Abstract
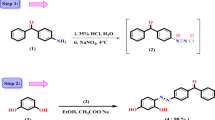
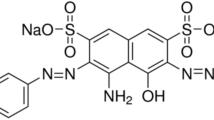
Invention of high-performance, environmentally friendly disazo acid dyes (D1-D4) intended for sustainable textile coloring and pH-responsive sensing applications is reported in this study. Sulphanilic acid and other aromatic derivatives were used in simplified diazotization-coupling procedure to create dyes. Effective integration of azo and sulfonate groups, guaranteeing superior water solubility, was verified by structural characterization. Dyes created bright, high-affinity orange and red colors with remarkable wash and light fastness (ratings: 4–5) when applied to wool and nylon. λmax values in UV-vis spectra varied according to substituent location, from 479 to 485 nm. Notably, protonation-deprotonation balance drives Dye D1’s reversible, “smart” color shift from brown to pink in response to pH changes. Among synthesized dyes, D1 showed a clear and reversible pH-responsive color change, going from brown to pink under increasingly acidic conditions, while D3 showed mild pH sensitivity and dyes D2 and D4 remained color-stable throughout tested pH range of 2–4, displaying distinct chromatic stability profiles. Compared to nylon, the K/S and fastness qualities of wool materials were higher. These results show that synthesized dyes have great promise for creation of novel, pH-sensitive smart fabrics in addition to offering excellent technical performance and high fixing, which reduces environmental leaching.
Similar content being viewed by others
Data availability
The data relating to experimental findings is already reported within the paper, and it can also be available from the corresponding author upon a reasonable request.
Abbreviations
- Conc.:
-
Concentration
- Dyeings:
-
Dyed textile fiber
- ISO:
-
International organization of standard methods
- o.w.f:
-
Of weight of fiber
- Scoured fabric:
-
Fabric free from dirt, oils and fats
- λmax :
-
Wavelength of maximum absorption
References
Ahluwalia, V. K. & Goyal, M. A Textbook of Organic Chemistry 896–903 (Varosa Publishing House, 2000).
Rani, S. Effect of dyes on different types of fabrics. Int. J. Sci. Res. 5 (10), 939–942 (2016).
Li, X., Wang, R., Fan, G. & Song, F. Morphological quantification of the higher-order contact normal fabrics for granular materials. Tribol. Int. 214, 111348 (2026).
Saini, R. & Choudhary, K. Toxic potential of Azo dyes: A broader Understanding. In Hazardous Chemicals. 469–481 (2025).
Aspland, J. R. Textile Dyeing and Coloration 264 (American Association of Textile Chemists and Colorists, 1997).
Roy, A. K. Textile Preparation and Dyeing 647–650 (Science, 2006).
Zhang et al. Functional textiles with smart properties: their fabrications and sustainable applications. Adv. Funct. Mater. 33 (33), 2301607 (2023).
De Giorgi, M. R., Carpignano, R. & Crisponi, G. Structure optimization in a series of acid dyes for wool and nylon. Dyes Pigm. 34 (1), 1–12 (1997).
Hunger, K. Industrial Dyes: Chemistry, Properties, Applications 3rd edn, 277–278 (Wiley-VCH, 2003).
Kumar, A. et al. Structure and properties of dyes and pigments. In Dyes and pigments-novel applications and waste treatment. IntechOpen, (2021).
Tasli, P. T. et al. Experimental and computational studies of newly synthesized azo dyes based materials. J. Mol. Struct. pp 1201, 127098 (2020).
Mello, M. L. S., Anjos, D. & de Campos Vidal, B. Usefulness of sulfonated azo dyes to evaluate macromolecularly oriented protein substrates. Acta histochemica 126(3), 152154 (2024).
Satake, M. & Mido, Y. Chemistry of Color. 13–14 (Discovery Publishing House, 1995).
Dhake, A. N., Patil, C. J. & Chaudhari, G. R. Coupling Reactions of Aryldiazonium Salt. Part-XI: Review on Coupling of Aryldiazonium Salts of Aminobenzothiazoles with Aromatic and Heterocyclic Components. Int. J. Pharma Sci. Rev. Res. 70(2), 75–99 (2021).
