Abstract
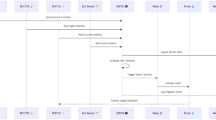
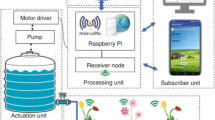
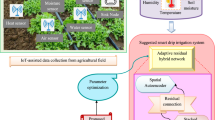
Sustainable water management in agriculture is a major challenge, particularly in regions facing water scarcity and the growing impacts of climate change. The lack of efficiency of traditional irrigation methods often leads to water waste, reduced productivity, and increased pressure on natural resources. In this context, it is imperative to develop innovative solutions to optimize water use while maintaining agricultural performance. This paper proposes a smart irrigation system based on the internet of things (IoT) and cloud computing. The system incorporates several sensors to measure key environmental parameters, such as temperature, air humidity, soil moisture, and water level. An embedded ESP32 microcontroller collects and transmits the data to the thingsBoard cloud platform, where it is analyzed in real time to determine precise irrigation needs. The system’s algorithm automatically makes the necessary decisions to activate or deactivate the irrigation pump, ensuring optimal and accurate water management. Experimental results demonstrate that the system significantly reduces water waste while optimizing irrigation based on the actual needs of the soil and crops. Real-time measurements and automated decision-making ensure accurate and efficient irrigation that adapts to fluctuations in environmental conditions. Performance analysis shows that the proposed approach significantly improves water resource management compared to traditional methods. The integration of cloud computing and the IoT facilitates remote monitoring and automated decision-making, making the system adaptable to a variety of crops and agricultural lands. The estimated cost of implementing the smart irrigation system is approximately $44.00, confirming its economic feasibility and appeal to small and medium-sized farms seeking to optimize water use. This solution also helps to build farmers’ resilience to climate change and water scarcity. The system presented represents a significant advance in the field of smart and sustainable irrigation. By optimizing water use and improving agricultural productivity, the system directly contributes to food security, water resource conservation, and climate resilience. Thus, this study provides a replicable and adaptable model for the development of large-scale smart and sustainable agricultural solutions.
Similar content being viewed by others
Data availability
Data are available on request from Abdennabi Morchid (abdennabi.morchid@usmba.ac.ma).
Code availability
The custom code for the smart irrigation system described in this study is provided as a supplementary file (Supplementary Code 1).
References
Ingrao, C., Strippoli, R., Lagioia, G. & Huisingh, D. Water scarcity in agriculture: an overview of causes, impacts and approaches for reducing the risks. Heliyon 9, e18507. https://doi.org/10.1016/j.heliyon.2023.e18507 (2023).
Young S.L. et al. Perspective: the importance of water security for ensuring food security, good Nutrition, and Well-being. Adv. Nutr. 12, 1058–1073. https://doi.org/10.1093/advances/nmab003 (2021).
Javan, K. et al. A review of interconnected challenges in the water–energy–food nexus: urban pollution perspective towards sustainable development. Sci. Total Environ. 912, 169319. https://doi.org/10.1016/j.scitotenv.2023.169319 (2024).
Wu, C., Liu, W. & Deng, H. Urbanization and the emerging water crisis: identifying water scarcity and environmental risk with multiple applications in urban agglomerations in Western China. Sustainability 15, 12977. https://doi.org/10.3390/su151712977 (2023).
Chang, H. et al. Evaluation of the coupling coordination and sustainable development of Water–Energy–Land–Food system on a 40-Year scale: A case study of Hebei, China. Land 13, 1089. https://doi.org/10.3390/land13071089 (2024).
Why water security is our most urgent challenge today. World Bank Blogs (n.d.). accessed January 2, (2025). https://blogs.worldbank.org/en/water/why-water-security-our-most-urgent-challenge-today
Boretti, A. & Rosa, L. Reassessing the projections of the world water development report. Npj Clean. Water. 2, 1–6. https://doi.org/10.1038/s41545-019-0039-9 (2019).
