Abstract
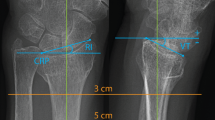
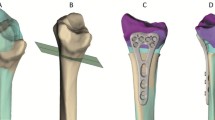
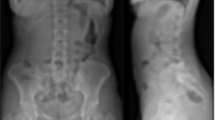
This study evaluates the morphometric characteristics of the volar distal radius, specifically volar curvature, scaphoid and lunate facet inclinations, and ulnar variance, in the Anatolian population. By identifying these population specific morphological variations, the study seeks to support improved anatomical compatibility of volar implants and enhance surgical planning for distal radius fracture fixation. Morphometric measurements were analyzed retrospectively on three-dimensional computed tomography images of 103 intact distal radii. Standardized sagittal sections were created through the midpoints of the scaphoid and lunate fossae, and volar curvature was quantified as the angle between the radial shaft axis and the volar cortex at 1 cm and 2 cm proximal to the distal radius volar rim on each section. Volar inclination angles were measured at 1 cm and 2 cm. Additionally, volar width (G), scaphoid facet inclination (SFI), lunate facet inclination (LFI), interfacet angle (IFA), and ulnar variance were evaluated. Volar curvature measured 1 cm and 2 cm proximal to the scaphoid and lunate fossae was significantly greater in males than females (p < .05). The mean transverse volar width was 26.5 mm, with no significant differences according to gender, age, or laterality (p > .05). The mean ulnar variance was − 2.0 ± 2.2 mm, while the mean LFI, SFI, and IFA were − 0.1° ± 8.4°, 26.1° ± 6.9°, and 24.2° ± 10.4°, respectively. This study demonstrates notable anatomical variations in the volar distal radius within the Anatolian population, particularly in volar curvature, scaphoid and lunate facet inclinations, and ulnar variance. These population specific morphometric differences underscore the importance of integrating multiple volar parameters into preoperative planning, as they may directly influence implant selection and improve the accuracy of distal radius fracture fixation.
Similar content being viewed by others
Data availability
The datasets generated and analysed during the current study are not publicly available due to the nature of the data (reconstructed radiological CT images obtained from the hospital archive), but are available from the corresponding author on reasonable request.
References
Court-Brown, C. M. & Caesar, B. Epidemiology of adult fractures: a review. Injury 37 (8), 691–697 (2006).
Nalbantoglu, U. et al. Comparison between fixation with dorsal T plate and palmar locking plate in the treatment of unstable displaced distal radius fractures. Acta Orthop. Traumatol. Turc. 42 (5), 365–372 (2008).
Imatani, J. & Akita, K. Volar distal radius anatomy applied to the treatment of distal radius fracture. J. Wrist Surg. 6 (03), 174–177 (2017).
Waitayawinyu, T. et al. Comparative Biomechanical study of fragment-specific plates and headless screws for radial styloid and lunate facet fixation in distal radius fracture evaluated in a synthetic composite. J. Hand. Surg. 50 (7), 887 (2025). e1-887. e10.
Yoneda, H. et al. Interindividual anatomical variations affect the plate-to‐bone fit during osteosynthesis of distal radius fractures. J. Orthop. Res. 34 (6), 953–960 (2016).
Yildirim, T., Unsal, S. S. & Armangil, M. Association of the interfacet angle and the lunate facet inclination angle with Kienböck disease. J. Hand. Surg. 47 (4), 391 (2022). e1-391. e6.
Altamimi, A. R. Association between carpal height ratio and ulnar variance in normal wrist radiography. BMC Musculoskelet. Disord. 25 (1), 524 (2024).
Oppermann, J. et al. Distal radius: anatomical morphometric gender characteristics. Do anatomical pre-shaped plates pay attention on it? Arch. Orthop. Trauma Surg. 135, 133–139 (2015).
Singh, T. S. P., Sadagatullah, A. N. & Yusof, A. H. Morphology of distal radius curvatures: a CT-based study on the Malaysian Malay population. Singapore Med. J. 56 (10), 562 (2015).
Ghalimah, B. A. et al. A preliminary exploration of ulnar variance in healthy wrists at a tertiary hospital in Jeddah. Saudi Med. J. 37 (8), 843 (2016).
Arik, A. et al. Facet inclinations and interfacet angle of the distal radius on posteroanterior radiographs. J. Hand. Surg. 45 (1), 65 (2020). e1-65. e8.
