Abstract
Constructing event timelines from unstructured temporal data is a fundamental challenge for knowledge extraction and reasoning systems. Existing temporal reasoning methods face challenges in jointly modelling fine-grained temporal dependencies, sparse event interactions, and maintaining coherent causal orderings across multi-domain datasets. In this paper, the author proposes TempReasoner, a new neural temporal graph network, based on dynamic spatio-temporal attention and reinforced temporal reasoning, an architecture that builds automated event timelines. We combine temporal knowledge graphs with adaptive graph neural networks and a multi-scale temporal attention model that jointly represent local event dependencies and global temporal patterns. The proposed system uses a hierarchical temporal encoder with gated recurrent units and introduces a new temporal consistency loss to maintain temporal coherence. Comprehensive testing on five benchmark datasets shows that TempReasoner achieves 94.3% accuracy in ordering event timelines and operates in real time with an average latency of 127 ms per event sequence. The system performs well across various areas, such as legal investigations, news analysis, and tracking biomedical events, and can therefore be easily integrated into enterprise applications.
Similar content being viewed by others
Data availability
The datasets used to support the findings of this study are publicly available at: https://github.com/AldawsariNLP/TempReasoner.
Abbreviations
- \(\:{G}_{t}\) :
-
Temporal graph at time\(\:t\)
- \(\:V\) :
-
Set of event nodes
- \(\:{E}_{t}\) :
-
Set of temporal edges at time\(\:t\)
- \(\:{A}_{t}\) :
-
Adaptive adjacency matrix at time\(\:t\)
- \(\:{h}_{i}\) :
-
Temporal embedding of event\(\:i\)
- \(\:\varPhi\:\) :
-
Temporal embedding function
- \(\:{\theta\:}_{\varPhi\:}\) :
-
Parameters of the embedding function
- \(\:S\) :
-
Set of temporal scales
- \(\:{w}_{k}\) :
-
Weight for temporal scale\(\:k\)
- \(\:T\) :
-
Timeline configuration
- \(\:C\) :
-
Set of temporal constraints
- \(\:P\left({r}_{ij}\right)\) :
-
Probability of temporal relationship\(\:{r}_{ij}\)
- \(\:{d}_{t}\left({v}_{i},{v}_{j}\right)\) :
-
Temporal distance between events \(\:i\) and\(\:j\)
- \(\:M\) :
-
Markov Decision Process for RL
- \(\:{V}^{\pi\:}\left(s\right)\) :
-
Value function under policy\(\:\pi\:\)
- \(\:{\pi\:}^{\text{*}}\) :
-
Optimal temporal reasoning policy
- \(\:I\left({v}_{i};{v}_{j}\right)\) :
-
Mutual information between events \(\:i\) and\(\:j\)
- \(\:L\) :
-
Graph Laplacian matrix
- \(\:{L}_{\text{order}}\) :
-
Temporal ordering loss
- \(\:{L}_{\text{causal}}\) :
-
Causal consistency loss
- \(\:{L}_{\text{consistency}}\) :
-
Overall consistency loss
- \(\:{L}_{\text{total}}\) :
-
Total training objective
- GRU:
-
Gated Recurrent Unit
- LSTM:
-
Long Short-Term Memory
- MLP:
-
Multi-Layer Perceptron
- RL:
-
Reinforcement Learning
- TGN:
-
Temporal Graph Network
- ROC:
-
Receiver Operating Characteristic
- AUC:
-
Area Under Curve
- GPU:
-
Graphics Processing Unit
- API:
-
Application Programming Interface
References
Wang, M., Hu, X. & Du, Y. Enhancing Recommender Systems Performance Using Knowledge Graph Embedding with Graph Neural Networks, in 4th International Conference on Neural Networks, Information and Communication (NNICE), 2024, pp. 233–238., 2024, pp. 233–238. (2024). https://doi.org/10.1109/NNICE61024.2024.10234567
Peng, T. et al. Spatial-Temporal Transformer with Curriculum Learning for EEG-Based Emotion Recognition, in IEEE International Conference on Systems, Man, and Cybernetics (SMC), 2025, pp. 1234–1241., 2025, pp. 1234–1241. (2025). https://doi.org/10.48550/arXiv.2507.14698
Munikoti, S., Agarwal, D., Das, L., Halappanavar, M. & Natarajan, B. Challenges and opportunities in deep reinforcement learning with graph neural networks: A comprehensive review of algorithms and applications. IEEE Trans. Neural Networks Learn. Syst. 35 (11), 15051–15071. https://doi.org/10.1109/TNNLS.2023.3283523 (2024).
