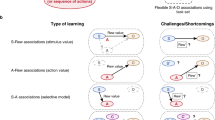
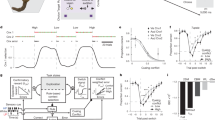
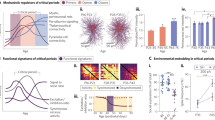
Abstract
Classical views of sensory perception describe a hierarchical organization, extending from the sensory periphery to static representations in the primary sensory cortex, with downstream regions supporting decision-making and action. There is growing evidence that suggests a more flexible role of primary sensory cortex, with behaviorally relevant functions distributed across multiple levels of the early sensory pathway that can change in response to context. In this Perspective, we first examine primary sensory cortex beyond sensory representations through the lens of sufficiency to predict behavior. We then consider the necessity of primary sensory cortex in sensory-driven behaviors, explored through a range of inactivation and lesioning studies. Finally, we provide evidence that points to an adaptive and flexible role for primary sensory cortex, where function is shaped by experience and context. This adaptive nature demands a more holistic investigative approach that challenges sensory pathways with adaptive behaviors in response to changing environments, behavioral contexts and injury.
This is a preview of subscription content, access via your institution
Access options
Access Nature and 54 other Nature Portfolio journals
Get Nature+, our best-value online-access subscription
$32.99 / 30 days
cancel any time
Subscribe to this journal
Receive 12 print issues and online access
$259.00 per year
only $21.58 per issue
Buy this article
- Purchase on SpringerLink
- Instant access to the full article PDF.
USD 39.95
Prices may be subject to local taxes which are calculated during checkout





Similar content being viewed by others
References
Tootell, R. B. H., Silverman, M. S., Switkes, E. & de Valois, R. L. Deoxyglucose analysis of retinotopic organization in primate striate cortex. Science 218, 902–904 (1982).
Petersen, C. C. H. The functional organization of the barrel cortex. Neuron 56, 339–355 (2007).
Fallon, J. B., Irvine, D. R. F. & Shepherd, R. K. Cochlear implants and brain plasticity. Hear. Res. 238, 110–117 (2008).
Hubel, D. H. & Wiesel, T. N. Receptive fields, binocular interaction and functional architecture in the cat’s visual cortex. J. Physiol. 160, 106–154 (1962).
Hubel, D. H. & Wiesel, T. N. Receptive fields and functional architecture of monkey striate cortex. J. Physiol. 195, 215–243 (1968).
Waiblinger, C., McDonnell, M. E., Reedy, A. R., Borden, P. Y. & Stanley, G. B. Emerging experience-dependent dynamics in primary somatosensory cortex reflect behavioral adaptation. Nat. Commun. 13, 534 (2022).
Morelli, M., Casagrande, M. & Forte, G. Decision making: a theoretical review. Integr. Psychol. Behav. Sci. 56, 609–629 (2022).
Heekeren, H. R., Marrett, S. & Ungerleider, L. G. The neural systems that mediate human perceptual decision making. Nat. Rev. Neurosci. 9, 467–479 (2008).
Green, D. M. & Swets, J. A. Signal Detection Theory and Psychophysics (John Wiley & Sons, 1966).
Hautus, M. J., Macmillan, N. A. & Creelman, C. D. Detection Theory: A User’s Guide (Routledge, 2021).
Schall, J. D. Neural basis of deciding, choosing and acting. Nat. Rev. Neurosci. 2, 33–42 (2001).
Gold, J. I. & Shadlen, M. N. The neural basis of decision making. Annu. Rev. Neurosci. 30, 535–574 (2007).
Romo, R. & Salinas, E. Flutter discrimination: neural codes, perception, memory and decision making. Nat. Rev. Neurosci. 4, 203–218 (2003).
Glimcher, P. W. The neurobiology of visual-saccadic decision making. Annu. Rev. Neurosci. 26, 133–179 (2003).
