560 (2023).
Yavuz, I. Dichotomy between the band and hopping transport in organic crystals: insights from experiments. Phys. Chem. Chem. Phys. 19, 25819–25828 (2017).
Yamashita, Y. et al. Transition between band and hopping transport in polymer field-effect transistors. Adv. Mater. 26, 8169–8173 (2014).
Fratini, S., Nikolka, M., Salleo, A., Schweicher, G. & Sirringhaus, H. Charge transport in high-mobility conjugated polymers and molecular semiconductors. Nat. Mater. 19, 491–502 (2020).
Giannini, S. et al. Transiently delocalized states enhance hole mobility in organic molecular semiconductors. Nat. Mater. 22, 1361–1369 (2023).
Huang, X. et al. A two-dimensional π–d conjugated coordination polymer with extremely high electrical conductivity and ambipolar transport behaviour. Nat. Commun. 6, 7408 (2015).
Perloff, D. S. Four-point sheet resistance correction factors for thin rectangular samples. Solid State Electron. 20, 681–687 (1977).
Ramadan, A. A., Gould, R. D. & Ashour, A. On the van der Pauw method of resistivity measurements. Thin Solid Films 239, 272–275 (1994).
Wu, T. et al. Revealing the charge transport physics in metallic coordination nanosheets by thermoelectric and magnetotransport measurements. Sci. Adv. 11, eadt9196 (2025).
Torsi, L., Magliulo, M., Manoli, K. & Palazzo, G. Organic field-effect transistor sensors: a tutorial review. Chem. Soc. Rev. 42, 8612–8628 (2013).
Braga, D. & Horowitz, G. High-performance organic field-effect transistors. Adv. Mater. 21, 1473–1486 (2009).
von Klitzing, K. The quantized Hall effect. Rev. Mod. Phys. 58, 519–531 (1986).
Werner, F. Hall measurements on low-mobility thin films. J. Appl. Phys. 122, 135306 (2017).
Ulbricht, R., Hendry, E., Shan, J., Heinz, T. F. & Bonn, M. Carrier dynamics in semiconductors studied with time-resolved terahertz spectroscopy. Rev. Mod. Phys. 83, 543–586 (2011).
Hempel, H. et al. Predicting solar cell performance from terahertz and microwave spectroscopy. Adv. Energy Mater. 12, 2102776 (2022).
Bretschneider, S. A., et al. Quantifying polaron formation and charge carrier cooling in lead-iodide perovskites. Adv. Mater. 30, 1707312 (2018).
Zhang, H. et al. Highly mobile hot holes in Cs2AgBiBr6 double perovskite. Sci. Adv. 7, eabj9066 (2021).
Tielrooij, K.-J. et al. Photoexcitation cascade and multiple hot-carrier generation in graphene. Nat. Phys. 9, 248–252 (2013).
Jensen, S. A. et al. Competing ultrafast energy relaxation pathways in photoexcited graphene. Nano Lett. 14, 5839–5845 (2014).
Gao, L. et al. Tailoring polaron dimensions in lead-tin hybrid perovskites. Adv. Mater. 36, 2406109 (2024).
Zhang, H. et al. Stable Mott polaron state limits the charge density in lead halide perovskites. ACS Energy Lett. 8, 420–428 (2022).
Cocker, T. L. et al. Microscopic origin of the Drude-Smith model. Phys. Rev. B 96, 205439 (2017).
Smith, N. Drude theory and the optical properties of liquid mercury. Phys. Lett. A 26, 126–127 (1968).
Smith, N. Classical generalization of the Drude formula for the optical conductivity. Phys. Rev. B 64, 155106 (2001).
Fratini, S., Ciuchi, S. & Mayou, D. Phenomenological model for charge dynamics and optical response of disordered systems: application to organic semiconductors. Phys. Rev. B 89, 235201 (2014).