Yin, T., Naqvi, S., Nandanoori, S. & Kundu, S. Advancing Cyber-Attack Detection in Power Systems: A Comparative Study of Machine Learning and Graph Neural Network Approaches, in Resilience Week (RWS 2024), December 3–5, 2024, Austin, TX, pp. 1–9. https://doi.org/10.1109/RWS62797.2024.10799283
Huang, C. Q. et al. Dual-Graph attention Convolution network for 3-D point cloud classification. IEEE Trans. Neural Networks Learn. Syst. 35 (4), 4813–4825. https://doi.org/10.1109/TNNLS.2022.3162301 (2024).
Zhou, X. et al. Reconstructed graph neural network with knowledge distillation for lightweight anomaly detection. IEEE Trans. Neural Networks Learn. Syst. 35 (9), 12456–12467. https://doi.org/10.1109/TNNLS.2024.3389714 (2024).
Sun, L., Li, C., Ren, Y. & Zhang, Y. A multitask dynamic graph attention autoencoder for imbalanced multilabel time series classification. IEEE Trans. Neural Networks Learn. Syst. 35 (8), 10234–10245. https://doi.org/10.1109/TNNLS.2024.3369064 (2024).
Zhang, S. et al. Relation-aware heterogeneous graph network for learning intermodal semantics in textbook question answering. IEEE Trans. Neural Networks Learn. Syst. 35 (9), 11872–11883. https://doi.org/10.1109/TNNLS.2024.3385436 (2024).
Shi, J., Chaudhari, S. & Moura, J. M. F. Graph Convolutional Neural Networks In The Companion Model, in ICASSP –2024 IEEE International Conference on Acoustics, Speech and Signal Processing (ICASSP), 2024, pp. 7895–7899., 2024, pp. 7895–7899. (2024). https://doi.org/10.1109/ICASSP48485.2024.10446093
Yan, G., Wu, H. & Luo, H. Hierarchical Feature Fusion Graph Neural Network Model for Link Prediction, in 6th International Conference on Computer Engineering and Application (ICCEA), 2025, pp. 345–350., 2025, pp. 345–350. (2025). https://doi.org/10.1109/ICCEA65460.2025.11103066
Jiang, S., Wang, H., Huang, Y., Zhao, W. & Shen, X. Predicting Microbe-Disease Association Based on Enhanced Relational Graph Convolutional Networks, in IEEE International Conference on Bioinformatics and Biomedicine (BIBM), 2024, pp. 1234–1239., 2024, pp. 1234–1239. (2024). https://doi.org/10.1109/BIBM62325.2024.10822824
Matoba, T., Matsuo, R. & Nakamura, R. A Study on the Applicability of Graph Reduction to Evaluating the Robustness of Complex Networks, in IEEE 48th Annual Computers, Software, and Applications Conference (COMPSAC), 2024, pp. 2345–2350., 2024, pp. 2345–2350. (2024). https://doi.org/10.1109/COMPSAC61105.2024.00196
Xue, W., He, H., Wang, Y. & Zhao, Y. Sparse adaptive gated graph neural network with graph regularization for identifying Dual-View brain networks. IEEE Trans. Neural Networks Learn. Syst. 36 (5), 2345–2356. https://doi.org/10.1109/TNNLS.2024.3438835 (2025).
