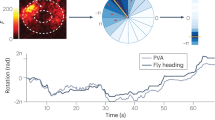
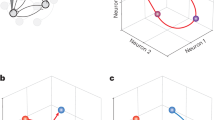
Abstract
Animal behavior arises from the coordinated activity of neural populations that span the entire brain. The activity of large neural populations from an increasing number of brain regions, behaviors and species shows low-dimensional structure. We posit that this structure arises as a result of neural manifolds. Neural manifolds are mathematical descriptions of a meaningful biological entity: the possible collective states of a population of neurons given the constraints, both intrinsic (for example, connectivity) and extrinsic (for example, behavior), to the neural circuit. Here, we explore the link between neural manifolds and behavior, and discuss the insights that the neural manifold framework can provide into brain function. To conclude, we explore existing conceptual gaps in this framework and discuss their implications when building an integrative view of brain function. We thus position neural manifolds as a crucial framework with which to describe how the brain generates behavior.
This is a preview of subscription content, access via your institution
Access options
Access Nature and 54 other Nature Portfolio journals
Get Nature+, our best-value online-access subscription
$32.99 / 30 days
cancel any time
Subscribe to this journal
Receive 12 print issues and online access
$259.00 per year
only $21.58 per issue
Buy this article
- Purchase on SpringerLink
- Instant access to the full article PDF.
USD 39.95
Prices may be subject to local taxes which are calculated during checkout





Similar content being viewed by others
References
Ramón y Cajal, S. Textura del sistema nervioso del hombre y de los vertebrados: estudios sobre el plan estructural y composición histológica de los centros nerviosos adicionados de consideraciones fisiológicas fundadas en los nuevos descubrimientos (N. Moya, 1899).
Georgopoulos, A. P., Kalaska, J. F., Caminiti, R. & Massey, J. T. On the relations between the direction of two-dimensional arm movements and cell discharge in primate motor cortex. J. Neurosci. 2, 1527–1537 (1982).
Humphrey, D. R., Schmidt, E. M. & Thompson, W. D. Predicting measures of motor performance from multiple cortical spike trains. Science 170, 758–762 (1970).
Hubel, D. H. & Wiesel, T. N. Receptive fields, binocular interaction and functional architecture in the cat’s visual cortex. J. Physiol. 160, 106–154 (1962).
O’Keefe, J. & Dostrovsky, J. The hippocampus as a spatial map. Preliminary evidence from unit activity in the freely-moving rat. Brain Res. 34, 171–175 (1971).
Brodmann, K. Vergleichende Lokalisationslehre der Grosshirnrinde in ihren Prinzipien dargestellt auf Grund des Zellenbaues (Barth, 1909).
Gallego, J. A., Perich, M. G., Miller, L. E. & Solla, S. A. Neural manifolds for the control of movement. Neuron 94, 978–984 (2017).
Perich, M. G. & Rajan, K. Rethinking brain-wide interactions through multi-region ‘network of networks’ models. Curr. Opin. Neurobiol. 65, 146–151 (2020).
Vyas, S., Golub, M. D., Sussillo, D. & Shenoy, K. V. Computation through neural population dynamics. Annu. Rev. Neurosci. 43, 249–275 (2020).
Mante, V., Sussillo, D., Shenoy, K. V. & Newsome, W. T. Context-dependent computation by recurrent dynamics in prefrontal cortex. Nature 503, 78–84 (2013).
Churchland, M. M. & Shenoy, K. V. Temporal complexity and heterogeneity of single-neuron activity in premotor and motor cortex. J. Neurophysiol. 97, 4235–4257 (2007).
Machens, C. K., Romo, R. & Brody, C. D. Functional, but not anatomical, separation of ‘what’ and ‘when’ in prefrontal cortex. J. Neurosci. 30, 350–360 (2010).
Stevenson, I. H. & Kording, K. P. How advances in neural recording affect data analysis. Nat. Neurosci. 14, 139–142 (2011).
Jun, J. J. et al. Fully integrated silicon probes for high-density recording of neural activity. Nature 551, 232–236 (2017).
Ahrens, M. B., Orger, M. B., Robson, D. N., Li, J. M. & Keller, P. J. Whole-brain functional imaging at cellular resolution using light-sheet microscopy. Nat. Methods 10, 413–420 (2013).
Chen, T. -W. et al. Ultrasensitive fluorescent proteins for imaging neuronal activity. Nature 499, 295–300 (2013).
Cunningham, J. P. & Yu, B. M. Dimensionality reduction for large-scale neural recordings. Nat. Neurosci. 17, 1500–1509 (2014).
Saxena, S. & Cunningham, J. P. Towards the neural population doctrine. Curr. Opin. Neurobiol. 55, 103–111 (2019).