Li, D. et al. MXenes with ordered triatomic-layer borate polyanion terminations. Nat. Mater. 23, 1085–1092 (2024).
Chen, Q. et al. Porphyrin-fused graphene nanoribbons. Nat. Chem. 16, 1133–1140 (2024).
Zheng, W. et al. Band transport by large Fröhlich polarons in MXenes. Nat. Phys. 18, 544–550 (2022).
Geuchies, J. J. et al. Anisotropic electron-phonon interactions in 2D lead-halide perovskites. Nano Lett. 24, 8642–8649 (2024).
Li, J. et al. Charge generation dynamics in organic photovoltaic blends under one-sun-equivalent illumination detected by highly sensitive terahertz spectroscopy. J. Am. Chem. Soc. 146, 20312–20322 (2024).
Zhang, T. et al. Two-dimensional polyaniline crystal with metallic out-of-plane conductivity. Nature 638, 411–417 (2025).
Giannazzo, F., Schilirò, E., Greco, G. & Roccaforte, F. Conductive atomic force microscopy of semiconducting transition metal dichalcogenides and heterostructures. Nanomaterials 10, 803 (2020).
Liu, J. et al. On-liquid-gallium surface synthesis of ultrasmooth thin films of conductive metal-organic frameworks. Nat. Synth. 3, 715–726 (2024).
Wang, Z. et al. Interfacial synthesis of layer-oriented 2D conjugated metal-organic framework films toward directional charge transport. J. Am. Chem. Soc. 143, 13624–13632 (2021).
Jin, E. et al. Two-dimensional sp2 carbon-conjugated covalent organic frameworks. Science 357, 673–676 (2017).
Zhuang, X. et al. A two-dimensional conjugated polymer framework with fully sp2-bonded carbon skeleton. Polym. Chem. 7, 4176–4181 (2016).
Kambe, T. et al. π-Conjugated nickel bis(dithiolene) complex nanosheet. J. Am. Chem. Soc. 135, 2462–2465 (2013).
Fu, S. et al. Dimensional evolution of charge mobility and porosity in covalent organic frameworks. Nat. Commun. 16, 2219 (2025).
Nyakuchena, J. et al. Direct evidence of photoinduced charge transport mechanism in 2D conductive metal organic frameworks. J. Am. Chem. Soc. 142, 21050–21058 (2020).
Wang, J. et al. Superior charge transport in Ni-diamine conductive MOFs. J. Am. Chem. Soc. 146, 20500–20507 (2024).
Lu, Y. et al. Precise tuning of interlayer electronic coupling in layered conductive metal-organic frameworks. Nat. Commun. 13, 7240 (2022).
Dou, J.-H. et al. Atomically precise single-crystal structures of electrically conducting 2D metal-organic frameworks. Nat. Mater. 20, 222–228 (2021).
Skorupskii, G. et al. Efficient and tunable one-dimensional charge transport in layered lanthanide metal–organic frameworks. Nat. Chem. 12, 131–136 (2020).
Zhang, J. et al. Wavy two-dimensional conjugated metal-organic framework with metallic charge transport. J. Am. Chem. Soc. 145, 23630–23638 (2023).
Skorupskii, G. et al. Porous lanthanide metal-organic frameworks with metallic conductivity. Proc. Natl Acad. Sci. USA 119, e2205127119 (2022).
Wang, D. et al. Dominant role of hole transport pathway in achieving record high photoconductivity in two-dimensional metal-organic frameworks. Angew. Chem. Int. Ed. 62, e202309505 (2023).
Su, A. Y., Apostol, P., Wang, J., Vlad, A. & Dincă, M. Electrochemical capacitance traces with interlayer spacing in two-dimensional conductive metal-organic frameworks. Angew. Chem. Int. Ed. 63, e202402526 (2024).
Noh, H.-J. et al. Tuning the structure-property relationships of metallophthalocyanine-based two-dimensional conductive metal-organic frameworks with different metal linkages. J. Am. Chem. Soc. 147, 8240–8249 (2025).
