Abstract
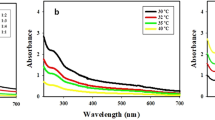
This study reports the eco-friendly synthesis of selenium nanoparticles (SeNPs) using the methanolic extract of Balanites aegyptiaca mesocarp and evaluates their biological activities. The synthesized spherical SeNPs (average size: 2.82 nm) were characterized by TEM, FESEM, and UV–Vis spectroscopy, confirming that phenolic compounds serve as both reducing and stabilizing agents. HPLC analysis revealed eight major phenolics, with gallic acid, chlorogenic acid, and daidzein being the predominant compounds. The SeNPs exhibited strong cytotoxicity against HCT-116 colorectal cancer cells (IC₅₀ = 30.03 µg/mL), potent antibacterial activity against Klebsiella pneumoniae, Escherichia coli, and Enterococcus faecalis, and induced concentration-dependent cytogenetic effects in Vicia faba root tips. Molecular docking studies suggested that phenolic compounds effectively interact with the CDK4 active site, supporting their potential anticancer properties. These findings highlight B. aegyptiaca-derived SeNPs as promising candidates for biomedical applications.
Similar content being viewed by others
Data availability
All data supporting the findings of this study are available within the paper and its Supplementary Information.
References
Amani, M. D. et al. Eco-friendly synthesis of zinc oxide nanoparticles by garcinia cambogia and evaluation of their obesity and antimicrobial activities. Egypt. J. Chem. 67 (2), 17–27 (2024).
Sahar, A. M. et al. Bioactive compounds from leaves and Bolls extracts of Gossypium Barbadense L. And assessment of their antioxidants & cytotoxic activities. Egypt. J. Chem. 66 (13), 1117–1124 (2023).
Kieliszek, M. & Błażejak, S. Current knowledge on the importance of selenium in food for living organisms: a review. Molecules 21 (5), 609 (2016).
Misra, S., Boylan, M., Selvam, A., Spallholz, J. E. & Björnstedt, M. Redox-active selenium compounds—From toxicity and cell death to cancer treatment. Nutrients 7 (5), 3536–3556 (2015).
mani, M. D. et al. Green biosynthesized selenium nanoparticles and bioactive compounds by Gossypium Barbadense L. Extract and their cytotoxic potential. Egypt. J. Chem. 66 (8), 439–448 (2023).
Ren, F., He, X., Wang, K. & Yin, J. Biosynthesis of gold nanoparticles using Catclaw buttercup (Radix ranunculi Ternati) and evaluation of its colloidal stability. J. Biomed. Nanotechnol. 8 (4), 586–593 (2012).
Boroumand, S., Safari, M., Shaabani, E., Shirzad, M. & Faridi-Majidi, R. Selenium nanoparticles: synthesis, characterization and study of their cytotoxicity, antioxidant and antibacterial activity. Mater. Res. Express. 6 (8), 0850d8 (2019).
Sharma, G. et al. Biomolecule-mediated synthesis of selenium nanoparticles using dried vitis vinifera (raisin) extract. Molecules 19 (3), 2761–2770 (2014).
Vyas, J., Rana, S. H. & A. F. K. A., T. Antioxidant activity and biogenic synthesis of selenium nanoparticles using the leaf extract of Aloe Vera. Int. J. Curr. Pharm. Res. 9, 147–152 (2017).
Vyas, J. & Rana, S. Antioxidant activity and green synthesis of selenium nanoparticles using allium sativum extract. Int. J. Phytomedicine. 9 (4), 634–641 (2017).
Anu, K. et al. Biogenesis of selenium nanoparticles and their anti-leukemia activity. J. King Saud University-Science. 32 (4), 2520–2526 (2020).
Deepa, B. & Ganesan, V. Biogenic synthesis and characterization of selenium nanoparticles using the flower of Bougainvillea spectabilis willd. IJSR 4, 690–695 (2015).
Zeebaree, S. Y. S., Zeebaree, A. Y. S. & Zebari, O. I. H. Diagnosis of the multiple effect of selenium nanoparticles decorated by asteriscus graveolens components in inhibiting HepG2 cell proliferation. Sustainable Chem. Pharm. 15, 100210 (2020).
Santanu, S., Sowmiya, R. & Balakrishnaraja, R. Biosynthesis of selenium nanoparticles using citrus reticulata Peel extract. World J. Pharm. Res. 4 (1), 1322–1330 (2015).