Wang, J., Narain, D., Hosseini, E. A. & Jazayeri, M. Flexible timing by temporal scaling of cortical responses. Nat. Neurosci. 21, 102–110 (2018).
Wang, Y. et al. Heterogeneity in the pyramidal network of the medial prefrontal cortex. Nat. Neurosci. 9, 534–542 (2006).
Riemann, B. On the Hypotheses Which Lie at the Bases of Geometry (Birkhäuser, 2016).
Dubrovin, B. A., Fomenko, A. T. & Novikov, S. P. Modern Geometry—Methods and Applications: Part II: The Geometry and Topology of Manifolds (Springer Science & Business Media, 2012).
Sadtler, P. T. et al. Neural constraints on learning. Nature 512, 423–426 (2014).
Mitchell-Heggs, R., Prado, S., Gava, G. P., Go, M. A. & Schultz, S. R. Neural manifold analysis of brain circuit dynamics in health and disease. J. Comput. Neurosci. 51, 1–21 (2023).
Stopfer, M., Jayaraman, V. & Laurent, G. Intensity versus identity coding in an olfactory system. Neuron 39, 991–1004 (2003).
Briggman, K. L., Abarbanel, H. D. I. & Kristan, W. B. Jr. Optical imaging of neuronal populations during decision-making. Science 307, 896–901 (2005).
Kato, S. et al. Global brain dynamics embed the motor command sequence of Caenorhabditis elegans. Cell 163, 656–669 (2015).
Bruno, A. M., Frost, W. N. & Humphries, M. D. A spiral attractor network drives rhythmic locomotion. Elife 6, e27342 (2017).
Ahrens, M. B. et al. Brain-wide neuronal dynamics during motor adaptation in zebrafish. Nature 485, 471–477 (2012).
Andalman, A. S. et al. Neuronal dynamics regulating brain and behavioral state transitions. Cell 177, 970–985 (2019).
Petrucco, L. et al. Neural dynamics and architecture of the heading direction circuit in zebrafish. Nat. Neurosci. 26, 765–773 (2023).
Churchland, M. M. et al. Neural population dynamics during reaching. Nature 487, 51–56 (2012).
Raposo, D., Kaufman, M. T. & Churchland, A. K. A category-free neural population supports evolving demands during decision-making. Nat. Neurosci. 17, 1784–1792 (2014).
Sauerbrei, B. A. et al. Cortical pattern generation during dexterous movement is input-driven. Nature 577, 386–391 (2020).
Stringer, C. et al. Spontaneous behaviors drive multidimensional, brainwide activity. Science 364, 255 (2019).
Miri, A. et al. Behaviorally selective engagement of short-latency effector pathways by motor cortex. Neuron 95, 683–696 (2017).
Rubin, A. et al. Revealing neural correlates of behavior without behavioral measurements. Nat. Commun. 10, 4745 (2019).
Chen, H. -T., Manning, J. R. & van der Meer, M. A. A. Between-subject prediction reveals a shared representational geometry in the rodent hippocampus. Curr. Biol. 31, 4293–4304 (2021).
Yoo, S. B. M. & Hayden, B. Y. The transition from evaluation to selection involves neural subspace reorganization in core reward regions. Neuron 105, 712–724 (2020).
Cueva, C. J. et al. Low-dimensional dynamics for working memory and time encoding. Proc. Natl Acad. Sci. USA 117, 23021–23032 (2020).
Sohn, H., Narain, D., Meirhaeghe, N. & Jazayeri, M. Bayesian computation through cortical latent dynamics. Neuron 103, 934–947 (2019).
Hennig, J. A. et al. Learning is shaped by abrupt changes in neural engagement. Nat. Neurosci. 24, 727–736 (2021).
Gallego, J. A. et al. Cortical population activity within a preserved neural manifold underlies multiple motor behaviors. Nat. Commun. 9, 4233 (2018).
Stavisky, S. D. et al. Neural ensemble dynamics in dorsal motor cortex during speech in people with paralysis. Elife 8, e46015 (2019).
Pandarinath, C. et al. Neural population dynamics in human motor cortex during movements in people with ALS. Elife 4, e07436 (2015).
Minxha, J., Adolphs, R., Fusi, S., Mamelak, A. N. & Rutishauser, U. Flexible recruitment of memory-based choice representations by the human medial frontal cortex. Science 368, eaba3313 (2020).
Dekleva, B. M. et al. Motor cortex retains and reorients neural dynamics during motor imagery. Nat. Hum. Behav. 8, 729–742 (2024).
Perich, M. G. et al. Motor cortical dynamics are shaped by multiple distinct subspaces during naturalistic behavior. Preprint at bioRxiv https://doi.org/10.1101/2020.07.30.228767 (2020).
