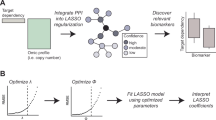
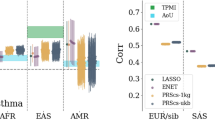
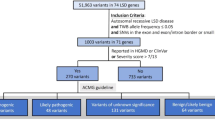
Abstract
Accurate identification of significant features in high-dimensional data is indispensable in high-throughput genomic analysis and association studies. Least Absolute Shrinkage and Selection Operator (LASSO) and its derivatives have been widely adapted to discover potential biomarkers as a feature selection scheme in various biological systems. Recently, bootstrap-based LASSO models, such as Random LASSO and Hi-LASSO, have been effective solutions for extremely high-dimensional but low sample size (EHDLSS) genomic data. However, the bootstrap-based LASSO models still have several drawbacks, such as multicollinearity within bootstrap samples, missing predictors in draw, and randomness in predictor sampling. To tackle the limitations, we propose a new bootstrap-based LASSO, named Stochastic LASSO, that effectively reduces multicollinearity in bootstrap samples and mitigates randomness in predictor sampling, resulting in remarkably outperforming benchmarks in feature selection and coefficient estimation. Furthermore, Stochastic LASSO provides a two-stage t-test strategy for selecting statistically significant features. The performance of Stochastic LASSO was assessed by comparing the existing benchmark models in extensive simulation experiments. In the simulation experiments, Stochastic LASSO consistently showed significant improvements in performance compared to the state-of-the-art LASSO models for feature selection, coefficient estimation, and robustness. We also applied Stochastic LASSO for the gene expression data of publicly available TCGA cancer datasets and identified statistically significant genes associated with survival month prediction. The source code is publicly available at: https://github.com/datax-lab/StochasticLASSO.
Similar content being viewed by others
Data availability
The datasets analyzed during the current study are all publicly available online from The Cancer Genome Atlas (TCGA). The open-source is available at: https://github.com/datax-lab/StochasticLASSO.
References
Wu, T. T., Chen, Y. F., Hastie, T., Sobel, E. & Lange, K. Genome-wide association analysis by lasso penalized logistic regression. Bioinformatics 25(6), 714–721 (2009).
Xu, C., Fang, J., Shen, H., Wang, Y. P. & Deng, H. W. EPS-LASSO: Test for high-dimensional regression under extreme phenotype sampling of continuous traits. Bioinformatics 34(12), 1996–2003 (2018).
Geeven, G., van Kesteren, R. E., Smit, A. B. & de Gunst, M. C. M. Identification of context-specific gene regulatory networks with GEMULA-gene expression modeling using LAsso. Bioinformatics 28(2), 214–221 (2012).
Tibshirani, R. Regression Shrinkage and Selection Via the Lasso. J. R. Stat. Soc., B: Stat. Methodol. 58(1), 267–288 (1996).
Wang, W. & Liu, W. Integration of gene interaction information into a reweighted Lasso-Cox model for accurate survival prediction. Bioinformatics 36(22–23), 5405–5414 (2020).
Fu, G. H., Yi, L. Z. & Pan, J. LASSO-based false-positive selection for class-imbalanced data in metabolomics. J. Chemom. 33(10), e3177 (2019).
Yu, B. et al. Prediction of protein-protein interactions based on elastic net and deep forest. Expert Syst. Appl. 176, 114876 (2021).
Sohn, I., Kim, J., Jung, S. H. & Park, C. Gradient lasso for Cox proportional hazards model. Bioinformatics 25(14), 1775–1781 (2009).
Zou, H. The adaptive lasso and its oracle properties. J. Am. Stat. Assoc. 101(476), 1418–1429 (2006).
Meinshausen, N. Relaxed Lasso. Comput. Stat. Data Anal. 52(1), 374–393 (2007).
Wang, H., Lengerich, B. J., Aragam, B. & Xing, E. P. Precision Lasso: Accounting for correlations and linear dependencies in high-dimensional genomic data. Bioinformatics 35(7), 1181–1187 (2019).
Zou, H. & Hastie, T. Regularization and variable selection via the elastic net. J. R. Stat. Soc., B: Stat. Methodol. 67(2), 301–320 (2005).
Wang, S., Nan, B., Rosset, S. & Zhu, J Random lasso. Ann. Appl. Stat. 5(1), 468–485, (2011).
Park, H., Imoto, S. & Miyano, S. Recursive random lasso (RRLasso) for identifying anti-cancer drug targets. PLoS ONE 10(11), e0141869 (2015).
Kim, Y., Hao, J., Mallavarapu, T., Park, J. & Kang, M. Hi-LASSO: High-Dimensional LASSO. IEEE Access 7, 44562–44573 (2019).
Fan, J. & Li, R. Variable selection via nonconcave penalized likelihood and its oracle properties. J. Am. Stat. Assoc. 96(456), 1348–1360 (2001).
Lustgarten, J. L., Gopalakrishnan, V. & Visweswaran, S. Measuring stability of feature selection in biomedical datasets. AMIA Annu. Symp. proc. 406–410, 2009 (2009).
Das, N. D. et al. Defining super-enhancers by highly ranked histone H4 multi-acetylation levels identifies transcription factors associated with glioblastoma stem-like properties. BMC Genomics 24(1), 574 (2023).
Zupančič, M. et al. Concerted transcriptional regulation of the morphogenesis of hypothalamic neurons by ONECUT3. Nat. Commun. 15(1), 8631 (2024).
Lee, M. An ensemble deep learning model with a gene attention mechanism for estimating the prognosis of low-grade glioma. Biology (Basel) 11(4), 586 (2022).
