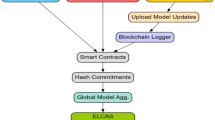
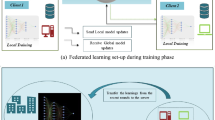
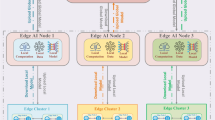
Abstract
Campus security systems empowered by edge Internet of Things (IoT) technologies face inherent conflicts among detection accuracy, resource efficiency, privacy protection, and adversarial robustness. Traditional Federated Learning (FL) frameworks and quantization methods often struggle to achieve balanced optimization under heterogeneous device conditions and strict ethical constraints. To address these challenges, this study proposes a Federated Reinforcement Learning (FRL)–driven multi-task collaborative optimization framework for secure and efficient edge IoT environments. The framework constructs a hierarchical perception–decision–constraint architecture that enables dynamic adaptation of quantization precision, defense intensity, and privacy parameters based on real-time environmental states. Ethical compliance is continuously ensured through distributed auditing and automated constraint enforcement, forming a closed-loop optimization mechanism integrating technical robustness and normative governance. Extensive experiments conducted on the NSL-KDD benchmark demonstrate that the proposed system achieves 94.3% intrusion detection accuracy across twelve heterogeneous nodes, with an F1-score of 89.3% for rare User-to-Root (U2R) attacks. The approach reduces energy consumption by 66.1%, latency by 72.8%, and limits adversarial attack success rate to 23.4%. Under Differential Privacy (DP) constraints with ε = 2.0, privacy leakage incidents are controlled within 2.4 occurrences per month, and the framework maintains stability over 168 h of continuous operation. Overall, this research provides an integrated, scalable, and ethically accountable solution for campus network security, demonstrating the potential of FRL to achieve synergistic optimization across performance, robustness, and compliance dimensions in edge intelligent systems.
Similar content being viewed by others
Data availability
The data that support the findings of this study are openly available in Figshare at http://doi.org/10.6084/m9.figshare.30415624.
References
Jiang, W. et al. Byzantine-robust federated reinforcement learning via critical parameter analysis. Int. J. Mach. Learn. Cybernet. 16, 1–14 (2025).
Wei, S. et al. HyperMem: Hypernetwork with Memory for Forgetting Problem in Federated Reinforcement Learning. Expert Syst. Appl. 294, 128671 (2025).
Sievers, J. et al. Federated reinforcement learning for sustainable and cost-efficient energy management. Energy AI 21, 100521 (2025).
Wang, Z. et al. Enhancing multi-task performance through associative adversarial learning based on selective attacks. Neurocomputing 640, 130229 (2025).
Li, Y. et al. FedRL-Hybrid: A federated hybrid reinforcement learning approach. Inf. Sci. 710, 122102 (2025).
Musaddiq, A. et al. Machine learning for resource management in industrial internet of Things. Front. Comput. Sci. 7, 1566353 (2025).
Pang, Y., Ni, Z. & Zhong, X. A fast federated reinforcement learning approach with phased weight-adjustment technique. Neurocomputing 626, 129550 (2025).
Chang, V. et al. Introduction to the special issue on big data and the internet of things in complex information Systems. Big Data. 13 (1), 1–2 (2025).
Bagdasaryan, E. et al. How to backdoor federated learning[C]//International conference on artificial intelligence and statistics. PMLR, : 2938–2948. (2020).
Fang, M. et al. Local model poisoning attacks to {Byzantine-Robust} federated learning[C]//29th USENIX security symposium (USENIX Security 20). 1605–1622. (2020).
Galloway, A., Taylor, G. W. & Moussa, M. Attacking binarized neural networks. arXiv preprint https://abs/arXiv.org/1711.00449 (2017)
Gupta, A. & Fernando, X. Federated reinforcement learning for collaborative intelligence in UAV-assisted C-V2X communications. Drones 8 (7), 321 (2024).
You, Z. et al. Location Privacy Preservation Crowdsensing with Federated Reinforcement learning. (IEEE Transactions on Dependable and Secure Computing, 2024).
Sagar, A. S. M. S., Haider, A. & Kim, H. S. A hierarchical adaptive federated reinforcement learning for efficient resource allocation and task scheduling in hierarchical IoT network. Comput. Commun. 229, 107969 (2025).
Qi, J. et al. Federated reinforcement learning: Techniques, applications, and open challenges. arXiv preprint at https//abs/arXiv.org/2108.11887 (2021).
Singh, S. et al. A framework for privacy-preservation of IoT healthcare data using federated learning and blockchain technology. Future Generation Comput. Syst. 129, 380–388 (2022).
Kang, J. et al. Incentive mechanism for reliable federated learning: A joint optimization approach to combining reputation and contract theory. IEEE Internet Things J. 6 (6), 10700–10714 (2019).
Wei, S. et al. HyperMem: Hypernetwork with memory for forgetting problem in federated reinforcement learning. Expert Syst. Appl. 294, 128671 (2025).