Kobak, D., Pardo-Vazquez, J. L., Valente, M., Machens, C. K. & Renart, A. State-dependent geometry of population activity in rat auditory cortex. Elife 8, e44526 (2019).
Gardner, R. J. et al. Toroidal topology of population activity in grid cells. Nature 602, 123–128 (2022).
Ebitz, R. B. & Hayden, B. Y. The population doctrine in cognitive neuroscience. Neuron 109, 3055–3068 (2021).
Jurewicz, K., Sleezer, B. J., Mehta, P. S., Hayden, B. Y. & Ebitz, R. B. Irrational choices via a curvilinear representational geometry for value. Nat. Commun. 15, 6424 (2024).
Gallego, J. A., Perich, M. G., Chowdhury, R. H., Solla, S. A. & Miller, L. E. Long-term stability of cortical population dynamics underlying consistent behavior. Nat. Neurosci. 23, 260–270 (2020).
Russo, A. A. et al. Motor cortex embeds muscle-like commands in an untangled population response. Neuron 97, 953–966 (2018).
Chaudhuri, R., Gerçek, B., Pandey, B., Peyrache, A. & Fiete, I. The intrinsic attractor manifold and population dynamics of a canonical cognitive circuit across waking and sleep. Nat. Neurosci. 22, 1512–1520 (2019).
Lindén, H., Petersen, P. C., Vestergaard, M. & Berg, R. W. Movement is governed by rotational neural dynamics in spinal motor networks. Nature 610, 526–531 (2022).
Gmaz, J. M. & van der Meer, M. A. A. Context coding in the mouse nucleus accumbens modulates motivationally relevant information. PLoS Biol. 20, e3001338 (2022).
Lanore, F., Cayco-Gajic, N. A., Gurnani, H., Coyle, D. & Silver, R. A. Cerebellar granule cell axons support high-dimensional representations. Nat. Neurosci. 24, 1142–1150 (2021).
Safaie, M. et al. Preserved neural dynamics across animals performing similar behaviour. Nature https://doi.org/10.1038/s41586-023-06714-0 (2023).
Ayar, E. C., Heusser, M. R., Bourrelly, C. & Gandhi, N. J. Distinct context- and content-dependent population codes in superior colliculus during sensation and action. Proc. Natl Acad. Sci. USA 120, e2303523120 (2023).
Allsop, S. A. et al. Corticoamygdala transfer of socially derived information gates observational learning. Cell 173, 1329–1342 (2018).
Nair, A. et al. An approximate line attractor in the hypothalamus encodes an aggressive state. Cell 186, 178–193 (2023).
Jahn, C. I. et al. Learning attentional templates for value-based decision-making. Cell 187, 1476–1489 (2024).
Markanday, A., Hong, S., Inoue, J., De Schutter, E. & Thier, P. Multidimensional cerebellar computations for flexible kinematic control of movements. Nat. Commun. 14, 2548 (2023).
Vinograd, A., Nair, A., Kim, J. H., Linderman, S. W. & Anderson, D. J. Causal evidence of a line attractor encoding an affective state. Nature 634, 910–918 (2024).
Talpir, I. & Livneh, Y. Stereotyped goal-directed manifold dynamics in the insular cortex. Cell Rep. 43, 114027 (2024).
Bush, N. E. & Ramirez, J. -M. Latent neural population dynamics underlying breathing, opioid-induced respiratory depression and gasping. Nat. Neurosci. 27, 259–271 (2024).
Nieh, E. H. et al. Geometry of abstract learned knowledge in the hippocampus. Nature 595, 80–84 (2021).
Schneider, S., Lee, J. H. & Mathis, M. W. Learnable latent embeddings for joint behavioural and neural analysis. Nature 617, 360–368 (2023).
Sun, X. et al. Cortical preparatory activity indexes learned motor memories. Nature 602, 274–279 (2022).
Perich, M. G., Gallego, J. A. & Miller, L. E. A neural population mechanism for rapid learning. Neuron 100, 964–976 (2018).
Cowley, B. R. et al. Slow drift of neural activity as a signature of impulsivity in macaque visual and prefrontal cortex. Neuron 108, 551–567 (2020).
Churchland, M. M. & Shenoy, K. V. Preparatory activity and the expansive null-space. Nat. Rev. Neurosci. 25, 213–236 (2024).
Vyas, S. et al. Neural population dynamics underlying motor learning transfer. Neuron 97, 1177–1186 (2018).
Kaufman, M. T., Churchland, M. M., Ryu, S. I. & Shenoy, K. V. Cortical activity in the null space: permitting preparation without movement. Nat. Neurosci. 17, 440–448 (2014).
Elsayed, G. F., Lara, A. H., Kaufman, M. T., Churchland, M. M. & Cunningham, J. P. Reorganization between preparatory and movement population responses in motor cortex. Nat. Commun. 7, 13239 (2016).