Parker, A. J. & Newsome, W. T. Sense and the single neuron: probing the physiology of perception. Annu. Rev. Neurosci. 21, 227–277 (1998).
Platt, M. L. Neural correlates of decisions. Curr. Opin. Neurobiol. 12, 141–148 (2002).
De Lafuente, V. & Romo, R. Neural correlate of subjective sensory experience gradually builds up across cortical areas. Proc. Natl Acad. Sci. USA 103, 14266–14271 (2006).
De Lafuente, V. & Romo, R. Neuronal correlates of subjective sensory experience. Nat. Neurosci. 8, 1698–1703 (2005).
Romo, R. & Rossi-Pool, R. Turning touch into perception. Neuron 105, 16–33 (2020).
Hernández, A., Zainos, A. & Romo, R. Neuronal correlates of sensory discrimination in the somatosensory cortex. Proc. Natl Acad. Sci. USA 97, 6191–6196 (2000).
Brody, C. D. & Hanks, T. D. Neural underpinnings of the evidence accumulator. Curr. Opin. Neurobiol. 37, 149–157 (2016).
Romo, R. & de Lafuente, V. Conversion of sensory signals into perceptual decisions. Prog. Neurobiol. 103, 41–75 (2013).
Carandini, M. & Churchland, A. K. Probing perceptual decisions in rodents. Nat. Neurosci. 16, 824–831 (2013).
Sheppard, J. P., Raposo, D. & Churchland, A. K. Dynamic weighting of multisensory stimuli shapes decision-making in rats and humans. J. Vis. 13, 4 (2013).
Raposo, D., Sheppard, J. P., Schrater, P. R. & Churchland, A. K. Multisensory decision-making in rats and humans. J. Neurosci. 32, 3726–3735 (2012).
Brunton, B. W., Botvinick, M. M. & Brody, C. D. Rats and humans can optimally accumulate evidence for decision-making. Science 340, 95–98 (2013).
Odoemene, O., Pisupati, S., Nguyen, H. & Churchland, A. K. Visual evidence accumulation guides decision-making in unrestrained mice. J. Neurosci. 38, 10143–10155 (2018).
Alabi, O. O., Fortunato, M. P. & Fuccillo, M. V. Behavioral paradigms to probe individual mouse differences in value-based decision making. Front. Neurosci. 13, 50 (2019).
Jaramillo, S. & Zador, A. M. Mice and rats achieve similar levels of performance in an adaptive decision-making task. Front. Syst. Neurosci. 8, 173 (2014).
Jaramillo, S., Borges, K. & Zador, A. M. Auditory thalamus and auditory cortex are equally modulated by context during flexible categorization of sounds. J. Neurosci. 34, 5291–5301 (2014).
Waiblinger, C., Wu, C. M., Bolus, M. F., Borden, P. Y. & Stanley, G. B. Stimulus context and reward contingency induce behavioral adaptation in a rodent tactile detection task. J. Neurosci. 39, 1088–1099 (2019).
Deisseroth, K. et al. Next-generation optical technologies for illuminating genetically targeted brain circuits. J. Neurosci. 26, 10380–10386 (2006).
Grewe, B. F. & Helmchen, F. Optical probing of neuronal ensemble activity. Curr. Opin. Neurobiol. 19, 520–529 (2009).
Knöpfel, T. & Song, C. Optical voltage imaging in neurons: moving from technology development to practical tool. Nat. Rev. Neurosci. 20, 719–727 (2019).
Borden, P. Y. et al. Genetically expressed voltage sensor ArcLight for imaging large scale cortical activity in the anesthetized and awake mouse. Neurophotonics 4, 031212 (2017).
Steinmetz, N. A., Koch, C., Harris, K. D. & Carandini, M. Challenges and opportunities for large-scale electrophysiology with Neuropixels probes. Curr. Opin. Neurobiol. 50, 92–100 (2018).
Trachtenberg, J. T. et al. Long-term in vivo imaging of experience-dependent synaptic plasticity in adult cortex. Nature 420, 788–794 (2002).