Gunti, L., Dass, R. S. & Kalagatur, N. K. Phyto fabrication of selenium nanoparticles from emblica officinalis fruit extract and exploring its biopotential applications: antioxidant, antimicrobial, and biocompatibility. Front. Microbiol. 10, 931 (2019).
Tripathi, R. M. et al. Biosynthesis of highly stable fluorescent selenium nanoparticles and the evaluation of their photocatalytic degradation of dye. BioNanoScience 10 (2), 389–396 (2020).
Alam, H., Khatoon, N., Raza, M., Ghosh, P. C. & Sardar, M. Synthesis and characterization of nano selenium using plant biomolecules and their potential applications. BioNanoScience 9 (1), 96–104 (2019).
Cui, D. et al. Green synthesis of selenium nanoparticles with extract of Hawthorn fruit induced HepG2 cells apoptosis. Pharm. Biol. 56 (1), 528–534 (2018).
Almutairi, H. H. et al. Metabolomic characterization of fresh and dried Korean red ginseng (panax ginseng) based on gc-ms analysis, alongside an exploration of the antioxidant and anticancer properties of their methanolic extract. Bull. Chem. Soc. Ethiop. 39 (10), 2039–2053 (2025).
Alagesan, V. & Venugopal, S. Green synthesis of selenium nanoparticle using leaves extract of Withania somnifera and its biological applications and photocatalytic activities. Bionanoscience 9 (1), 105–116 (2019).
Shehta, W. et al. The novel synthesis of a condensed triazine via the heterocyclization of an Azo derivative and its characterization, radiolabeling and bio-evaluation. RSC Adv. 15 (47), 39988–40005 (2025).
Sivakumar, C. & Jeganathan, K. In-vitro cytotoxicity of Java tea mediated selenium nanoballs against L6 cell lines. J. Drug Delivery Ther. 8 (6), 195–200 (2018).
Kirupagaran, R., Saritha, A. & Bhuvaneswari, S. Green synthesis of selenium nanoparticles from leaf and stem extract of leucas Lavandulifolia Sm. and their application. J. Nanosci. Technol. 2(5), 224–226 (2016).
Fardsadegh, B. & Jafarizadeh-Malmiri, H. Aloe Vera leaf extract mediated green synthesis of selenium nanoparticles and assessment of their in vitro antimicrobial activity against spoilage fungi and pathogenic bacteria strains. Green. Process. Synthesis. 8 (1), 399–407 (2019).
Anu, K., Singaravelu, G., Murugan, K. & Benelli, G. Green-synthesis of selenium nanoparticles using Garlic cloves (Allium sativum): biophysical characterization and cytotoxicity on Vero cells. J. Cluster Sci. 28 (1), 551–563 (2017).
Sowndarya, P., Ramkumar, G. & Shivakumar, M. S. Green synthesis of selenium nanoparticles conjugated Clausena dentata plant leaf extract and their insecticidal potential against mosquito vectors. Artif. Cells Nanomed. Biotechnol. 45 (8), 1490–1495 (2017).
Fadlallah, H. et al. Colorectal cancer: recent advances in management and treatment. World J. Clin. Oncol. 15 (9), 1136 (2024).
Sun, R. et al. Augmentation of the benzyl Isothiocyanate-Induced antiproliferation by NBDHEX in the HCT-116 human colorectal cancer cell line. Int. J. Mol. Sci. 26 (17), 8145 (2025).
Saltoğlu, G. T., Yalcin, S., Coşkun, B. F. & Arslan, H. S. Evaluating the cytotoxic and metastatic actions of cannabinol on HCT-116 colon cancer cells. Osmangazi Tıp Dergisi. 47 (4), 593–599 (2025).
Ikram, M., Javed, B., Raja, N. I. & Mashwani, Z. U. R. Biomedical potential of plant-based selenium nanoparticles: a comprehensive review on therapeutic and mechanistic aspects. Int. J. Nanomed. 16, 249–268 (2021).
Nagime, P. V. et al. Biogenic selenium nanoparticles: a comprehensive update on the multifaceted application, stability, biocompatibility, risk, and opportunity. Zeitschrift für Naturforschung C, (0). (2025).
Mohamed, A. A. et al. A combined therapy of meropenem–ZnO nanoparticles efficiently eliminates carbapenem-resistant Klebsiella pneumoniae biofilms, with reduced nephrotoxicity(in vitro). Lett. Appl. Microbiol. 77 (12), ovae136 (2024).
