Abstract
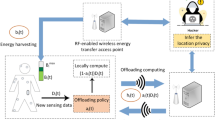
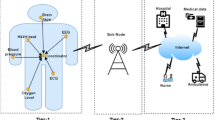
Reliable and continuous patient-environment monitoring is of great significance for the smart healthcare in hospitals, enabling proactive care and optimized clinical environments. However, the sustainable operation of wireless sensor nodes is critically challenged by energy shortage, which can interrupt data flows and lead to the loss of vital health information upon energy depletion. To address this, this work proposes a cooperative energy and data transfer framework for healthcare sensor networks. For wireless power transfer (WPT), a power beacon (PB) is selected either based on the best channel quality or randomly from multiple available PBs. Considering the limited amount of harvested energy at the sensor node, a set of relay nodes can be employed to assist in the data transmission from the sensor node to the access point (AP). We investigate an opportunistic decode-and-forward (DF) relaying strategy using two relay selection approaches: (1) selecting the relay node that provides the highest end-to-end achievable data rate, and (2) randomly selecting a relay node. With relay assistance, the transmission distance for sensor nodes can be shortened, thereby reducing energy consumption. Specifically, we properly model the sensor node’s nonlinear energy harvesting process and energy status, with channel fading characterized by the general Nakagami-m distribution. System outage probability is analyzed and minimized through numerically determining the WPT time, the sensor transmission time, and the location of relay nodes. Extensive simulations compare different PB and relay selection schemes and illustrate the impacts of key parameters on outage performance. The findings reveal that best relay selection contributes more substantially to system performance improvement than best PB selection. The proposed framework demonstrates the feasibility of building robust, energy-sustainable monitoring networks, which is a critical step toward realizing reliable and autonomous smart healthcare systems in hospital environments.
Similar content being viewed by others
Data Availability
The data that supports the findings of this study is available from the corresponding author upon reasonable request.
References
Yang, Y. et al. A review of IoT-enabled mobile healthcare: Technologies, challenges, and future trends. IEEE Internet Things J. 9, 9478–9502 (2022).
Kong, P.-Y. Cellular-assisted device-to-device communications for healthcare monitoring wireless body area networks. IEEE Sens. J. 20, 13139–13149 (2020).
Nia, A. M., Mozaffari-Kermani, M., Sur-Kolay, S., Raghunathan, A. & Jha, N. K. Energy-efficient long-term continuous personal health monitoring. IEEE Trans. Multi-Scale Comput. Syst. 1, 85–98 (2015).
Amjad, O., Bedeer, E., Ali, N. A. & Ikki, S. Robust energy efficiency optimization algorithm for health monitoring system with wireless body area networks. IEEE Commun. Lett. 24, 1142–1145 (2020).
Olatinwo, D. D., Abu-Mahfouz, A. M. & Hancke, G. P. Energy-aware hybrid MAC protocol for IoT enabled WBAN systems. IEEE Sens. J. 22, 2685–2699 (2022).
Velusamy, B. & Pushpan, S. C. An enhanced channel access method to mitigate the effect of interference among body sensor networks for smart healthcare. IEEE Sens. J. 19, 7082–7088 (2019).
Abbasi, U. F., Haider, N., Awang, A. & Khan, K. S. Cross-layer MAC/routing protocol for reliable communication in Internet of health things. IEEE Open J. Commun. Soc. 2, 199–216 (2021).
Fan, D., Ruiz, L. L., Gong, J. & Lach, J. EHDC: An energy harvesting modeling and profiling platform for body sensor networks. IEEE J. Biomed. Health Inform. 22, 33–39 (2018).
Tobola, A. et al. Self-powered multiparameter health sensor. IEEE J. Biomed. Health Inform. 22, 15–22 (2018).
Yoo, S. et al. Wireless power transfer and telemetry for implantable bioelectronics. Adv. Healthcare Mater. 10, 2100614 (2021).
