Abstract
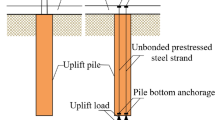
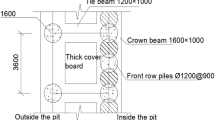
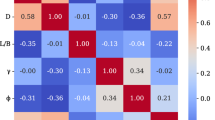
The soil squeezing effect of pile groups may cause displacements and deformation at the pile tops and ground surface around piles. In severe cases, it can cause problems such as broken piles, cracking of adjacent buildings or cracking of pipes. Artificial intelligence provides a new way to predict horizontal displacements of the pile tops and ground surface around piles caused by soil squeezing effect. The adaptive boosting (AdaBoost) algorithm was applied to the back propagation (BP) neural network model to form the Adaboost-BP model, which improved the learning ability of the BP neural network. For small sample datasets, the prediction accuracy of AdaBoost-BP model, Random Forest (RF) model and Deep Neural Networks (DNN) model is higher than that of BP model. For large sample datasets, the prediction accuracy of various models has improved, but the BP model is lower than that of other models. Analysis shows that the horizontal distance and angle between the center of the bearing platform and the center of the pile tops (or ground surface monitoring points) are the two most important influencing factors. The resting time is also an important influencing factor. Moisture content, relative density, and internal friction angle have a more significant influence on the horizontal displacements of the pile tops and ground surface around piles than other soil property indexes. Quantile regression analysis shows that the horizontal displacements is negatively correlated with the horizontal distance, and positively correlated with the rest time and moisture content. The prediction accuracy of machine learning algorithms (such as DNN) is higher than that of the cylindrical hole expansion method.
Similar content being viewed by others
Data availability
The sequence data supporting the results of this study can be obtained from the corresponding author.
References
Tan, N. & Bengt, H. F. Bidirectional static loading tests on barrette piles. A case history from Ho Chi Minh City, Vietnam. Canadian Geotechnical Journal 61(5), 872–884 (2024).
Pang, L., Jiang, C., Zeng, F. & Zhang, C. Cyclic response of long flexible piles in sands incorporating the cavity expansion/contraction theory. Ocean Eng. 310, 13 (2024).
Bellet, M., Keumo, T. J. & Zhang, Y. The inherent strain method for simulation of additive manufacturing–A critical assessment based on a new variant of the method. Int. J. Numer. Meth. Eng. 125(2), 7378 (2024).
Chen, S. L. & Abousleiman, Y. N. A graphical analysis-based method for undrained cylindrical cavity expansion in modified cam clay soil. Geotech.: Int. J. Soil Mech. 73(8), 736–746 (2022).
Gao, Z. & Shi, J. Theoretical solutions of soil-squeezing effect due to pile jacking considering geometrical characteristics of a pile. J. Geotech. Eng. 32(6), 956–962 (2010).
Liu, Y. H., Chen, Z. Z., Peng, Z. J., Gao, Y. S. & Gao, P. Analysis of pile driving effect of precast tubular pile using cylindrical cavity expansion theory. Rock and Soil Mechanics 28(10), 2167–2172 (2007).
Hight, D. W. & Bishop, A. W. The value of poisson’s ratio in saturated soils and rocks stressed under undrained conditions. Géotechnique 27(3), 369–384 (2015).
Lu, Q., Gong, X. N., Cui, W. W., Zhang, K. P. & Xu, M. H. Finite element analysis of compacting displacements of single jacked pile. Rock & Soil Mech. 28(11), 2426–2430. https://doi.org/10.1007/s11747-006-0011-3 (2007).
Luo, Z., Tao, Y., Gong, X. & Zou, B. Soil compacting displacements for two jacked piles considering shielding effects. Acta Geotech. 15(8), 2367–2377 (2020).
Shao, Y., Wang, S. & Guan, Y. Numerical simulation of soil squeezing effects of a jacked pipe pile in soft foundation soil and in foundation soil with an underlying gravel layer. Geotech. Geological Eng. 34(2), 493–499. https://doi.org/10.1007/s10706-015-9960-y (2016).
Zhou, H. & Shi, J. Test research on soil compacting effect of full scale jacked-in pile in saturated soft clay. Rock Soil Mech. 30(11), 3291–3296. https://doi.org/10.1016/S1874-8651(10)60073-7 (2009).
