Abstract
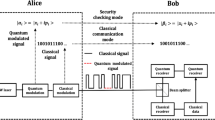
Current quantum audio watermarking schemes prioritize robustness but often overlook critical security vulnerabilities, leaving systems exposed to impersonation and unauthorized use. To address this gap, we propose a dual-security mechanism that synergistically integrates joint verification and certification of watermarks, inspired by the paging seal principle. Our framework incorporates Quantum Error Correction (QEC) coding to enhance resilience against qubit errors and malicious tampering. Experimental results show improved performance: the watermark maintains high imperceptible with SNR> 46 dB under increased embedding rates, and achieves a 62.5% reduction in average BER compared to several state-of-the-art methods at a qubit error probability of 0.10. These results suggest that the proposed approach offers enhanced security and robustness, representing a promising direction for secure quantum audio watermarking.
Similar content being viewed by others
Data availibility
The watermark image (MPU logo) is provided in Supplementary Figure S1. All simulation-generated data (processed audio and performance metrics) are included within this article and its supplementary materials. The MATLAB implementation code and original digital audio files used in experiments are permanently archived in Zenodo (DOI: 10.5281/zenodo.18072766).
References
Khan, T. M. & Robles-Kelly, A. Machine learning: Quantum vs classical. IEEE Access8, 219275–219294 (2020).
Maheshwari, D., Garcia-Zapirain, B. & Sierra-Sosa, D. Quantum machine learning applications in the biomedical domain: A systematic review. IEEE Access10, 80463–80484 (2022).
Fallahi, S. & Taghadosi, M. Quantum-behaved particle swarm optimization based on solitons. Sci. Rep.12, 13977 (2022).
Allende, M. et al. Quantum-resistance in blockchain networks. Sci. Rep.13, 5664 (2023).
Wang, Q., Wang, D., Cheng, C. & He, D. Quantum2fa: efficient quantum-resistant two-factor authentication scheme for mobile devices. IEEE Trans. Depend. Secur. Comput.20(1), 193–208 (2021).
Oliveiray, D. et al. A systematic methodology to compute the quantum vulnerability factors for quantum circuits. IEEE Trans. Depend. Secur. Comput.21(4), 2631–2644 (2023).
Yuan, X.-C., Pun, C.-M. & Chen, C. P. Robust mel-frequency cepstral coefficients feature detection and dual-tree complex wavelet transform for digital audio watermarking. Inf. Sci.298, 159–179 (2015).
Alzahrani, A. & Memon, N. A. Blind and robust watermarking scheme in hybrid domain for copyright protection of medical images. IEEE Access9, 113714–113734 (2021).
Shao, S. et al. Wfb: watermarking-based copyright protection framework for federated learning model via blockchain. Sci. Rep.14, 19453 (2024).
He, M., Wang, H., Zhang, F., Abdullahi, S. M. & Yang, L. Robust blind video watermarking against geometric deformations and online video sharing platform processing. IEEE Trans. Depend. Secur. Comput.20(6), 4702–4718 (2022).
Anand, A. & Singh, A. K. Dual watermarking for security of COVID-19 patient record. IEEE Trans. Depend. Secur. Comput.20, 859–866 (2022).
Wang, J. Qrda: quantum representation of digital audio. Int. J. Theor. Phys.55, 1622–1641 (2016).
Yan, F., Iliyasu, A. M., Guo, Y. & Yang, H. Flexible representation and manipulation of audio signals on quantum computers. Theor. Comput. Sci.752, 71–85 (2018).
Le, P. Q., Dong, F. & Hirota, K. A flexible representation of quantum images for polynomial preparation, image compression, and processing operations. Quantum Inf. Process.10, 63–84 (2011).
Chen, K., Yan, F., Iliyasu, A. M. & Zhao, J. Exploring the implementation of steganography protocols on quantum audio signals. Int. J. Theor. Phys57, 476–494 (2018).
Qu, Z.-G., He, H.-X. & Li, T. Novel quantum watermarking algorithm based on improved least significant qubit modification for quantum audio. Chin. Phys. B27, 010306 (2018).
Chen, K., Yan, F., Iliyasu, A. M. & Zhao, J. Dual quantum audio watermarking schemes based on quantum discrete cosine transform. Int. J. Theor. Phys.58, 502–521 (2019).
Chaharlang, J., Mosleh, M. & Rasouli-Heikalabad, S. A novel quantum steganography-steganalysis system for audio signals. Multimed. Tools Appl.79, 17551–17577 (2020).
Nejad, M. Y., Mosleh, M. & Heikalabad, S. R. A blind quantum audio watermarking based on quantum discrete cosine transform. J. Inf. Secur. Appl.55, 102495 (2020).
Nejad, M. Y., Mosleh, M. & Heikalabad, S. R. An lsb-based quantum audio watermarking using msb as arbiter. Int. J. Theor. Phys.58, 3828–3851 (2019).
