Abstract
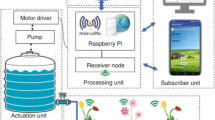
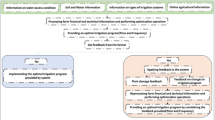
Real-time sensors for precision irrigation schedulating are used for enhancing water efficiency and optimizing resource usage. Poor resource management can negatively impact traditional farming practices, particularly in regions limited by water shortages. Agriculture is susceptible due to its heavy reliance on water resources. Due to global warming and its potential impacts, there is a growing emphasis on developing strategies to ensure a steady water supply for food production and consumption. As a result, research on reducing water usage in irrigation systems needs to be implemented. While traditional commercial irrigation sensors are often too expensive for smaller farms to adopt, manufacturers are now producing affordable alternatives that can be integrated with network systems to provide cost-effective solutions for efficient irrigation and agricultural monitoring. To minimize a farmer’s efforts, an Internet of Things (IoT)-based drip irrigation system is proposed in this work. Initially, the required data is collected using the IoT sensors. The gathered data is fed into the Adaptive Residual Hybrid network (ARHN) that is developed by using the Spatial Autoencoder and Stacked CapsNet. Here, the Modernized Random Variable-based Frilled Lizard Optimization (MRV-FLO) is utilized to tune the ARHN parameters. Therefore, the required water from the pump for the crops is provided by the ARHN model. In addition, this model makes the work simpler and avoids the wastage of water in the agricultural environment. Finally, the performance of the developed framework is validated over the existing works to prove the efficiency of the recommended method. The main experimental findings of the developed model achieve 99.24% and 97.32% in terms of accuracy and RMSE. Moreover, the statistical findings of the developed model shows 41.9%, 34.9%, 36.0% and 37.1% better performance than LEA-ARHN, FDA-ARHN, AOA-ARHN and FLO-ARHN in terms of best measure. Based on this performance enhancement, the developed model can effectively reduces the farmer’s effort and improves the crop productivity in the agricultural sectors.
Similar content being viewed by others
Data availability
The dataset utilized for the smart irrigation system is described below: Greenhouse data experiment drip irrigation 2016: Using https://data.4tu.nl/articles/dataset/Greenhouse_data_experiment_drip_irrigation_2016/12708971 this dataset is accessed on 2025–01-03. This drip irrigation dataset consists of parameter details like humidity, temperature, external rainwater intake, drain water flow and water supply.
References
Vinod Kumar, S. et al. IoT-based smart drip irrigation scheduling and wireless monitoring of microclimate in sweet corn crop under plastic mulching. Irrigation Sci. 45, 1–20 (2024).
Singh, C. D., Rao, K. V., Kumar, M. & Rajwade, Y. A. Development of a smart IoT‐based drip irrigation system for precision farming. Irrigation & Drainage 72(1) (2023).
Sharifnasab, H. et al. Evaluating the use of intelligent irrigation systems based on the IoT in grain corn irrigation. Water 15(7), 1394 (2023).
Chua, W. F. D., Lim, C. L., Koh, Y. Y. & Kok, C. L. A novel IoT photovoltaic-powered water irrigation control and monitoring system for sustainable city farming. Electronics 13(4), 676 (2024).
Roy, S. K., Misra, S., Raghuwanshi, N. S. & Das, S. K. AgriSens: IoT-based dynamic irrigation scheduling system for water management of irrigated crops. IEEE Internet of Things J. 8(6), 5023–5030 (2020).
Singh, C. D. & Kumar, V. S. Effects on growth and yields of sweet corn using internet of things (IoT) based smart drip irrigation and ETc based drip irrigation systems. RASSA J. Sci. Soc. 5(2), 87–95 (2023).
Behzadipour, F. et al. A smart IoT-based irrigation system design using AI and prediction model. Neural Comput. Appl. 35(35), 24843–24857 (2023).
de Jesús, P. S. A. IoT-based Drip Irrigation Monitoring and Controlling System using NB-IOT, ESP32+ Raspberry Pi," Revista Cubana de Ciencias Informáticas (2023).
Jain, R. K. et al. Experimental performance of soil monitoring system using IoT technique for automatic drip irrigation. Int. J. Commun. Syst. 36(18), e5617 (2023).
