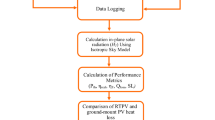
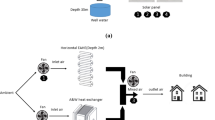
Abstract
The rising demand for air conditioning units driven by climate change underscores the importance of using sustainable energy sources, which help reduce greenhouse gas emissions and mitigate environmental impact. The present work focuses on the design and construction of a solar air conditioning system by integrating photovoltaic panels or solar thermal collectors to power the cooling cycle, providing a sustainable and eco-friendly alternative to conventional systems. A solar air conditioning unit entails the design, integration, and performance evaluation of a system that harnesses solar energy to provide space cooling. This study focuses on the design and construction of a solar air conditioning unit for cooling a defined space, with performance evaluated under varying solar radiation levels and panel tilt angles. Thermal comfort parameters and power factors were analyzed to determine the system’s overall efficiency. Experiments were carried out under Dubai’s climatic conditions by varying the incident solar radiation from 700 to 1400 W/m2 and adjusting the panel inclination angle between 15° and 25° which determined the performance parameters and the thermal comfort. The unit achieved maximum values for moisture removal rate, thermal efficiency, and solar coefficient of performance at 0.74 g/s, 95%, and 1.03, respectively. Power ratios were observed to decrease with increasing incident radiation. A solar panel tilt angle of 25° yielded the highest moisture removal rate 0.78 g/s, solar coefficient of performance 1.1, and solar direct consumption ratio 0.61. Thermal comfort parameters, including the Predicted Mean Vote (PMV) and Predicted Percentage of Dissatisfied (PPD), were calculated to be − 0.21 and 12.7%, respectively, both falling within acceptable comfort ranges.
Similar content being viewed by others
Data availability
The data that support the findings of this study are openly available in Mendeley Data at DOI: https://doi.org/10.17632/ggnpp9wt48.1.
Abbreviations
- SRRR:
-
Solar radiation reception rate
- PTSP:
-
Poly tilted segmented panel
- ISRPI:
-
Incident solar radiation presiction index
- DASH:
-
Dual angle solar harvest
- PMV:
-
Predicted mean vote
- PPD:
-
Predicted percentage of dissatisfied
- CON R:
-
Condenser power ratio
- COP:
-
Coefficient of performance
- CR:
-
Compressor power ratio
- DBT:
-
Dry bulb temperature (ᵒC)
- DC:
-
Direct current
- ER:
-
Evaporator power ratio
- SPV:
-
Solar photovoltaic
- PV:
-
Photovoltaic
- RH:
-
Relative humidity
- SDCR:
-
Solar direct consumed ratio
- SF:
-
Solar fraction
- VCR:
-
Vapor compression refrigeration
- WBT:
-
Wet bulb temperature (°C)
- \(\dot{W}\) :
-
Power supplied to the compressor (W)
- \(\dot{{m}_{a}}\) :
-
Mass flow rate of air (kg/s)
- \(\dot{{m}_{c}}\) :
-
Condensation rate (g/s)
- \({W}_{1}\) :
-
Specific humidity at the inlet (g/kg)
- \({W}_{2}\) :
-
Specific humidity at the outlet (g/kg)
- \({\dot{Q}}_{C}\) :
-
Cooling effect (Watts)
- Pbattery :
-
Power consumed by battery (Watts)
- \({\eta }_{Thermal}\) :
-
Thermal efficiency (%)
- \({\eta }_{Cooling}\) :
-
Cooling efficiency (%)
- I:
-
Incident radiation (W/m2)
- As :
-
Surface area of the collector (m2)
- \({COP}_{Solar}\) :
-
Solar COP
- \({\dot{W}}_{C}\) :
-
Power consumed by compressor (Watts)
- \({\dot{W}}_{e}\) :
-
Power consumed by evaporator (Watts)
- \({\dot{W}}_{con}\) :
-
Power consumed by condenser (Watts)
- M:
-
Metabolic rate (W/m2)
- H:
-
Sensitive heat loss (W/m2)
- W:
-
Mechanical power (W/m2)
- Ec :
-
Heat exchange due to evaporation of skin (W/m2)
- Cres :
-
Heat exchange by convection (W/m2)
- Eres :
-
Heat exchange by evaporation (W/m2)
- fcl :
-
Clothing surface area factor which is equal to 1
- tcl :
-
Clothing surface temperature, ⁰C
- tr :
-
Mean radiant temperature, ⁰C
- ta :
-
Ambient temperature, ⁰C
- RH:
-
Relative humidity , %
- Pv :
-
Vapor pressure, Pa
- Pa :
-
Water vapor partial pressure, Pa
- AF:
-
Angle factor
- V:
-
Air velocity in m/s.