Jeon, M. et al. Computational prediction of stacking mode in conductive two-dimensional metal-organic frameworks: an exploration of chemical and electrical property changes. ACS Sens. 8, 3068–3075 (2023).
Jain, C. et al. Tailoring COFs: transforming nonconducting 2D layered COF into a conducting quasi-3D architecture via interlayer knitting with polypyrrole. J. Am. Chem. Soc. 146, 487–499 (2024).
Wang, S. et al. Covalent organic frameworks: a platform for the experimental establishment of the influence of intermolecular distance on phosphorescence. J. Mater. Chem. C 6, 5369–5374 (2018).
Cai, S. et al. Reversible interlayer sliding and conductivity changes in adaptive tetrathiafulvalene-based covalent organic frameworks. ACS Appl. Mater. Interfaces 12, 19054–19061 (2020).
Sick, T. et al. Switching on and off interlayer correlations and porosity in 2D covalent organic frameworks. J. Am. Chem. Soc. 141, 12570–12581 (2019).
Kang, C. et al. Interlayer shifting in two-dimensional covalent organic frameworks. J. Am. Chem. Soc. 142, 12995–13002 (2020).
Kang, C. et al. Tunable interlayer shifting in two-dimensional covalent organic frameworks triggered by CO2 sorption. J. Am. Chem. Soc. 144, 20363–20371 (2022).
Jin, S. et al. Two-dimensional tetrathiafulvalene covalent organic frameworks: towards latticed conductive organic salts. Chem. Eur. J. 20, 14608–14613 (2014).
Xing, G. et al. Nonplanar rhombus and kagome 2D covalent organic frameworks from distorted aromatics for electrical conduction. J. Am. Chem. Soc. 144, 5042–5050 (2022).
Jiang, G. et al. Tuning the interlayer interactions of 2D covalent organic frameworks enables an ultrastable platform for anhydrous proton transport. Angew. Chem. Int. Ed. 61, e202208086 (2022).
Li, M. et al. Constructing 2D phthalocyanine covalent organic framework with enhanced stability and conductivity via interlayer hydrogen bonding as electrocatalyst for CO2 reduction. Small 20, 2310147 (2024).
Li, Z. et al. Ultrafine spatial modulation of diazapyrene-based two-dimensional conjugated covalent organic frameworks. J. Am. Chem. Soc. 146, 23497–23507 (2024).
Wu, X., Han, X., Liu, Y., Liu, Y. & Cui, Y. Control interlayer stacking and chemical stability of two-dimensional covalent organic frameworks via steric tuning. J. Am. Chem. Soc. 140, 16124–16133 (2018).
Chen, X., Addicoat, M., Irle, S., Nagai, A. & Jiang, D. Control of crystallinity and porosity of covalent organic frameworks by managing interlayer interactions based on self-complementary π-electronic force. J. Am. Chem. Soc. 135, 546–549 (2013).
Li, Y. et al. Interlayer slipping facilitating manipulation of electronic properties of few-layer two-dimensional conjugated polymers. SmartMat 6, e70019 (2025).
Dou, J.-H. et al. Signature of metallic behavior in the metal-organic frameworks M3(hexaiminobenzene)2 (M = Ni, Cu). J. Am. Chem. Soc. 139, 13608–13611 (2017).
Frey, L. et al. Oriented thiophene-extended benzotrithiophene covalent organic framework thin films: directional electrical conductivity. Adv. Funct. Mater. 32, 2205949 (2022).
Wang, Z. et al. A low-symmetry copper benzenehexathiol coordination polymer with in-plane electrical anisotropy. Angew. Chem. Int. Ed. 64, e202423341 (2025).
Yang, M. et al. Two-dimensional conjugated metal–organic frameworks with a ring-in-ring topology and high electrical conductance. Angew. Chem. Int. Ed. 63, e202405333 (2024).
