Abstract
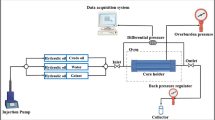
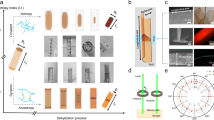
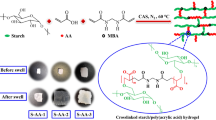
To address the limitations of conventional CO₂-responsive plugging materials (fixed network structure, slow response, and poor long-term stability) in fractured reservoirs, a novel terpolymer hydrogel poly(acrylamide-co-2-acrylamido-2-methylpropane sulfonic-co-acid-methylenebis(acrylamide)) hydrogel, denoted as P(AM-AMPS-MDA) was designed via solution copolymerization. The hydrogel features a hybrid network of covalent crosslinks (from MDA with tunable ethyleneamino chain length n = 1–3) and CO₂-induced ionic clusters, with precise reactant ratios (AM: AMPS: MDA = 90:16:4, K₂S₂O₈:Na₂SO₃=2:1) ensuring reproducibility. Comprehensive characterizations (FTIR, TGA/DSC, rheology, strain sweep) confirmed its superior performance: the optimized MDA₂ hydrogel (n = 2) exhibits rapid CO₂ response (< 10 min), balanced swelling ratio (~ 18), high storage modulus (1790 Pa), and excellent thixotropy (> 90% recovery in 30 s). It maintains structural integrity at 80 °C (Td ≈ 617 °C) and retains > 85% mass over 10-year reservoir simulation. Core flooding tests and visual demonstrations validate its effective plugging (residual resistance coefficient > 20) and injectability. This design resolves key trade-offs in existing systems, providing a promising candidate for conformance control in CO₂-enhanced oil recovery and sequestration.
Similar content being viewed by others
Data availability
The original contributions presented in this study are included in the article/supplementary material. Further inquiries can be directed to the corresponding author.
References
Liang, H. et al. Li. Adsorption models for shale gas: A Mini-Review. Energy Fuels. 36, 12946–12960 (2022).
Wang, S., Sun, Z., Zhu, Q., Cao, X. & Feng, Y. Yin. In situ generated hydrogels exhibiting simultaneous High-Temperature and High-Salinity resistance for deep hydrocarbon reservoir exploitation. Ind. Eng. Chem. Res. 63, 18263–18278 (2024).
Yang, S., Yu, W., Zhao, M., Ding, F. & Zhang, Y. A review of weak gel fracturing fluids for deep shale gas reservoirs. Gels 10, e345 (2024).
Chen, Y. et al. Chen. Research on flow patterns of Two-Phase fracturing fluid in hydraulic fracture considering the fluid Leak-off. ACS Omega. 9, 2432–2442 (2024).
Huang, C., Mu, L. & Gong, X. Development and characterization of environmentally responsive thickening agents for fracturing fluids in shale gas reservoir stimulation. Processes 13, e1253 (2025).
Yu, Y. et al. Effect of Ultra-High temperature degradation on the physical properties and chemical structure of an AMPS-Based copolymer Oil-Well cement additive PADIM in aqueous solution. Polymers 17, e591 (2025).
Lei, S., Sun, J., Lv, K., Zhang, Q. & Yang, J. Types and performances of polymer gels for Oil-Gas drilling and production: A review. Gels 8, e386 (2022).
Abdel-Azeim, S. Phase behavior and interfacial properties of Salt-Tolerant polymers: insights from molecular dynamics simulations. ACS Appl. Polym. Mater. 3, 6488–6501 (2021).
Si, S. et al. Ma. Salt resistance mechanism and oil displacement performance evaluation of a new zwitterionic polymer. Energy Fuels. 39, 13443–13453 (2025).
Han, J., Sun, J., Lv, K., Yang, J. & Li, Y. Polymer gels used in Oil–Gas drilling and production engineering. Gels 8, e637 (2022).
Luo, M. et al. Experimental study on the temporary plugging performance of magnetic responsive hydrogel in hydraulic fracturing of hydrocarbon reservoirs. Colloids Surf., A. 646, e128981 (2022).
Sun, C. et al. Lu. Shale gas exploration and development in china: current Status, geological Challenges, and future directions. Energy Fuels. 35, 6359–6379 (2021).
You, L. et al. Zero flowback rate of hydraulic fracturing fluid in shale gas reservoirs: Concept, Feasibility, and significance. Energy Fuels. 35, 5671–5682 (2021).
Da, Q., Yao, C., Zhang, X., Li, L. & Lei, G. Reservoir damage induced by Water-Based fracturing fluids in tight reservoirs: A review of formation mechanisms and treatment methods. Energy Fuels. 38, 18093–18115 (2024).