Javadzadeh, M. & Hofer, S. B. Dynamic causal communication channels between neocortical areas. Neuron 110, 2470–2483 (2022).
Semedo, J. D., Zandvakili, A., Machens, C. K., Yu, B. M. & Kohn, A. Cortical areas interact through a communication subspace. Neuron 102, 249–259 (2019).
Veuthey, T. L., Derosier, K., Kondapavulur, S. & Ganguly, K. Single-trial cross-area neural population dynamics during long-term skill learning. Nat. Commun. 11, 4057 (2020).
Semedo, J. D. et al. Feedforward and feedback interactions between visual cortical areas use different population activity patterns. Nat. Commun. 13, 1099 (2022).
Jazayeri, M. & Afraz, A. Navigating the neural space in search of the neural code. Neuron 93, 1003–1014 (2017).
Oby, E. R. et al. New neural activity patterns emerge with long-term learning. Proc. Natl Acad. Sci. USA 116, 15210–15215 (2019).
Brennan, C. & Proekt, A. A quantitative model of conserved macroscopic dynamics predicts future motor commands. Elife 8, e46814 (2019).
Hermansen, E., Klindt, D. A. & Dunn, B. A. Uncovering 2-D toroidal representations in grid cell ensemble activity during 1-D behavior. Nat. Commun. 15, 5429 (2024).
Fortunato, C. et al. Nonlinear manifolds underlie neural population activity during behaviour. Preprint at bioRxiv https://doi.org/10.1101/2023.07.18.549575 (2023).
Guo, W., Zhang, J. J., Newman, J. P. & Wilson, M. A. Latent learning drives sleep-dependent plasticity in distinct CA1 subpopulations. Cell Rep. 43, 115028 (2024).
Remington, E. D., Narain, D., Hosseini, E. A. & Jazayeri, M. Flexible sensorimotor computations through rapid reconfiguration of cortical dynamics. Neuron 98, 1005–1019 (2018).
Okazawa, G., Hatch, C. E., Mancoo, A., Machens, C. K. & Kiani, R. Representational geometry of perceptual decisions in the monkey parietal cortex. Cell 184, 3748–3768 (2021).
Langdon, C., Genkin, M. & Engel, T. A. A unifying perspective on neural manifolds and circuits for cognition. Nat. Rev. Neurosci. 24, 363–377 (2023).
Tsodyks, M., Kenet, T., Grinvald, A. & Arieli, A. Linking spontaneous activity of single cortical neurons and the underlying functional architecture. Science 286, 1943–1946 (1999).
Okun, M. et al. Diverse coupling of neurons to populations in sensory cortex. Nature 521, 511–515 (2015).
Marshel, J. H. et al. Cortical layer-specific critical dynamics triggering perception. Science 365, eaaw5202 (2019).
Dahmen, D. et al. Strong and localized recurrence controls dimensionality of neural activity across brain areas. Preprint at bioRxiv https://doi.org/10.1101/2020.11.02.365072 (2023).
Harris, K. D. & Shepherd, G. M. G. The neocortical circuit: themes and variations. Nat. Neurosci. 18, 170–181 (2015).
Park, J. et al. Motor cortical output for skilled forelimb movement is selectively distributed across projection neuron classes. Sci. Adv. 8, eabj5167 (2022).
Azcorra, M. et al. Unique functional responses differentially map onto genetic subtypes of dopamine neurons. Nat. Neurosci. 26, 1762–1774 (2023).
Musall, S. et al. Pyramidal cell types drive functionally distinct cortical activity patterns during decision-making. Nat. Neurosci. 26, 495–505 (2023).
Bugeon, S. et al. A transcriptomic axis predicts state modulation of cortical interneurons. Nature 607, 330–338 (2022).
Nakai, S., Kitanishi, T. & Mizuseki, K. Distinct manifold encoding of navigational information in the subiculum and hippocampus. Sci. Adv. 10, eadi4471 (2024).
Lara, A. H., Cunningham, J. P. & Churchland, M. M. Different population dynamics in the supplementary motor area and motor cortex during reaching. Nat. Commun. 9, 2754 (2018).
Stringer, C., Pachitariu, M., Steinmetz, N., Carandini, M. & Harris, K. D. High-dimensional geometry of population responses in visual cortex. Nature 571, 361–365 (2019).
Recanatesi, S., Bradde, S., Balasubramanian, V., Steinmetz, N. A. & Shea-Brown, E. A scale-dependent measure of system dimensionality. Patterns 3, 100555 (2022).
Park, J. et al. Conjoint specification of action by neocortex and striatum. Neuron 113, 620–636 (2025).