Singh, C. D., Ramana Rao, K. V. R., Rajwade, Y. A., Kumar, M. Jawaharlal, D. & Asha, K. R. IoT-based Smart Drip Irrigation Scheduling and Wireless Monitoring of Microclimate in Sweet Corn Crop under Plastic Mulching (2024).
Jani, K. A. & Chaubey, N. K. SDIPMIoT: Smart drip irrigation and preventative maintenance using IoT. SSRG Int. J. Electric. Electron. Eng. 10(7), 22–30 (2023).
Kok, C. L., Kusuma, I. M. B. P., Koh, Y. Y., Tang, H. & Lim, A. B. Smart aquaponics: An automated water quality management system for sustainable urban agriculture. Electronics 13, 820 (2024).
Benzaouia, M., Hajji, B., Mellit, A. & Rabhi, A. "Fuzzy-IoT smart irrigation system for precision scheduling and monitoring. Comput. Electron. Agric. 215, 108407 (2023).
Akshay, D. V. S. et al. Optimizing growth and yield in aerobic rice through IoT-based drip irrigation and fertigation. Int. J. Plant Soil Sci. 36(7), 190–200 (2024).
Dharshan, Y., D. Devasena, S. Kayalvizhi, & Sharmila, B. IoT-based automatic drip irrigation control using intelligent agriculture. In Drone Data Analytics in Aerial Computing 187–203 (2023).
Rehman, D. et al. Enhancing crop production and water conservation through IoT-based smart irrigation system. J. Comput. Biomed. Inf. 5(01), 96–104 (2023).
Et-taibi, B. et al. Enhancing water management in smart agriculture: A cloud and IoT-Based smart irrigation system. Results Eng. 22, 102283 (2024).
Santosh, D. T. et al. Development of IoT based intelligent irrigation system using particle swarm optimization and XGBoost techniques. Bullet. Electric. Eng. Inf. 13(3), 1927–1934 (2024).
Vinod Kumar, S. et al. IoT-based smart drip irrigation scheduling and wireless monitoring of microclimate in sweet corn crop under plastic mulching. Irrigat. Sci. 43, 1107–1126 (2024).
Anagha, C. S., Pawar, P. M. & Tamizharasan, P. S. Cost-effective IoT-based intelligent irrigation system. Int. J. Syst. Assur. Eng. Manag. 14, 263–274 (2023).
Yadav, S., Singh, P., Yadav, P., Srivastav, P., Yadav, S. K. & Singh, S. Implementation of Solar Powered Based Smart Drip Irrigation System Using IoT. In 2024 10th International Conference on Electrical Energy Systems (ICEES) 1–6 (2024).
Jain, R. K. Experimental performance of smart IoT-enabled drip irrigation system using and controlled through web-based applications. Smart Agric. Technol. 4, 100215 (2023).
Inayah, I., Agustirandi, B., Budiman, M., Djamal, M. & Faizal, A. Experimental Design: Implementation of IoT-based drip irrigation to enhance the productivity of Cilembu sweet potato (Ipomoea batatas) cultivation. Results Eng. 25, 103600 (2024).
Kumar, V. et al. Evaluation of IoT based smart drip irrigation and ETc based system for sweet corn. Smart Agric. Technol. 5, 100248 (2023).
Suresh, P. et al. IoT with evolutionary algorithm based deep learning for smart irrigation system. Comput. Mater. Continua 71(1), 1713–1728 (2022).
Lakshmi, G. S. P. et al. An intelligent IOT sensor coupled precision irrigation model for agriculture. Measur. Sensors 25, 100608 (2023).
Ahmad, U., Alvino, A. & Marino, S. Solar fertigation: A sustainable and smart IoT-based irrigation and fertilization system for efficient water and nutrient management. Agronomy 12(5), 1012 (2022).
Amiri, Z., Heidari, A., Navimipour, N. J., Esmaeilpour, M. & Yazdani, Y. The deep learning applications in IoT-based bio- and medical informatics: A systematic literature review. Neural Comput. Appl. 36, 5757–5797 (2024).
Morchid, A. et al. IoT-based smart irrigation management system to enhance agricultural water security using embedded systems, telemetry data, and cloud computing. Results Eng. 23, 102829 (2024).
Kumar, P., Udayakumar, A., Kumar, A. A., Kannan, K. S. & Krishnan, N. Multiparameter optimization system with DCNN in precision agriculture for advanced irrigation planning and scheduling based on soil moisture estimation. Environ. Monitor. Assess. 195(1), 13 (2023).
