Abstract
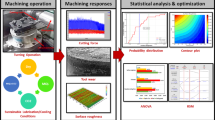
Hastelloy C276 is renowned for its exceptional resistance to corrosion and elevated temperatures, rendering it a preferred material for aerospace and chemical processing applications. However, its high strength and work-hardening tendency pose significant challenges during machining. This study systematically investigates the machinability of Hastelloy C276 under four sustainable lubrication and cooling environments—dry machining, minimum quantity lubrication (MQL), nano-enhanced MQL (NMQL), and cryogenic CO₂ (CCO₂). Experiments were designed using a Taguchi L16 orthogonal array, and the influence of cutting speed and feed rate on surface roughness, cutting force, tool wear, and cutting temperature was analysed using ANOVA. Compared to dry machining, cryogenic CO₂ cooling resulted in a reduction of surface roughness and cutting force by approximately 30–40%, along with a substantial decrease in tool wear and cutting temperature, whereas NMQL demonstrated moderate improvements due to enhanced lubrication at the tool–chip interface. ANOVA results revealed that feed rate and cutting speed were the most significant parameters, contributing up to 38.35% and 48.56% to variations in surface roughness and cutting temperature, respectively. To identify optimal machining conditions, Particle Swarm Optimization (PSO) and Teaching–Learning-Based Optimization (TLBO) algorithms were employed. Over 100 iterations, PSO achieved a higher optimization success rate of 83.6% compared to 79.1% for TLBO, while TLBO exhibited faster convergence with a computation time of 6.5 s against 9 s for PSO. The findings demonstrate that cryogenic CO₂-assisted machining combined with evolutionary optimization provides an effective and sustainable strategy for enhancing the machinability of Hastelloy C276.
Similar content being viewed by others
Data availability
Data supporting this study’s findings are available from the corresponding author upon reasonable request.
References
Aydın, K., Özlü, B. & Uğur, L. Investigation of machining performance of Ti6Al4V alloy in face milling process considering the energy consumption and carbon emission. Arab. J. Sci. Eng., 1–21. (2025).
Nas, E. & Kara, F. Optimization of EDM machinability of Hastelloy C22 super alloys. Machines 10 (12), 1131 (2022).
Hamıd, M. W. H., Özlü, B., Ulaş, H. B. & Demir, H. Prediction of cutting parameters and reduction of output parameters using machine learning in milling of inconel 718 alloy. Sci. Rep. 15 (1), 33309 (2025).
Akgün, M., Özlü, B. & Kara, F. Effect of PVD-TiN and CVD-Al2O3 coatings on cutting force, surface roughness, cutting power, and temperature in hard turning of AISI H13 steel. J. Mater. Eng. Perform. 32 (3), 1390–1401 (2023).
Arun, M. Experimental investigation on energy and exergy analysis of solar water heating system using zinc oxide-based nanofluid. Arab. J. Sci. Eng. 48 (3), 3977–3988 (2023).
Ramana, M. V. et al. Effect of machining conditions on shear angle in turning of A286 iron based nickel super alloy. Mater. Today Proc., 44, 2319–2324. (2021).
Arun, M. & Gopan, G. Effects of natural light on improving the lighting and energy efficiency of buildings: toward low energy consumption and CO2 emission. Int. J. Low-Carbon Technol. 20, 1047–1056 (2025).
Arun, M. Investigation of a deep learning-based waste recovery framework for sustainability and a clean environment using IoT. Sustainable Food Technol. 3 (2), 599–611 (2025).
Kara, F. Investigation of the effect of Al2O3 nanoparticle-added MQL lubricant on sustainable and clean manufacturing. Lubricants 12 (11), 393 (2024).
Özbek, N. A., Karadag, M. İ. & Özbek, O. Optimization of flank wear and surface roughness during turning of AISI 304 stainless steel using the Taguchi method. Mater. Test. 62 (9), 957–961 (2020).