Kutsuwada, T. et al. Molecular diversity of the NMDA receptor channel. Nature 358, 36–41 (1992).
Nakanishi, S. Molecular diversity of glutamate receptors and implications for brain function. Science 258, 597–603 (1992).
Fişek, M. et al. Cortico-cortical feedback engages active dendrites in visual cortex. Nature https://doi.org/10.1038/s41586-023-06007-6 (2023).
Srivastava, K. H. et al. Motor control by precisely timed spike patterns. Proc. Natl Acad. Sci. USA 114, 1171–1176 (2017).
Riehle, A., Grün, S., Diesmann, M. & Aertsen, A. Spike synchronization and rate modulation differentially involved in motor cortical function. Science 278, 1950–1953 (1997).
Perea, G. et al. Activity-dependent switch of GABAergic inhibition into glutamatergic excitation in astrocyte-neuron networks. Elife 5, e20362 (2016).
Mu, Y. et al. Glia accumulate evidence that actions are futile and suppress unsuccessful behavior. Cell 178, 27–43 (2019).
Hsueh, B. et al. Cardiogenic control of affective behavioural state. Nature 615, 292–299 (2023).
Cahill, M. K. et al. Network-level encoding of local neurotransmitters in cortical astrocytes. Nature 629, 146–153 (2024).
Gao, P. et al. A theory of multineuronal dimensionality, dynamics and measurement. Preprint at bioRxiv https://doi.org/10.1101/214262 (2017).
Chung, S. & Abbott, L. F. Neural population geometry: an approach for understanding biological and artificial neural networks. Curr. Opin. Neurobiol. 70, 137–144 (2021).
Zhou, J. et al. Evolving schema representations in orbitofrontal ensembles during learning. Nature 590, 606–611 (2021).
Shuvaev, S., Lachi, D., Koulakov, A. & Zador, A. Encoding innate ability through a genomic bottleneck. Proc. Natl Acad. Sci. USA 121, e2409160121 (2024).
Driscoll, L. N., Shenoy, K. & Sussillo, D. Flexible multitask computation in recurrent networks utilizes shared dynamical motifs. Nat. Neurosci. 27, 1349–1363 (2024).
Feulner, B. & Clopath, C. Neural manifold under plasticity in a goal driven learning behaviour. PLoS Comput. Biol. 17, e1008621 (2021).
Simpson, G. G. The Baldwin effect. Evolution 7, 110–117 (1953).
Hiesinger, P. R. The Self-Assembling Brain: How Neural Networks Grow Smarter (Princeton University Press, 2022).
Mitchell, K. J. Innate: How the Wiring of Our Brains Shapes Who We Are (Princeton University Press, 2020).
Martini, F. J., Guillamón-Vivancos, T., Moreno-Juan, V., Valdeolmillos, M. & López-Bendito, G. Spontaneous activity in developing thalamic and cortical sensory networks. Neuron 109, 2519–2534 (2021).
Glanz, R. M., Sokoloff, G. & Blumberg, M. S. Neural decoding reveals specialized kinematic tuning after an abrupt cortical transition. Cell Rep. 42, 113119 (2023).
Maimon-Mor, R. O., Schone, H. R., Henderson Slater, D., Faisal, A. A. & Makin, T. R. Early life experience sets hard limits on motor learning as evidenced from artificial arm use. Elife 10, e66320 (2021).
Seelig, J. D. & Jayaraman, V. Neural dynamics for landmark orientation and angular path integration. Nature 521, 186–191 (2015).
O’Shea, D. J. et al. Direct neural perturbations reveal a dynamical mechanism for robust computation. Preprint at bioRxiv https://doi.org/10.1101/2022.12.16.520768 (2022).
Dowling, M., Zhao, Y. & Park, I. M. eXponential FAmily Dynamical Systems (XFADS): large-scale nonlinear Gaussian state-space modeling. In Advances in Neural Information Processing Systems 38 (2024).
Zhang, F. et al. Multimodal fast optical interrogation of neural circuitry. Nature 446, 633–639 (2007).
Lovett-Barron, M. et al. Ancestral circuits for the coordinated modulation of brain state. Cell 171, 1411–1423 (2017).
Sylwestrak, E. L. et al. Cell-type-specific population dynamics of diverse reward computations. Cell 185, 3568–3587 (2022).
Esparza, J. et al. Cell-type-specific manifold analysis discloses independent geometric transformations in the hippocampal spatial code. Neuron https://doi.org/10.1016/j.neuron.2025.01.022 (2025).
Chan, K. Y. et al. Engineered AAVs for efficient noninvasive gene delivery to the central and peripheral nervous systems. Nat. Neurosci. 20, 1172–1179 (2017).
Cardin, J. A. et al. Targeted optogenetic stimulation and recording of neurons in vivo using cell-type-specific expression of Channelrhodopsin-2. Nat. Protoc. 5, 247–254 (2010).