Shawky, M., Kalaba, M. H. & El-Sherbiny, G. M. Combined impact of biosynthesized selenium nanoparticles and Imipenem against carbapenem-resistant Pseudomonas aeruginosa and their associated virulence factors. BMC Microbiol. 25 (1), 235 (2025).
USEPA. Nanotechnology White Paper (Science Policy Council, USEPA, 2007).
Mehrian, S. K. & Lima, D. R. Nanoparticles cyto and genotoxicity in plants: mechanisms and abnormalities. Environ. Nanotech Monit. Manag. 6, 184–193 (2016).
Pakrashi, S. et al. In vivo genotoxicity assessment of titanium dioxide nanoparticles by allium Cepa root tip assay at high exposure concentrations. PLoS ONE. 9, e87789 (2014).
Patel, S., Patel, P. & Bakshi, S. R. Titanium dioxide nanoparticles:an in vitro study of DNA binding, chromosome aberrationassay, and comet assay. Cytotechnology 69, 245–263 (2017).
George, N. M., Abdelhaliem, E. & Abdel-Haleem, M. Phytochemical profiling of bioactive metabolites in methanolic extract of two wild solanum species and evaluation of their antioxidant activity. JAPS: J. Anim. Plant. Sci. 32(6), 1713–1723 (2022).
Abdelsalam, N. R. et al. Genotoxicity effects of silver nanoparticles on wheat (Triticum aestivum L.) root tip cells. Ecotox Environ. Safe. 155, 76–85 (2009).
Cox, A., Venkatachalam, P., Sahi, S. & Sharma, N. Silver and titanium dioxide nanoparticle toxicity in plants: a review of current research. Plant. Physiol. Biochem. 107, 147–163 (2016).
Abdelsattar, A. S., Dawoud, A. & Helal, M. A. Interaction of nanoparticles with biological macromolecules: A review of molecular Docking studies. Nanotoxicology 15 (1), 66–95 (2021).
Ibrahim, G. S., Marzouk, M. S., Elmansy, E. A. & Gomaa, M. Exploring the Antiviral, antioxidant Potentials, and UPLC-MS/MS characterization of Stenotrophomonas maltophilia GMM methanolic extract. Egypt. J. Chem. 68 (4), 549–559 (2025).
Ibrahim, S. S. S. et al. Recent progress in the green synthesis, characterization, and applications of selenium nanoparticles. BIO Integr. 5 (1), 969 (2024).
Elmesallamy, A., El-Zaidy, M., Younes, M. & Hussein, S. A. A. Green biosynthesized selenium nanoparticles and bioactive compounds by Gossypium Barbadense L extract and their cytotoxic potential. Egyptian J. Chemistry, 66(8), 439–448 ; https://doi.org/10.21608/ejchem.2022.171646.7132(2023).
El-mesallamy, A. M. A. N. I., Alahwany, A. K., El-Zaidy, M. I. & Hussein, S. A. A. Eco-friendly synthesis of zinc oxide nanoparticles by garcinia cambogia and evaluation of their obesity and antimicrobial activities. Egypt. J. Chem. 67 (2), 17–27. https://doi.org/10.21608/ejchem.2023.212794.8008 (2024).
George, N. M., Abdelhaliem, E. & Abdel-Haleem, M. GC-MS identification of bioactive compounds in unripe solanum nigrum berries and assessment of antioxidant and anticancer activities. Lat Am. J. Pharm. 40 (11), 2702–2708 (2021).
Luo, L., Wang, Q. & Liao, Y. The inhibitors of CDK4/6 from a library of marine compound database: a pharmacophore, ADMET, molecular Docking and molecular dynamics study. Mar. Drugs. 20 (5), 319. https://doi.org/10.3390/md20050319 (2022).
Rondla, R. et al. Selective ATP competitive leads of CDK4: discovery by 3D-QSAR pharmacophore mapping and molecular Docking approach. Comput. Biol. Chem. 71, 224–229. https://doi.org/10.1016/j.compbiolchem.2017.11.005 (2017).
Srivastava, V., Devi, U., Nackwal, K., Ahmed, M. Z. & Shukla, P. K. In Silico identification of novel CDK4 inhibitors for retinoblastoma. Chem. Phys. Impact. 9, 100743. https://doi.org/10.1016/j.chphi.2024.100743 (2024).
Silva, G. H. & Monteiro, R. T. Toxicity assessment of silica nanoparticles on allium Cepa. Ecotox Environ. Contam. 12, 25–31 (2017).