Morchid, A. et al. IoT-enabled smart agriculture for improving water management: A smart irrigation control using embedded systems and Server-Sent events. Sci. Afr. 27, e02527. https://doi.org/10.1016/j.sciaf.2024.e02527 (2025).
Morchid, A., Jebabra, R., Alami, R. E., Charqi, M. & Boukili, B. Smart Agriculture for Sustainability: The Implementation of Smart Irrigation Using Real-Time Embedded System Technology, in: 2024 4th International Conference on Innovative Research in Applied Science, Engineering and Technology (IRASET), : pp. 1–6. (2024). https://doi.org/10.1109/IRASET60544.2024.10548972
Morchid, A. et al. IoT-based smart irrigation management system to enhance agricultural water security using embedded systems, telemetry data, and cloud computing. Results Eng. 23, 102829. https://doi.org/10.1016/j.rineng.2024.102829 (2024).
Khalifeh, A. F. et al. An environmental remote sensing and prediction model for an IoT smart irrigation system based on an enhanced wind-driven optimization algorithm. Comput. Electr. Eng. 122, 109889. https://doi.org/10.1016/j.compeleceng.2024.109889 (2025).
Liopa-Tsakalidi, A., Thomopoulos, V., Barouchas, P., Boursianis, A. D. & Goudos, S. K. A LoRaWAN-based IoT platform for smart irrigation in Olive groves. Smart Agricultural Technol. 9, 100673. https://doi.org/10.1016/j.atech.2024.100673 (2024).
Manocha, A., Sood, S. K. & Bhatia, M. IoT-digital twin-inspired smart irrigation approach for optimal water utilization. Sustainable Computing: Inf. Syst. 41, 100947. https://doi.org/10.1016/j.suscom.2023.100947 (2024).
Benzaouia, M., Hajji, B., Mellit, A. & Rabhi, A. Fuzzy-IoT smart irrigation system for precision scheduling and monitoring. Comput. Electron. Agric. 215, 108407. https://doi.org/10.1016/j.compag.2023.108407 (2023).
Togneri, R., Prati, R., Nagano, H. & Kamienski, C. Data-driven water need Estimation for IoT-based smart irrigation: A survey. Expert Syst. Appl. 225, 120194. https://doi.org/10.1016/j.eswa.2023.120194 (2023).
Parvathi Sangeetha, B. et al. IOT based smart irrigation management system for environmental sustainability in India. Sustain. Energy Technol. Assess. 52, 101973. https://doi.org/10.1016/j.seta.2022.101973 (2022).
Muthuramalingam, R., Rathnam Velu, R. & Baskar, H. M.H. Vellan Saminathan, An IoT-Based Smart Irrigation System, Engineering Proceedings 66 13. (2024). https://doi.org/10.3390/engproc2024066013
Khan, A. I., Alsolami, F., Alqurashi, F., Abushark, Y. B. & Sarker, I. H. Novel energy management scheme in IoT enabled smart irrigation system using optimized intelligence methods. Eng. Appl. Artif. Intell. 114, 104996. https://doi.org/10.1016/j.engappai.2022.104996 (2022).
Di Gennaro, S. F., Cini, D., Berton, A. & Matese, A. Development of a low-cost smart irrigation system for sustainable water management in the mediterranean region. Smart Agricultural Technol. 9, 100629. https://doi.org/10.1016/j.atech.2024.100629 (2024).
Qian, M., Qian, C., Xu, G., Tian, P. & Yu, W. Smart irrigation systems from Cyber–Physical perspective: state of Art and future directions. Future Internet. 16, 234. https://doi.org/10.3390/fi16070234 (2024).
Sankarasubramanian, P. Enhancing precision in agriculture: A smart predictive model for optimal sensor selection through IoT integration. Smart Agricultural Technol. 10, 100749. https://doi.org/10.1016/j.atech.2024.100749 (2025).
Md, R. A., Mamun, A. K., Ahmed, S. M., Upoma, M. M. & Haque, M. Ashik-E-Rabbani, IoT-Enabled Solar-Powered smart irrigation for precision agriculture. Smart Agricultural Technol. 100773. https://doi.org/10.1016/j.atech.2025.100773 (2025).