Economo, M. N. et al. A platform for brain-wide imaging and reconstruction of individual neurons. Elife 5, e10566 (2016).
Prinz, A. A., Bucher, D. & Marder, E. Similar network activity from disparate circuit parameters. Nat. Neurosci. 7, 1345–1352 (2004).
Randi, F., Sharma, A. K., Dvali, S. & Leifer, A. M. Neural signal propagation atlas of Caenorhabditis elegans. Nature 623, 406–414 (2023).
Pospisil, D. A. et al. The fly connectome reveals a path to the effectome. Nature 634, 201–209 (2024).
Roth, B. L. DREADDs for neuroscientists. Neuron 89, 683–694 (2016).
Krakauer, J. W., Ghazanfar, A. A., Gomez-Marin, A., MacIver, M. A. & Poeppel, D. Neuroscience needs behavior: correcting a reductionist bias. Neuron 93, 480–490 (2017).
Gomez-Marin, A. & Ghazanfar, A. A. The life of behavior. Neuron 104, 25–36 (2019).
Gmaz, J. M., Keller, J. A., Dudman, J. T. & Gallego, J. A. Integrating across behaviors and timescales to understand the neural control of movement. Curr. Opin. Neurobiol. 85, 102843 (2024).
Mizes, K. G. C., Lindsey, J., Escola, G. S. & Ölveczky, B. P. Dissociating the contributions of sensorimotor striatum to automatic and visually guided motor sequences. Nat. Neurosci. 26, 1791–1804 (2023).
Ganguly, K. & Carmena, J. M. Emergence of a stable cortical map for neuroprosthetic control. PLoS Biol. 7, e1000153 (2009).
Lai, C., Tanaka, S., Harris, T. D. & Lee, A. K. Volitional activation of remote place representations with a hippocampal brain-machine interface. Science 382, 566–573 (2023).
Barack, D. L. & Krakauer, J. W. Two views on the cognitive brain. Nat. Rev. Neurosci. 22, 359–371 (2021).
Humphreys, P. Emergence: a Philosophical Account (Oxford University Press, 2016).
Kim, J. Emergence: core ideas and issues. Synthese 151, 547–559 (2006).
Anderson, P. W. More is different. Science https://doi.org/10.1126/science.177.4047.393 (1972).
Marder, E. & Goaillard, J. -M. Variability, compensation and homeostasis in neuron and network function. Nat. Rev. Neurosci. 7, 563–574 (2006).
Kilgard, M. P. et al. Sensory input directs spatial and temporal plasticity in primary auditory cortex. J. Neurophysiol. 86, 326–338 (2001).
Chang, J. C., Perich, M. G., Miller, L. E., Gallego, J. A. & Clopath, C. De novo motor learning creates structure in neural activity that shapes adaptation. Nat. Commun. 15, 4084 (2024).
Degenhart, A. D. et al. Stabilization of a brain-computer interface via the alignment of low-dimensional spaces of neural activity. Nat. Biomed. Eng. 4, 672–685 (2020).
Lee, J. Introduction to Topological Manifolds (Springer Science & Business Media, 2010).
Dijkstra, J. J. & van Mill, J. Erdos Space and Homeomorphism Groups of Manifolds (American Mathematical Society, 2010).
Jazayeri, M. & Ostojic, S. Interpreting neural computations by examining intrinsic and embedding dimensionality of neural activity. Curr. Opin. Neurobiol. 70, 113–120 (2021).
Manley, J. et al. Simultaneous, cortex-wide dynamics of up to 1 million neurons reveal unbounded scaling of dimensionality with neuron number. Neuron 112, 1694–1709 (2024).
Marshall, N. J. et al. Flexible neural control of motor units. Nat. Neurosci. 25, 1492–1504 (2022).
Trautmann, E. M. et al. Accurate estimation of neural population dynamics without spike sorting. Neuron 103, 292–308 (2019).
DePasquale, B., Sussillo, D., Abbott, L. F. & Churchland, M. M. The centrality of population-level factors to network computation is demonstrated by a versatile approach for training spiking networks. Neuron 111, 631–649 (2023).
Kobak, D. et al. Demixed principal component analysis of neural population data. Elife 5, e10989 (2016).
Aoi, M. C., Mante, V. & Pillow, J. W. Prefrontal cortex exhibits multidimensional dynamic encoding during decision-making. Nat. Neurosci. 23, 1410–1420 (2020).
Pandarinath, C. et al. Inferring single-trial neural population dynamics using sequential auto-encoders. Nat. Methods 15, 805–815 (2018).
Hurwitz, C. et al. Targeted neural dynamical modeling. Adv. Neural Inf. Process. Syst. 34, 29379–29392 (2021).
