Abstract
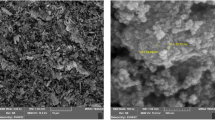
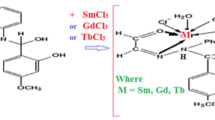
We report the synthesis and multi-technique characterization of tetrakis (5-nitrosalicylate) hafnium (IV), a previously unreported hafnium–organic complex with potential photonic applications. Optimized chelation of Hf (IV) with 5-nitrosalicylic acid yielded the target compound at 67% efficiency. Multimodal structural validation (XRD/FT-IR/EDX) confirmed an octacoordinated crystalline lattice featuring cyclic chelate motifs, exhibiting elemental homogeneity and thermal resilience. Spectroscopic ellipsometry uncovered dual-range optical functionality: In the UV-Vis region, the material exhibits strong ligand-to-metal charge-transfer (LMCT) characteristics in the UV. Conversely, across Vis-NIR wavelengths, it exhibited dielectric characteristics with positive dispersion and declining absorption, confirming high visible transparency. Nonlinear optical studies using the Z-scan technique demonstrated significant third-order susceptibility, featuring self-defocusing refraction and two-photon absorption. Calculated figures of merit confirmed its suitability for all-optical switching devices. This bifunctional optical response—dominated by strong ligand-to-metal charge-transfer (LMCT) absorption in the UV and dielectric behavior in the Vis–NIR—positions the complex as a promising material for UV-selective photodetection, UV-driven photocatalysis, and devices that exploit strong, spectrally selective absorption (e.g., optical sensors and nonlinear optical limiters). By integrating molecular chelate design with optoelectronic functionality, this work advances metal-organic frameworks for next-generation photonic technologies.
Similar content being viewed by others
Data availability
All data generated or analyzed during this study are included in this published article.
References
Saleh, B. E. A. & Teich, M. C. Fundamentals of Photonics (Wiley, 2008).
Zhou, W. et al. Hafnium-based metal-organic framework nanoparticles as a radiosensitizer to improve radiotherapy efficacy in esophageal cancer. ACS Omega 7, 562 (2022).
Kalyanasundaram, K. & Grätzel, M. Applications of functionalized transition metal complexes in photonic and optoelectronic devices. Coord. Chem. Rev. 177, 347–414 (1998).
Hu, Z., Wang, Y. & Zhao, D. The chemistry and applications of hafnium and cerium(iv) metal-organic frameworks. Chem. Soc. Rev. 50, 562. https://doi.org/10.1039/d0cs00920b (2021).
Al-Kuhaili, M. F. Optical properties of hafnium oxide thin films and their application in energy-efficient windows. Opt. Mater. (Amst). 27, 383–387 (2004).
Cotton, S. A. Chemistry of Precious Metals (Springer Science & Business Media, 2012).
Zeng, B. et al. Cooperative photocatalysis of hafnium-based metal–organic framework and TEMPO for selective oxidation of sulfides. Chem. Eng. J. 474, 963 (2023).
Davidovich, R. L., Marinin, D. V., Stavila, V. & Whitmire, K. H. Stereochemistry of fluoride and mixed-ligand fluoride complexes of zirconium and hafnium. Coord. Chem. Rev. 257, 3074–3088 (2013).
Ma, Y. & Zhang, X. Structure tuning of hafnium metal–organic frameworks through a mixed solvent approach. Crystals (Basel) 12, 785 (2022).
Ihlefeld, J. F. et al. Compositional dependence of linear and nonlinear optical response in crystalline hafnium zirconium oxide thin films. J Appl. Phys. 128, 145 (2020).
Fraústo, D. & Silva, J. J. R. The chelate effect redefined. J. Chem. Educ. 60, 390–392 (1983).
Miessler, G. L., Fischer, P. J. & Tarr, D. A. The crystalline solid state. Inorg. Chem. 4, 220–229 (2013).
Stability of Metal Complexes and Chelation. - Chemistry LibreTexts. https://chem.libretexts.org/Bookshelves/Inorganic_Chemistry/Supplemental_Modules_and_Websites_(Inorganic_Chemistry)/Coordination_Chemistry/Complex_Ion_Equilibria/Stability_of_Metal_Complexes_and_Chelation (2023).