Pandey, K. & Datta, S. Machinability Study of Inconel 825 Superalloy Under Nanofluid MQL: Application of Sunflower Oil as a Base Cutting Fluid with MWCNTs and nano-Al 2O3 as Additives 151 (Sustainable Manufacturing and Design, 2021).
Li, B. et al. Heat transfer performance of MQL grinding with different nanofluids for Ni-based alloys using vegetable oil. J. Clean. Prod. 154, 1–11 (2017).
Wu, Y. et al. In-situ EBSD study on twinning activity caused by deep cryogenic treatment (DCT) for an as-cast AZ31 Mg alloy. J. Mater. Res. Technol. 30, 3840–3850 (2024).
Özlü, B., Ulaş, H. B. & Kara, F. Investigation of the effects of cutting tool coatings and machining conditions on cutting force, specific energy consumption, surface roughness, cutting temperature, and tool wear in the milling of Ti6Al4V alloy. Lubricants 13 (8), 363 (2025).
Danish, M. et al. Thermal analysis during turning of AZ31 magnesium alloy under dry and cryogenic conditions. Int. J. Adv. Manuf. Technol. 91, 2855–2868 (2017).
Özbek, O. Evaluation of nano fluids with minimum quantity lubrication in turning of Ni-base Superalloy UDIMET 720. Lubricants 11 (4), 159 (2023).
Altan Özbek, N., Özbek, O., Kara, F. & Saruhan, H. Effect of eco-friendly minimum quantity lubrication in hard machining of Vanadis 10: a high strength steel. Steel Res. Int. 93 (7), 2100587 (2022).
Khan, M. M. A., Mithu, M. A. H. & Dhar, N. R. Effects of minimum quantity lubrication on turning AISI 9310 alloy steel using vegetable oil-based cutting fluid. J. Mater. Process. Technol. 209 (15–16), 5573–5583 (2009).
Kuram, E., Ozcelik, B., Bayramoglu, M., Demirbas, E. & Simsek, B. T. Optimization of cutting fluids and cutting parameters during end milling by using D-optimal design of experiments. J. Clean. Prod. 42, 159–166 (2013).
Debnath, S., Reddy, M. M. & Yi, Q. S. Environmental friendly cutting fluids and cooling techniques in machining: a review. J. Clean. Prod. 83, 33–47 (2014).
Wang, Y. et al. Experimental evaluation of the lubrication properties of the wheel/workpiece interface in minimum quantity lubrication (MQL) grinding using different types of vegetable oils. J. Clean. Prod. 127, 487–499 (2016).
Mia, M., Gupta, M. K., Singh, G., Królczyk, G. & Pimenov, D. Y. An approach to cleaner production for machining hardened steel using different cooling-lubrication conditions. J. Clean. Prod. 187, 1069–1081 (2018).
Krämer, A., Klocke, F., Sangermann, H. & Lung, D. Influence of the lubricoolant strategy on thermo-mechanical tool load. CIRP J. Manufact. Sci. Technol. 7 (1), 40–47 (2014).
Kishore, K., Chauhan, S. R. & Sinha, M. K. Application of machine learning techniques in environmentally benign surface grinding of inconel 625. Tribol. Int. 188, 108812 (2023).
Dhananchezian, M. & Kumar, M. P. Cryogenic turning of the Ti–6Al–4V alloy with modified cutting tool inserts. Cryogenics 51 (1), 34–40 (2011).
Al-Ghamdi, K. A., Iqbal, A. & Hussain, G. Machinability comparison of AISI 4340 and Ti-6Al-4V under cryogenic and hybrid cooling environments: A knowledge engineering approach. Proc. Institution Mech. Eng. Part. B: J. Eng. Manuf. 229 (12), 2144–2164 (2015).
Shokrani, A., Dhokia, V. & Newman, S. T. Investigation of the effects of cryogenic machining on surface integrity in CNC end milling of Ti–6Al–4V titanium alloy. J. Manuf. Process. 21, 172–179 (2016).
Iqbal, A. et al. Sustainable milling of Ti-6Al-4V: investigating the effects of milling orientation, cutter′ s helix angle, and type of cryogenic coolant. Metals 10 (2), 258 (2020).