Nguyen, T., Nguyen, H. & Gia, T. N. Exploring the integration of edge computing and blockchain iot: Principles, architectures, security, and applications. J. Netw. Comput. Appl. 226, 103884 (2024).
Guo, S. et al. Real-Time Memory Data Optimization Mechanism of Edge IoT Agent. Intelligent Automation & Soft Computing 37(1) (2023).
Padmini, M. S. & Kuzhalvaimozhi, S. Critical analysis of life span improvement techniques in energy constraints edge IoT Devices. SN Comput. Sci. 4 (3), 221 (2023).
Nandanwar, H. & Katarya, R. A secure and privacy-preserving ids for iot networks using hybrid blockchain and federated learning[C]//International Conference on Next-Generation Communication and Computing. 207–219. ( Springer Nature, 2024).
Nandanwar, H. & Katarya, R. Optimized intrusion detection and secure data management in IoT networks using GAO-Xgboost and ECC-integrated blockchain framework. Knowl. Inf. Syst. 1–56. (2025).
Keum, S. S., Park, Y. J. & Kang, S. J. Edge computing-based self-organized device network for awareness activities of daily living in the home. Appl. Sci. 10 (7), 2475 (2020).
Nasir, M. et al. Feature engineering and deep learning-based intrusion detection framework for Securing edge IoT. J. Supercomputing. 78 (6), 8852–8866 (2022).
Tanghatari, E. et al. Distributing DNN training over IoT edge devices based on transfer learning. Neurocomputing 467, 56–65 (2022).
Lim, H. K. et al. Federated reinforcement learning acceleration method for precise control of multiple devices. IEEE Access. 9, 76296–76306 (2021).
Hu, Y. et al. Reward shaping based federated reinforcement learning. IEEE Access. 9, 67259–67267 (2021).
Nandanwar, H. & Katarya, R. Deep learning enabled intrusion detection system for industrial IOT environment. Expert Syst. Appl. 249, 123808 (2024).
Nandanwar, H. & Katarya, R. TL-BILSTM iot: transfer learning model for prediction of intrusion detection system in IoT environment. Int. J. Inf. Secur. 23 (2), 1251–1277 (2024).
Nandanwar, H. & Katarya, R. Securing industry 5.0: an explainable deep learning model for intrusion detection in cyber-physical systems. Comput. Electr. Eng. 123, 110161 (2025).
Nandanwar, H. & Katarya, R. A hybrid blockchain-based framework for Securing intrusion detection systems in internet of things. Cluster Comput. 28 (7), 471 (2025).
Setyowati, D. L. et al. Simulating water efficiency management at UNNES Campus, Semarang, Indonesia using EDGE application[C]//IOP Conference Series: Earth and Environmental Science. 485(1): 012038 (IOP Publishing, 2020).
Kang, J. et al. Dynamic offloading model for distributed collaboration in edge computing: a use case on forest fires management. Appl. Sci. 10 (7), 2334 (2020).
Nandanwar, H., Katarya, R. & secure and privacy-preserving data sharing in 6G‐enabled blockchain iot healthcare systems. Secur. Priv. 8(6): e70105 (2025).
Funding
This work was supported by Top talent cultivation funding project of Anhui Universities of China (Grant No. gxbjZD57) and Anhui Natural Science Foundation of China (Grant No. 2108085MF230).
Author information
Authors and Affiliations
Contributions
Yi Li: Writing-original draft, Writing—Review & Editing, Conceptualization, Formal analysis, Methodology. Haitao Wang: Conceptualization, Methodology, Validation, Supervision. Guoming Xu: Conceptualization, Validation, Supervision, Funding Acquisition. All authors reviewed the manuscript.
Corresponding author
Ethics declarations
Competing interests
The authors declare no competing interests.
Additional information
Publisher’s note
Springer Nature remains neutral with regard to jurisdictional claims in published maps and institutional affiliations.
Rights and permissions
Open Access This article is licensed under a Creative Commons Attribution-NonCommercial-NoDerivatives 4.0 International License, which permits any non-commercial use, sharing, distribution and reproduction in any medium or format, as long as you give appropriate credit to the original author(s) and the source, provide a link to the Creative Commons licence, and indicate if you modified the licensed material. You do not have permission under this licence to share adapted material derived from this article or parts of it. The images or other third party material in this article are included in the article’s Creative Commons licence, unless indicated otherwise in a credit line to the material. If material is not included in the article’s Creative Commons licence and your intended use is not permitted by statutory regulation or exceeds the permitted use, you will need to obtain permission directly from the copyright holder. To view a copy of this licence, visit http://creativecommons.org/licenses/by-nc-nd/4.0/.
About this article
Cite this article
Li, Y., Wang, H. & Xu, G. Federated reinforcement learning–driven multi-task optimization for robust and ethical edge internet of things security. Sci Rep (2026). https://doi.org/10.1038/s41598-025-34879-3
Received:
Accepted:
Published:
DOI: https://doi.org/10.1038/s41598-025-34879-3