Bartosiak, M., Giersz, J. & Jankowski, K. Analytical monitoring of selenium nanoparticles green synthesis using photochemical vapor generation coupled with MIP-OES and UV–Vis spectrophotometry. Microchem. J. 145, 1169–1175 (2019).
Ingole, A. R., Thakare, S. R., Khati, N. T., Wankhade, A. V. & Burghate, D. K. Green synthesis of selenium nanoparticles under ambient condition. Chalcogenide Lett. 7 (7), 485–489 (2010).
Satgurunathan, T., Bhavan, P. S. & Komathi, S. Green synthesis of selenium nanoparticles from sodium selenite using Garlic extract and its enrichment on artemia nauplii to feed the freshwater Prawn macrobrachium Rosenbergii post-larvae. Res. J. Chem. Environ. 21 (10), 1–12 (2017).
Elmesallamy, A., El-Zaidy, M., Younes, M. & Hussein, S. A. A. Green biosynthesized selenium nanoparticles and bioactive compounds by Gossypium Barbadense L extract and their cytotoxic potential. Egypt. J. Chem. 66 (8), 439–448 (2023).
Yang, N. & Li, W. H. Mango Peel extract mediated novel route for synthesis of silver nanoparticles and antibacterial application of silver nanoparticles loaded onto non-woven fabrics. Ind. Crops Prod. 48, 81–88 (2013).
Elmosallamy, A., El-zaidy, M. & Hussein, S. A. A. Green synthesis of silver nanoparticles using mangifera indica L.(Musk) peels extract and evaluation of its cytotoxic activities. Egypt. J. Chem. 65 (7), 1–6 (2022).
Mulvaney, P. Surface plasmon spectroscopy of nanosized metal particles. Langmuir 12 (3), 788–800 (1996).
Lin, Z. H. & Wang, C. C. Evidence on the size-dependent absorption spectral evolution of selenium nanoparticles. Mater. Chem. Phys. 92 (2–3), 591–594 (2005).
Hernández-Díaz, J. A. et al. Antibacterial activity of biosynthesized selenium nanoparticles using extracts of calendula officinalis against potentially clinical bacterial strains. Molecules 26 (19), 5929 (2021).
Fardsadegh, B., Vaghari, H., Mohammad-Jafari, R., Najian, Y. & Jafarizadeh-Malmiri, H. Biosynthesis, characterization and antimicrobial activities assessment of fabricated selenium nanoparticles using pelargonium Zonale leaf extract. Green. Process. Synthesis. 8 (1), 191–198 (2019).
Deepa, B. & Ganesan, V. Bioinspiredsynthesis of selenium nanoparticles using flowers of catharanthus roseus (L.) G. Don. And peltophorum pterocarpum (DC.) backer ex Heyne–a comparison. Int. J. Chem. Technol. Res. 7, 725–733 (2015).
Prasad, K. S. & Selvaraj, K. Biogenic synthesis of selenium nanoparticles and their effect on as (III)-induced toxicity on human lymphocytes. Biol. Trace Elem. Res. 157 (3), 275–283 (2014).
Yedurkar, S., Maurya, C. & Mahanwar, P. Biosynthesis of zinc oxide nanoparticles using Ixora coccinea leaf extract—a green approach. Open. J. Synthesis Theory Appl. 5 (1), 1–14 (2016).
Surinut, P., Kaewsutthi, S. & Surakarnkul, R. Radical scavenging activity in fruit extracts. In III WOCMAP Congress on Medicinal and Aromatic Plants-Volume 5: Quality, Efficacy, Safety, Processing and Trade in Medicinal 679 (pp. 201–203); (2003)., February https://doi.org/10.17660/ActaHortic.2005.679.25
Kokila, K., Elavarasan, N. & Sujatha, V. Diospyros Montana leaf extract-mediated synthesis of selenium nanoparticles and their biological applications. New J. Chem. 41 (15), 7481–7490 (2017).
Puri, A. et al. Plant-derived selenium nanoparticles: investigating unique morphologies, enhancing therapeutic uses, and leading the way in tailored medical treatments. Mater. Adv. 5 (9), 3602–3628 (2024).
El-Telbany, M. et al. Combination of meropenem and zinc oxide nanoparticles; antimicrobial synergism, exaggerated antibiofilm activity, and efficient therapeutic strategy against bacterial keratitis. Antibiotics 11 (10), 1374 (2022).