Christie, R. H. et al. Growth arrest of individual senile plaques in a model of Alzheimer’s disease observed by in vivo multiphoton microscopy. J. Neurosci. 21, 858–864 (2001).
Yang, H., Kwon, S. E., Severson, K. S. & O’Connor, D. H. Origins of choice-related activity in mouse somatosensory cortex. Nat. Neurosci. 19, 127–134 (2016).
Musall, S., Kaufman, M. T., Juavinett, A. L., Gluf, S. & Churchland, A. K. Single-trial neural dynamics are dominated by richly varied movements. Nat. Neurosci. 22, 1677–1686 (2019).
Adhikari, B. M., Sathian, K., Epstein, C. M., Lamichhane, B. & Dhamala, M. Oscillatory activity in neocortical networks during tactile discrimination near the limit of spatial acuity. NeuroImage 91, 300–310 (2014).
Miyashita, T. & Feldman, D. E. Behavioral detection of passive whisker stimuli requires somatosensory cortex. Cereb. Cortex 23, 1655–1662 (2013).
Sachidhanandam, S., Sreenivasan, V., Kyriakatos, A., Kremer, Y. & Petersen, C. C. H. Membrane potential correlates of sensory perception in mouse barrel cortex. Nat. Neurosci. 16, 1671–1677 (2013).
Kwon, S. E., Yang, H., Minamisawa, G. & O’Connor, D. H. Sensory and decision-related activity propagate in a cortical feedback loop during touch perception. Nat. Neurosci. 19, 1243–1249 (2016).
Hong, Y. K., Lacefield, C. O., Rodgers, C. C. & Bruno, R. M. Sensation movement and learning in the absence of barrel cortex. Nature 561, 542–546 (2018).
Le Merre, P. et al. Reward-based learning drives rapid sensory signals in medial prefrontal cortex and dorsal hippocampus necessary for goal-directed behavior. Neuron 97, 83–91 (2018).
Oryshchuk, A. et al. Distributed and specific encoding of sensory, motor, and decision information in the mouse neocortex during goal-directed behavior. Cell Rep. 43, 113618 (2024).
Esmaeili, V. et al. Rapid suppression and sustained activation of distinct cortical regions for a delayed sensory-triggered motor response. Neuron 109, 2183–2201 (2021).
El-Boustani, S. et al. Anatomically and functionally distinct thalamocortical inputs to primary and secondary mouse whisker somatosensory cortices. Nat. Commun. 11, 3342 (2020).
Takahashi, N. et al. Active dendritic currents gate descending cortical outputs in perception. Nat. Neurosci. 23, 1277–1285 (2020).
Zareian, B., Lam, A. & Zagha, E. Dorsolateral striatum is a bottleneck for responding to task-relevant stimuli in a learned whisker detection task in mice. J. Neurosci. 43, 2126–2139 (2023).
Sippy, T., Lapray, D., Crochet, S. & Petersen, C. C. H. Cell-type-specific sensorimotor processing in striatal projection neurons during goal-directed behavior. Neuron 88, 298–305 (2015).
Theyel, B. B., Llano, D. A. & Sherman, S. M. The corticothalamocortical circuit drives higher-order cortex in the mouse. Nat. Neurosci. 13, 84–88 (2010).
Rodgers, C. C. et al. Sensorimotor strategies and neuronal representations for shape discrimination. Neuron 109, 2308–2325 (2021).
Buetfering, C. et al. Behaviorally relevant decision coding in primary somatosensory cortex neurons. Nat. Neurosci. 25, 1225–1236 (2022).
Banerjee, A. et al. Value-guided remapping of sensory cortex by lateral orbitofrontal cortex. Nature 585, 245–250 (2020).
Simoncelli, E. P. & Olshausen, B. A. Natural image statistics and neural representation. Annu. Rev. Neurosci. 24, 1193–1216 (2001).