Kundu, C. K., Li, Z., Song, L. & Hu, Y. Nylon Textiles: A Shift towards Eco-Friendly Approaches. Flame retardant and thermally insulating polymers, 89 (2021).
Ramlow, H., Andrade, K. L. & Immich, A. P. S. Smart textiles: an overview of recent progress on chromic textiles. J. Text. Inst. 112 (1), 152–171 (2021).
Tasli, P. T., Atay, Ç. K., Demirturk, T. & Tilki, T. Experimental and computational studies of newly synthesized azo dyes based materials. J. Mol. Struct. 1201, 127098 (2020).
Acknowledgements
This work was supported by Princess Nourah bint Abdulrahman University Researchers Supporting Project number (PNURSP2026R398), Princess Nourah bint Abdulrahman University, Riyadh, Saudi Arabia.
Author information
Authors and Affiliations
Contributions
***Conceptualization*** : Kiran Shahzadi; ***Methodology*** *:* Kiran Shahzadi and Muneerah Alomar; ***Data curation*** : Kiran Shahzadi, Muneerah Alomar, and Maryam Al Huwayz.; ***Software*** : Kiran Shahzadi, Muneerah Alomar, and Maryam Al Huwayz.; ***Validation*** : Kiran Shahzadi, Muneerah Alomar, Maryam Al Huwayz, and Muhammad Sarfraz.; ***Visualization*** : Kiran Shahzadi, Muneerah Alomar, Maryam Al Huwayz, and Muhammad Sarfraz.; ***Formal analysis*** : Kiran Shahzadi, Muneerah Alomar, Maryam Al Huwayz, and Muhammad Sarfraz.; ***Investigation*** : Kiran Shahzadi, Muneerah Alomar, Maryam Al Huwayz, and Muhammad Sarfraz.; ***Writing-original draft preparation*** : Kiran Shahzadi, Muneerah Alomar and Maryam Al Huwayz; ***Writing-review and editing*** : Kiran Shahzadi, Muneerah Alomar, Maryam Al Huwayz, Muhammad Sarfraz, and A.A. Adediran; ***Project administration*** : Kiran Shahzadi, Muneerah Alomar, and Maryam Al Huwayz. ***Resources*** : Kiran Shahzadi, Muneerah Alomar, and Maryam Al Huwayz. ***Funding acquisition*** : Kiran Shahzadi, Muneerah Alomar, and Maryam Al Huwayz. All authors have read and agreed to the published version of the manuscript.
Corresponding authors
Ethics declarations
Competing interests
The authors declare no competing interests.
Consent for publication
All authors agreed upon the current version of the submission for publication.
Additional information
Publisher’s note
Springer Nature remains neutral with regard to jurisdictional claims in published maps and institutional affiliations.
Rights and permissions
Open Access This article is licensed under a Creative Commons Attribution-NonCommercial-NoDerivatives 4.0 International License, which permits any non-commercial use, sharing, distribution and reproduction in any medium or format, as long as you give appropriate credit to the original author(s) and the source, provide a link to the Creative Commons licence, and indicate if you modified the licensed material. You do not have permission under this licence to share adapted material derived from this article or parts of it. The images or other third party material in this article are included in the article’s Creative Commons licence, unless indicated otherwise in a credit line to the material. If material is not included in the article’s Creative Commons licence and your intended use is not permitted by statutory regulation or exceeds the permitted use, you will need to obtain permission directly from the copyright holder. To view a copy of this licence, visit http://creativecommons.org/licenses/by-nc-nd/4.0/.
About this article
Cite this article
Shahzadi, K., Sarfraz, M., Alomar, M. et al. Designing eco-friendly pH-responsive Azo dyes for sustainable textile fabrics. Sci Rep (2026). https://doi.org/10.1038/s41598-026-35135-y
Received:
Accepted:
Published:
DOI: https://doi.org/10.1038/s41598-026-35135-y