Abstract
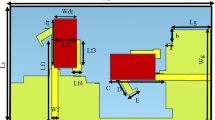
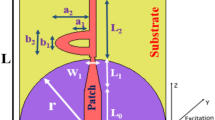
This paper discussed a frequency-dependent distributed beamforming technique to improve the reliability in implant multiple-input multiple-output (MIMO)-ultra wideband (UWB) communications. To realize distributed beamforming for implant MIMO-UWB systems, we propose an optimization method to theoretically determine the weight coefficients optimized for the implant UWB communication. To evaluate the performance improvement, the propagation characteristics of the implant channel in the low band UWB (3.4–4.8 GHz) were analyzed by the finite difference time domain (FDTD) method with a numerical human model. Subsequently, this study conducted computer simulations based on the derived propagation channel model. The evaluation results demonstrate that the proposed beamforming effectively improved the \(E_b/N_0\) performance by 5 dB in a capsule endoscopy scenario, compared to the conventional method, which can improve implantable medical devices in the future.
Similar content being viewed by others
Data availability
The datasets generated and/or analysed during the current study are not publicly available due to Patent restrictions, but are available from the corresponding author on reasonable request.
References
Li, H. B. & Kohno, R. Body Area Network and Its Standardization at IEEE 802.15.6 BAN (2008).
Wang, J. & Wang, Q. Body Area Communication (Wiley–IEEE, 2013).
Jhunjhunwala, V. K. et al. Flexible UWB and MIMO antennas for wireless body area network: A review. Sensors https://doi.org/10.3390/s22239549 (2022).
Xiao, C., Liang, Z. & Yang, J. Radiation characteristic analysis of antenna deeply implanted in human body and localization sensor array. IEEE Trans. Instrum. Meas. 71, 1–12. https://doi.org/10.1109/TIM.2022.3141723 (2022).
Yuce, M. R. & Dissanayake, T. Easy-to-swallow wireless telemetry. IEEE Microw. Mag. 13, 90–101. https://doi.org/10.1109/MMM.2012.2205832 (2012).
Yuce, M. R., Dissanayake, T. & Keong, H. C. Wireless telemetry for electronic pill technology. IEEE Sens. J. https://doi.org/10.1109/JSEN.2009.2032193 (2009).
Jung, J., Shin, S., Li, M. & Kim, Y. T. telemetry transmission to support bidirectional communication for capsule endoscope using human body communication. IEEE Microw. Wirel. Compon. Lett. 31, 905–908. https://doi.org/10.1109/LMWC.2021.3078089 (2021).
Jung, J., Li, M. & Kim, Y. T. Study on 13.56-MHz out-to-in body channel and its coexistence with human body communication for capsule endoscope. Microw. Opt. Technol. Lett. 63, 2819–2825. https://doi.org/10.1002/mop.32915 (2021).
Ministry of Internal Affairs and Communications. Current Situation of Spectrum Use in Japan. https://www.tele.soumu.go.jp/e/adm/freq/search/myuse/0002/index.htm (2025).
Ando, H. et al. Wireless multichannel neural recording with a 128-Mbps UWB transmitter for an implantable brain–machine interfaces. IEEE Trans. Biomed. Circuits Syst. 10, 1068–1078. https://doi.org/10.1109/TBCAS.2016.2514522 (2016).
Cheraghinia, M. et al. A comprehensive overview on UWB radar: Applications, standards, signal processing techniques, datasets, radio chips, trends and future research directions. IEEE Commun. Surv. Tutorials 27, 2283–2324. https://doi.org/10.1109/COMST.2024.3488173 (2024).
Anzai, D. et al. Experimental evaluation of implant UWB-IR transmission with living animal for body area network. IEEE Trans. Microw. Theory Tech. 62, 183–192. https://doi.org/10.1109/TMTT.2013.2292799 (2014).
Nagaraj, S. & Rassam, F. G. Improved noncoherent UWB receiver for implantable biomedical devices. IEEE Trans. Biomed. Eng. 63, 2220–2225. https://doi.org/10.1109/TBME.2015.2511538 (2016).
Shi, J., Anzai, D. & Wang, J. Channel modeling and performance analysis of diversity reception for implant UWB wireless link. IEICE Trans. Commun. E95–B, 3197–3205. https://doi.org/10.1587/transcom.E95.B.3197 (2012).
Takizawa, K., Aoyagi, T., Hamaguchi, K. & Kohno, R. Performance evaluation of wireless communications through capsule endoscope. In Annu. Int. Conf. IEEE Eng. Med. Biol. Soc. (EMBC), 6897–6900, https://doi.org/10.1109/IEMBS.2009.5334484 (2009).