Liu, Y. et al. Vinylene-linked 2D conjugated covalent organic frameworks by Wittig reaction. Angew. Chem. Int. Ed. 134, e202209762 (2022).
Jin, E. et al. Module-patterned polymerization towards crystalline 2D sp2-carbon covalent organic framework semiconductors. Angew. Chem. Int. Ed. 134, e202115020 (2021).
Huang, S. et al. Carbazolylene-ethynylene macrocycle based conductive covalent organic frameworks. Angew. Chem. Int. Ed. 62, e202303538 (2023).
Zhu, Y. et al. Iodine-doped covalent organic frameworks with coaxially stacked cruciform anthracenes for high Hall mobility. Chem. Commun. 58, 6606–6609 (2022).
Li, Y. et al. Targeted synthesis of isomeric naphthalene-based 2D kagome covalent organic frameworks. Angew. Chem. Int. Ed. 62, e202216795 (2023).
Burke, D. W. et al. Synthesis, hole doping, and electrical properties of a semiconducting azatriangulene-based covalent organic framework. J. Am. Chem. Soc. 145, 11969–11977 (2023).
Rotter, J. M. et al. Highly conducting Wurster-type twisted covalent organic frameworks. Chem. Sci. 11, 12843–12853 (2020).
Apostol, P. et al. Controlling charge transport in 2D conductive MOFs — the role of nitrogen-rich ligands and chemical functionality. J. Am. Chem. Soc. 145, 24669–24677 (2023).
Aubrey, M. L. et al. Electron delocalization and charge mobility as a function of reduction in a metal–organic framework. Nat. Mater. 17, 625–632 (2018).
Pham, H. T. B. et al. Imparting functionality and enhanced surface area to a 2D electrically conductive MOF via macrocyclic linker. J. Am. Chem. Soc. 144, 10615–10621 (2022).
Huang, X. et al. Control of the hydroquinone/benzoquinone redox state in high-mobility semiconducting conjugated coordination polymers. Angew. Chem. Int. Ed. 63, e202320091 (2024).
Fang, Z., Bueken, B., DeVos, D. E. & Fischer, R. A. Defect-engineered metal-organic frameworks. Angew. Chem. Int. Ed. 54, 7234–7254 (2015).
Qi, H. et al. Near-atomic-scale observation of grain boundaries in a layer-stacked two-dimensional polymer. Sci. Adv. 6, eabb5976 (2020).
Haase, F. et al. Topochemical conversion of an imine- into a thiazole-linked covalent organic framework enabling real structure analysis. Nat. Commun. 9, 2600 (2018).
Castano, I. et al. Mapping grains, boundaries, and defects in 2D covalent organic framework thin films. Chem. Mater. 33, 1341–1352 (2021).
Du, K. et al. Impact of structural defects on the electronic properties of two-dimensional covalent organic frameworks. ACS Mater. Lett. 6, 335–344 (2024).
Sheberla, D. et al. High electrical conductivity in Ni3(2,3,6,7,10,11-hexaiminotriphenylene)2, a semiconducting metal–organic graphene analogue. J. Am. Chem. Soc. 136, 8859–8862 (2014).
Day, R. W. et al. Single crystals of electrically conductive two-dimensional metal-organic frameworks: structural and electrical transport properties. ACS Cent. Sci. 5, 1959–1964 (2019).
Foster, M. E., Sohlberg, K., Allendorf, M. D. & Talin, A. A. Unraveling the semiconducting/metallic discrepancy in Ni3(HITP)2. J. Phys. Chem. Lett. 9, 481–486 (2018).
Debela, T. T., Yang, M. C. & Hendon, C. H. Ligand-mediated hydrogenic defects in two-dimensional electrically conductive metal-organic frameworks. J. Am. Chem. Soc. 145, 11387–11391 (2023).
