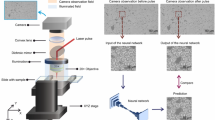
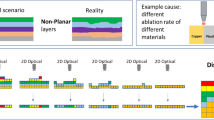
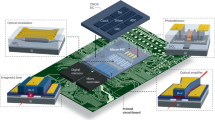
Abstract
Accurately reconstructing the metal layers of semiconductor chips is essential for legacy hardware support, design validation, and failure analysis. Conventional methods such as mechanical polishing, chemical etching, and focused ion beam (FIB) delayering, while established, tend to be slow, inconsistent, and resource-intensive—making them less suitable for systematic or scalable workflows. To address these limitations, we developed a streamlined approach combining laser-based delayering with high-resolution multimodality microscopy, offering a more efficient and reproducible alternative. Building on our earlier work with infrared laser delayering, which faces challenges related to selective material interactions and uneven ablation, in this work, we have investigated the use of a green (515 nm) laser. This alternative wavelength offers reduced sensitivity to material variations, allowing for more uniform and controlled removal of chip layers. Through a thorough parameter space exploration and optimization process, we achieved significantly cleaner delayering and exposure of underlying structures. The effectiveness of this method is demonstrated through comparative imaging using confocal microscopy and SEM, as well as material analysis via EDS, all showing notable significant improvements in layer clarity and debris reduction. These results highlight the green laser’s potential as a powerful tool for high-fidelity chip analysis in modern diagnostics and reverse engineering workflows.
Similar content being viewed by others
Data availability
All data generated or analyzed during this study are included in this published article.
Referencess
R. Torrance and D. James, ‘"The State-of-the-Art in Semiconductor Reverse Engineering,",2007.
C. Boit, ‘"Failure Analysis of Integrated Circuits: Tools and Techniques,", 2010.
R. Roy and E. Shehab, ‘"Industrial Product-Service Systems (IPS2 ): Proceedings of the 1st CIRP IPS2 Conference, 01-02 April 2009, Cranfield University, UK,", 2009.
Gurushankar, N. Ensuring Security in Semiconductor Design through Verification. J. Biosens. Bioelectr. Res. 1, 1 (2023).
Lin, Q., Wu, H. & Jia, G. "Review of the Global Trend of Interconnect Reliability for Integrated Circuit. Circuits Sys. 9(2), 9–21 (2018).
Zhang, F. et al. "Bronze and Iron Age genomes reveal the integration of diverse ancestries in the Tarim Basin. Current Biology 35(15), 3759 (2025).
Choi, H. et al. "Rapid three-dimensional reconstruction of printed circuit board using femtosecond laser delayering and digital microscopy. Microelectr. Reliab. 138, 114659 (2022).
N. May, H. Choi, M. Emanuel, P. Mahyari, M. Maniscalco, T. Bliznakov, T. Moore, M.T.M. Anaei, A. Phoulady, A. Blagojevic, S. Shahbazmohamadi and P. Tavousi, ‘"High-resolution 3D volumetric imaging using laser-enabled delayering techniques,", vol. 13353, pp. 70–78.
Zschech, E., Yun, W. & Schneider, G. "High-resolution X-ray imaging—a powerful nondestructive technique for applications in semiconductor industry. Appl. Phys. A 92(3), 423–429 (2008).
May, N. et al. "Gas-assisted femtosecond pulsed laser machining: A high-throughput alternative to focused ion beam for creating large, high-resolution cross sections. PLOS ONE 18(5), e0285158 (2023).
Anonymous ‘"Intelligent Multi-Dimensional Material Processing and Imaging Using Femtosecond Lasers - ProQuest,", vol. 2025, no. Jul 21.
Maniscalco, M. et al. "Fast reverse engineering of chips using lasers, Focused Ion Beams, and confocal and scanning electron microscopy. Microelectronics Reliability 168, 115697 (2025).
Jiang, L. J. et al. "Femtosecond laser direct writing in transparent materials based on nonlinear absorption. MRS Bulletin 41(12), 975–983 (2016).
Chang, J. J., Warner, B. E., Dragon, E. P. & Martinez, M. W. "Precision micromachining with pulsed green lasers. Journal of Laser Applications 10(6), 285–291 (1998).
Wang, L., Zhao, Y., Yang, Y., Zhang, M. & Zhao, Y. "Experimental Investigation on Ablation of 4H-SiC by Infrared Femtosecond Laser. Micromachines 13(8), 1291 (2022).
Phoulady, A. et al. "Rapid high-resolution volumetric imaging via laser ablation delayering and confocal imaging. Sci Rep 12(1), 12277.s (2022).
Acknowledgment
We thank CHEST for proving funding and support for this project. We thank MITRE for providing chip samples and for their feedback and support throughout this research.
Funding
This project leveraged funding from Center for Hardware and Embedded System Security and Trust (CHEST).
Author information
Authors and Affiliations
Contributions
Mohammad Taghi Mohammadi Anaei, Matthew Maniscalco, Hongbin Choi, Marcus Emanuel, Wesley Roser, Todor Bliznakov, Toni Moore, Adrian Phoulady, Parisa Mahyari, Alexander Blagojevic, Nicholas May, Garth Egan, Sina Shahbazmohamadi, Pouya Tavousi contributed to manuscript writing and reviewing.
Corresponding authors
Ethics declarations
Competing interests
Sina Shahbazmohamadi, Pouya Tavousi and Nicholas May decalre financial interest with Tescan FemtoInnovations.
Additional information
Publisher’s note
Springer Nature remains neutral with regard to jurisdictional claims in published maps and institutional affiliations.
Rights and permissions
Open Access This article is licensed under a Creative Commons Attribution 4.0 International License, which permits use, sharing, adaptation, distribution and reproduction in any medium or format, as long as you give appropriate credit to the original author(s) and the source, provide a link to the Creative Commons licence, and indicate if changes were made. The images or other third party material in this article are included in the article’s Creative Commons licence, unless indicated otherwise in a credit line to the material. If material is not included in the article’s Creative Commons licence and your intended use is not permitted by statutory regulation or exceeds the permitted use, you will need to obtain permission directly from the copyright holder. To view a copy of this licence, visit http://creativecommons.org/licenses/by/4.0/.
About this article
Cite this article
Anaei, M.T.M., Maniscalco, M., Choi, H. et al. High-fidelity chip delayering using green (515 nm) femtosecond lasers. Sci Rep (2026). https://doi.org/10.1038/s41598-026-35091-7
Received:
Accepted:
Published:
DOI: https://doi.org/10.1038/s41598-026-35091-7