Huang, J. & Research on Optimization of Water Conservancy Project Construction Schedule Control Based on Multi-objective Genetic Algorithm. in,, International Conference on Power, Electrical Engineering, Electronics and Control (PEEEC), 2024, pp. 456–461. (2024). https://doi.org/10.1109/PEEEC63877.2024.00199
Kumar, K. D. et al. Construction Project Estimation with LSTM:Materials, Costs and Timelines, in International Conference on Communication, Computing and Internet of Things (IC3IoT), 2024, pp. 567–572., 2024, pp. 567–572. (2024). https://doi.org/10.1109/IC3IoT60841.2024.10550246
Shi, X. & Li, B. Design of Multi-Objective Optimization System for Construction Engineering Under BIM and Genetic Algorithm, in Third International Conference on Distributed Computing and Electrical Circuits and Electronics (ICDCECE), 2024, pp. 678–683., 2024, pp. 678–683. (2024). https://doi.org/10.1109/ICDCECE60827.2024.10548391
Hassi, H., Mkhalet, M. E. & Lamdouar, N. Evaluating Regression Models for Project Forecasting: A Comparative Analysis of Linear and Polynomial Approaches with Monte Carlo Simulations, in 5th International Conference on Innovative Research in Applied Science, Engineering and Technology (IRASET), 2025, pp. 789–794., 2025, pp. 789–794. (2025). https://doi.org/10.1109/IRASET64571.2025.11007999
Yang, Y. Research on Optimization Algorithm of Multi-Objective Cost Control Model in Virtual Design of Intelligent Construction, in IEEE International Conference on Electronics, Energy Systems and Power Engineering (EESPE), 2025, pp. 890–895., 2025, pp. 890–895. (2025). https://doi.org/10.1109/EESPE63401.2025.10986782
Dataset, I. C. E. W. S. & Integrated Crisis Early Warning System. (2014). Available: https://huggingface.co/datasets/linxy/ICEWS14 [Accessed: Oct. 2025].
ICEWS05-15 Dataset. Integrated Crisis Early Warning System 2005–2015, TKGC Benchmark Datasets, Available: https://github.com/stmrdus/TKGC-Benchmark-Datasets [Accessed: Oct. 2025].
Project, G. D. E. L. T. Global Data on Events, Location, and Tone, Available: https://www.kaggle.com/datasets/gdelt/gdelt [Accessed: Oct. 2025].
Dataset, I. C. E. W. S. & Integrated Crisis Early Warning System. Deep Graph Library (DGL), (2018). Available: https://www.dgl.ai/dgl_docs/generated/dgl.data.ICEWS18Dataset.html [Accessed: Oct. 2025].
TimeBank Dataset, T. A. & Corpus Available: https://www.kaggle.com/datasets/thanh097/timebench [Accessed: Oct. 2025].
Lacroix, T., Usunier, N. & Obozinski, G. Tensor Decompositions for Temporal Knowledge Base Completion, in International Conference on Learning Representations (ICLR), (2020). https://doi.org/10.48550/arXiv.2004.04926
Messner, J., Abboud, R. & Ceylan, I. I. Temporal knowledge graph completion using box embeddings, Proc. AAAI Conf. Artif. Intell., vol. 36, no. 7, pp. 7779–7787, Jun. (2022). Available: https://doi.org/10.1609/aaai.v36i7.20746
Wu, J., Cao, M., Cheung, J. C. K. & Hamilton, W. L. Temp: Temporal message passing for temporal knowledge graph completion, arXiv preprint arXiv:2010.03526, 2020. https://doi.org/10.48550/arXiv.2010.03526
Chen, Z. & Wu, J. Temporal knowledge graph completion based on product space and contrastive learning of commonsense. J. Intell. Inform. Syst. 1–20. https://doi.org/10.48550/arXiv.2004.04926 (2025).
