Abstract
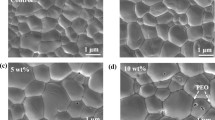
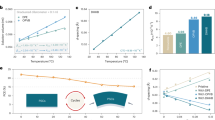
Incorporating polymer additives into hybrid perovskite solar cells is an effective strategy to enhance stability while retaining high efficiency. This study examines the impact of three polymers: polyvinylpyrrolidone (PVP), polyethylene glycol (PEG), and polyvinyl alcohol (PVA) added at varying concentrations on the stability of perovskite as the absorber layer. Structural, optical, and electrochemical analyses demonstrate that adding PEG 0.3 mg/ml significantly improves perovskite films’ morphology, light absorption, and charge transport while reducing recombination losses and enhancing long-term stability. Specifically, at room temperature and 30% relative humidity, the optimized perovskite sample with 0.3 mg/mL PEG maintained stability for up to 1000 h. Additionally, The UV analysis determined the band gap to be 1.58 eV. The electrochemical impedance spectroscopy analysis evaluated the charge transfer resistance (Rct) to be 1408 Ωcm², lower than other samples modified with polymer. The findings reveal that polymer modification significantly enhances the stability and efficiency of perovskite solar cells, improving their reliability and market competitiveness.
Similar content being viewed by others
Data availability
All data generated or analysed during this study are included in this published article.
References
Hosseini, S. R. et al. Investigating the effect of non-ideal conditions on the performance of a planar CH₃NH₃PbI₃ based perovskite solar cell through SCAPS-1D simulation. Heliyon 8, e11471 (2022).
Moradi, A. et al. Thermal modeling of perovskite solar cells: electron and hole transfer layers effects. Optik 302, 171683 (2024).
Gholami-Milani, A. et al. Performance analyses of highly efficient inverted all-perovskite bilayer solar cell. Sci. Rep. 13, 8274 (2023).
Chang, C. Y. et al. Tuning perovskite morphology by polymer additive for high-efficiency solar cell. ACS Appl. Mater. Interfaces. 7, 4955–4961 (2015).
Kim, N. K. et al. Investigation of thermally induced degradation in CH₃NH₃PbI₃ perovskite solar cells using in-situ synchrotron radiation analysis. Sci. Rep. 7, 4645 (2017).
Jiang, J. et al. Polymer doping for high-efficiency perovskite solar cells with improved moisture stability. Adv. Energy Mater. 8, 1701757 (2018).
Kalantari, N., Delibaş, N. & Niaei, A. Unveiling the potential of additives in optimizing halide perovskite solar cells performance and reliability. Mater. Today Sustain. 101011 (2024).
Girish, K. H. et al. Role of conducting polymers in enhancing the stability and performance of perovskite solar cells: a brief review. Mater. Today Sustain. 17, 100090 (2022).
Kundu, S. et al. In situ studies of the degradation mechanisms of perovskite solar cells. Eco Mat. 2, e12025 (2020).
Kato, Y. et al. Maximum efficiencies and performance-limiting factors of inorganic and hybrid perovskite solar cells. Phys. Rev. Appl. 12, 024039 (2019).
Fu, W. et al. Stability of perovskite materials and devices. Mater. Today. 58, 275–296 (2022).
Lee, S. W. et al. UV degradation and recovery of perovskite solar cells. Sci. Rep. 6, 38150 (2016).
Wang, Z. et al. Advances in perovskite solar cells: film morphology control and interface engineering. J. Clean. Prod. 317, 128368 (2021).
Prajongtat, P. et al. Moisture-resistant electrospun polymer membranes for efficient and stable fully printable perovskite solar cells prepared in humid air. ACS Appl. Mater. Interfaces. 11, 27677–27685 (2019).
Liu, P. et al. High-quality Ruddlesden–Popper perovskite film formation for high‐performance perovskite solar cells. Adv. Mater. 33, 2002582 (2021).
Kim, D. I. et al. A high-efficiency and stable perovskite solar cell fabricated in ambient air using a polyaniline passivation layer. Sci. Rep. 12, 697 (2022).