Lin, C. Y. et al. Integration of freestanding hafnium zirconium oxide membranes into two-dimensional transistors as a high-κ ferroelectric dielectric. Nat. Electron. https://doi.org/10.1038/s41928-025-01398-y (2025).
Wang, H. et al. High-performance opto-electronics with emerging materials (2022).
Panda, P. & Chakroborty, S. Optical sensor technology and its application in detecting environmental effluents: a review. Int. J. Environ. Anal. Chem. https://doi.org/10.1080/03067319.2022.2098480 (2024).
Sun, Y., Le, X., Zhou, S. & Chen, T. Recent progress in smart polymeric gel-based information storage for anti-counterfeiting. Adv. Mater. 34, 2201262 (2022).
Weiner, J. & Ho, P. -Tong. Light-matter interaction. Fundam. Appl. (2003).
Jiang, X. et al. Iron photocatalysis via Brønsted acid-unlocked ligand-to-metal charge transfer. Nat. Commun. 15, 6115 (2024).
Mayo, D. W., Pike, R. M. & Forbes, D. C. Microscale Organic Laboratory : with Multistep and Multiscale Syntheses 622 (Wiley, 2015).
Ratnani, S. Experimental Organic Chemistry (Oxford, 2012).
Frisch, M. J. et al. Gaussian 16. Preprint at (2016).
Humphrey, W., Dalke, A. & Schulten, K. VMD: visual molecular dynamics. J. Mol. Graph. 14, 33–38 (1996).
Motallebi Aghkonbad, E. & Jafari, A. Iron nanoparticles supported on graphene nanosheets by pulsed laser ablation method in deionized water. Phys. Scr. 99, 095406 (2024).
Ungeheuer, K., Marszalek, K. W., Mitura-Nowak, M. & Rydosz, A. Spectroscopic ellipsometry modelling of Cr + implanted copper oxide thin films. Sci. Rep. 13, 22116 (2023).
Liu, J., Zhang, D., Yu, D., Ren, M. & Xu, J. Machine learning powered ellipsometry. Light Sci. Appl. 10, 55 (2021).
Aghgonbad, M. M. & Sedghi, H. Spectroscopic-ellipsometry measurement of the optical properties of zinc oxide thin films prepared by sol–gel method: coating speed effect. Micro Nano Lett. 13, 959–964 (2018).
Tompkins, H. G. & Hilfiker, J. N. Spectroscopic Ellipsometry : Practical Application to Thin Film Characterization 159 (Momentum Press, 2016).
May, A. M. & Dempsey, J. L. A new era of LMCT: leveraging ligand-to-metal charge transfer excited States for photochemical reactions. Chem. Sci. 15, 6661–6678 (2024).
Fox, M. Optical Properties of Solids (Oxford University Press, 2010).
Fujiwara, H. Spectroscopic Ellipsometry: Principles and Applications (Wiley, 2007).
Peter, Y. U. & Cardona, M. Fundamentals of Semiconductors: Physics and Materials Properties (Springer Science & Business Media, 2010).
Maier, S. A. Plasmonics: Fundamentals and Applications (Springer, 2007).
Stryland, E. W., Van, Said, A. A. & Sheik-Bahae, M. High-sensitivity, single-beam n2 measurements. Opt. Lett. 14, 955–957 (1989).
Sheik-Bahae, M., Said, A. A., Wei, T. H., Hagan, D. J. & Van Stryland, E. W. Sensitive measurement of optical nonlinearities using a single beam. IEEE J. Quantum Electron. 26, 760–769 (1990).
Zhang, Q., Wu, X. & Han, J. The influence of laser-induced alignment on Z-scan properties of 2D carbon nanomaterials suspension dependent on polarization. Sci. Rep. 12, 10127 (2022).
Tahmasbi, A., Jafari, A. & Nikoo, A. Synthesis, characterization, and nonlinear optical properties of copper (II) ligand schiff base complexes derived from 3-Nitrobenzohydrazide and benzyl. Sci. Rep. 13, 10988 (2023).
Melnik, M., Vorontsova, I., Putilin, S., Tcypkin, A. & Kozlov, S. Methodical inaccuracy of the Z-scan method for few-cycle Terahertz pulses. Sci. Rep. 9, 9146 (2019).
