Abstract
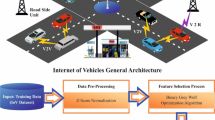
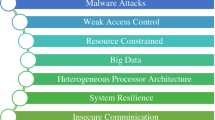
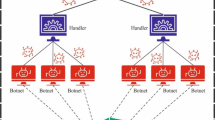
Today, smartphones are used by the majority of internet users worldwide, and Android has become the most popular smartphone operating system on the market. The growth in the use of smartphones in general, and the Android system specifically, results in a stronger requirement to successfully protect Android, as malware developers aim to create advanced and sophisticated malware applications. Cybercriminals utilize fraudulent attack tactics, namely obfuscation or dynamic code triggering, to evade the system. A standard static investigation method failed to recognize such attacks. Mitigating a wide variety of evasive attacks requires a refined, dynamic, and analytical framework. Conventional artificial intelligence (AI), particularly machine learning (ML) methodologies, are no longer effective in detecting all new and complex malware types. A deep learning (DL) model, which is very different from conventional ML models, has a possible solution to the detection issue of each version of malware. In this manuscript, an Approach for Improving Malware Detection Performance Using a Hybrid Deep Learning Framework (IMDP-HDL) is proposed. The primary objective of the IMDP-HDL methodology is to ensure the effective and scalable deployment of malware detection in real-world cybersecurity environments. Initially, the Z-score standardization is utilized to ensure consistent feature scaling and model performance. For the malware detection process, a hybrid model combining a convolutional neural network, bi-directional long short-term memory, and self-attention mechanism (CBiLSTM-SA) is employed. A broad range of experimentation with the IMDP-HDL model is performed using the Android malware dataset. The comparison analysis of the IMDP-HDL model demonstrated a superior accuracy value of 99.22% over existing techniques.
Similar content being viewed by others
Data availability
The data supporting the findings of this study are openly available in the Kaggle dataset [https://www.kaggle.com/datasets/shashwatwork/android-malware-dataset-for-machine-learning? select=dataset-features-categories.csv](https:/www.kaggle.com/datasets/shashwatwork/android-malware-dataset-for-machine-learning? select=dataset-features-categories.csv), https://www.kaggle.com/datasets/subhajournal/android-malware-detection, [https://www.kaggle.com/datasets/saurabhshahane/android-permission-dataset](https:/www.kaggle.com/datasets/saurabhshahane/android-permission-dataset), reference number [31, 32, 33].
Code Availability
1Anuradha Anumolu, “IMDP-HDL: Algorithm Supplementary Document”. Zenodo, Dec. 06, 2025. https://doi.org/10.5281/zenodo.17836199.
References
Harika, T. & Pradeepini, G. Enhanced malware classification: A hybrid model utilizing denoising autoencoder and CNN based on visualization method. J. Cybersecur. Inform. Management 16, 1 (2025).
Elayan, O. N. & Mustafa, A. M. Android malware detection using deep learning. Procedia Comput. Sci. 184, 847–852 (2021).
Xing, X., Jin, X., Elahi, H., Jiang, H. & Wang, G. A malware detection approach using autoencoder in deep learning. Ieee Access. 10, 25696–25706 (2022).
John, T. S. & Thomas, T. Adaptive rank-based mutation for android malware detection under adversarial attacks. J. Cyber Secur. Technol. 8, 1–26 (2025).
Hemalatha, J., Roseline, S. A., Geetha, S., Kadry, S. & Damaševičius, R. An efficient densenet-based deep learning model for malware detection. Entropy, 23(3), 344. (2021).
Alomari, E. S. et al. Malware detection using deep learning and correlation-based feature selection. Symmetry, 15(1), 123. (2023).
He, K. & Kim, D. S. Malware detection with malware images using deep learning techniques. In 2019 18th IEEE international conference on trust, security and privacy in computing and communications/13th IEEE international conference on big data science and engineering (TrustCom/BigDataSE) (pp. 95–102). IEEE. (2019).
Akhtar, M. S. & Feng, T. Detection of malware by deep learning as CNN-LSTM machine learning techniques in real time. Symmetry, 14(11), 2308. (2022).
Zhang, R. & Liu, Y. Ransomware detection with a 2-tier machine learning approach using a novel clustering algorithm. (2024).
BP, D. S. V. Incremental research on cyber security metrics in android applications by implementing the ML algorithms in malware classification and detection. J. Cybersecur. Inform. Manage. 3 (1), 14–20 (2020).
Anand, S. et al. Malite: Lightweight Malware Detection and Classification for Constrained Devices. IEEE Trans. Emerg. Top. Comput. (2025).
Jeon, J., Jeong, B., Baek, S. & Jeong, Y. S. TMaD: Three-tier malware detection using multi‐view feature for secure convergence ICT environments. Expert Syst. 42 (2), e13684 (2025).
Baawi, S. S., Oleiwi, Z. C., Al-Muqarm, A. M. A., Al-Shammary, D. & Sufi, F. Efficient malware detection based on machine learning for enhanced cloud privacy protection. Evol. Syst. 16 (1), 1–17 (2025).
Poornima, S. & Mahalakshmi, R. Automated malware detection using machine learning and deep learning approaches for android applications. Sensors 32, 100955 (2024).
Kumar, S. & Kumar, A. Image-based malware detection based on convolution neural network with autoencoder in Industrial Internet of Things using Software Defined Networking Honeypot. Eng. Appl. Artif. Intell. 133, 108374 (2024).
Jo, J., Cho, J. & Moon, J. A malware detection and extraction method for the related information using the ViT attention mechanism on android operating system. Appl. Sc. 13(11), 6839 (2023).