Gong, W. et al. Embracing self-powered wearables for intelligent healthcare data management. IEEE Internet Things J. 11, 25674–25681 (2024).
Zhumayeva, M., Dautov, K., Hashmi, M. & Nauryzbayev, G. Wireless energy and information transfer in WBAN: A comprehensive state-of-the-art review. Alex. Eng. J. 85, 261–285 (2023).
Guo, W., Hou, Y., Gan, Y. & Guo, W. Efficient data transmission mechanisms in energy harvesting wireless body area networks: A survey. Comput. Netw. 254, 110769 (2024).
Liu, Z., Liu, B. & Chen, C. W. Joint power-rate-slot resource allocation in energy harvesting-powered wireless body area networks. IEEE Trans. Veh. Technol. 67, 12152–12164 (2018).
Mosavat-Jahromi, H., Maham, B. & Tsiftsis, T. A. Maximizing spectral efficiency for energy harvesting-aware WBAN. IEEE J. Biomed. Health Inform. 21, 732–742 (2017).
Ibarra, E., Antonopoulos, A., Kartsakli, E., Rodrigues, J. J. P. C. & Verikoukis, C. QoS-aware energy management in body sensor nodes powered by human energy harvesting. IEEE Sens. J. 16, 542–549 (2016).
Mohammadi, R. & Shirmohammadi, Z. Optimizing energy harvesting in wireless body area networks: A deep reinforcement learning approach to dynamic sampling. Alex. Eng. J. 109, 157–175 (2024).
Gao, Z. et al. Advanced energy harvesters and energy storage for powering wearable and implantable medical devices. Adv. Mater. 36, 2404492 (2024).
Shaw, T. et al. Metamaterial integrated highly efficient wireless power transfer system for implantable medical devices. Int. J. Electron. Commun. (AEÜ) 173, 155010 (2024).
Desai, N., Yoo, J. & Chandrakasan, A. P. A scalable, 2.9 mW, 1 Mb/s e-textiles body area network transceiver with remotely-powered nodes and bi-directional data communication. IEEE J. Solid-State Circuits 49, 1995–2004 (2014).
Yoo, J., Yan, L., Lee, S., Kim, Y. & Yoo, H.-J. A 5.2 mW self-configured wearable body sensor network controller and a 12 \(\mu\)W wirelessly powered sensor for a continuous health monitoring system. IEEE J. Solid-State Circuits 45, 178–188 (2010).
Toh, W. Y., Tan, Y. K., Koh, W. S. & Siek, L. Autonomous wearable sensor nodes with flexible energy harvesting. IEEE Sens. J. 14, 2299–2306 (2014).
Laneman, J. N., Tse, D. & Wornell, G. W. Cooperative diversity in wireless networks: Efficient protocols and outage behavior. IEEE Trans. Inf. Theory 50, 3062–3080 (2004).
Bletsas, A., Shin, H. & Win, M. Z. Cooperative communications with outage-optimal opportunistic relaying. IEEE Trans. Wireless Commun. 6, 3450–3460 (2007).
Zhou, X., Zhang, R. & Ho, C.-K. Wireless information and power transfer: Architecture design and rate-energy tradeoff. IEEE Trans. Commun. 61, 4754–4767 (2013).
Huang, K. & Lau, V. K. N. Enabling wireless power transfer in cellular networks: Architecture, modeling and deployment. IEEE Trans. Wireless Commun. 13, 902–912 (2014).
Boshkovska, E., Ng, D. W. K., Zlatanov, N., Koelpin, A. & Schober, R. Robust resource allocation for MIMO wireless powered communication networks based on a non-linear EH model. IEEE Trans. Commun. 65, 1984–1999 (2017).
Kosu, S., Babaei, M., Özgür Ata, S., Durak-Ata, L. & Yanikomeroglu, H. Linear/non-linear energy harvesting models via multi-antenna relay cooperation in V2V communications. IEEE Trans. Green Commun. Netw. 7, 1725–1738 (2023).