Gosztolai, A., Peach, R. L., Arnaudon, A., Barahona, M. & Vandergheynst, P. MARBLE: interpretable representations of neural population dynamics using geometric deep learning. Nat. Methods 22, 612–620 (2025).
Tenenbaum, J. B., de Silva, V. & Langford, J. C. A global geometric framework for nonlinear dimensionality reduction. Science 290, 2319–2323 (2000).
Balasubramanian, M. & Schwartz, E. L. The isomap algorithm and topological stability. Science 295, 7 (2002).
Roweis, S. T. & Saul, L. K. Nonlinear dimensionality reduction by locally linear embedding. Science 290, 2323–2326 (2000).
Lafon, S., Keller, Y. & Coifman, R. R. Data fusion and multicue data matching by diffusion maps. IEEE Trans. Pattern Anal. Mach. Intell. 28, 1784–1797 (2006).
Belkin, M. & Niyogi, P. Laplacian eigenmaps for dimensionality reduction and data representation. Neural Comput. 15, 1373–1396 (2003).
van der Maaten, L. & Hinton, G. Visualizing data using t-SNE. J. Machine Learn. Res. 9, 2579–2605 (2008).
McInnes, L., Healy, J. & Melville, J. UMAP: uniform manifold approximation and projection for dimension reduction. Preprint at https://arxiv.org/abs/1802.03426 (2018).
Zhang, Z. & Zha, H. Principal manifolds and nonlinear dimensionality reduction via tangent space alignment. SIAM J. Sci. Comput. 26, 313–338 (2004).
Kohli, D., Cloninger, A. & Mishne, G. LDLE: Low distortion local eigenmaps. J. Mach. Learn. Res. 22, 1–64 (2021).
Kohli, D., Nieuwenhuis, J., S., Cloninger, A., Mishne, G. & Narain, D. RATS: Unsupervised manifold learning using low-distortion alignment of tangent spaces. Preprint at bioRxiv https://doi.org/10.1101/2024.10.31.621292 (2024).
Rajan, K., Abbott, L. F. & Sompolinsky, H. Stimulus-dependent suppression of chaos in recurrent neural networks. Phys. Rev. E Stat. Nonlin. Soft Matter Phys. 82, 011903 (2010).
Mastrogiuseppe, F. & Ostojic, S. Linking connectivity, dynamics, and computations in low-rank recurrent neural networks. Neuron 99, 609–623 (2018).
Rajan, K., Harvey, C. D. & Tank, D. W. Recurrent network models of sequence generation and memory. Neuron 90, 128–142 (2016).
Perich, M. G. et al. Inferring brain-wide interactions using data-constrained recurrent neural network models. Preprint at bioRxiv https://doi.org/10.1101/2020.12.18.423348 (2021).
Fisher, D., Olasagasti, I., Tank, D. W., Aksay, E. R. F. & Goldman, M. S. A modeling framework for deriving the structural and functional architecture of a short-term memory microcircuit. Neuron 79, 987–1000 (2013).
Dinc, F., Shai, A., Schnitzer, M. & Tanaka, H. CORNN: convex optimization of recurrent neural networks for rapid inference of neural dynamics. In Advances in Neural Information Processing Systems 36 https://proceedings.neurips.cc/paper_files/paper/2023/file/a103529738706979331778377f2d5864-Paper-Conference.pdf (2023).
Laje, R. & Buonomano, D. V. Robust timing and motor patterns by taming chaos in recurrent neural networks. Nat. Neurosci. 16, 925–933 (2013).
Sussillo, D. & Abbott, L. F. Generating coherent patterns of activity from chaotic neural networks. Neuron 63, 544–557 (2009).
Sussillo, D., Churchland, M. M., Kaufman, M. T. & Shenoy, K. V. A neural network that finds a naturalistic solution for the production of muscle activity. Nat. Neurosci. 18, 1025–1033 (2015).
Sussillo, D. & Barak, O. Opening the black box: low-dimensional dynamics in high-dimensional recurrent neural networks. Neural Comput. 25, 626–649 (2013).
Beiran, M., Meirhaeghe, N., Sohn, H., Jazayeri, M. & Ostojic, S. Parametric control of flexible timing through low-dimensional neural manifolds. Neuron 111, 739–753 (2023).
Valente, A., Ostojic, S. & Pillow, J. W. Probing the relationship between latent linear dynamical systems and low-rank recurrent neural network models. Neural Comput. 34, 1871–1892 (2022).
Pollock, E. & Jazayeri, M. Engineering recurrent neural networks from task-relevant manifolds and dynamics. PLoS Comput. Biol. 16, e1008128 (2020).