Striolo, A. & Cole, D. R. Understanding shale gas: recent progress and remaining challenges. Energy Fuels. 31, 10300–10310 (2017).
Liu, X. et al. Preparation and performance of salt tolerance and thermal stability cellulose nanofibril hydrogels and their application in drilling engineering. Paper Biomaterials. 4, 10–19 (2019).
Wang, S. et al. A hydroxypropyl Methyl Cellulose-Based graft copolymer with excellent thermothickening and Anti-salt ability for enhanced oil recovery. Energy Fuels. 36, 2488–2502 (2022).
Srivastava, A., Mandal, P. & Kumar, R. Solid state thermal degradation behaviour of graft copolymers of carboxymethyl cellulose with vinyl monomers. Int. J. Biol. Macromol. 87, 357–365 (2016).
Balding, P., Li, M., Wu, Q. & Volkovinsky, R. Russo. Cellulose Nanocrystal–Polyelectrolyte hybrids for bentonite Water-Based drilling fluids. ACS Appl. Bio Mater. 3, 3015–3027 (2020).
Zhang, Z. et al. Smith. Experimental evaluation of a novel modification of anionic Guar gum with maleic anhydride for fracturing fluid. Rheol. Acta. 58, 173–181 (2019).
Bahamdan, A. Daly. Poly(oxyalkylene) grafts to Guar gum with applications in hydraulic fracturing fluids. Polym. Adv. Technol. 17, 679–681 (2006).
Lu, T. & Chen, F. Multiwfn: A multifunctional wavefunction analyzer. J. Comput. Chem. 33, 580–592 (2012).
Wang, Y. C., Zha, H., Cheng, P. Y., Zhang, S. & Liu, X. W. Wu. Vanadium(V) complexes containing unsymmetrical N-Heterocyclic carbene ligands: highly efficient synthesis and catalytic behaviour towards Ethylene/Propylene copolymerization. Chin. J. Polym. Sci. 42, 32–41 (2024).
Fang, Y., Yue, T., Zhang, S. L. & Liu, J. Zhang. Molecular dynamics simulations of Self-Healing topological copolymers with a Comb-like structure. Macromolecules 54, 1095–1105 (2021).
Di, W. et al. Probing the state of water in oil-based drilling fluids. Colloids Surf., A. 650, e129770 (2022).
Zhang, C. et al. Quantitative characterization of the crosslinking degree of hydroxypropyl Guar gum fracturing fluid by low-field NMR. Int. J. Biol. Macromol. 277, e134445 (2024).
Gao, Y., Li, A., Chen, J., Cui, Z. & Wu, Y. Quaternized sodium Alginate-g-Ethyl-Oxazoline copolymer brushes and their supramolecular networks via hydrogen bonding. ACS Biomaterials Sci. Eng. 8, 3424–3437 (2022).
Li, A., Li, J. L., Zhang, J. M. & Ma, J. Y. Wu. In-situ synthesis of chemically stable hybrid networks of Poly(thioctic acid) with Fe³⁺ via Controlled/living cationic Ring-opening polymerization. Macromol. Rapid Commun. 4, e2401115 (2025).
Wen, B. et al. Cheng. Facile assembly strategy for luminescent lanthanide nanoparticles with antibacterial activity using Aggregation-Inducing emission polymers. Macromolecules 56, 1884–1897 (2023).
Li, A., Zhang, J., Yi, Q., Wang, Y. & Wu, Y. Optical performance of hybrid Co-Networks of Poly(thioctic Acid) coordinated with Fe³⁺: optical focusing and photothermal conversion. Adv. Opt. Mater. 13, e01148 (2025).
Yang, J., Dong, T., Yi, J. & Jiang, G. Development of multiple crosslinked polymers and its application in Synthetic-Based drilling fluids. Gels 10, e120 (2024).
Ahmad, H. M., Iqbal, T., Kamal, M. S. & Al-Harthi, M. A. Influence of hydrophobically modified polymer and Titania nanoparticles on shale hydration and swelling properties. Energy Fuels. 34, 16456–16468 (2020).
de Leon, A. C. C., da Silva, Í. G. M., Pangilinan, K. D., Chen, Q. & Caldona, E. B. Advincula. High performance polymers for oil and gas applications. Reactive Funct. Polym. 162, e104878 (2021).
Liu, X., Liu, K., Gou, S., Liang, L. & Luo, C. Guo. Water-Soluble acrylamide sulfonate copolymer for inhibiting shale hydration. Ind. Eng. Chem. Res. 53, 2903–2910 (2014).