Choi, J. Y. & Park, J. Enhancing electrical conductivity of semiconducting MOFs via defect healing. ACS Appl. Electron. Mater. 3, 4197–4202 (2021).
Pan, Y., Ho, C.-H., Paesani, F. & Ghosh, R. Engineering flat and dispersive bands in 2D layered COFs via interlayer stacking and donor–acceptor strategy. Chem. Mater. 35, 6235–6245 (2023).
Luo, Y. et al. Defect engineering to tailor metal vacancies in 2D conductive metal-organic frameworks: an example in electrochemical sensing. ACS Nano 16, 20820–20830 (2022).
Wang, X. et al. Robust ultrathin nanoporous MOF membrane with intra-crystalline defects for fast water transport. Nat. Commun. 13, 266 (2022).
Park, G., Demuth, M. C., Hendon, C. H. & Park, S. S. Acid-dependent charge transport in a solution-processed 2D conductive metal-organic framework. J. Am. Chem. Soc. 146, 11493–11499 (2024).
Liu, X. et al. Magnetoresistance in organic spin valves based on acid-exfoliated 2D covalent organic frameworks thin films. Angew. Chem. Int. Ed. 62, e202308921 (2023).
Yu, H. & Wang, D. Metal-free magnetism in chemically doped covalent organic frameworks. J. Am. Chem. Soc. 142, 11013–11021 (2020).
Lakshmi, V. et al. A two-dimensional poly(azatriangulene) covalent organic framework with semiconducting and paramagnetic states. J. Am. Chem. Soc. 142, 2155–2160 (2020).
Cui, B. et al. Realization of Lieb lattice in covalent-organic frameworks with tunable topology and magnetism. Nat. Commun. 11, 66 (2020).
Field, B., Schiffrin, A. & Medhekar, N. V. Correlation-induced magnetism in substrate-supported 2D metal-organic frameworks. npj Comput. Mater. 8, 227 (2022).
Yu, Q. & Wang, D. Room-temperature magnetism in two-dimensional metal–organic frameworks enabled by electrostatic gating. J. Mater. Chem. A 11, 5548–5558 (2023).
Yan, X., Su, X., Chen, J., Jin, C. & Chen, L. Two-dimensional metal-organic frameworks towards spintronics. Angew. Chem. Int. Ed. 62, e202305408 (2023).
Feng, S. et al. Intrinsic room-temperature ferromagnetism in a two-dimensional semiconducting metal-organic framework. Nat. Commun. 14, 7063 (2023).
Zhang, L.-C. et al. Two-dimensional magnetic metal-organic frameworks with the Shastry-Sutherland lattice. Chem. Sci. 10, 10381–10387 (2019).
Grisan Qiu, Y. Y., et al. Conformation-driven nickel redox states and magnetism in 2D metal–organic frameworks. Adv. Funct. Mater. 35, 2418186 (2025).
Dong, R. et al. A coronene-based semiconducting two-dimensional metal-organic framework with ferromagnetic behavior. Nat. Commun. 9, 2637 (2018).
Lu, Y. et al. Tunable charge transport and spin dynamics in two-dimensional conjugated metal–organic frameworks. J. Am. Chem. Soc. 146, 2574–2582 (2024).
Ohlrich, M. F. et al. Flat bands and unconventional superconductivity in a simple model of metal-organic frameworks. Phys. Rev. B 111, L100503 (2025).
Thomas, S., Li, H. & Bredas, J.-L. Emergence of an antiferromagnetic Mott insulating phase in hexagonal π-conjugated covalent organic frameworks. Adv. Mater. 31, 1900355 (2019).
Hu, T., Zhang, T., Mu, H. & Wang, Z. Intrinsic second-order topological insulator in two-dimensional covalent organic frameworks. J. Phys. Chem. Lett. 13, 10905–10911 (2022).
Ni, X., Huang, H. & Brédas, J.-L. Organic higher-order topological insulators: heterotriangulene-based covalent organic frameworks. J. Am. Chem. Soc. 144, 22778–22786 (2022).