Sujono, H. A. & Nainggolan, W. P. Drip irrigation control system based on Mamdani fuzzy logic and Internet of Things (IoT). Prz Elektrotech 1, 65–69 (2024).
Heidari, A., Navimipour, N. J. & Unal, M. A secure intrusion detection platform using blockchain and radial basis function neural networks for internet of drones. IEEE Internet of Things J. 10(10), 8445–8454 (2023).
Heidari, A., Amiri, Z., Jamali, M. A. J. & Jafari, N. "Assessment of reliability and availability of wireless sensor networks in industrial applications by considering permanent faults. Concurren. Computat. Pract. Exper. 36(27), 8252 (2024).
Amiri, Z., Heidari, A. & Navimipour, N. J. Comprehensive survey of artificial intelligence techniques and strategies for climate change mitigation. Energy 308, 132827 (2024).
Vakili, A. et al. "A new service composition method in the cloud-based Internet of things environment using a grey wolf optimization algorithm and MapReduce framework. Concurren. Comput. Pract. Exper. 36(16), 8091 (2024).
Heidari, A., Shishehlou, H., Darbandi, M., Navimipour, N. J. & Yalcin, S. A reliable method for data aggregation on the industrial internet of things using a hybrid optimization algorithm and density correlation degree. Clust. Comput. 27, 7521–7539 (2024).
Amiri, Z., Heidari, A., Zavvar, M., Navimipour, N. J. & Esmaeilpour, M. The applications of nature-inspired algorithms in Internet of Things-based healthcare service: A systematic literature review. Trans. Emerg. Telecommun. Technol. 35(6), 4969 (2024).
Zanbouri, K. M., Darbandi, M. N., Heidari, A., Navimipour, N. J. & Yalcın, S. A GSO-based multi-objective technique for performance optimization of blockchain-based industrial Internet of things. Int. J. Commun. Syst. 37(15), 5886 (2024).
Heidari, A., Navimipour, N. J., Zeadally, S. & Chamola, V. Everything you wanted to know about ChatGPT: Components, capabilities, applications, and opportunities. Internet Technol. Lett. 7(6), 530 (2024).
Asadi, M., Jamali, M. A. J., Heidari, A. & Navimipour, N. J. Botnets unveiled: A comprehensive survey on evolving threats and defense strategies. Trans. Emerg. Telecommun. Technol. 35(11), 5056 (2024).
Heidari, A., Jamali, M. A. J. & Navimipour, N. J. Fuzzy logic multicriteria decision-making for broadcast storm resolution in vehicular ad hoc networks. Int. J. Commun. Syst. 38(5), 6034 (2024).
Heidari, A., Amiri, Z., Jamali, M. A. J. & Navimipour, N. J. Enhancing solar convection analysis with multi-core processors and GPUs. Eng. Rep. 7(1), 13050 (2024).
Toumaj, S., Heidari, A., Shahhosseini, R. & Navimipour, N. J. Applications of deep learning in Alzheimer’s disease: a systematic literature review of current trends, methodologies, challenges, innovations, and future directions. Artif. Intell. Rev. 58, 44 (2025).
Heidari, A. Jafari Navimipour, N. & Unal, M. The history of computing in Iran (Persia)—since the Achaemenid Empire. Technologies Vol. 10 (2022).
Amiri, Z., Heidari, A., Jafari, N. & Hosseinzadeh, M. Deep study on autonomous learning techniques for complex pattern recognition in interconnected information systems. Comput. Sci. Rev. 54, 100666 (2024).
Jamali, M. A. J. Bahrami, B., Heidari, A. Allahverdizadeh, P. & Norouzi, F The IoT Landscape. Towards the Internet of Things 1–8 (2019).
Dalirinia, E., Jalali, M., Yaghoobi, M. & Tabatabaee, H. Lotus effect optimization algorithm (LEA): A lotus nature-inspired algorithm for engineering design optimization. J. Supercomput. 80(1), 761–799 (2024).
Karami, H., Anaraki, M. V., Farzin, S. & Mirjalili, S. Flow direction algorithm (FDA): a novel optimization approach for solving optimization problems. Comput. Ind. Eng. 156, 107224 (2021).
Drias, H., Bendimerad, L. S. & Drias, Y. A three-phase artificial orcas algorithm for continuous and discrete problems. Int. J. Appl. Metaheuristic Comput. (IJAMC) 13(1), 1–20 (2022).