Jafari, A., Zeynizadeh, B. & Darvishi, S. Study of linear and nonlinear optical properties of nickel immobilized on acid-activated montmorillonite and copper ferrite nanocomposites. J. Mol. Liq. 253, 119–126 (2018).
Ganeev, R. A. et al. Nonlinear refraction in CS2. Appl. Phys. B 78, 433–438 (2004).
Sutherland, R. L. Handbook of Nonlinear Optics (CRC, 2003).
Eccleston, J. F., Martin, S. R. & Schilstra, M. J. Rapid kinetic techniques. Methods Cell. Biol. 84, 445–477 (2008).
Majles Ara, M. H. & Dehghani, Z. Measurement of nonlinear responses and optical limiting behavior of TIO 2 / PS nano-composite by single beam technique with different incident intensities. Int. J. Mod. Phys. Conf. Ser. 05, 277–283 (2012).
French, R. H. Electronic band structure of AI,O3, with comparison to alon and AIN. J Am. Ceram. SOC (1990).
Stegeman, G. I., Wright, E. M., Finlayson, N., Zanoni, R. & Seaton, C. T. Third order nonlinear integrated optics. J. Lightwave Technol. 6, 953–970 (1988).
Li, G. et al. Study on the third-order nonlinear optical properties of four Dmit complexes by Z-scan technique. Appl. Phys. A-materials Sci. Process. 104, 1099–1103 (2011).
Stegeman, G. I. & Wright, E. M. All-optical waveguide switching. Opt. Quantum Electron. 22, 95–122 (1990).
Alqahtani, B., Li, H., Syed, A. M. & El-Atab, N. From light sensing to adaptive learning: hafnium diselenide reconfigurable memcapacitive devices in neuromorphic computing. Light Sci. Appl. 14, 30 (2025).
Aliqab, K., Sorathiya, V., Alsharari, M., Dave, K. & Armghan, A. Numerical analysis of hafnium oxide and phase change material-based multi-layered infrared and visible frequency sensor for biomolecules sensing application. Sci. Rep. 13, 7698 (2023).
Wang, X. et al. Bio-inspired optoelectronic devices and systems for energy-efficient in-sensor computing. Npj Unconv. Comput. 2, 15 (2025).
Zhang, W. et al. Ultrahigh dielectric permittivity in Hf0.5Zr0.5O2 thin-film capacitors. Nat. Commun. 16, 2679 (2025).
Acknowledgements
The authors gratefully appreciated the financial support of this work by the Research Council of Urmia University.
Funding
This research did not receive any specific grant from funding agencies in the public, commercial, or not-for-profit sectors.
Author information
Authors and Affiliations
Contributions
All authors contributed equally to this manuscript. They contributed to writing the original draft and discussed the results and wrote the final version of the manuscript along with review & editing.Ali Azadegan, Akbar Jafari, Abbas Nikoo, Maryam Motallebi Aghgonbad.
Corresponding author
Ethics declarations
Competing interests
The authors declare no competing interests.
Additional information
Publisher’s note
Springer Nature remains neutral with regard to jurisdictional claims in published maps and institutional affiliations.
Rights and permissions
Open Access This article is licensed under a Creative Commons Attribution-NonCommercial-NoDerivatives 4.0 International License, which permits any non-commercial use, sharing, distribution and reproduction in any medium or format, as long as you give appropriate credit to the original author(s) and the source, provide a link to the Creative Commons licence, and indicate if you modified the licensed material. You do not have permission under this licence to share adapted material derived from this article or parts of it. The images or other third party material in this article are included in the article’s Creative Commons licence, unless indicated otherwise in a credit line to the material. If material is not included in the article’s Creative Commons licence and your intended use is not permitted by statutory regulation or exceeds the permitted use, you will need to obtain permission directly from the copyright holder. To view a copy of this licence, visit http://creativecommons.org/licenses/by-nc-nd/4.0/.
About this article
Cite this article
Azadegan, A., Jafari, A., Nikoo, A. et al. Synthesis and investigation of linear and nonlinear optical parameters of hafnium nitrosalicylate complex. Sci Rep (2026). https://doi.org/10.1038/s41598-026-35221-1
Received:
Accepted:
Published:
DOI: https://doi.org/10.1038/s41598-026-35221-1