Wang, Y. et al. Identification of a five-pseudogene signature for predicting survival and its ceRNA network in glioma. Front. Oncol. 9, 1059 (2019).
Liu, B. et al. A prognostic signature of five pseudogenes for predicting lower-grade gliomas. Biomed. Pharmacother. 117, 109116 (2019).
Akiyoshi, K. et al. Expression of mRNAs of Urocortin in the STKM-1 gastric cancer cell line. Anticancer Res. 33(12), 5289–5294 (2013).
Kamada, M. et al. Expression of mRNAs of urocortin and corticotropin-releasing factor receptors in malignant glioma cell lines. Anticancer Res. 32(12), 5299–5307 (2012).
Yan, B. et al. Artificial intelligence-based radiogenomics reveals the potential immunoregulatory role of COL22A1 in glioma and its induced autoimmune encephalitis. Front. Immunol. 16, 1562070 (2025).
Liu, H., Zeng, Z. & Sun, P. Prognosis and immunoinfiltration analysis of angiogene-related genes in grade 4 diffuse gliomas. Aging (Albany NY) 15(18), 9842–9857 (2023).
Barbosa, L. C., Machado, G. C., Heringer, M. & Ferrer, V. P. Identification of established and novel extracellular matrix components in glioblastoma as targets for angiogenesis and prognosis. Neurogenetics 25(3), 249–262 (2024).
Gu, S., Wang, Y., Lei, D. & Zhao, H. Analysis and construction of ceRNA networks reveal 4 mRNAs as potential biomarkers of temozolomide-resistant glioblastomas. Research Square (preprint) (2021).
Li, Y. et al. Distinct genomic aberrations between low-grade and high-grade gliomas of Chinese patients. PLoS One 8(2), e57168 (2013).
Kanehisa, M. & Goto, S. KEGG: Kyoto Encyclopedia of Genes and Genomes. Nucleic Acids Res. 28(1), 27–30 (2000).
Xu, H. et al. Comprehensive molecular characterization of long-term glioblastoma survivors. Cancer Lett. 593, 216938 (2024).
Hauffe, L. et al. Eukaryotic translation initiation factor 4E binding protein 1 (EIF4EBP1) expression in glioblastoma is driven by ETS1- and MYBL2-dependent transcriptional activation. Cell Death Discov. 8(1), 91 (2022).
Yi, G. Z. et al. Identification of key candidate proteins and pathways associated with temozolomide resistance in glioblastoma based on subcellular proteomics and bioinformatical analysiss. BioMed Res. Int. 2018, 5238760 (2018).
Qi, T. et al. Glioma-associated oncogene homolog 1 in breast invasive carcinoma: a comprehensive bioinformatic analysis and experimental validation. Front. Cell Dev. Biol. 12, 1478478 (2024).
Sun, Z., Qi, X. & Zhang, Y. Bioinformatics Analysis of the Expression of ATP Binding Cassette Subfamily C Member 3 (ABCC3) in Human Glioma. Open Med. (Warsaw) 15, 107–113 (2020).
Hermawan, A. & Putri, H. Systematic analysis of potential targets of the curcumin analog pentagamavunon-1 (PGV-1) in overcoming resistance of glioblastoma cells to bevacizumab. Saudi Pharm. J. 29(11), 1289–1302 (2021).
Swiatek-Machado, K. & Kaminska, B. STAT Signaling in Glioma Cells. In Glioma Signaling (ed. Barańska, J.) 203–222 (Springer International Publishing, Cham, 2020).
Funding
This work was supported by the National Science Foundation Major Research Instrumentation (NSF MRI) (Grant#:2117941), the National Research Foundation of Korea (NRF) (NRF-2021R1I1A3048029), and the MSIT (Ministry of Science and ICT) under the ICAN (ICT Challenge and Advanced Network of HRD) support program (IITP-2024-RS-2022-00156409) supervised by the IITP (Institute for Information & Communications Technology Planning & Evaluation) in South Korea.
Author information
Authors and Affiliations
Contributions
B.B.: Methodology, Software, Validation, Investigation, Writing - Original Draft, Writing - Review & Editing, Visualization; J.J: Methodology, Investigation; M.K.: Conceptualization, Methodology, Validation, Resources, Writing - Original Draft, Writing - Review & Editing, Supervision, Project administration, Funding acquisition; Y.K.: Conceptualization, Methodology, Validation, Resources, Writing - Original Draft, Writing - Review & Editing, Supervision, Funding acquisition
Corresponding authors
Ethics declarations
Competing interests
The authors declare no competing interests.
Additional information
Publisher’s note
Springer Nature remains neutral with regard to jurisdictional claims in published maps and institutional affiliations.
Supplementary Information
Rights and permissions
Open Access This article is licensed under a Creative Commons Attribution-NonCommercial-NoDerivatives 4.0 International License, which permits any non-commercial use, sharing, distribution and reproduction in any medium or format, as long as you give appropriate credit to the original author(s) and the source, provide a link to the Creative Commons licence, and indicate if you modified the licensed material. You do not have permission under this licence to share adapted material derived from this article or parts of it. The images or other third party material in this article are included in the article’s Creative Commons licence, unless indicated otherwise in a credit line to the material. If material is not included in the article’s Creative Commons licence and your intended use is not permitted by statutory regulation or exceeds the permitted use, you will need to obtain permission directly from the copyright holder. To view a copy of this licence, visit http://creativecommons.org/licenses/by-nc-nd/4.0/.
About this article
Cite this article
Baek, B., Jo, J., Kang, M. et al. Stochastic LASSO for extremely high-dimensional genomic data. Sci Rep (2026). https://doi.org/10.1038/s41598-026-35273-3
Received:
Accepted:
Published:
DOI: https://doi.org/10.1038/s41598-026-35273-3