Floor, P. A. et al. In-body to on-body ultrawideband propagation model derived from measurements in living animals. IEEE J. Biomed. Health Inform. 19, 938–948. https://doi.org/10.1109/JBHI.2015.2417805 (2015).
Särestöniemi, M., Pomalaza-Raez, C. & Iinatti, J. Radio channel study for colon capsule endoscopy with low-band UWB multiple antenna system. In 2022 IEEE 16th International Symposium on Medical Information and Communication Technology (ISMICT), 1–6, https://doi.org/10.1109/ISMICT56646.2022.9828189 (2022).
Shimizu, Y. et al. Performance evaluation of an ultra-wideband transmit diversity in a living animal experiment. IEEE Trans. Microw. Theory Tech. 65, 2596–2606. https://doi.org/10.1109/TMTT.2017.2652463 (2017).
Shimizu, Y., Furukawa, T., Anzai, D. & Wang, J. Performance improvement by transmit diversity technique for implant ultra-wideband communication. IET Microw. Antennas Propag. 10, 1106–1112. https://doi.org/10.1049/iet-map.2015.0663 (2016).
Li, R. & Guo, Y. A conformal UWB dual-polarized antenna for wireless capsule endoscope systems. IEEE Antennas Wirel. Propag. Lett. 20, 483–487. https://doi.org/10.1109/LAWP.2021.3054825 (2021).
Shang, J. & Yu, Y. An ultrawideband capsule antenna for biomedical applications. IEEE Antennas Wirel. Propag. Lett. 18, 2548–2551. https://doi.org/10.1109/LAWP.2019.2936664 (2019).
Prasad, R., Dixit, S., Nee, R. V. & Ojanpera, T. Globalization of Mobile and Wireless Communications: Today and in 2020 (Springer, 2011).
Barbarossa, S. & Scutari, G. Distributed space-time coding strategies for wideband multihop networks: regenerative vs. non-regenerative relays. In Proc. IEEE Int. Conf. Acoust., Speech, Signal Process. (ICASSP), 501–504, https://doi.org/10.1109/ICASSP.2004.1326347 (2004).
Jayaprakasam, S., Rahim, S. K. A. & Leow, C. Y. Distributed and collaborative beamforming in wireless sensor networks: Classifications, trends, and research directions. IEEE Commun. Surv. Tutor. 19, 2092–2116. https://doi.org/10.1109/COMST.2017.2728102 (2017).
Xu, X. et al. Power-efficient distributed beamforming for full-duplex MIMO relaying networks. IEEE Trans. Veh. Technol. 66, 1087–1103. https://doi.org/10.1109/TVT.2016.2580519 (2017).
Prananta, N., Hara, S. & Hara, Y. Go green with distributed beamforming. In Wireless Pers. Multimedia Commun. (WPMC), 1–5 (2011).
Kisseleff, S., Akyildiz, I. F. & Gerstacker, W. Distributed beamforming for magnetic induction based body area sensor network. In Proc. IEEE Glob. Commun. Conf. (GLOBECOM), 1–7, https://doi.org/10.1109/GLOCOM.2016.7842165 (2016).
Muralidharan, A. & Mostofi, Y. Energy optimal distributed beamforming using unmanned vehicles. IEEE Trans. Control Netw. Syst. 5, 1529–1540. https://doi.org/10.1109/TCNS.2017.2748064 (2017).
Wang, R. & Brown, D. R. Optimal wireless power transfer with distributed transmit beamforming. IEEE J. Commun. Netw. 19, 134–146 (2017).
Ding, Y., Fusco, V. & Zhang, J. Phase error effects on distributed transmit beamforming for wireless communications. In Eur. Conf. Antennas Propag. (EuCAP), 3100–3103, https://doi.org/10.23919/EuCAP.2017.7928706 (2017).
Nanzer, J. A., Mghabghab, S. R., Ellison, S. M. & Schlegel, A. Distributed phased arrays: Challenges and recent advances. IEEE Trans. Microw. Theory Tech. 69, 4893–4907. https://doi.org/10.1109/TMTT.2021.3092401 (2021).
Shah, S. M. A. et al. Miniaturized four-port MIMO implantable antenna for high-data-rate wireless-capsule-endoscopy applications. IEEE Trans. Antennas Propag. 71, 3123–3133. https://doi.org/10.1109/TAP.2023.3243984 (2023).