Chhabria, S. & Desai, K. Selenium nanoparticles and their applications. Encyclopedia Nanosci. Nanatechnol. 20, 1–32 (2016).
Nayak, V., Singh, K. R., Singh, A. K. & Singh, R. P. Potentialities of selenium nanoparticles in biomedical science. New J. Chem. 45 (6), 2849–2878 (2021).
Menon, S. & Shanmugam, V. K. Chemopreventive mechanism of action by oxidative stress and toxicity induced surface decorated selenium nanoparticles. J. Trace Elem. Med Biol. 62, 126549 (2020).
Sakr, T. M., Korany, M. & Katti, K. V. Selenium nanomaterials in biomedicine—An overview of new opportunities in nanomedicine of selenium. J. Drug Deliv. Sci. Technol. 46, 223–233 (2018).
Hu, N. et al. Uniform and disperse selenium nanoparticles stabilized by inulin Fructans from Codonopsis pilosula and their anti-hepatoma activities. Int. J. Biol. Macromol. 203, 105–115 (2022).
EL-Baghdady, K. Z., Khalil, M. M., El Borhamy, M. I. & Meligi, G. Biosynthesis, characterization and cytotoxicity of selenium nanoparticles using Bacillus tropicus Ism 2. Egypt. Acad. J. Biol. Sci. G Microbiol. 11 (1), 47–57 (2019).
Li, H. et al. Arabinogalactan from Ixeris chinensis (Thunb.) Nakai as a stabilizer to decorate senps and enhance their anti-hepatocellular carcinoma activity via the mitochondrial pathway. J. Carbohydr. Chem. 41 (5), 329–345 (2022).
Mohamed, A. A., Seyam, E. A., Hussein, S. A. & Abdel-Haleem, M. Quercetin-mediated Repression of adrA Gene Expression in Escherichia Coli: Dual Roles in Antibiofilm Activity and Oxidative Stress Regulation 1–11 (Biologia, 2025).
Soliman, M. K. & Salem, S. S. Uncovering the potential of biofabricated Ananas comosus Peel selenium nanoparticles for antibacterial, antibiofilm, suppression of virulence genes (can and LuxS), anticancer, and antioxidant properties. BMC Biotechnol. 25 (1), 1–21 (2025).
Mehrian, S. K. & De Lima, R. Nanoparticles Cyto and Genotoxicity in Plants: Mechanisms and Abnormalities Vol. 6, 184–193 (Environmental Nanotechnology, Monitoring & Management, 2016).
Soliman, M. I. et al. Antibacterial, antioxidant activities, GC-mass characterization, and cyto/genotoxicity effect of green synthesis of silver nanoparticles using latex of Cynanchum acutum L. Plants 12 (1), 172 (2022).
Alsubaie, B. et al. Phytocytokines: Key Regulators of Plant Immunity and Emerging Tools for Sustainable Agriculture 102889 (Physiological and Molecular Plant Pathology, 2025).
Badr, A. Cytotoxic effects of herbicide Nitralin on mistosis in allium Cepa root tips. Delta J. Sci. 3, 24–38 (1979).
Dey, H. & Shaili, S. Exploring the Phytochemical Diversity and Pharmacological Potentials of Balanite Aegyptiaca: A Review 53–63 (International Journal of Newgen Research in Pharmacy & Healthcare, 2023).
Ibrahim, O. H. et al. Investigation of potential in vitro anticancer and antimicrobial activities of balanites aegyptiaca (L.) delile fruit extract and its phytochemical components. Plants 11 (19), 2621 (2022).
Zhou, F., Peterson, T., Fan, Z. & Wang, S. The commonly used stabilizers for phytochemical-based nanoparticles: stabilization effects, mechanisms, and applications. Nutrients 15 (18), 3881 (2023).
Malik, A. Q. et al. A review on the green synthesis of nanoparticles, their biological applications, and photocatalytic efficiency against environmental toxins. Environ. Sci. Pollut. Res. 30 (27), 69796–69823 (2023).
Dhaka, A., Raj, S., Githala, C. K., Mali, C., Trivedi, R. & S., & Balanites aegyptiaca leaf extract-mediated synthesis of silver nanoparticles and their catalytic dye degradation and antifungal efficacy. Front. Bioeng. Biotechnol. 10, 977101 (2022).
Prabhaker, N., Patel, A. & Jain, U. K. Development of silver nanoparticles of balanites aegyptiaca plant extract for the effective treatment of fungal diseases. Asian J. Pharm. Res. Dev. 12 (4), 43–47 (2024).
