Abstract
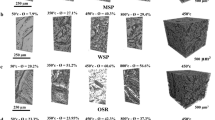
To explore new strategies for utilising waste biomass energy, this study investigated the partial substitution of aluminium powder in traditional rock-breaking incendiary agents with corn straw. Ballistic projection, DTA-TG, TG-FTIR, and infrared thermal imaging were employed to analyse the reaction mechanisms and performance changes of incendiary agents composed of corn straw, aluminium powder, and potassium nitrate. The thermal decomposition process occurred in three stages: The first stage corresponds to the evaporation of moisture absorbed by maize straw (390–570 K). The second weight loss stage can be divided into two parts: the first reflects the slow pyrolysis of hemicellulose, cellulose, and lignin, with some pyrolysis products forming charcoal (610–780 K); the second mainly involves the pyrolysis of a small amount of KNO₃ to produce NO₂ and O₂ (823–1154 K). The addition of 9% corn straw increased external work capacity by 38%, raised ignition input energy by 174 J/g, reduced the average size of rock fragments by approximately 29%, and decreased the uniformity coefficient by 31%. Theoretical gas production reached 207.58 cm³/g, 2.45 times higher than the original value. These findings indicate that corn straw significantly enhance gas generation, improve rock fragmentation, and contribute to greater safety and efficiency. Overall, incorporating corn straw provides a cost-effective approach to improve rock-breaking performance and promote the reuse of agricultural waste.
Similar content being viewed by others
Data availability
The data supporting the findings of this study are available within the article and its supplementary materials.
References
Sanchidrián, J. A., Segarra, P. & Lopez, L. M. Energy components in rock blasting. Int. J. Rock. Mech. Min. Sci. 44, 130–147 (2007).
Tian, X. X., Song, Z. P. & Wang, J. B. Study on the propagation law of tunnel blasting vibration in stratum and blasting vibration reduction technology. Soil Dyn. Earthq. Eng. 126 (2019).
Fan, C. H. & Ge, J. F. Dynamic calculation method of vibration response of Building blasting based on differential equation. Environ. Technol. Inno. 20 (2020).
Zhang, Z. et al. Dynamic response and safety control of civil air defense tunnel under excavation blasting of subway tunnel. Tunn. Undergr. Sp. Tech. 112 (2021).
Xu, M. et al. A study on Hollow effect and safety design of deep crossing caverns under blasting vibration. Tunn. Undergr. Sp. Tech. 111 (2021).
Wang, X., Li, J. C., Zhao, X. B. & Liang, Y. Propagation characteristics and prediction of blast-induced vibration on closely spaced rock tunnels. Tunn. Undergr. Sp. Tech. 123 (2022).
Sui, H. Y., Su, T. M., Hu, R. L., Yang, K. & Cheng, Y. X. Liquid CO2 Phase-Transition rock fracturing: A novel technology for safe rock excavation. Appl. Sci. Basel 12 (2022).
Shao, J. W. et al. X. Mechanical and restrained shrinkage behaviors of cement mortar incorporating waste tire rubber particles and expansive agent. Constr. Build. Mater. 296 (2021).
Cao, F. Z., Liu, Y. & Yan, P. Y. Properties and mechanism of the compound MgO expansive agent (CMEA) produced by calcining the mixture of dolomite and serpentine tailings. Constr. Build. Mater. 277 (2021).
Zhong, Z. et al. Experimental and numerical explorations on the optimized applications of SCDA in cracking concrete blocks. Measurement 206 (2023).
Jiang, Z. S. et al. The use of soundless chemical demolition agents in reinforced concrete deep beam demolition: experimental and numerical study. J. Build. Eng. 69 (2023).
Kaji, Y., Ishikawa, T. & Sugihara, H. Expansion agent utilizing thermite reaction. Sci. Technol. Energ. Ma. 80, 50–53 (2019).
Xie, Q., Zhu, M. L., Wang, H. X., Xie, X. H. & Li, H. Thermal decomposition behavior and kinetics of rock-breaking incendiary agent based on peanut shell. React. Kinet Mech. Cat. 136, 3105–3126 (2023).
Oh, S. et al. Deflagration characteristics of thermite reaction mixtures under decoupled charges. Sci. Technol. Energ. Ma. 81, 114–120 (2020).
Kuang, T. et al. Functional carbon Dots derived from biomass and plastic wastes. Green. Chem. 25, 6581–6602 (2023).
Kumar, J. A. et al. Agricultural waste biomass for sustainable bioenergy production: Feedstock, characterization and pre-treatment methodologies (Publication with Expression of Concern. See vol. 356, 2024). Chemosphere 331 (2023).
Pordesimo, L. O., Capareda, S., Sokhansanj, S. & Fernando, S. AGRO 156-Enhancement and stabilization of biomass feedstock quality through utilisation/recycling biological waste streams. Abstr. Pap. Am. Chem. Soc. 236 (2008).
Zhang, C., Nie, J. & Yan, X. Estimation of biomass utilisation potential in China and the impact on carbon peaking. Environ. Sci. Pollut Res. 30, 94255–94275 (2023).
Zhang, Q., Parmeswaran, B. & Lee, D. J. Accelerating agricultural biomass utilisation for sustainable development: The oeuvres of the 4th subject specialized conference of international bioprocessing association preface. Bioresour. Technol. 317 (2020).
Solarte-Toro, J. C., González-Aguirre, J. A., Giraldo, J. A. P. & Alzate, C. A. C. Thermochemical processing of Woody biomass: A review focused on energy-driven applications and catalytic upgrading. Renew. Sustain. Energ. Rev. 136 (2021).