Bagaria, H. G. et al. Bielawski, K. P. Johnston. Stabilization of iron oxide nanoparticles in high sodium and calcium Brine at high temperatures with adsorbed sulfonated copolymers. Langmuir 29, 3195–3206 (2013).
Wang, J., Ran, D., Lu, H., Zhang, J. & Wu, Y. Realizing the efficient dissolution of drag reducer upon pH-Induced demulsification of inverse polymer emulsion. Langmuir 40, 15869–15876 (2024).
Davoodi, S., Al-Shargabi, M., Wood, D. A. & Rukavishnikov, V. S. Minaev. Synthetic polymers: A review of applications in drilling fluids. Pet. Sci. 21, 475–518 (2024).
Al-Hajri, S., Negash, B. M., Rahman, M. M. & Haroun, M. Al-Shami. Perspective review of polymers as additives in Water-Based fracturing fluids. ACS Omega. 7, 7431–7443 (2022).
Drozdov, A. D. & deClaville Christiansen, J. Swelling of Thermo-Responsive gels in aqueous solutions of salts: A predictive model. Molecules 27 (16), 5177 (2022).
Chimani, F. M. et al. Enhancing CO₂ adsorption kinetics in direct air capture: the role of steam desorption in Amine-Based anion exchange sorbents. J. CO₂ Util. 100, 103184 (2025).
Jilin Oilfield Company. Geological Evaluation Report of Block H59 CO₂ Flooding Reservoir (Jilin Petroleum Industry, 2020).
Ferry, J. D. Viscoelastic Properties of Polymers (4th ed.); John Wiley & Sons: New York, (1980).
Williams, M. L., Landel, R. F. & Ferry, J. D. The temperature dependence of relaxation mechanisms in amorphous polymers and other Glass-Forming liquids. J. Am. Chem. Soc. 77, 3701–3707 (1955).
Larson, R. G. The Structure and Rheology of Complex Fluids (Oxford University Press, 1999).
Wang, S., Sun, Z. & Yin, H. Temperature dependence of viscoelasticity in ionic crosslinked hydrogels for enhanced oil recovery. Ind. Eng. Chem. Res. 63, 18263–18278 (2024).
Xiong, D. et al. CO₂-Switchable Self-Healing of ionic Liquids-Based hydrogels. J. Colloid Interface Sci. 693, 137594 (2025).
Gao, C. et al. Optimization of CO₂ flooding under dual goals of oil recovery and CO₂ storage: numerical case studies of the First-Ever CCUS pilot in Changqing oilfield. Geoenergy Sci. Eng. 240, 213063 (2024).
Funding
General Project of Natural Science Basic Research Program of Shaanxi Province (for Young Scholars) (No. 2023-JC-QN-0373).
Author information
Authors and Affiliations
Contributions
Yuanzi Yan, Conceptualization, Investigation, Writing—original draft.Yan Tao, Methodology, Writing—review and editing.Shaoli Zhou, Methodology, Writing—review and editing.Yunfeng Fan, Data Curation, Formal analysis.Peng Zhang, Data Curation, Formal analysis.All authors have read and agreed to the published version of the manuscript.
Corresponding author
Ethics declarations
Competing interests
The authors declare no competing interests.
Additional information
Publisher’s note
Springer Nature remains neutral with regard to jurisdictional claims in published maps and institutional affiliations.
Supplementary Information
Below is the link to the electronic supplementary material.
Rights and permissions
Open Access This article is licensed under a Creative Commons Attribution-NonCommercial-NoDerivatives 4.0 International License, which permits any non-commercial use, sharing, distribution and reproduction in any medium or format, as long as you give appropriate credit to the original author(s) and the source, provide a link to the Creative Commons licence, and indicate if you modified the licensed material. You do not have permission under this licence to share adapted material derived from this article or parts of it. The images or other third party material in this article are included in the article’s Creative Commons licence, unless indicated otherwise in a credit line to the material. If material is not included in the article’s Creative Commons licence and your intended use is not permitted by statutory regulation or exceeds the permitted use, you will need to obtain permission directly from the copyright holder. To view a copy of this licence, visit http://creativecommons.org/licenses/by-nc-nd/4.0/.
About this article
Cite this article
Yan, Y., Tao, Y., Zhou, S. et al. CO2-responsive terpolymer hydrogels with adjustable dynamic networks for fractured plugging in the reservoir. Sci Rep (2026). https://doi.org/10.1038/s41598-026-35469-7
Received:
Accepted:
Published:
DOI: https://doi.org/10.1038/s41598-026-35469-7