Schoop, J., Sales, W. F. & Jawahir, I. S. High speed cryogenic finish machining of Ti-6Al4V with polycrystalline diamond tools. J. Mater. Process. Technol. 250, 1–8 (2017).
Sadik, M. I. & Isakson, S. The role of PVD coating and coolant nature in wear development and tool performance in cryogenic and wet milling of Ti-6Al-4V. Wear 386, 204–210 (2017).
Bordin, A., Sartori, S., Bruschi, S. & Ghiotti, A. Experimental investigation on the feasibility of dry and cryogenic machining as sustainable strategies when turning Ti6Al4V produced by additive manufacturing. J. Clean. Prod. 142, 4142–4151 (2017).
Danish, M. et al. Machinability investigations on CFRP composites: a comparison between sustainable cooling conditions. Int. J. Adv. Manuf. Technol. 114, 3201–3216 (2021).
Sharma, P., Kishore, K., Singh, V. & Sinha, M. K. Optimization of process parameters for better surface morphology of electrical discharge machining-processed inconel 825 using hybrid response surface methodology-desirability function and multi-objective genetic algorithm approaches. J. Mater. Eng. Perform., 1–17. (2023).
Sinha, M. K., Kishore, K. & Kumar, R. Archana, Hybrid approach for modelling and optimizing MQL grinding of inconel 625 with machine learning and MCDM techniques. Int. J. Interact. Des. Manuf. (IJIDeM), 1–17. (2024).
Pan, F., Zhang, Q., Liu, J., Li, W. & Gao, Q. Consensus analysis for a class of stochastic PSO algorithm. Appl. Soft Comput. 23, 567–578 (2014).
Li, G., Niu, P., Zhang, W. & Liu, Y. Model nox emissions by least squares support vector machine with tuning based on ameliorated teaching–learning-based optimization. Chemometr. Intell. Lab. Syst. 126, 11–20 (2013).
Yu, K., Wang, X. & Wang, Z. Self-adaptive multi-objective teaching-learning-based optimization and its application in ethylene cracking furnace operation optimization. Chemometr. Intell. Lab. Syst. 146, 198–210 (2015).
Chen, D., Zou, F., Li, Z., Wang, J. & Li, S. An improved teaching–learning-based optimization algorithm for solving global optimization problem. Inf. Sci. 297, 171–190 (2015).
Rao, R. V., Savsani, V. J. & Vakharia, D. P. Teaching–learning-based optimization: a novel method for constrained mechanical design optimization problems. Comput. Aided Des. 43 (3), 303–315 (2011).
Rao, R. V., Savsani, V. J. & Vakharia, D. P. Teaching–learning-based optimization: an optimization method for continuous non-linear large scale problems. Inf. Sci. 183 (1), 1–15 (2012).
Zou, F., Chen, D. & Xu, Q. A survey of teaching–learning-based optimization. Neurocomputing 335, 366–383 (2019).
Akhlaghi, M. Optimization of the plasmonic nano-rods-based absorption coefficient using TLBO algorithm. Optik 126 (24), 5033–5037 (2015).
Kennedy, J. & Eberhart, R. Particle swarm optimization. In Proceedings of ICNN’95-international conference on neural networks (Vol. 4, pp. 1942–1948). IEEE. (1995).
Jain, M., Saihjpal, V., Singh, N. & Singh, S. B. An overview of variants and advancements of PSO algorithm. Appl. Sci. 12 (17), 8392 (2022).
Jewell, W. T., Ramakumar, R. & Hill, S. R. A study of dispersed photovoltaic generation on the PSO system. IEEE Trans. Energy Convers. 3 (3), 473–478 (1988).
Soepangkat, B. O. P., Norcahyo, R., Effendi, M. K. & Pramujati, B. Multi-response optimization of carbon fiber reinforced polymer (CFRP) drilling using back propagation neural network-particle swarm optimization (BPNN-PSO). Eng. Sci. Technol. Int. J. 23 (3), 700–713 (2020).