Enel, P., Procyk, E., Quilodran, R. & Dominey, P. F. Reservoir computing properties of neural dynamics in prefrontal cortex. PLoS Comput. Biol. 12, e1004967 (2016).
Schuessler, F., Dubreuil, A., Mastrogiuseppe, F., Ostojic, S. & Barak, O. Dynamics of random recurrent networks with correlated low-rank structure. Phys. Rev. Res. 2, 013111 (2020).
Burak, Y. & Fiete, I. R. Accurate path integration in continuous attractor network models of grid cells. PLoS Comput. Biol. 5, e1000291 (2009).
Michaels, J. A., Schaffelhofer, S., Agudelo-Toro, A. & Scherberger, H. A goal-driven modular neural network predicts parietofrontal neural dynamics during grasping. Proc. Natl Acad. Sci. USA 117, 32124–32135 (2020).
Yang, G. R., Joglekar, M. R., Song, H. F., Newsome, W. T. & Wang, X. -J. Task representations in neural networks trained to perform many cognitive tasks. Nat. Neurosci. 22, 297–306 (2019).
Litwin-Kumar, A. & Doiron, B. Slow dynamics and high variability in balanced cortical networks with clustered connections. Nat. Neurosci. 15, 1498–1505 (2012).
Feulner, B. et al. Small, correlated changes in synaptic connectivity may facilitate rapid motor learning. Nat. Commun. 13, 5163 (2022).
Feulner, B., Perich, M. G., Miller, L. E., Clopath, C. & Gallego, J. A. A neural implementation model of feedback-based motor learning. Nat. Commun. 16, 1805 (2025).
Darshan, R. & Rivkind, A. Learning to represent continuous variables in heterogeneous neural networks. Cell Rep. 39, 110612 (2022).
Pezon, L., Schmutz, V. & Gerstner, W. Linking neural manifolds to circuit structure in recurrent networks. Preprint at bioRxiv https://doi.org/10.1101/2024.02.28.582565 (2024).
Dubreuil, A., Valente, A., Beiran, M., Mastrogiuseppe, F. & Ostojic, S. The role of population structure in computations through neural dynamics. Nat. Neurosci. 25, 783–794 (2022).
Hennequin, G., Vogels, T. P. & Gerstner, W. Optimal control of transient dynamics in balanced networks supports generation of complex movements. Neuron 82, 1394–1406 (2014).
Fuhs, M. C. & Touretzky, D. S. A spin glass model of path integration in rat medial entorhinal cortex. J. Neurosci. 26, 4266–4276 (2006).
Acknowledgements
We thank J. W. Krakauer for the movie analogy, Carolina Massumoto for her input during figure conceptualisation, and R. H. Chowdhury and G. Mishne for comments on this manuscript. M.G.P. received funding (chercheurs-boursiers en intelligence artificielle) from the Fonds de recherche du Québec Santé. D.N. received funding from the Netherlands Organisation for Scientific Research (NWO Vidi - VI.Vidi.193.076, Aspasia 015.016.012 and Gravitation - DBI2 - 024.005.022) and the Nationaal Groeifonds NGF.1609.241.021. J.A.G. received funding from the EPSRC (EP/T020970/1), Advanced Research + Invention Agency (Scalable neural interfaces SCNI-PR01-P09) and the European Research Council (ERC-2020-StG-949660).
Author information
Authors and Affiliations
Contributions
M.G.P. and J.A.G. conceived of the overall concept for the manuscript. M.G.P., D.N. and J.A.G. wrote and edited the manuscript.
Corresponding authors
Ethics declarations
Competing interests
J.A.G. receives funding from Meta Platform Technologies and InBrain Neuroelectronics. M.G.P. and D.N. declare no competing interests.
Peer review
Peer review information
Nature Neuroscience thanks Joao Barbosa and Srdjan Ostojic for their contribution to the peer review of this work.
Additional information
Publisher’s note Springer Nature remains neutral with regard to jurisdictional claims in published maps and institutional affiliations.
Rights and permissions
Springer Nature or its licensor (e.g. a society or other partner) holds exclusive rights to this article under a publishing agreement with the author(s) or other rightsholder(s); author self-archiving of the accepted manuscript version of this article is solely governed by the terms of such publishing agreement and applicable law.
About this article
Cite this article
Perich, M.G., Narain, D. & Gallego, J.A. A neural manifold view of the brain. Nat Neurosci 28, 1582–1597 (2025). https://doi.org/10.1038/s41593-025-02031-z
Received:
Accepted:
Published:
Version of record:
Issue date:
DOI: https://doi.org/10.1038/s41593-025-02031-z
This article is cited by
-
A generative spike prediction model using behavioral reinforcement for re-establishing neural functional connectivity
Nature Computational Science (2026)
-
Locomotion engages context-dependent motor strategies for head stabilization in primates
Communications Biology (2026)