Zhang, S. & Zhang, X. Study on influencing factors of soil compaction effect of pipe pile in soft soil area. Front. Earth Sci. 12, 1495866 (2025).
Yuan, B. X., Li, Z., Zhao, Z., Ni, H. & Li, Z. Experimental study of displacement field of layered soils surrounding laterally loaded pile based on transparent soil. J. Soils Sediments 4, 1–12 (2021).
Yuan, B. X., Chen, R. R., Teng, J., Peng, T. & Feng, Z. W. Effect of passive pile on 3d ground deformation and on active pile response. Sci. World J. 2014, 1–6 (2014).
Mustafa, R. & Ahmad, M. T. Reliability analysis of pile foundation in cohesionless soil using machine learning techniques. Transportation Infrastructure Geotechnology 11(4), 2671–2699 (2024).
Al-Haddad, L. A., Fattah, M. Y., Al-Soudani, W. H. S., Al-Haddad, S. A. & Jaber, A. A. Enhanced load-settlement curve forecasts for open-ended pipe piles incorporating soil plug constraints using shallow and deep neural net-works. China Ocean Eng. 2025(3), 562–572 (2025).
Tran, T. H., Nguyen, B. P. & Tran, T. D. Machine learning applications in pile load capacity prediction: advanced analysis of pile driving forces and depths in urban ho chi minh city construction sites. Indian Geotech. J. 55(3), 1795–1800 (2025).
Ren, J. & Sun, X. Prediction of ultimate bearing capacity of pile foundation based on two optimization algorithm models. Buildings 13(5), 2075–5309 (2023).
Honarjoo, A. & Ghiasi, V. Analyzing analytical and software methods for deep foundation analysis and presenting a new solution for determining pile capacity using the pda test. Int. J. Geo-Eng. 16, 14 (2025).
Kordjazi, A., Nejad, F. P. & Jaksa, M. B. Prediction of ultimate axial load-carrying capacity of piles using a support vector machine based on CPT data. Comput. Geotech. 55, 91–102. https://doi.org/10.1016/j.compgeo.2013.08.001 (2014).
Shahin, M. A. Load–settlement modeling of axially loaded steel driven piles using CPT-based recurrent neural networks. Soils Found. 54(3), 515–522. https://doi.org/10.1016/j.sandf.2014.04.015 (2014).
Moayedi, H. & Hayati, S. Applicability of a cpt-based neural network solution in predicting load-settlement responses of bored pile. Int. J. Geomech. 18(6), 1943–1954 (2018).
Tan, N., Duy-Khuong, L., Jim, S. & Phi, N. D. Optimizing load-displacement prediction for bored piles with the 3mSOS algorithm and neural networks. Ocean Eng. 304, 117758. https://doi.org/10.1016/j.oceaneng.2024.117758 (2024).
Tan, N., Duy-Khuong, L., Thien, Q. H. & Thanh, T. N. Soft computing for determining base resistance of super-long piles in soft soil A coupled SPBO-XGBoost approach. Comput. Geotech. 162, 105707. https://doi.org/10.1016/j.compgeo.2023.105707 (2023).
Tram, B. N., Duy-Khuong, L., Tan, N. & Nguyen-Thoi, T. Sustainable foundation design, Hybrid TLBO-XGB model with confidence interval enhanced load–displacement prediction for PGPN piles. Adv. Eng. Inform. 65, 103288. https://doi.org/10.1016/j.aei.2025.103288 (2025).
Tram, B. N., Tan, N., Minh-The, N. Q. & Jim, S. Predicting load–displacement of driven PHC pipe piles using stacking ensemble with Pareto optimization. Eng. Struct. 316, 118574. https://doi.org/10.1016/j.engstruct.2024.118574 (2024).
Yuan, B. X. et al. Study on the interaction between pile and soil under lateral load in coral sand. Geomech. Energy Environ. 42, 100674 (2025).
Tiwari, M. K. & Chatterjee, C. Uncertainty assessment and en-semble flood forecasting using Boostrap based Artificial Neurial Networks. J. Hydrol. 382, 20–33 (2010).
Guo, S. L., Zheng, D. J., Zhao, L. H. & Liu, X. K. ANN-AdaBoost model for the strength-weakening coefficient of soft clay in port engineering. Sadhana, Academy Proceed. Eng. Sci. 48(4), 234. https://doi.org/10.1007/s12046-023-02276-z (2023).