Falahah, I. A., Al-Baik, O. Alomari, S., Bektemyssova, G., Gochhait, S., Leonova, I., Malik, O. P., Werner, F. & Dehghani, M. Frilled Lizard Optimization: A Novel Nature-Inspired Metaheuristic Algorithm for Solving Optimization Problems. (2024).
Finn, C., Tan, X. Y. Duan, Y. Darrell, T. Levine, S & Abbeel, P. Deep spatial autoencoders for visuomotor learning. In 2016 IEEE International Conference on Robotics and Automation (ICRA) 512–519 (2016).
Opoku, M., Weyori, B. A., Adebayo, F. A. & Adu, K. SFFT-CapsNet: Stacked Fast Fourier Transform for Retina Optical Coherence Tomography Image Classification using Capsule Network. International Journal of Advanced Computer Science and Applications. 14(9) (2023).
Sarkar, R. Hazra, A., Sadhu, K. & Ghosh, P. A novel method for pneumonia diagnosis from chest X-ray images using deep residual learning with separable convolutional networks. In Computer Vision and Machine Intelligence in Medical Image Analysis: International Symposium, ISCMM 2019, 1–12. (2019).
Zhao, J., Liu, X. & Tian, M. An efficient task offloading method for drip irrigation and fertilization at edge nodes based on quantum chaotic genetic algorithm. AIP Advances 14 (2024).
Teja Santosh, D. et al. "Development of IoT based intelligent irrigation system using particle swarm optimization and XGBoost techniques. Bullet. Electric. Eng. Inf. 13(3), 1927–1934 (2024).
Singh, N., Kethavath Ajaykumar, L. K. & Dhruw, B. U. C. "Optimization of irrigation timing for sprinkler irrigation system using convolutional neural network-based mobile application for sustainable agriculture. Smart Agricult. Technol. 5, 100305 (2023).
Jenitha, R. & Rajesh, K. Intelligent irrigation scheduling scheme based on deep bi-directional LSTM technique. Int. J. Environ. Sci. Technol. 21, 1905–1922 (2024).
Acknowledgements
Princess Nourah bint Abdulrahman University Researchers Supporting Project number (PNURSP2025R79), Princess Nourah bint Abdulrahman University, Riyadh, Saudi Arabia.
Funding
This research is funded by Princess Nourah bint Abdulrahman University Researchers Supporting Project number (PNURSP2025R79), Princess Nourah bint Abdulrahman University, Riyadh, Saudi Arabia.
Author information
Authors and Affiliations
Contributions
Ahmad Y.A. Bani Ahmad, Jafar A. Alzubi, and Chanthirasekaran K.: Conceptualization, Methodology, Software Data curation, Writing- Original draft preparation, Reviewing and Editing, Software, Validation. ShabanaUrooj, Mohammad Shahzad, and Yogapriya J.: Funding Acquistion, Writing- Reviewing and Editing, Visualization, Investigation.
Corresponding author
Ethics declarations
Competing interests
The authors declare no competing interests.
Ethical approval
Not applicable.
Additional information
Publisher’s note
Springer Nature remains neutral with regard to jurisdictional claims in published maps and institutional affiliations.
Rights and permissions
Open Access This article is licensed under a Creative Commons Attribution-NonCommercial-NoDerivatives 4.0 International License, which permits any non-commercial use, sharing, distribution and reproduction in any medium or format, as long as you give appropriate credit to the original author(s) and the source, provide a link to the Creative Commons licence, and indicate if you modified the licensed material. You do not have permission under this licence to share adapted material derived from this article or parts of it. The images or other third party material in this article are included in the article’s Creative Commons licence, unless indicated otherwise in a credit line to the material. If material is not included in the article’s Creative Commons licence and your intended use is not permitted by statutory regulation or exceeds the permitted use, you will need to obtain permission directly from the copyright holder. To view a copy of this licence, visit http://creativecommons.org/licenses/by-nc-nd/4.0/.
About this article
Cite this article
Ahmad, A.Y.A.B., Alzubi, J.A., K., C. et al. Automated smart drip irrigation system in internet of things using adaptive residual hybrid network for precision farming. Sci Rep (2026). https://doi.org/10.1038/s41598-025-31804-6
Received:
Accepted:
Published:
DOI: https://doi.org/10.1038/s41598-025-31804-6