Koch, C., Massimini, M., Boly, M. & Tononi, G. Neural correlates of consciousness: progress and problems. Nat. Rev. Neurosci. 17, 307–321 (2016).
Lampl, I. & Katz, Y. Neuronal adaptation in the somatosensory system of rodents. Neuroscience 343, 66–76 (2017).
Van Essen, D. C. & Maunsell, J. H. R. Hierarchical organization and functional streams in the visual cortex. Trends Neurosci. 6, 370–375 (1983).
Hochstein, S. & Ahissar, M. View from the top: hierarchies and reverse hierarchies in the visual system. Neuron 36, 791–804 (2002).
Gilbert, C. D. & Li, W. Top-down influences on visual processing. Nat. Rev. Neurosci. 14, 350–363 (2013).
Rao, R. P. N. & Ballard, D. H. Predictive coding in the visual cortex: a functional interpretation of some extra-classical receptive-field effects. Nat. Neurosci. 2, 79–87 (1999).
Hinton, G. E. Learning multiple layers of representation. Trends Cogn. Sci. 11, 428–434 (2007).
Friston, K. The free-energy principle: a unified brain theory?. Nat. Rev. Neurosci. 11, 127–138 (2010).
Olshausen, B. A. & Field, D. J. Sparse coding of sensory inputs. Curr. Opin. Neurobiol. 14, 481–487 (2004).
Bastos, A. M. et al. Canonical microcircuits for predictive coding. Neuron 76, 695–711 (2012).
Gdalyahu, A. et al. Associative fear learning enhances sparse network coding in primary sensory cortex. Neuron 75, 121–132 (2012).
Kok, P. & de Lange, F. P. in An Introduction to Model-Based Cognitive Neuroscience 1st edn (eds Forstmann, B. U. & Wagenmakers, E.-J.) 221–244 (Springer, 2015).
Wood, K. C., Angeloni, C. F., Oxman, K., Clopath, C. & Geffen, M. N. Neuronal activity in sensory cortex predicts the specificity of learning in mice. Nat. Commun. 13, 1167 (2022).
Poort, J. et al. Learning enhances sensory and multiple non-sensory representations in primary visual cortex. Neuron 86, 1478–1490 (2015).
Rabinovich, R. J., Kato, D. D. & Bruno, R. M. Learning enhances encoding of time and temporal surprise in mouse primary sensory cortex. Nat. Commun. 13, 5504 (2022).
Makino, H. & Komiyama, T. Learning enhances the relative impact of top-down processing in the visual cortex. Nat. Neurosci. 18, 1116–1122 (2015).
Pollmann, S. & Maertens, M. Shift of activity from attention to motor-related brain areas during visual learning. Nat. Neurosci. 8, 1494–1496 (2005).
Mukai, I. et al. Activations in visual and attention-related areas predict and correlate with the degree of perceptual learning. J. Neurosci. 27, 11401–11411 (2007).
Sigman, M. et al. Top-down reorganization of activity in the visual pathway after learning a shape identification task. Neuron 46, 823–835 (2005).
Gilbert, C. D. & Li, W. Adult visual cortical plasticity. Neuron 75, 250–264 (2012).
Waiblinger, C., Whitmire, C. J., Sederberg, A., Stanley, G. B. & Schwarz, C. Primary tactile thalamus spiking reflects cognitive signals. J. Neurosci. 38, 4870–4885 (2018).
Suga, N. Role of corticofugal feedback in hearing. J. Comp. Physiol. A Neuroethol. Sens. Neural Behav. Physiol. 194, 169–183 (2008).
Jones, H. E. et al. Figure-ground modulation in awake primate thalamus. Proc. Natl Acad. Sci. USA 112, 7085–7090 (2015).
Reinhold, K., Resulaj, A. & Scanziani, M. Brain state-dependent modulation of thalamic visual processing by cortico-thalamic feedback. J. Neurosci. 43, 1540–1554 (2023).