- X:
-
Independent variable
- Y:
-
Uncertainty intervals
- G:
-
Uncertainty function
- YG :
-
Total uncertanity
- \(\frac{\partial (\dot{{m}_{W}})}{\dot{{m}_{W}}}\) :
-
Uncertainty of condensation rate
- \(\frac{\partial ({\eta }_{Thermal})}{{\eta }_{Thermal}}\) :
-
Uncertainty of thermal efficiency
- \(\frac{\partial (SDCR)}{SDCR}\) :
-
Uncertainty of solar direct consumed ratio
- \(\frac{\partial ({\eta }_{Cooling})}{{\eta }_{Cooling}}\) :
-
Uncertainty of cooling efficiency
- \(\frac{\partial (SF)}{SF}\) :
-
Uncertainty of solar fraction
- 1:
-
Inlet
- 2:
-
Outlet
- a:
-
Air
- c:
-
Cooling
- C:
-
Compressor
- Con:
-
Condenser
- e:
-
Expansion
- G:
-
Uncertainty
- v:
-
Vapor
- cl:
-
Cloth
- res:
-
Exchange
- s:
-
Surface
- r:
-
Radiant
References
Villarini, M., Tascioni, R., Arteconi, A. & Cioccolanti, L. Influence of the incident radiation on the energy performance of two small-scale solar organic Rankine cycle trigenerative systems: A simulation analysis. Appl. Energy. 242, 1176–1188 (2019).
Rubaiee, S. & Fazal, M. A. The influence of various solar radiations on the efficiency of a photovoltaic solar module integrated with a passive cooling system. Energies 15 (24), 9584 (2022).
Shaik, F., Lingala, S. S. & Veeraboina, P. Effect of various parameters on the performance of solar PV power plant: a review and the experimental study. Sustain. Energy Res. 10 (1), 6 (2023).
Nasrin, R., Hasanuzzaman, M. & Rahim, N. A. Effect of high irradiation on photovoltaic power and energy. Int. J. Energy Res. 42 (3), 1115–1131 (2018).
Mamun, M. A. A., Islam, M. M., Hasanuzzaman, M. & Selvaraj, J. Effect of Tilt angle on the performance and electrical parameters of a PV module: comparative indoor and outdoor experimental investigation. Energy Built Environ. 3 (3), 278–290 (2022).
Wardhana, A. S. J., Damarwan, E. S. & Hakim, M. L. The Effect of Inclination Angle of The Solar Panel on The Resulting Output Voltage. In Journal of Physics: Conference Series, vol. 2111, No. 1, 012053 (IOP Publishing, 2021).
Božiková, M. et al. The effect of azimuth and Tilt angle changes on the energy balance of photovoltaic system installed in the Southern Slovakia region. Appl. Sci. 11 (19), 8998 (2021).
Gholami, H. & Nils Røstvik, H. Dataset for the solar incident radiation and electricity production BIPV/BAPV system on the Northern/Southern façade in dense urban areas. Data 6 (6), 57 (2021).