Alahmer, S., El-Noss, M. & Farid, A. Preparation of Chitosan nanoparticles loaded with balanites aegyptiaca extract for treatment of streptozotocin-induced diabetes in rats. Int. J. Biol. Macromol. 262, 130061 (2024).
Teklu, B., Kadiri, S. K. & Vidavalur, S. Green synthesis of copper oxide nanoparticles using balanites aegyptiaca stem bark extract and investigation of antibacterial activity. Results Chem. 6, 101152 (2023).
Vashishth, D. & Kataria, S. K. Active phytoconstituents from balanites aegyptiaca and pterocarpus marsupium and their role in antioxidant defense and cytotoxicity against liver (HepG2) and brain (U87MG) cancer cell lines. J. Appl. Nat. Sci. 17(2), 561–573 (2025).
Xie, W., Guo, Z., Zhao, L. & Wei, Y. Metal-phenolic networks: facile assembled complexes for cancer theranostics. Theranostics 11 (13), 6407 (2021).
Okaiyeto, K. & Oguntibeju, O. O. African herbal medicines: adverse effects and cytotoxic potentials with different therapeutic applications. Int. J. Environ. Res. Public Health. 18 (11), 5988 (2021).
Rahim, S. A. & Al-Nahi, A. S. Cytogenetic effect of Tribulus terrestris fruit aqueous extract on Chromosome Aberrations and Mitotic Index in Sorafinib treated albino male rats. In BIO Web of Conferences (Vol. 139, p. 06002). EDP Sciences. (2024).
Ismail, H. H., Hamdalla, M. S. & Al-Ahmed, H. I. Activity of crude phenolic extract from trigonella to reduce side effects of Paclitaxel drug on chromosomal Aberrations, sperm Parameters, and sperm DNA fragmentation. J. Bioscience Appl. Res. 11 (2), 490–501 (2025).
Manoharan, S., Govindaraju, I., Venkatesan, V. & Perumal, E. A comprehensive review of targeting early-stage biomarkers by small molecules and phytochemicals in hepatocellular carcinoma. Phytochem. Rev. 1–43. (2025). https://doi.org/10.1007/s11101-025-10165-y
Funding
Open access funding provided by The Science, Technology & Innovation Funding Authority (STDF) in cooperation with The Egyptian Knowledge Bank (EKB).
Author information
Authors and Affiliations
Contributions
MI: Conceptualization, Data curation, Formal analysis, Investigation, Methodology, Validation, Writing – original draft, Writing – review & editing (Lead author; main contributor); HA: Supervision, Project administration, Data curation, Investigation, Writing – review & editing; GE: Supervision, Project administration, Conceptualization, Formal analysis, Writing – review & editing; AAI: Supervision, Methodology, Project administration, Conceptualization, Formal analysis, Writing – review & editing; MAH: Conceptualization, Formal analysis, Methodology, Project administration, Resources, Supervision, Writing – original draft, Writing – review & editing (Senior/corresponding author).
Corresponding authors
Ethics declarations
Competing interests
The authors declare no competing interests.
Additional information
Publisher’s note
Springer Nature remains neutral with regard to jurisdictional claims in published maps and institutional affiliations.
Supplementary Information
Below is the link to the electronic supplementary material.
Rights and permissions
Open Access This article is licensed under a Creative Commons Attribution 4.0 International License, which permits use, sharing, adaptation, distribution and reproduction in any medium or format, as long as you give appropriate credit to the original author(s) and the source, provide a link to the Creative Commons licence, and indicate if changes were made. The images or other third party material in this article are included in the article’s Creative Commons licence, unless indicated otherwise in a credit line to the material. If material is not included in the article’s Creative Commons licence and your intended use is not permitted by statutory regulation or exceeds the permitted use, you will need to obtain permission directly from the copyright holder. To view a copy of this licence, visit http://creativecommons.org/licenses/by/4.0/.
About this article
Cite this article
El-Zaidy, M.I.M., Ayoub, H.G., El-Akabawy, G. et al. Eco-friendly synthesis of Balanites aegyptiaca-derived selenium nanoparticles: extract and assessment of their anticancer, antimicrobial, cytogenetic and molecular docking insights. Sci Rep (2026). https://doi.org/10.1038/s41598-026-35358-z
Received:
Accepted:
Published:
DOI: https://doi.org/10.1038/s41598-026-35358-z