Hu, T., Zhong, W., Zhang, T., Wang, W. & Wang, Z. F. Identifying topological corner states in two-dimensional metal-organic frameworks. Nat. Commun. 14, 7092 (2023).
Deng, T. et al. Designing intrinsic topological insulators in two-dimensional metal–organic frameworks. J. Phys. Chem. Lett. 12, 6934–6940 (2021).
Wang, L. et al. Metal-organic frameworks: strain-tunable quantum phase transition and high-order topological insulator and emergent fermions. Phys. Rev. B 111, 035102 (2025).
Zhang, T., Su, N., Hu, T., Wang, W. & Wang, Z. Topological band engineering of one-dimensional π-d conjugated metal–organic frameworks. J. Am. Chem. Soc. 146, 30539–30547 (2024).
Colson, J. W. et al. Oriented 2D covalent organic framework thin films on single-layer graphene. Science 332, 228–231 (2011).
Cusin, L. et al. Synthesis of micrometre-thick oriented 2D covalent organic framework films by a kinetic polymerization pathway. Nat. Synth. 4, 632–641 (2025).
Liu, J. et al. Ammonia-assisted chemical vapor deposition growth of two-dimensional conjugated coordination polymer thin films. J. Am. Chem. Soc. 147, 18190–18196 (2025).
Wang, Z. et al. A Cu3BHT-graphene van der Waals heterostructure with strong interlayer coupling for highly efficient photoinduced charge separation. Adv. Mater. 36, 2311454 (2024).
Su, X. et al. De novo design and facile synthesis of highly crystalline 2D conductive metal–organic frameworks: a “rotor-stator” strategy. J. Am. Chem. Soc. 146, 9036–9044 (2024).
Xing, G. et al. Conjugated nonplanar copper-catecholate conductive metal-organic frameworks via contorted hexabenzocoronene ligands for electrical conduction. J. Am. Chem. Soc. 145, 8979–8987 (2023).
Song, M. et al. Catalysis-assisted synthesis of two-dimensional conductive metal–organic framework films with controllable orientation. J. Am. Chem. Soc. 147, 17058–17067 (2025).
Wang, C., et al. Enhancing the carrier transport in monolayer MoS2 through interlayer coupling with 2D covalent organic frameworks. Adv. Mater. 36, 2305882 (2024).
Gao, Z. et al. Laterally engineering lanthanide-MOFs epitaxial heterostructures for spatially resolved planar 2D photonic barcoding. Angew. Chem. Int. Ed. 60, 24519–24525 (2021).
Zhan, G. et al. Moiré two-dimensional covalent organic framework superlattices. Nat. Chem. 17, 518–524 (2025).
Weng, W. & Guo, J. Chiral covalent organic framework films with enhanced photoelectrical performances. J. Am. Chem. Soc. 146, 13201–13209 (2024).
Han, X., Jiang, C., Hou, B., Liu, Y. & Cui, Y. Covalent organic frameworks with tunable chirality for chiral-induced spin selectivity. J. Am. Chem. Soc. 146, 6733–6743 (2024).
Chen, H., Gu, Z.-G. & Zhang, J. Chiral-induced ultrathin covalent organic frameworks nanosheets with tunable circularly polarized luminescence. J. Am. Chem. Soc. 144, 7245–7252 (2022).
Zhou, J. et al. Mobility enhancement in heavily doped semiconductors via electron cloaking. Nat. Commun. 13, 2482 (2022).
Zhang, X., Zhou, Y., Cui, B., Zhao, M. & Liu, F. Theoretical discovery of a superconducting two-dimensional metal-organic framework. Nano Lett. 17, 6166–6170 (2017).
Zanca, F. et al. Computational techniques for characterisation of electrically conductive MOFs: quantum calculations and machine learning approaches. J. Mater. Chem. C 9, 13584–13599 (2021).