Alqurashi, F., Nciri, R., Alghamdi, A., Ali, C. & Nasri, F. Control of the solar radiation reception rate (SRRR) using a novel Poly-Tilted segmented panel (PTSP) in the region of Makkah. Saudi Arabia Energies. 15 (7), 2357 (2022).
Khan, M. S., Ramli, M. A., Sindi, H. F., Hidayat, T. & Bouchekara, H. R. Estimation of solar radiation on a PV panel surface with an optimal Tilt angle using electric charged particles optimization. Electronics 11 (13), 2056 (2022).
Masili, M. & Ventura, L. Local tilt optimization of photovoltaic solar panels for maximum radiation absorption. Int. J. Photoenergy. 2019, 1–10 (2019).
Alqaed, S., Mustafa, J., Almehmadi, F. A. & Jamil, B. Estimation of ideal Tilt angle for solar-PV panel surfaces facing south: a case study for Najran City, Saudi Arabia. J. Therm. Anal. Calorim. 148 (16), 8641–8654 (2023).
Ferreira, A. C., Menezes, N., Teixeira, I. M., Teixeira, S. F. & Martins, L. A. Influence of typical meteorological years on the optimization of incident solar radiation for PV applications in Portugal. In International Conference on Electronic Engineering and Renewable Energy Systems, 925–932 (Springer Nature Singapore, 2022).
Wu, Z., Ren, Y. & Chen, L. Evaluating urban geometry impacts on incident solar radiation on building envelopes. Environ. Model. Assess. 26, 113–123 (2021).
Kafka, J. & Miller, M. A. The dual angle solar harvest (DASH) method: an alternative method for organizing large solar panel arrays that optimizes incident solar energy in conjunction with land use. Renew. Energy. 155, 531–546 (2020).
Sivakumar, B., Navakrishnan, S., Cibi, M. R. & Senthil, R. Experimental study on the electrical performance of a solar photovoltaic panel by water immersion. Environ. Sci. Pollut. Res. 28, 42981–42989 (2021).
Ganesan, K. et al. A new method for improving the solar photovoltaic unit efficiency through Neem oil as coolant medium for high power applications—an experimental investigation. Electr. Eng. 106 (5), 6251–6264 (2024).
Garni, A. The impact of soiling on PV module performance in Saudi Arabia. Energies 15 (21), 8033 (2022).
Hassan, M. K., Alqurashi, I. M., Salama, A. E. & Mohamed, A. F. Investigation the performance of PV solar cells in extremely hot environments. J. Umm Al-Qura Univ. Eng. Archit. 13 (1), 18–26 (2022).
Abdelgaied, M., Saber, M. A., Bassuoni, M. M. & Khaira, A. M. Performance improvement of solar-assisted air-conditioning systems by using an innovative configuration of a desiccant dehumidifier and thermal recovery unit. J. Therm. Anal. Calorim. 148 (14), 7003–7018 (2023).
Reda, A. M., Ali, A. H. H., Morsy, M. G. & Taha, I. S. Optimization and performance of a small scale adsorption cooling system fully powered by solar energy for hot arid areas. SN Appl. Sci. 1, 1–14 (2019).
Akyüz, A., Yıldırım, R., Gungor, A. & Tuncer, A. D. Experimental investigation of a solar-assisted air conditioning system: energy and life cycle climate performance analysis. Therm. Sci. Eng. Progr. 43, 101960 (2023).
Aguilar, F. J., Ruiz, J., Lucas, M. & Vicente, P. G. Performance analysis and optimisation of a solar on-grid air conditioner. Energies 14 (23), 8054 (2021).
Kaneesamkandi, Z. & Sayeed, A. Performance of solar hybrid cooling operated by solar compound parabolic collectors under weather conditions in Riyadh, Kingdom of Saudi Arabia. Appl. Sci. 13 (12), 7343 (2023).
Ayadi, O., Rinchi, B. & Alsaleem, F. Experimental evaluation of a solar-powered air conditioner. Sol. Energy. 272, 112466.