Lin, E., Lin, C. & Lane, H. Y. Prediction of functional outcomes of schizophrenia with genetic biomarkers using a bagging ensemble machine learning method with feature selection. Sci. Rep. 11, 10179 (2021).
Huang, G., Liu, Z., Maaten, L. V. D. & Weinberger, K. Q. Densely connected convolutional networks. IEEE Comput. Soc. 7, 4700–4708. https://doi.org/10.1109/CVPR.2017.243 (2016).
Zhang, C., Lv, W. C., Guo, Z. C., Liu, Y. & Xie, S. C. An optimized combined prediction model for surface subsidence based on GA-KF and BP-Adaboost. J. Geodesy Geodynamics 43(2), 203–208 (2023).
He, Q. P., Si, Y. B. & Li S. Y. Settlement prediction of high-speed railway subgrade based on MIDBO-BP-Adaboost. Journal of beijing jiaotong university 49(3) (2025).
Wang, Z. Parameter optimization and state evaluation of basketball teaching based on BPNN. Mobile Inform. Syst. 2022, 1. https://doi.org/10.1155/2022/4327356 (2022).
Deng, J., Gu, D., Li, X. & Zhong, Q. Structural reliability analysis for implicit performance functions using artificial neural network. Struct. Saf. 27(1), 25–48. https://doi.org/10.1016/j.strusafe.2004.03.004 (2014).
Murmu, S. et al. Identification of potent phytochemicals against magnaporthe oryzae through machine learning aided-virtual screening and molecular dynamics simulation approach. Comput. Biol. Med. 188, 109862 (2025).
Chen, X., Ding, H., Fang, S. & Chen, W. Predicting the success of internet social welfare crowdfunding based on text information. Appl. Sci. 12(3), 1572. https://doi.org/10.3390/app12031572 (2022).
Khandel, O. & Soliman, M. Integrated framework for assessment of time-variant flood fragility of bridges using deep learning neural networks. J. Infrastruct. Syst. 27(1), 1943–1955. https://doi.org/10.1061/(ASCE)IS.1943-555X.0000587 (2021).
Mohammad, A. et al. Hybrid deep neural network optimization with particle swarm and grey wolf algorithms for sunburst attack detection. Computers 14(3), 107–107. https://doi.org/10.3390/COMPUTERS14030107 (2025).
Li, J., Zhang, Y., Chen, H. & Liang, F. Analytical solutions of spherical cavity expansion near a slope due to pile installation. J. Appl. Math. 2013(4), 1–11 (2013).
Funding
This work was financially supported by the Major Science and Technology Research and Development Project of China Harbour Engineering Co., Ltd. in 2023 (METRO1-CS-E-230407), and Tianjin Technology Innovation Guidance Special Fund (23YDTPJC00110).
Author information
Authors and Affiliations
Contributions
(Corresponding Author)Shaolong Guo: Conceptualization, Methodology, Software, Investigation, Formal Analysis, Writing Original Draft; Penglin Li: Data Curation, Writing—Original Draft; Manman Liang: Visualization, Investigation, Software, Validation; Qun Lu: Visualization, Writing—Review & Editing.
Corresponding author
Ethics declarations
Competing interests
The authors declare no competing interests.
Additional information
Publisher’s note
Springer Nature remains neutral with regard to jurisdictional claims in published maps and institutional affiliations.
Rights and permissions
Open Access This article is licensed under a Creative Commons Attribution-NonCommercial-NoDerivatives 4.0 International License, which permits any non-commercial use, sharing, distribution and reproduction in any medium or format, as long as you give appropriate credit to the original author(s) and the source, provide a link to the Creative Commons licence, and indicate if you modified the licensed material. You do not have permission under this licence to share adapted material derived from this article or parts of it. The images or other third party material in this article are included in the article’s Creative Commons licence, unless indicated otherwise in a credit line to the material. If material is not included in the article’s Creative Commons licence and your intended use is not permitted by statutory regulation or exceeds the permitted use, you will need to obtain permission directly from the copyright holder. To view a copy of this licence, visit http://creativecommons.org/licenses/by-nc-nd/4.0/.
About this article
Cite this article
Li, P., Guo, S., Liang, M. et al. Prediction of the displacements of the pile tops and ground surface around piles based on machine learning algorithms. Sci Rep (2026). https://doi.org/10.1038/s41598-026-36502-5
Received:
Accepted:
Published:
DOI: https://doi.org/10.1038/s41598-026-36502-5