Kumar, V. et al. A comprehensive review on smart and sustainable agriculture using IoT technologies. Smart Agricultural Technol. 8, 100487. https://doi.org/10.1016/j.atech.2024.100487 (2024).
Thomopoulos, V., Tolis, F., Blounas, T. F., Tsipianitis, D. & Kavga, A. Application of fuzzy logic and IoT in a small-scale smart greenhouse system. Smart Agricultural Technol. 8, 100446. https://doi.org/10.1016/j.atech.2024.100446 (2024).
Kumar, V. et al. Evaluation of IoT based smart drip irrigation and etc based system for sweet corn. Smart Agricultural Technol. 5, 100248. https://doi.org/10.1016/j.atech.2023.100248 (2023).
Gebresenbet, G. et al. A concept for application of integrated digital technologies to enhance future smart agricultural systems. Smart Agricultural Technol. 5, 100255. https://doi.org/10.1016/j.atech.2023.100255 (2023).
Choudhary, V., Machavaram, R., Singh, N. & Nagar, H. Assessment of sensor-based automatic smart watering unit for paddy nurseries under Indian perspective. Smart Agricultural Technol. 8, 100518. https://doi.org/10.1016/j.atech.2024.100518 (2024).
Veerachamy, R., Ramar, R., Balaji, S. & Sharmila, L. Autonomous application controls on smart irrigation. Comput. Electr. Eng. 100, 107855. https://doi.org/10.1016/j.compeleceng.2022.107855 (2022).
Al-Ali, A. R. et al. IoT-solar energy powered smart farm irrigation system. J. Electron. Sci. Technol. 17, 100017. https://doi.org/10.1016/j.jnlest.2020.100017 (2019).
Galaverni, M. et al. An IoT-based data analysis system: A case study on tomato cultivation under different irrigation regimes. Comput. Electron. Agric. 229, 109660. https://doi.org/10.1016/j.compag.2024.109660 (2025).
Jamshidi, B. et al. Internet of things-based smart system for Apple orchards monitoring and management. Smart Agricultural Technol. 10, 100715. https://doi.org/10.1016/j.atech.2024.100715 (2025).
Pereira G. P., ChaariM.Z. & DarogeF. IoT-Enabled smart drip irrigation system using ESP32. IoT 4, 221–243. https://doi.org/10.3390/iot4030012 (2023).
Hoque, M. J., Islam, M. S. & Khaliluzzaman, M. A fuzzy Logic- and internet of Things-Based smart irrigation system. Eng. Proc. 58, 93. https://doi.org/10.3390/ecsa-10-16243 (2023).
Liu, X., Zhao, Z. & Rezaeipanah, A. Intelligent and automatic irrigation system based on internet of things using fuzzy control technology. Sci. Rep. 15, 14577. https://doi.org/10.1038/s41598-025-98137-2 (2025).
Hassan, E. S., Alharbi, A. A., Oshaba, A. S. & El-Emary, A. Enhancing smart irrigation efficiency: A new WSN-Based localization method for water conservation. Water 16, 672. https://doi.org/10.3390/w16050672 (2024).
Oukaira, A., Benelhaouare, A. Z., Kengne, E. & Lakhssassi, A. FPGA-Embedded smart monitoring system for irrigation decisions based on soil moisture and temperature sensors. Agronomy 11, 1881. https://doi.org/10.3390/agronomy11091881 (2021).
Kasera, R. K. & Acharjee, T. A comprehensive IoT edge based smart irrigation system for tomato cultivation. Internet Things. 28, 101356. https://doi.org/10.1016/j.iot.2024.101356 (2024).
Kaur, A., Bhatt, D. P. & Raja, L. Developing a hybrid irrigation system for smart agriculture using IoT sensors and machine learning in Sri Ganganagar, Rajasthan. J. Sens. 2024, 6676907. https://doi.org/10.1155/2024/6676907 (2024).
