Abstract
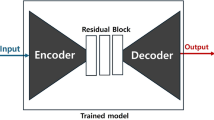
Real-time video enhancement on mobile devices is crucial for modern services like video calling, augmented reality, medical imaging, and surveillance. However, limited processing power, battery life, and memory limit the selection of video enhancement algorithms. Techniques aim to reduce noise, improve resolution, and enhance contrast, but their effectiveness depends on processing speed, visual quality, power consumption, and implementation complexity. Balancing these performance parameters is a challenge in real-time applications. Optimally selecting real-time video enhancement algorithms is very difficult and risky when using the classical model. Therefore, we develop a new decision-making model based on fuzzy neural networks with Sugeno-Weber norms. The proposed model selects a real-time video enhancement algorithm. The proposed model provides Deep Learning Super Resolution as an optimal real-time video enhancement algorithm. The decision results are verified based on well-known decision approaches to assess the accuracy of the comparison.
Similar content being viewed by others
Data availability
No datasets were generated or analysed during the current study. All data is available in this paper.
References
Mohammed, A. & Kora, R. A comprehensive review on ensemble deep learning: opportunities and challenges. J. King Saud Univ.-Comput. Inform. Sci. 35(2), 757–774 (2023).
Askin, S., Burkhalter, D., Calado, G., Dakrouni, E. & S Artificial intelligence applied to clinical trials: opportunities and challenges. Health Technol. 13 (2), 203–213 (2023).
Linka, K. & Kuhl, E. A new family of constitutive artificial neural networks towards automated model discovery. Comput. Methods Appl. Mech. Eng. 403, 115731 (2023).
Kasongo, S. M. A deep learning technique for intrusion detection system using a recurrent neural networks based framework. Comput. Commun. 199, 113–125 (2023).
Weiss, S. A. Chloride ion dysregulation in epileptogenic neuronal networks. Neurobiol. Dis. 177, 106000 (2023).
Zhang, X., Fu, J., Hua, S., Liang, H. & Zhang, Z. K. Complexity of government response to COVID-19 pandemic: a perspective of coupled dynamics on information heterogeneity and epidemic outbreak. Nonlinear Dyn. 111 (23), 22055–22074 (2023).
Grimm, D. et al. A numerical verification method for multi-class feed-forward neural networks. Exp. Syst. Appl. 247, 123345 (2024).
Nagarathna, C. R., Kusuma, M. & Seemanthini, K. Classifying the stages of alzheimer’s disease by using multi layer feed forward neural network. Proc. Comput. Sci. 218, 1845–1856 (2023).
Hiew, S. Y., Teoh, K. B., Raman, S. N., Kong, D. & Hafezolghorani, M. Prediction of ultimate conditions and stress–strain behaviour of steel-confined ultra-high-performance concrete using sequential deep feed-forward neural network modelling strategy. Eng. Struct. 277, 115447 (2023).
Sowparnika, B. et al. Innovative method for detecting liver cancer using auto encoder and single feed forward neural network. In 2023 2nd international conference on applied artificial intelligence and computing (ICAAIC) (pp. 156–161). IEEE. (2023).
Zadeh, L. A. Fuzzy sets. Inf. Control. 8 (3), 338–353 (1965).
Zadeh, L. A. The concept of a linguistic variable and its application to approximate reasoning—I. Inf. Sci. 8 (3), 199–249 (1975).
Ma, L. et al. A novel fuzzy neural network architecture search framework for defect recognition with uncertainties. IEEE Trans. Fuzzy Syst. 32 (5), 3274–3285 (2024).
Zhang, L., Shi, Y., Chang, Y. C. & Lin, C. T. Robust fuzzy neural network with an adaptive inference engine. IEEE Trans. Cybern. 54(5), 3275–3285 (2023).
Wu, S. et al. Quantum assisted hierarchical fuzzy neural network for image classification. IEEE Trans. Fuzzy Syst. (2024).
Tavakoli, M., Tajally, A., Ghanavati-Nejad, M. & Jolai, F. A Markovian-based fuzzy decision-making approach for the customer-based sustainable-resilient supplier selection problem. Soft. Comput. 27 (20), 15153–15184 (2023).
Kou, G. et al. Innovative solution suggestions for financing electric vehicle charging infrastructure investments with a novel artificial intelligence-based fuzzy decision-making modelling. Artif. Intell. Rev. 58(1), 16 (2024).