Li, Y. & Feng, Q. Ultrawideband conformal MIMO antenna with ferrite-based modified inverted-f structure for wireless capsule endoscopy applications. IEEE Antennas Wirel. Propag. Lett. 24, 2854–2858. https://doi.org/10.1109/LAWP.2025.3575376 (2025).
Krishnan, S. & Hafez, M. A. On the importance of accurate utilization of pathloss model for real-time uwb-based wireless capsule endoscopy localization and communication in individual. In In 2024 Int. Conf. Commun. Signal Process (ICCSP), 553–558, https://doi.org/10.1109/ICCSP60870.2024.10544068 (2024).
Taricco, G. Information rate optimization for the non-regenerative linear MIMO relay channel with a direct link and variable duty cycle. IEEE Trans. Inf. Theory 68, 5889–5900. https://doi.org/10.1109/TIT.2022.3166073 (2022).
Luo, J., Zhao, S., Yang, Z., Huang, G. & Tang, D. Data-driven-based relay selection and cooperative beamforming for non-regenerative multi-antenna relay networks. IEEE Access 9, 167154–167161. https://doi.org/10.1109/ACCESS.2021.3136332 (2021).
Kavitha, K. & Sivakumar, T. A comprehensive survey on beamforming and antenna selection in MIMO systems using deep learning and machine learning techniques with future research directions. In 2024 2nd World Conference on Communication & Computing (WCONF), 1–8, https://doi.org/10.1109/WCONF61366.2024.10692227 (2024).
Tse, D. & Viswanath, P. Fundamentals of Wireless Communication (Cambridge University Press, 2005).
Haykin, S. Adaptive Filter Theory, Third Edition (Prentice-Hall, 1996).
Li, Y. G., Winters, J. H. & Sollenberger, N. R. MIMO-OFDM for wireless communications: Signal detection with enhanced channel estimation. IEEE Trans. Commun. 50, 1471–1477 (2002).
Nagaoka, T. et al. Development of realistic high-resolution whole-body voxel models of Japanese adult males and females of average height and weight, and application of models to radio-frequency electromagnetic-field dosimetry. Phys. Med. Biol. 49, 1–15. https://doi.org/10.1088/0031-9155/49/1/001 (2004).
Goldsmith, A. Wireless Communications (Cambridge University Press, Cambridge, 2005).
Anzai, D., Koya, T. & Wang, J. Throughput evaluation on multilevel modulation with local frequency offset spatial diversity for 400 MHz band implant communications. IET Microw. Antennas Propag. 11, 593–599. https://doi.org/10.1049/iet-map.2016.0604 (2017).
Acknowledgements
The authors would like to thank Mr. Takuma Suzaki for his contribution to the communication performance evaluation.
Funding
This research was supported in part by JST Moonshot R&D Grant Number JPMJMS2214-06, the JSPS KAKENHI Grant Number 24K00885 and MIC/FORWARD Grant Number JPMI250830001.
Author information
Authors and Affiliations
Contributions
T.K., J.H., M.F. and D.A. conceived the experiments, J.H. M.F. and T.K. conducted the simulations, and analysed the communication performance results. D.A. provided the project funding acquisition. All authors contributed to the writing and review of the manuscript.
Corresponding author
Ethics declarations
Competing interests
The authors declare no competing interests.
Additional information
Publisher’s note
Springer Nature remains neutral with regard to jurisdictional claims in published maps and institutional affiliations.
Supplementary Information
Rights and permissions
Open Access This article is licensed under a Creative Commons Attribution-NonCommercial-NoDerivatives 4.0 International License, which permits any non-commercial use, sharing, distribution and reproduction in any medium or format, as long as you give appropriate credit to the original author(s) and the source, provide a link to the Creative Commons licence, and indicate if you modified the licensed material. You do not have permission under this licence to share adapted material derived from this article or parts of it. The images or other third party material in this article are included in the article’s Creative Commons licence, unless indicated otherwise in a credit line to the material. If material is not included in the article’s Creative Commons licence and your intended use is not permitted by statutory regulation or exceeds the permitted use, you will need to obtain permission directly from the copyright holder. To view a copy of this licence, visit http://creativecommons.org/licenses/by-nc-nd/4.0/.
About this article
Cite this article
Kobayashi, T., Hyry, J., Fujimoto, M. et al. Weight optimization of MIMO-UWB distributed beamforming for implant communications. Sci Rep (2026). https://doi.org/10.1038/s41598-026-36694-w
Received:
Accepted:
Published:
DOI: https://doi.org/10.1038/s41598-026-36694-w