Zayed, M. E., Aboelmaaref, M. M. & Chazy, M. Design of solar air conditioning system integrated with photovoltaic panels and thermoelectric coolers: experimental analysis and machine learning modeling by random vector functional link coupled with white Whale optimization. Therm. Sci. Eng. Progr. 44, 102051 (2023).
Kumar, K. S. et al. Experimental investigation to enhancing the energy efficiency of a solar-powered Visi cooler. Sci. Rep. 15 (1), 18327 (2025).
Ali, K. A. M., Osman, Y. K. O. T., El-wahhab, G. G. A., Abdelwahab, T. A. M. & Fodah, A. E. M. Improving solar PV performance under bird-dropping conditions with a dual-cooling approach. Sci. Rep. 15 (1), 8211 (2025).
Salins, S. S., Reddy, S. K. & Kumar, S. Experimental investigation of the influence of vapor compression refrigeration in a multistage reciprocating dehumidifier test rig. Appl. Therm. Eng. 199, 117546 (2021).
Li, Y., Zhang, G., Lv, G. Z., Zhang, A. N. & Wang, R. Z. Performance study of a solar photovoltaic air conditioner in the hot summer and cold winter zone. Sol. Energy. 117, 167–179 (2015).
Huang, B. J. et al. Design of direct solar PV driven air conditioner. Renew. Energy. 88, 95–101 (2016).
Salins, S. S. et al. Performance characterization of an adaptive-controlled air handling unit to achieve thermal comfort in Dubai climate. Energy 273, 127186 (2023).
Kim, G. Y., Han, D. S. & Lee, Z. Solar panel Tilt angle optimization using machine learning model: a case study of Daegu City, South Korea. Energies 13 (3), 529 (2020).
Jafarkazemi, F. & Saadabadi, S. A. Optimum tilt angle and orientation of solar surfaces in Abu Dhabi, UAE. Renew. Energy 56, 44–49 (2013).
Sulaiman, A. Y. et al. A solar powered off-grid air conditioning system with natural refrigerant for residential buildings: A theoretical and experimental evaluation. Clean. Energy Syst. 5, 100077 (2023).
Alahmer, A., Wang, X. & Alam, K. A. Dynamic and economic investigation of a solar thermal-driven two-bed adsorption chiller under Perth Climatic conditions. Energies 13 (4), 1005 (2020).
Acknowledgements
This project work is carried out in the lab of School of Engineering and IT at MAHE Dubai.
Funding
Open access funding provided by Manipal Academy of Higher Education, Manipal. No funding was received for the above work.
Author information
Authors and Affiliations
Contributions
All authors have read and approved the final version of the manuscript. Sampath Suranjan Salins performed the experiments and data collection. Shiva Kumar analyzed the results and prepared the manuscript. Krishna Prasad did the validation.
Corresponding author
Ethics declarations
Competing interests
The authors declare no competing interests.
Additional information
Publisher’s note
Springer Nature remains neutral with regard to jurisdictional claims in published maps and institutional affiliations.
Rights and permissions
Open Access This article is licensed under a Creative Commons Attribution 4.0 International License, which permits use, sharing, adaptation, distribution and reproduction in any medium or format, as long as you give appropriate credit to the original author(s) and the source, provide a link to the Creative Commons licence, and indicate if changes were made. The images or other third party material in this article are included in the article’s Creative Commons licence, unless indicated otherwise in a credit line to the material. If material is not included in the article’s Creative Commons licence and your intended use is not permitted by statutory regulation or exceeds the permitted use, you will need to obtain permission directly from the copyright holder. To view a copy of this licence, visit http://creativecommons.org/licenses/by/4.0/.
About this article
Cite this article
Salins, S.S., Kumar, S. & Prasad, K. Sustainable cooling solutions in Dubai: the impact of incident radiation and panel angles on solar AC performance. Sci Rep (2026). https://doi.org/10.1038/s41598-026-36069-1
Received:
Accepted:
Published:
DOI: https://doi.org/10.1038/s41598-026-36069-1