Corporation, I. IBM SPSS Statistics for MAC OS, Version 26.0. Armonk, NY IBM Corp. (2019).
Koo, T. K. & Li, M. Y. A guideline of selecting and reporting intraclass correlation coefficients for reliability research. J. Chiropr. Med. 15 (2), 155–163 (2016).
Ağir, I. et al. Distal radius measurements and efficacy of fixed-angle locking volar plates. Turk. J. Med. Sci. 44 (1), 36–41 (2014).
RiKli, D. A. & Regazzoni, P. Fractures of the distal end of the radius treated by internal fixation and early function: a preliminary report of 20 cases. J. Bone Joint Surg. Br. Volume. 78 (4), 588–592 (1996).
Nalbant, A. et al. Evaluación Radiológica Del Ángulo cortical volar En La Población Anatoliana. Int. J. Morphology. 41 (5), 1508–1512 (2023).
Tanaka, Y. et al. Effect of distal radius volar plate position on contact pressure between the flexor pollicis longus tendon and the distal plate edge. J. Hand. Surg. 36 (11), 1790–1797 (2011).
Afshar, A., Aminzadeh-Gohari, A. & Yekta, Z. The association of Kienböck’s disease and ulnar variance in the Iranian population. J. Hand Surg. (European Volume). 38 (5), 496–499 (2013).
Gehweiler, D. et al. Computerized anatomy of the distal radius and its relevance to volar plating, research, and teaching. Clin. Anat. 32 (3), 361–368 (2019).
Sato, K. et al. Volar locking plates not touching the flexor pollicis longus tendon appear as prominences on radiographs: a cadaver study. J. Orthop. Traumatol. 20, 1–7 (2019).
Kwon, B. C. et al. Morphometric variations in the volar aspect of the distal radius. Clin. Orthop. Surg. 10 (4), 462–467 (2018).
Yalçın, A. & Polat, A. Evaluation of radiographic measurements of the wrist in the Turkish population. J. Surg. Med. 6 (1), 36–42 (2022).
Lee, S. et al. CT-based three-dimensional kinematic comparison of dart-throwing motion between wrists with malunited distal radius and contralateral normal wrists. Clin. Radiol. 69 (5), 462–467 (2014).
Li, L., Liu, X. & Zhang, L. Real-time biofeedback monitoring rehabilitation of distal radius fracture. J. Neuroeng. Rehabil. 22 (1), 211 (2025).
Acknowledgements
The authors would like to sincerely thank the Acıbadem University Scientific Research Projects Office for their support in the planning and execution of this study. Special thanks are also extended to the academics and staff of the Department of Anatomy at Istanbul University-Cerrahpaşa for their valuable contributions throughout the study.
Author information
Authors and Affiliations
Contributions
Author Contributions: P.İ. collected, compiled, and analyzed the data, and wrote the manuscript. U.N. conceptualized the study and curated the data. O.K. performed formal analysis and data validation. A.B. supervised the project and reviewed the manuscript. A.V.İ. created the figures and assisted with the methodology. G.K.Y. supervised and edited the manuscript.
Corresponding author
Ethics declarations
Competing interests
The authors declare no competing interests.
Additional information
Publisher’s note
Springer Nature remains neutral with regard to jurisdictional claims in published maps and institutional affiliations.
Rights and permissions
Open Access This article is licensed under a Creative Commons Attribution 4.0 International License, which permits use, sharing, adaptation, distribution and reproduction in any medium or format, as long as you give appropriate credit to the original author(s) and the source, provide a link to the Creative Commons licence, and indicate if changes were made. The images or other third party material in this article are included in the article’s Creative Commons licence, unless indicated otherwise in a credit line to the material. If material is not included in the article’s Creative Commons licence and your intended use is not permitted by statutory regulation or exceeds the permitted use, you will need to obtain permission directly from the copyright holder. To view a copy of this licence, visit http://creativecommons.org/licenses/by/4.0/.
About this article
Cite this article
İsmailoğlu, P., Nalbantoğlu, U., Tok, O. et al. Distal radius morphometry of volar curvature along with scaphoid and lunate facet inclinations and ulnar variance in the Anatolian population. Sci Rep (2026). https://doi.org/10.1038/s41598-026-35123-2
Received:
Accepted:
Published:
DOI: https://doi.org/10.1038/s41598-026-35123-2