Murad, R., Iraqi, A., Aziz, S. B., Abdullah, N. & Brza, M. A. Conducting polymers for optoelectronic devices and organic solar cells: a review. Polymers 12, 2627 (2020).
Zhong, M., Chai, L., Wang, Y. & Di, J. Enhanced efficiency and stability of perovskite solar cell by adding polymer mixture in perovskite photoactive layer. J. Alloys Compd. 864, 158793 (2021).
Wu, Z. et al. Passivation strategies for enhancing device performance of perovskite solar cells. Nano Energy 108731 (2023).
Kim, H. S. & Park, N. G. Future research directions in perovskite solar cells: exquisite photon management and thermodynamic phase stability. Adv. Mater. 35, 2204807 (2023).
Sai-Anand, G. et al. Additive-assisted morphological optimization of the photoactive layer in polymer solar cells. Sol Energy Mater. Sol Cells. 182, 246–254 (2018).
Bi, E. et al. Mitigating ion migration in perovskite solar cells. Trends Chem. 3, 575–588 (2021).
Zhao, X. C. et al. Cesium-containing Methylammonium lead iodide light absorber for planar perovskite solar cells. J. Nanosci. Nanotechnol. 20, 1008–1012 (2020).
Yang, Y. et al. Effect of Cs⁺ fraction on photovoltaic performance of perovskite solar cells based on CsₓMA₁₋ₓPbI₃ absorption layers. J. Electron. Mater. 49, 7044–7053 (2020).
Zuo, L. et al. Polymer-modified halide perovskite films for efficient and stable planar heterojunction solar cells. Sci. Adv. 3, e1700106 (2017).
Zhang, Y. et al. A polymer scaffold for self-healing perovskite solar cells. Nat. Commun. 7, 10228 (2016).
Xiang, L. et al. Defect passivation effect of chemical groups on perovskite solar cells. ACS Appl. Mater. Interfaces. 14, 34161–34170 (2021).
Saliba, M. et al. Incorporation of rubidium cations into perovskite solar cells improves photovoltaic performance. Science 354, 206–209 (2016).
Zhang, Z. et al. Enhancing the efficiency and stability of perovskite solar cells using polymeric additives. J. Mater. Chem. A. 5, 4580–4586 (2017).
Fairfield, D. et al. Structure and chemical stability in perovskite–polymer hybrid photovoltaic materials. J. Mater. Chem. A. 7, 1687–1699 (2019).
Jiang, Q. et al. Surface passivation of perovskite film for efficient solar cells. Nat. Photonics. 13, 460–466 (2019).
Kojima, A., Teshima, K., Shirai, Y. & Miyasaka, T. Organometal halide perovskites as visible-light sensitizers for photovoltaic cells. J. Am. Chem. Soc. 131, 6050–6051 (2009).
Bi, D. et al. Polymer-templated nucleation and crystal growth of perovskite films for solar cells with efficiency greater than 21%. Nat. Energy. 1, 16142 (2016).
De Wolf, S. et al. Organometallic halide perovskites: Sharp optical absorption edge and its relation to photovoltaic performance. J. Phys. Chem. Lett. 5, 1035–1039 (2014).
Conings, B. et al. Intrinsic thermal instability of Methylammonium lead trihalide perovskite. Adv. Energy Mater. 5, 1500477 (2015).
Troughton, J. et al. Ultra-thin high-efficiency semitransparent perovskite solar cells. Adv. Energy Mater. 7, 1602939 (2017).
Li, X. et al. Improved performance and stability of perovskite solar cells by crystal crosslinking with alkylphosphonic acid omega-ammonium chlorides. Nat. Chem. 7, 703–711 (2015).
Stoumpos, C. C., Malliakas, C. D. & Kanatzidis, M. G. Semiconducting Tin and lead iodide perovskites with organic cations: phase transitions, high mobilities, and near-infrared photoluminescent properties. Inorg. Chem. 52, 9019–9038 (2013).
Zhou, H. et al. Interface engineering of highly efficient perovskite solar cells. Science 345, 542–546 (2014).
Leijtens, T. et al. Stability of metal halide perovskite solar cells. Adv. Energy Mater. 5, 1500963 (2015).