Nasir, A. A., Zhou, X., Durrani, S. & Kennedy, R. A. Relaying protocols for wireless energy harvesting and information processing. IEEE Trans. Wireless Commun. 12, 3622–3636 (2013).
Chen, Z., Cai, L. X., Cheng, Y. & Shan, H. Sustainable cooperative communication in wireless powered networks with energy harvesting relay. IEEE Trans. Wireless Commun. 16, 8175–8189 (2017).
Zhai, C., Zheng, L., Lan, P. & Chen, H. Wireless powered cooperative communication using two relays: Protocol design and performance analysis. IEEE Trans. Veh. Technology 67, 3598–3611 (2018).
Panse, V., Sharma, P. K., Jain, T. K. & Kothari, A. Relay selection and nonlinear energy harvesting in full-duplex multi-relay cooperative network. Phys. Commun. 56, 101946 (2023).
Zanella, A. et al. A general connectivity model for non-linear SWIPT systems with spatially randomly distributed relays. IEEE Trans. Commun. 73, 2088–2102 (2025).
He, Z. et al. Energy minimization for UAV-enabled wireless power transfer and relay networks. IEEE Internet Things J. 10, 19141–19152 (2023).
Yang, Z., Feng, L., Zhou, F., Qiu, X. & Li, W. Ergodic capacity analysis of IRS aided wireless-powered relay communication network. IEEE Trans. Cogn. Commun. Netw. 9, 1241–1256 (2023).
Ju, H. & Zhang, R. Throughput maximization in wireless powered communication networks. IEEE Trans. Wirel. Commun. 13, 418–428 (2014).
Simon, M. K. & Alouini, M. S. Digital Communication over Fading Channels, 2nd edition. John Wiley & Sons, Inc., (2005).
Gradshteyn, I. S. & Ryzhik, I. M. Talbe of Integrals, Series, and Products, 7th Edition. Academic Press, (2007).
Yu, J., Zhai, C., Yu, Z., Yang, Y. & Zheng, L. Nonlinear wireless energy harvesting based uplink transmission in K-tier heterogeneous networks over Nakagami-m fading channels. Alex. Eng. J. 88, 276–286 (2024).
Funding
No Funding.
Author information
Authors and Affiliations
Contributions
J. proposed the system model conception and presented the utilization scenario. C. improved the communication protocol, analyzed the performance and performed simulations. J. and C. wrote the main manuscript text. All authors reviewed the manuscript.
Corresponding author
Ethics declarations
Conflicts of Interest
The authors declare that they have no conflicts of interest.
Competing interests
The authors declare no competing interests.
Additional information
Publisher’s note
Springer Nature remains neutral with regard to jurisdictional claims in published maps and institutional affiliations.
Rights and permissions
Open Access This article is licensed under a Creative Commons Attribution-NonCommercial-NoDerivatives 4.0 International License, which permits any non-commercial use, sharing, distribution and reproduction in any medium or format, as long as you give appropriate credit to the original author(s) and the source, provide a link to the Creative Commons licence, and indicate if you modified the licensed material. You do not have permission under this licence to share adapted material derived from this article or parts of it. The images or other third party material in this article are included in the article’s Creative Commons licence, unless indicated otherwise in a credit line to the material. If material is not included in the article’s Creative Commons licence and your intended use is not permitted by statutory regulation or exceeds the permitted use, you will need to obtain permission directly from the copyright holder. To view a copy of this licence, visit http://creativecommons.org/licenses/by-nc-nd/4.0/.
About this article
Cite this article
Li, J., Zhai, C. Patient-environment monitoring for smart healthcare in hospitals with cooperative power-data transfer. Sci Rep (2026). https://doi.org/10.1038/s41598-026-36580-5
Received:
Accepted:
Published:
DOI: https://doi.org/10.1038/s41598-026-36580-5