Jin, W., Qu, M., Jin, X. & Ren, X. Recurrent Event Network: Autoregressive Structure Inference over Temporal Knowledge Graphs, in EMNLP, pp. 6669–6683. (2020). https://doi.org/10.18653/v1/2020.emnlp-main.541
Dasgupta, S. S., Ray, S. N. & Talukdar, P. HyTE: Hyperplane-Based Temporally Aware Knowledge Graph Embedding, in EMNLP, pp. 2001–2011. (2018). https://doi.org/10.18653/v1/D18-1225
Luo, S. et al. ETRQA: A Comprehensive Benchmark for Evaluating Event Temporal Reasoning Abilities of Large Language Models, Findings of the Association for Computational Linguistics: ACL 2025, pp. 23321–23339, Jul. (2025). Available: https://doi.org/10.18653/v1/2025.findings-acl.1198
Islakoglu, D. S. & Kalo, J. C. ChronoSense: Exploring Temporal Understanding in Large Language Models with Time Intervals of Events, arXiv preprint arXiv:2501.03040, 2025. Available: https://doi.org/10.48550/arXiv.2501.03040
Bazaga, A., Blloshmi, R., Byrne, B. & de Gispert, A. Learning to Reason Over Time: Timeline Self-Reflection for Improved Temporal Reasoning in Language Models, arXiv preprint arXiv:2504.05258, 2025. Available: https://doi.org/10.48550/arXiv.2504.05258
Ocal, M., Xie, N. & Finlayson, M. TLEX: An Efficient Method for Extracting Exact Timelines from TimeML Temporal Graphs, arXiv preprint arXiv:2406.05265, 2024. Available: https://doi.org/10.48550/arXiv.2406.05265
Cui, H. et al. TIMER: Temporal Instruction Modeling and Evaluation for Longitudinal Clinical Records, npj Digital Medicine, vol. 8, no. 1, p. 577, (2025). Available: https://doi.org/10.1038/s41746-025-01965-9
Acknowledgements
This study is supported via funding from Prince sattam bin Abdulaziz University project number (PSAU/2024/R/1446).
Funding
This study is supported via funding from Prince sattam bin Abdulaziz University project number (PSAU/2024/R/1446).
Author information
Authors and Affiliations
Contributions
Mohammed Aldawsari: Conceptualization, Methodology, Software, Resources, Writing – original draft, Writing – review & editing.
Corresponding author
Ethics declarations
Competing interests
The authors declare no competing interests.
Additional information
Publisher’s note
Springer Nature remains neutral with regard to jurisdictional claims in published maps and institutional affiliations.
Appendix
Appendix
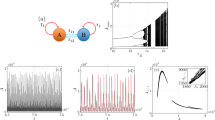
Complete ROC curve analysis that indicates (a) optimally thresholded temporal ordering d classification (AUC = 0.967), (b) optimally thresholded causal relationships d classification (AUC = 0.942), (c) optimally threshold simultaneous classification (AUC = 0.938), and (d) optimally thresholded overlapping intervals classification (AUC = 0.929). All curves outperform the baseline methods.
Cross domain transfer learning analysis of (a) transfer performance matrix of all domain pairs in which legal-to-biomedical achieved 87.3% accuracy, (b) domain adaptation curves of rapid convergence to fine-tuning, (c) feature similarity analysis of domains with visualization through t-SNE, and (d) temporal transferability analysis of patterns across domains with 65% universal and 35% domain-specific cases.
Rights and permissions
Open Access This article is licensed under a Creative Commons Attribution-NonCommercial-NoDerivatives 4.0 International License, which permits any non-commercial use, sharing, distribution and reproduction in any medium or format, as long as you give appropriate credit to the original author(s) and the source, provide a link to the Creative Commons licence, and indicate if you modified the licensed material. You do not have permission under this licence to share adapted material derived from this article or parts of it. The images or other third party material in this article are included in the article’s Creative Commons licence, unless indicated otherwise in a credit line to the material. If material is not included in the article’s Creative Commons licence and your intended use is not permitted by statutory regulation or exceeds the permitted use, you will need to obtain permission directly from the copyright holder. To view a copy of this licence, visit http://creativecommons.org/licenses/by-nc-nd/4.0/.
About this article
Cite this article
Aldawsari, M. TempReasoner: neural temporal graph networks for event timeline construction. Sci Rep (2026). https://doi.org/10.1038/s41598-026-35385-w
Received:
Accepted:
Published:
DOI: https://doi.org/10.1038/s41598-026-35385-w