Adamo, T., Caivano, D., Colizzi, L., Dimauro, G. & Guerriero, E. Optimization of irrigation and fertigation in smart agriculture: an IoT-based micro-services framework. Smart Agricultural Technol. 11, 100885. https://doi.org/10.1016/j.atech.2025.100885 (2025).
Roy, S. & Chakraborty, R. S. Low-cost smart irrigation solution for efficient water use and requirement prediction. Comput. Electr. Eng. 125, 110420. https://doi.org/10.1016/j.compeleceng.2025.110420 (2025).
Bouarroudj, K., Babaa, F. & Touil, A. IoT-based monitoring and control for optimized plant growth in smart greenhouses using soil and hydroponic systems. Internet Things. 33, 101710. https://doi.org/10.1016/j.iot.2025.101710 (2025).
Bushnag, A. et al. Smart agriculture: IoT-Based smart irrigation with advanced fuzzy logic control. Expert Syst. Appl. 299, 130168. https://doi.org/10.1016/j.eswa.2025.130168 (2026).
Garg, M., Kumar, S. & Arya, V. Picture fuzzy novel score function and knowledge measure with application in IoT based smart irrigation system selection. SN Comput. Sci. 6, 866. https://doi.org/10.1007/s42979-025-04367-6 (2025).
arduino.cc/en/software/, (n.d.). https://www.arduino.cc/en/software/ (accessed January 6, 2026).
ThingsBoard & Cloud (eds), (n.d.). accessed January 6, (2026). https://thingsboard.cloud/.
Acknowledgement
The authors used generative AI tools to assist in grammar correction, clarity improvement, and refinement of language throughout this manuscript. All content was reviewed and validated by the authors to ensure accuracy, originality, and adherence to ethical standards.
Funding
This research received no external funding.
Author information
Authors and Affiliations
Contributions
**Abdennabi Morchid: ** Conceived and designed the experiments; Performed the experiments; Analyzed and interpreted the data; Contributed reagents; Materials; Analysis tools or Data; Writing – original draft.**Hassan Qjidaa: ** Analyzed and interpreted the data; Contributed reagents; Materials; Analysis tools or Data; Writing – review & editing.**Rachid El Alami: ** Analyzed and interpreted the data; Contributed reagents; Materials; Analysis tools or Data; Writing – review & editing.**Salah Mobayen: ** Analyzed and interpreted the data; Contributed reagents; Materials; Analysis tools or Data; Writing – review & editing.**Paweł Skruch: ** Analyzed and interpreted the data; Contributed reagents; Materials; Analysis tools or Data; Writing – review & editing.**Badre Bossoufi: ** Analyzed and interpreted the data; Contributed reagents; Materials; Analysis tools or Data; Writing – review & editing.
Corresponding authors
Ethics declarations
Competing interests
The authors declare no competing interests.
Additional information
Publisher’s note
Springer Nature remains neutral with regard to jurisdictional claims in published maps and institutional affiliations.
Supplementary Information
Below is the link to the electronic supplementary material.
Rights and permissions
Open Access This article is licensed under a Creative Commons Attribution-NonCommercial-NoDerivatives 4.0 International License, which permits any non-commercial use, sharing, distribution and reproduction in any medium or format, as long as you give appropriate credit to the original author(s) and the source, provide a link to the Creative Commons licence, and indicate if you modified the licensed material. You do not have permission under this licence to share adapted material derived from this article or parts of it. The images or other third party material in this article are included in the article’s Creative Commons licence, unless indicated otherwise in a credit line to the material. If material is not included in the article’s Creative Commons licence and your intended use is not permitted by statutory regulation or exceeds the permitted use, you will need to obtain permission directly from the copyright holder. To view a copy of this licence, visit http://creativecommons.org/licenses/by-nc-nd/4.0/.
About this article
Cite this article
Morchid, A., Qjidaa, H., Alami, R.E. et al. Smart irrigation-based internet of things and cloud computing technologies for sustainable farming. Sci Rep (2026). https://doi.org/10.1038/s41598-026-35810-0
Received:
Accepted:
Published:
DOI: https://doi.org/10.1038/s41598-026-35810-0