Nejad, M. Y., Mosleh, M. & Heikalabad, S. R. An enhanced lsb-based quantum audio watermarking scheme for nano communication networks. Multimed. Tools Appl.79, 26489–26515 (2020).
Velayatipour, M., Mosleh, M., Nejad, M. Y. & Kheyrandish, M. Quantum reversible circuits for audio watermarking based on echo hiding technique. Quantum Inf. Process.21, 316 (2022).
Li, P., Wang, B., Xiao, H. & Liu, X. Quantum representation and basic operations of digital signals. Int. J. Theor. Phys.57, 3242–3270 (2018).
Jiang, N. & Wang, L. Quantum image scaling using nearest neighbor interpolation. Quantum Inf. Process.14, 1559–1571 (2015).
Sivak, V. et al. Real-time quantum error correction beyond break-even. Nature616, 50–55 (2023).
Bombin, H. et al. Logical blocks for fault-tolerant topological quantum computation. PRX Quantum4, 020303 (2023).
Chiaverini, J. et al. Realization of quantum error correction. Nature432, 602–605 (2004).
Devitt, S. J., Munro, W. J. & Nemoto, K. Quantum error correction for beginners. Rep. Prog. Phys.76, 076001 (2013).
Zhou, R.-G., Hu, W. & Fan, P. Quantum watermarking scheme through Arnold scrambling and lsb steganography. Quantum Inf. Process.16, 1–21 (2017).
Barenco, A. et al. Elementary gates for quantum computation. Phys. Rev. A52, 3457 (1995).
Nielsen, M. A. & Chuang, I. L. Quantum computation and quantum information. Phys. Today54, 60 (2001).
Yang, L., Yang, Y., Hasna, M. O. & Alouini, M.-S. Coverage, probability of snr gain, and dor analysis of ris-aided communication systems. IEEE Wirel. Commun. Lett.9, 1268–1272 (2020).
Nazar, A. W., Hassan, S. A., Jung, H., Mahmood, A. & Gidlund, M. Ber analysis of a backscatter communication system with non-orthogonal multiple access. IEEE Trans. Green Commun. Netw.5, 574–586 (2021).
Probst, D. Aiming beyond slight increases in accuracy. Nat. Rev. Chem.7, 227–228 (2023).
Hou, F. et al. Improved mask r-cnn with distance guided intersection over union for gpr signature detection and segmentation. Autom. Constr.121, 103414 (2021).
Weber, A. G. The usc-sipi image database: Version 5. http://sipi.usc.edu/database/ (2006).
Fisher, K. A. et al. Quantum computing on encrypted data. Nat. Commun.5, 3074 (2014).
Kuang, R. & Perepechaenko, M. Quantum encryption with quantum permutation pad in ibmq systems. EPJ Quantum Technol.9, 26 (2022).
Perepechaenko, M. & Kuang, R. Quantum encryption of superposition states with quantum permutation pad in ibm quantum computers. EPJ Quantum Technol.10, 7 (2023).
Xu, D. et al. Nested hash access with post quantum encryption for mission-critical iot communications. IEEE Internet Things J.10, 12204–12218 (2023).
Acknowledgements
This work was supported by the Project of Guangdong University Engineering Technology Center (No. 2022GCZX013), and Macao Polytechnic University under grant RP/FCA-04/2024.
Author information
Authors and Affiliations
Contributions
Z.X. conceived the methods and experiments, Z.X. and X.Y. conducted the experiments, Z.X. and CT.L. analysed the results. All authors wrote and reviewed the manuscript.
Corresponding author
Ethics declarations
Competing interests
The authors declare no competing interests.
Additional information
Publisher’s note
Springer Nature remains neutral with regard to jurisdictional claims in published maps and institutional affiliations.
Rights and permissions
Open Access This article is licensed under a Creative Commons Attribution 4.0 International License, which permits use, sharing, adaptation, distribution and reproduction in any medium or format, as long as you give appropriate credit to the original author(s) and the source, provide a link to the Creative Commons licence, and indicate if changes were made. The images or other third party material in this article are included in the article’s Creative Commons licence, unless indicated otherwise in a credit line to the material. If material is not included in the article’s Creative Commons licence and your intended use is not permitted by statutory regulation or exceeds the permitted use, you will need to obtain permission directly from the copyright holder. To view a copy of this licence, visit http://creativecommons.org/licenses/by/4.0/.
About this article
Cite this article
Xing, Z., Lam, CT. & Yuan, X. Enhancing quantum audio watermarking security through joint verification and certification. Sci Rep (2026). https://doi.org/10.1038/s41598-026-36535-w
Received:
Accepted:
Published:
DOI: https://doi.org/10.1038/s41598-026-36535-w