Lin, J. et al. Machine learning-driven discovery and structure-activity relationship analysis of conductive metal-organic frameworks. Chem. Mater. 36, 5436–5445 (2024).
Wang, D., Lv, H., Wan, Y., Wu, X. & Yang, J. Band-edge prediction of 2D covalent organic frameworks from molecular precursor via machine learning. J. Phys. Chem. Lett. 14, 6757–6764 (2023).
Fu, A., Yi, G. & Li, Y. Phonon-limited electron transport in a highly conductive two-dimensional covalent organic framework: a computational study. J. Phys. Chem. C 126, 20127–20134 (2022).
Bashiri, R. et al. Discovery of dual ion-electron conductivity of metal-organic frameworks via machine learning-guided experimentation. Chem. Mater. 37, 1143–1153 (2025).
Acknowledgements
This work is financially supported by CRC 1415 (Chemistry of Synthetic Two-Dimensional Materials, number 417590517, to X.F.), SPP 2244 (2DMP, to X.F.) and RTG 2861 (number 491865171, to X.F. and R.D.). R.D. thanks the National Natural Science Foundation of China (22272092; 22472085), Natural Science Foundation of Shandong Province (ZR2023JQ005), and Taishan Scholars Program of Shandong Province (tsqn201909047). E.J. acknowledges the National Natural Science Foundation of China (grant 22371087), the National Key Research and Development Program of China (grant 2024YFB3815700), the ‘111 Center’ (B17020) and the start-up grant of Jilin University.
Author information
Authors and Affiliations
Contributions
X.F., H.I.W. and M.B. conceived the theme of the manuscript. S.F. and J.Z. researched data for the article. S.F. led the drafting of the manuscript. All authors contributed to the discussion and writing of the manuscript before submission.
Corresponding authors
Ethics declarations
Competing interests
The authors declare no competing interests.
Peer review
Peer review information
Nature Reviews Materials thanks Jinhu Dou, Christopher Hendon and the other, anonymous, reviewer(s) for their contribution to the peer review of this work.
Additional information
Publisher’s note Springer Nature remains neutral with regard to jurisdictional claims in published maps and institutional affiliations.
Glossary
- BBL
-
Poly(benzimidazobenzophenanthroline).
- BHT
-
Benzenehexathiol.
- DHTTB
-
2,5-Dihydroxy-1,3,4,6-tetrathiolbenzene.
- F4TCNQ
-
2,3,5,6-Tetrafluoro-tetracyanoquinodimethane.
- HHTC
-
2,3,8,9,14,15-Hexahydroxytribenzocyclyne.
- HHTP
-
2,3,6,7,10,11-Hexahydroxytriphenylene.
- HIB
-
Hexaiminobenzene.
- HITT
-
2,3,7,8,12,13-Hexaiminotetraazanaphthotetraphene.
- Magic Blue
-
Tris(4-bromophenyl)ammoniumylachloroantimonate.
- TCNQ
-
7,7,8,8-Tetracyanoquinododimethane.
- THQ
-
Tetrahydroxyquinone.
- THT
-
2,3,6,7,10,11-Triphenylenehexathiol.
- TTBQ
-
1,2,4,5-Tetrathiolbenzoquinone.
- TTHQ
-
1,2,4,5-Tetrathiolhydroquinone.
Rights and permissions
Springer Nature or its licensor (e.g. a society or other partner) holds exclusive rights to this article under a publishing agreement with the author(s) or other rightsholder(s); author self-archiving of the accepted manuscript version of this article is solely governed by the terms of such publishing agreement and applicable law.
About this article
Cite this article
Fu, S., Zhang, J., Li, X. et al. Fundamentals of charge transport in two-dimensional framework materials. Nat Rev Mater (2025). https://doi.org/10.1038/s41578-025-00840-z
Accepted:
Published:
Version of record:
DOI: https://doi.org/10.1038/s41578-025-00840-z