Glushkov, D. O., Nyashina, G. S., Anand, R. & Strizhak, P. A. Composition of gas produced from the direct combustion and pyrolysis of biomass. Process. Saf. Environ. 156, 43–56 (2021).
Ji, W. Q., Richter, F., Gollner, M. J. & Deng, S. L. Autonomous kinetic modeling of biomass pyrolysis using chemical reaction neural networks. Combust Flame 240 (2022).
Wu, Y. J. & Liu, B. Mg (NO)•6HO-modified porous carbon derived from peanut shell: formation mechanism and efficient removal of p-nitrophenol. React. Kinet Mech. Cat. 135, 2085–2098 (2022).
Santos, V. O. et al. Analysis of thermal degradation of Peach palm(Kunth) seed using isoconversional models. React. Kinet Mech. Cat. 135, 367–387 (2022).
Zhang, P., Liu, S. Y., Lu, J. & Wang, J. Analysis of the combustion process and combustion kinetics of straw-bale fuel. Biomass Convers. Bior. 14, 19295–19304 (2024).
Li, Y., Li, X., Xiong, S. & Wen, Y. New formula for fragment velocity in the aiming direction of an asymmetrically initiated warhead. Propellants Explos Pyrotech. 43, 496–505 (2018).
Song, S. et al. Influence of vent area on aluminized explosive behavior in fast Cook-off. Propellants Explos. Pyrotech. 12038 (2025).
Rtibi, D., Boa, D., Hellali, D. & Zamali, H. Experimental investigation and calculation of the phase diagram of the isobaric binary system (KNO3 + T1NO3). J. Alloys Compd. 721, 419–430 (2017).
Che, Y. et al. Vacuum residue thermal cracking: product yield determination and characterization using Thermogravimetry-Fourier transform infrared spectrometry and a fluidized bed reactor. Energy Fuel. 32, 1348–1357 (2018).
Nel, H. A. et al. An untargeted thermogravimetric Analysis-Fourier transform Infrared-Gas Chromatography-Mass spectrometry approach for plastic polymer identification. Environ. Sci. Technol. 55, 8721–8729 (2021).
Jiang, J., Luo, J., Wu, Y. & Qu, W. The influence of ammonium polyphosphate on the smoke toxicity of wood materials. Thermochimica Acta 725 (2023).
Jiang, J. R., Luo, J. M., Wu, Y. Z. & Qu, W. The influence of ammonium polyphosphate on the smoke toxicity of wood materials. Thermochimica Acta 725 (2023).
Ioannidou, O. et al. Investigating the potential for energy, fuel, materials and chemicals production from corn residues (cobs and stalks) by non-catalytic and catalytic pyrolysis in two reactor configurations. Renew. Sust Energ. Rev. 13, 750–762 (2009).
Tosun, A. & Konak, G. Estimation of loader capacity based on the heap size distribution calculated by using numerical models. J. Min. Sci. 49, 441–449 (2013).
Schnedl, G. & Hartnuth, H. Characterization of product uniformity using the example of the early strength of cement. Zkg Int. 60, 96–103 (2007).
Sun, Y., Shen, Y. & Chen, C. A grading parameter for evaluating the grading-dependence of the shear stiffness of granular aggregates. Particuology 36, 193–198 (2018).
Sabatini, J. J. A review of illuminating pyrotechnics. Propellants Explos Pyrotech. 43, 28–37 (2018).
Acknowledgements
This work was supported by the Natural Science Research Project of Anhui Educational Committee (Project No. 2022AH050842), the Scientific Research Foundation for High-level Talents of Anhui University of Science and Technology (Project No. 2021yjrc08), and the University-level Military Special Projects of Anhui University of Science and Technology (Project No. JGZX2022-01).
Author information
Authors and Affiliations
Contributions
Qiang Xie, Lei Liu, Meng Wang, Hui Li, Tengfei Wei, Qingyu Qian, Shunxin Wang, Xinghua Xie, Zongshan Zou, Guangbing Wang and Jiyu Wang wrote the main manuscript text. All authors reviewed the manuscript.
Corresponding author
Ethics declarations
Competing interests
The authors declare no competing interests.
Additional information
Publisher’s note
Springer Nature remains neutral with regard to jurisdictional claims in published maps and institutional affiliations.
Rights and permissions
Open Access This article is licensed under a Creative Commons Attribution-NonCommercial-NoDerivatives 4.0 International License, which permits any non-commercial use, sharing, distribution and reproduction in any medium or format, as long as you give appropriate credit to the original author(s) and the source, provide a link to the Creative Commons licence, and indicate if you modified the licensed material. You do not have permission under this licence to share adapted material derived from this article or parts of it. The images or other third party material in this article are included in the article’s Creative Commons licence, unless indicated otherwise in a credit line to the material. If material is not included in the article’s Creative Commons licence and your intended use is not permitted by statutory regulation or exceeds the permitted use, you will need to obtain permission directly from the copyright holder. To view a copy of this licence, visit http://creativecommons.org/licenses/by-nc-nd/4.0/.
About this article
Cite this article
Xie, Q., Liu, L., Wang, M. et al. Effects of corn straw on the performance of rock-breaking incendiary agents. Sci Rep (2026). https://doi.org/10.1038/s41598-026-35665-5
Received:
Accepted:
Published:
DOI: https://doi.org/10.1038/s41598-026-35665-5