Vatankhah Ghadim, H., Tarafdar Hagh, M. & Ghassem Zadeh, S. Fermat-curve based fuzzy inference system for the fuzzy logic controller performance optimization in load frequency control application. Fuzzy Optim. Decis. Making. 22 (4), 555–586 (2023).
Abdrabo, K. I. et al. An integrated indicator-based approach for constructing an urban flood vulnerability index as an urban decision-making tool using the PCA and AHP techniques: A case study of Alexandria, Egypt. Urban Clim. 48, 101426 (2023).
Umutoni, L. & Samadi, V. Application of machine learning approaches in supporting irrigation decision making: A review. Agric. Water Manag. 294, 108710 (2024).
Patawari, A., Kumar, S. & Das, P. A modified iterative PINN algorithm for strongly coupled system of boundary layer originated convection diffusion reaction problems in MHD flows with analysis. Netw. Heterogen. Media 20(3), 1026–1060 (2025).
Patawari, A. & Das, P. From traditional to computationally efficient scientific computing algorithms in option pricing: Current progresses with future directions. Arch. Comput. Methods Eng. 85, 1–40 (2025).
Sabawi, Y. A., Santra, S., Das, P. Mohammad, N. A. H1 stability and convergence analysis of the L1/L1-2 legendre spectral method for non-local weakly singular integro-PDEs. Calcolo 62(4), 1–46 (2025).
Santra, S., Das, P. & Jorgensen, P. A unified multifaceted space-time wavelet framework and its singularity analysis for weakly singular non-local partial integro-differential equations in high dimensions. Acta Appl. Math. 200(1), 1–42 (2025).
Sarkar, A. et al. Sugeno-Weber triangular norm-based aggregation operators under T-spherical fuzzy hypersoft context. Inform Sci. 645, 119305 (2023).
Gul, R. & Sarfraz, M. Enhancing artificial intelligence models with Interval-Valued picture fuzzy sets and Sugeno-Weber triangular norms. Spectr. Eng. Manage. Sci. 3 (1), 126–146 (2025).
Rong, Y. & Wan, G. An integrated fermatean fuzzy group decision method based on sugeno-weber operators for the selection of reverse logistics supplier. Comput. Decis. Mak. Int. J. 2, 508–529 (2025).
Gong, X. et al. HSRoadNet: Hard-swish activation function and improved squeeze-excitation module network for road extraction using satellite remote sensing imagery. IEEE J. Select. Top. Appl. Earth Observ. Remote Sens. (2025).
Zhou, Y., MacPhee, C., Gunawan, W., Farahani, A. & Jalali, B. Real-time low-light video enhancement on smartphones. J. Real-Time Image Process. 21(5), 155 (2024).
Acknowledgements
The authors extend their appreciation to the Deanship of Research and Graduate Studies at King Khalid University for funding this work through Small Research Project under grant number RGP1/108/46.
Funding
The research is not supported by any institutions.
Author information
Authors and Affiliations
Contributions
All authors equally contributed to this manuscript.
Corresponding author
Ethics declarations
Competing interests
The authors declare no competing interests.
Ethical approval
N/A.
Additional information
Publisher’s note
Springer Nature remains neutral with regard to jurisdictional claims in published maps and institutional affiliations.
Rights and permissions
Open Access This article is licensed under a Creative Commons Attribution-NonCommercial-NoDerivatives 4.0 International License, which permits any non-commercial use, sharing, distribution and reproduction in any medium or format, as long as you give appropriate credit to the original author(s) and the source, provide a link to the Creative Commons licence, and indicate if you modified the licensed material. You do not have permission under this licence to share adapted material derived from this article or parts of it. The images or other third party material in this article are included in the article’s Creative Commons licence, unless indicated otherwise in a credit line to the material. If material is not included in the article’s Creative Commons licence and your intended use is not permitted by statutory regulation or exceeds the permitted use, you will need to obtain permission directly from the copyright holder. To view a copy of this licence, visit http://creativecommons.org/licenses/by-nc-nd/4.0/.
About this article
Cite this article
Khan, M., Rahman, M.I. & Ziar, R.A. A neural network framework for selecting real-time video enhancement algorithms on mobile devices. Sci Rep (2026). https://doi.org/10.1038/s41598-026-36099-9
Received:
Accepted:
Published:
DOI: https://doi.org/10.1038/s41598-026-36099-9