Buriro, A., Buriro, A. B., Ahmad, T., Buriro, S. & Ullah, S. MalwD&C: a quick and accurate machine learning-based approach for malware detection and categorization. Appl. Sci. 13, 2508 (2023).
Dabas, N., Ahlawat, P. & Sharma, P. An effective malware detection method using hybrid feature selection and machine learning algorithms. Arab. J. Sci. Eng. 48 (8), 9749–9767 (2023).
Al-Ghanem, W. K. et al. MAD-ANET: malware detection using Attention-Based deep neural networks. CMES-Computer Model. Eng. Sci. 143 (1), 1009–1027 (2025).
Chen, J., Wu, M. & Huang, H. LDAM: A lightweight dual attention module for optimizing automotive malware classification. Array, 26, 100396. (2025).
Wajahat, A. et al. An adaptive semi-supervised deep learning-based framework for the detection of android malware. J. Intell. Fuzzy Syst. 45 (3), 5141–5157 (2023).
Alsumaidaee, Y. A. M., Yahya, M. M. & Yaseen, A. H. Optimizing malware detection and classification in real-time using hybrid deep learning approaches. Int. J. Saf. Secur. Eng. 15, 1 (2025).
Qureshi, S. et al. Analysis of challenges in modern network forensic framework. Secur. Commun. Netw. 2021(1), 8871230. (2021).
Alohali, M. A. et al. Two stage malware detection model in internet of vehicles (IoV) using deep learning-based explainable artificial intelligence with optimization algorithms. Sci. Rep. 15(1), 20615. (2025).
Wajahat, A. et al. An effective deep learning scheme for android malware detection leveraging performance metrics and computational resources. Intell. Decis. Technol. 18 (1), 33–55 (2024).
Al Ogaili, R. R. N. et al. AntDroidNet cybersecurity model: A hybrid integration of ant colony optimization and deep neural networks for android malware detection. Mesopotamian J. Cybersecur. 5 (1), 104–120 (2025).
Wajahat, A. et al. Outsmarting android malware with Cutting-Edge feature engineering and machine learning techniques. Comput. Mater. Contin., 79(1). (2024).
Awwal, P. & Naval, S. Development of heuristic adapted Serial-based deep learning for efficient adversarial malware detection framework in windows. Knowl. Based Syst. 114032. (2025).
Fu, N., Lee, J. H., Liu, J., Lee, S. & Kim, M. K. Electricity Demand Forecasting for Cultural Institutions: A Comparative Study of Lstm and Cnn-Lstm Models with Three Data Normalization Techniques Using Weather and Price Data–Case Studies from Norwegian Museums. Available at SSRN 5262024.
Dong, J., Wei, Y., Wang, D. & Chen, Y. Groundwater Level Prediction Based on Ssa-Optimized Self-Attention Mechanism and Bilstm Hybrid Model. Available at SSRN 5246902.
https://www.kaggle.com/datasets/subhajournal/android-malware-detection
https://www.kaggle.com/datasets/saurabhshahane/android-permission-dataset
Al-Khayyat, A., Ahmed, M. A., Azar, A. T., Haider, Z. & Ibraheem, I. K. Hybrid artificial fish swarm optimization with deep Learning-Driven cloud assisted cyberattack detection. Int. J. Intell. Eng. Syst. 17(4). (2024).
Chimeleze, C., Jamil, N., Alturki, N. & Zain, Z. M. A Lightweight malware detection technique based on hybrid fuzzy simulated annealing clustering in Android apps. Egypt. Inform. J. 28, 100560. (2024).
Zhou, H., Yang, X., Pan, H. & Guo, W. An android malware detection approach based on SIMGRU. IEEE Access. 8, 148404–148410 (2020).
Pathak, A., Barman, U. & Kumar, T. S. Machine learning approach to detect android malware using feature-selection based on feature importance score. J. Eng. Res. (2024).
Mahindru, A. et al. PermDroid a framework developed using proposed feature selection approach and machine learning techniques for Android malware detection. Sci. Rep. 14(1), 10724. (2024).
Funding
None.
Author information
Authors and Affiliations
Contributions
The manuscript was written through the contributions of all authors. All authors have approved the final version of the manuscript.
Corresponding author
Ethics declarations
Competing interests
The authors declare no competing interests.
Ethics approval
This article does not contain any studies with human participants performed by any of the authors.
Consent to participate
Not applicable.
Informed consent
Not applicable.
Additional information
Publisher’s note
Springer Nature remains neutral with regard to jurisdictional claims in published maps and institutional affiliations.
Rights and permissions
Open Access This article is licensed under a Creative Commons Attribution-NonCommercial-NoDerivatives 4.0 International License, which permits any non-commercial use, sharing, distribution and reproduction in any medium or format, as long as you give appropriate credit to the original author(s) and the source, provide a link to the Creative Commons licence, and indicate if you modified the licensed material. You do not have permission under this licence to share adapted material derived from this article or parts of it. The images or other third party material in this article are included in the article’s Creative Commons licence, unless indicated otherwise in a credit line to the material. If material is not included in the article’s Creative Commons licence and your intended use is not permitted by statutory regulation or exceeds the permitted use, you will need to obtain permission directly from the copyright holder. To view a copy of this licence, visit http://creativecommons.org/licenses/by-nc-nd/4.0/.
About this article
Cite this article
Anuradha, A., Chouhan, A.S. & Srinivas Rao, S. Improving malware detection performance using hybrid deep representation learning with heuristic search algorithms. Sci Rep (2026). https://doi.org/10.1038/s41598-026-35481-x
Received:
Accepted:
Published:
DOI: https://doi.org/10.1038/s41598-026-35481-x