Habeeb, H. H., Abou-El-Hossein, K. A., Mohammad, B. & Kadirgama, K. Effect of tool holder geometry and cutting condition when milling nickel-based alloy 242. J. Mater. Process. Technol. 201 (1–3), 483–485 (2008).
Ezugwu, E. O., Wang, Z. M. & Machado, A. R. The machinability of nickel-based alloys: a review. J. Mater. Process. Technol. 86 (1–3), 1–16 (1999).
Wu, Q., Zhou, X. & Pan, X. Cutting tool wear monitoring in milling processes by integrating deep residual convolution network and gated recurrent unit with an attention mechanism. Proceedings of the Institution of Mechanical Engineers, Part B: J. Eng. Manufact., 237(8), 1171–1181. (2023).
Zhang, F. et al. Data-driven and knowledge-guided prediction model of milling tool life grade. Int. J. Comput. Integr. Manuf. 37 (6), 669–684 (2024).
Özlü, B., Demir, H. & Nas, E. CNC Tornalama işleminde yüzey pürüzlülüğü ve Kesme Kuvvetlerine Etki Eden parametrelerin matematiksel Olarak modellenmesi. İleri Teknoloji Bilimleri Dergisi. 3 (2), 75–86 (2014).
Özlü, B. & Akgün, M. Evaluation of the machinability performance of PH 13 – 8 mo Maraging steel used in the aerospace industry. Proc. Institution Mech. Eng. Part. E: J. Process. Mech. Eng. 238 (2), 687–699 (2024).
Nas, E. & Özlü, B. Experimental and Statistical Investigation of the Effect of Input Parameters on Output Parameters in Laser Cutting of Stainless Steel Material (Ironmaking & Steelmaking, 2025).
Yıldırım, Ç. V., Sarıkaya, M., Kıvak, T. & Şirin, Ş. The effect of addition of hBN nanoparticles to nanofluid-MQL on tool wear patterns, tool life, roughness and temperature in turning of Ni-based inconel 625. Tribol. Int. 134, 443–456 (2019).
Author information
Authors and Affiliations
Contributions
M. M. Abualhaj and K. D. Parmar wrote the main manuscript text. B. Venkatesh, Akanksha Mishra, and Abinash Mahapatro contributed to data collection and analysis. Arunkumar D. T., Ripendeep Singh, and V. K. Bupesh Raja prepared figures and assisted with manuscript editing. Abhijit Bhowmik provided supervision and critical revisions. Yalew Tamene conceived the study, coordinated the project, and finalized the manuscript. All authors reviewed and approved the final version of the manuscript.
Corresponding author
Ethics declarations
Competing interests
The authors declare no competing interests.
Consent for publication
All authors have given their consent for the publication of this manuscript.
Additional information
Publisher’s note
Springer Nature remains neutral with regard to jurisdictional claims in published maps and institutional affiliations.
Rights and permissions
Open Access This article is licensed under a Creative Commons Attribution-NonCommercial-NoDerivatives 4.0 International License, which permits any non-commercial use, sharing, distribution and reproduction in any medium or format, as long as you give appropriate credit to the original author(s) and the source, provide a link to the Creative Commons licence, and indicate if you modified the licensed material. You do not have permission under this licence to share adapted material derived from this article or parts of it. The images or other third party material in this article are included in the article’s Creative Commons licence, unless indicated otherwise in a credit line to the material. If material is not included in the article’s Creative Commons licence and your intended use is not permitted by statutory regulation or exceeds the permitted use, you will need to obtain permission directly from the copyright holder. To view a copy of this licence, visit http://creativecommons.org/licenses/by-nc-nd/4.0/.
About this article
Cite this article
Abualhaj, M.M., Venkatesh, B., Parmar, K.D. et al. Data-driven optimization of machining parameters for Hastelloy C276 using PSO and TLBO frameworks. Sci Rep (2026). https://doi.org/10.1038/s41598-026-36275-x
Received:
Accepted:
Published:
DOI: https://doi.org/10.1038/s41598-026-36275-x