Abstract
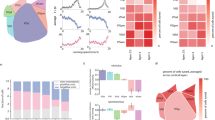
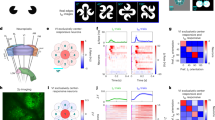
Intrinsic optical signal imaging (IOSI) enables non-invasive monitoring of neural activity in the mouse cortex, yet quantitative analysis remains hindered by low signal intensity, complex spatiotemporal patterns, and the lack of standardized benchmarks. To tackle this challenge, we present MouseCortex-IOS, a novel open accessible video segmentation dataset specifically designed for standardizing IOS analysis in awake rodent models, comprising 5732 images from 14 experimental subjects. Meanwhile, we implement an efficient processing pipeline leveraging foundation models to ensure annotation consistency while minimizing manual intervention. The dataset supports quantitative characterization of neural activation parameters including signal propagation velocity and trajectory, serving as a critical benchmark for developing automated analysis tools. Furthermore, this resource facilitates technique development in neuroimaging studies and accelerates the integration of computational approaches in IOS-based neuroscience research.
Similar content being viewed by others
Data availability
The dataset is publicly available on figshare: https://doi.org/10.6084/m9.figshare.28601813.
Code availability
The preprocessing code and other scripts that have been used in the pipeline are accessible at: https://github.com/ZhangWang-hub/MouseCortex-IOS. The open-source labeling tool can be download at: https://github.com/yatengLG/ISAT_with_segment_anything.
References
Zepeda, A., Arias, C. & Sengpiel, F. Optical imaging of intrinsic signals: Recent developments in the methodology and its applications. J. Neurosci. Methods 136, 1–21 (2004).
Li, P., Luo, W., Luo, Q. & Cheng, S. An evaluation of data analysis methods for optical intrinsic signal imaging. in (eds. Luo, Q., Tuchin, V. V., Gu, M. & Wang, L. V.) 542, https://doi.org/10.1117/12.546565 (Wuhan, China, 2003).
Crouzet, C., Phan, T., Wilson, R. H., Shin, T. J. & Choi, B. Intrinsic, widefield optical imaging of hemodynamics in rodent models of alzheimer’s disease and neurological injury. Neurophotonics 10 (2023).
Trizna, E. Y. et al. Brightfield vs fluorescent staining dataset–a test bed image set for machine learning based virtual staining. Sci. Data 10, 160 (2023).
Lu, H. D., Chen, G., Cai, J. & Roe, A. W. Intrinsic signal optical imaging of visual brain activity: Tracking of fast cortical dynamics. NeuroImage 148, 160–168 (2017).
Li, J., Zheng, A., Chen, X. & Zhou, B. Primary video object segmentation via complementary CNNs and neighborhood reversible flow. in 2017 IEEE International Conference on Computer Vision (ICCV) 1426–1434, https://doi.org/10.1109/ICCV.2017.158 (IEEE, Venice, 2017).
Wang, W., Lu, X., Shen, J., Crandall, D. & Shao, L. Zero-shot video object segmentation via attentive graph neural networks. in 2019 IEEE/CVF International Conference on Computer Vision (ICCV) 9235–9244, https://doi.org/10.1109/ICCV.2019.00933 (IEEE, Seoul, Korea (South), 2019).
Fragkiadaki, K., Arbelaez, P., Felsen, P. & Malik, J. Learning to segment moving objects in videos. in 2015 IEEE Conference on Computer Vision and Pattern Recognition (CVPR) 4083–4090, https://doi.org/10.1109/CVPR.2015.7299035 (IEEE, Boston, MA, USA, 2015).
Li, M., Li, S., Zhang, X. & Zhang, L. UniVS: Unified and universal video segmentation with prompts as queries. in 2024 IEEE/CVF Conference on Computer Vision and Pattern Recognition (CVPR) 3227–3238, https://doi.org/10.1109/CVPR52733.2024.00311 (IEEE, Seattle, WA, USA, 2024).
Mattjie, C. et al. “Zero-Shot Performance of the Segment Anything Model (SAM) in 2D Medical Imaging: A Comprehensive Evaluation and Practical Guidelines,” 2023 IEEE 23rd International Conference on Bioinformatics and Bioengineering (BIBE), Dayton, OH, USA, pp. 108-112, https://doi.org/10.1109/BIBE60311.2023.00025 (2023).
Yan, Z. et al. Biomedical SAM2: Segment Anything in Biomedical Images and Videos. Preprint at http://arxiv.org/abs/2408.03286 (2024).
Zhu, J., Hamdi, A., Qi, Y., Jin, Y. & Wu, J. Medical SAM2: Segment medical images as video via segment anything model 2. Preprint at, https://doi.org/10.48550/arXiv.2408.00874 (2024).
Kirillov A. et al. Segment Anything. 2023 IEEE/CVF International Conference on Computer Vision (ICCV), Paris, France, pp. 3992–4003, https://doi.org/10.1109/ICCV51070.2023.00371 (2023).
Ravi, N. et al. SAM 2: Segment anything in images and videos. Preprint at, https://doi.org/10.48550/arXiv.2408.00714 (2024).
Zhang, W. et al. MouseCortex-IOS dataset. Figshare https://doi.org/10.6084/m9.figshare.28601813 (2024).
Cohen, J. A coefficient of agreement for nominal scales. Educational and psychological measurement 20(1), 37–46 (1960).
Acknowledgements
The research was funded by Guangdong Basic and Applied Basic Research Foundation (2021A1515220151), Guangzhou Science and Technology Planning Program (No. 202201020518), Guangzhou Science and Technology Projects (2023A03J0958), Guangzhou Municipal Key R and D Program, China (2024B03J0947). Additionally, the authors would like to express sincere gratitude to the developers of the open-sourced AI toolkit ISAT_with_segment_anything (ISAT) for making this valuable resource publicly available.
Author information
Authors and Affiliations
Contributions
W.Z. created the dataset, performed the analysis and post-processing, and wrote the manuscript. G.Z. designed and constructed the optical acquisition platform, conducted experimental data acquisition, and performed partial data preprocessing. Z.Z., H.L., W.Q. and J.L. analyzed the results and provided suggestions. All authors actively participated in revising the manuscript.
Corresponding authors
Ethics declarations
Competing interests
The authors declare no competing interests.
Additional information
Publisher’s note Springer Nature remains neutral with regard to jurisdictional claims in published maps and institutional affiliations.
Rights and permissions
Open Access This article is licensed under a Creative Commons Attribution-NonCommercial-NoDerivatives 4.0 International License, which permits any non-commercial use, sharing, distribution and reproduction in any medium or format, as long as you give appropriate credit to the original author(s) and the source, provide a link to the Creative Commons licence, and indicate if you modified the licensed material. You do not have permission under this licence to share adapted material derived from this article or parts of it. The images or other third party material in this article are included in the article’s Creative Commons licence, unless indicated otherwise in a credit line to the material. If material is not included in the article’s Creative Commons licence and your intended use is not permitted by statutory regulation or exceeds the permitted use, you will need to obtain permission directly from the copyright holder. To view a copy of this licence, visit http://creativecommons.org/licenses/by-nc-nd/4.0/.
About this article
Cite this article
Zhang, W., Zeng, G., Zheng, Z. et al. A Mouse Cortex Video Segmentation Dataset for Intrinsic Optical Signal Tracking and Neural Activity Analysis. Sci Data (2026). https://doi.org/10.1038/s41597-026-06580-1
Received:
Accepted:
Published:
DOI: https://doi.org/10.1038/s41597-026-06580-1