Born, G. et al. Corticothalamic feedback sculpts visual spatial integration in mouse thalamus. Nat. Neurosci. 24, 1711–1720 (2021).
Dash, S., Autio, D. M. & Crandall, S. R. State-dependent modulation of activity in distinct layer 6 corticothalamic neurons in barrel cortex of awake mice. J. Neurosci. 42, 6551–6565 (2022).
Voigts, J., Deister, C. A. & Moore, C. I. Layer 6 ensembles can selectively regulate the behavioral impact and layer-specific representation of sensory deviants. eLife 9, e48957 (2020).
Dimwamwa, E. D., Pala, A., Chundru, V., Wright, N. C. & Stanley, G. B. Dynamic corticothalamic modulation of the somatosensory thalamocortical circuit during wakefulness. Nat. Commun. 15, 3529 (2024).
Schultz, W., Dayan, P., & Montague, P. R. A neural substrate of prediction and reward. Science 275, 1593–1599 (1997).
Nienborg, H. & Cumming, B. G. Decision-related activity in sensory neurons may depend on the columnar architecture of cerebral cortex. J. Neurosci. 34, 3579–3585 (2014).
Palmer, C., Cheng, S.-Y. & Seidemann, E. Linking neuronal and behavioral performance in a reaction-time visual detection task. J. Neurosci. 27, 8122–8137 (2007).
Resulaj, A., Ruediger, S., Olsen, S. R. & Scanziani, M. First spikes in visual cortex enable perceptual discrimination. eLife 7, e34044 (2018).
Isa, T., Tohyama, T. & Kinoshita, M. Phylogenetic view of the compensatory mechanisms in motor and sensory systems after neuronal injury. Curr. Res. Neurobiol. 3, 100058 (2022).
Guo, L., Weems, J. T., Walker, W. I., Levichev, A. & Jaramillo, S. Choice-selective neurons in the auditory cortex and in its striatal target encode reward expectation. J. Neurosci. 39, 3687–3697 (2019).
Takamiya, S. et al. Auditory cortex neurons show task-related and learning-dependent selectivity toward sensory input and reward during the learning process of an associative memory task. eNeuro 9, ENEURO.0046-22.2022 (2022).
O’Sullivan, C., Weible, A. P. & Wehr, M. Auditory cortex contributes to discrimination of pure tones. eNeuro 6, ENEURO.0340-19.2019 (2019).
Acknowledgements
This work was supported by NIH National Institute of Neurological Disorders and Stroke (NINDS) BRAIN (grants R01NS104928 and RF1NS128896) and National Institute of Biomedical Imaging and Bioengineering BRAIN (grant R01EB029857). The authors would like to thank C. Petersen and the other anonymous reviewers for providing valuable critiques and suggestions for this Perspective.
Author information
Authors and Affiliations
Contributions
All authors contributed equally to conceptualization and to writing and revising the manuscript. All authors approved the final version.
Corresponding author
Ethics declarations
Competing interests
All authors declare no competing interests.
Peer review
Peer review information
Nature Neuroscience thanks Carl Petersen and the other, anonymous, reviewer(s) for their contribution to the peer review of this work.
Additional information
Publisher’s note Springer Nature remains neutral with regard to jurisdictional claims in published maps and institutional affiliations.
Rights and permissions
Springer Nature or its licensor (e.g. a society or other partner) holds exclusive rights to this article under a publishing agreement with the author(s) or other rightsholder(s); author self-archiving of the accepted manuscript version of this article is solely governed by the terms of such publishing agreement and applicable law.
About this article
Cite this article
Waiblinger, C., Reedy, A.R. & Stanley, G.B. An adaptive and flexible role for primary sensory cortex. Nat Neurosci 29, 2–12 (2026). https://doi.org/10.1038/s41593-025-02124-9
Received:
Accepted:
Published:
Version of record:
Issue date:
DOI: https://doi.org/10.1038/s41593-025-02124-9