Ahn, N. et al. Highly reproducible perovskite solar cells with an average efficiency of 18.3% and best efficiency of 19.7% fabricated via Lewis base adduct of lead(II) iodide. J. Am. Chem. Soc. 137, 8696–8699 (2015).
Kim, G. Y. et al. Role and contribution of polymeric additives in perovskite solar cells: crystal growth templates and grain boundary passivators. Solar RRL. 5 (1), 2000783 (2021).
Wang, Y. et al. Influence of polymer additives on the efficiency and stability of Ambient-Air Solution‐Processed planar perovskite solar cells. Energy Technol. 6 (11), 2252–2259 (2018).
Mohammed, M. I. & El-Sayed, F. PEG’s impact as a plasticizer on the PVA polymer’s Structural, Thermal, Mechanical, Optical, and dielectric characteristics. Opt. Quant. Electron. 55 (10), 5420 (2023).
Potti, D. et al. An ultra-wideband rectenna using optically transparent Vivaldi antenna for radio frequency energy harvesting. Int. J. RF and Microwave Comput. Aided Eng. 30.10, e22362 (2020).
Nie, W. et al. High-efficiency solution-processed perovskite solar cells with millimeter-scale grains. Science 347, 522–525 (2015).
Jeon, J. et al. Compositional engineering of perovskite materials for high-performance solar cells. Nature 517, 476–480 (2015).
Yu, E. et al. Charge carrier lifetimes exceeding 15 µs in Methylammonium lead iodide single crystals. J. Phys. Chem. Lett. 7, 923–928 (2016).
Mei, A. et al. A hole-conductor-free, fully printable mesoscopic perovskite solar cell with high stability. Science 345, 295–298 (2014).
Liu, M., Johnston, M. B. & Snaith, H. J. Efficient planar heterojunction perovskite solar cells by vapor deposition. Nature 501, 395–398 (2013).
Yang, J. et al. Origin of the thermal instability in CH₃NH₃PbI₃ thin films deposited on ZnO. Chem. Mater. 27, 4229–4236 (2015).
Yang, W. S. et al. High-performance photovoltaic perovskite layers fabricated through intramolecular exchange. Science 348, 1234–1237 (2015).
Stranks, S. D. et al. Electron-hole diffusion lengths exceeding 1 micron in an organometal trihalide perovskite absorber. Science 342, 341–344 (2013).
Dong, Z. et al. Grain boundary defect passivation and iodine migration Inhibition for efficient and stable perovskite solar cells. Electrochim. Acta. 507, 145129 (2024).
You, Y. et al. PEG modified CsPbIBr2 perovskite film for efficient and stable solar cells. Adv. Mater. Interfaces. 7, 13, 2000537 (2020).
Noh, J. H. et al. Chemical management for colorful, efficient, and stable inorganic-organic hybrid nanostructured solar cells. Nano Lett. 13, 1764–1769 (2013).
Bi, Q. et al. Non-wetting surface-driven high-aspect-ratio crystalline grain growth for efficient hybrid perovskite solar cells. Nat. Commun. 6, 7747 (2015).
Acknowledgements
The authors thank to the University of Tabriz in Iran and Sakarya University(BAP 2024-25-63-96) in Turkey for their collaboration.
Author information
Authors and Affiliations
Contributions
M.B. Conceptualization, Methodology, Writing—original draft preparation. A.N. Conceptualization, writing—reviewing and editing, Supervision. E.A. Conceptualization, writing—reviewing and editing. S. J. P. Conceptualization, Writing—reviewing and editing.N.D. Conceptualization, Writing—reviewing and editing.
Corresponding author
Ethics declarations
Competing interests
The authors declare no competing interests.
Additional information
Publisher’s note
Springer Nature remains neutral with regard to jurisdictional claims in published maps and institutional affiliations.
Supplementary Information
Below is the link to the electronic supplementary material.
Rights and permissions
Open Access This article is licensed under a Creative Commons Attribution-NonCommercial-NoDerivatives 4.0 International License, which permits any non-commercial use, sharing, distribution and reproduction in any medium or format, as long as you give appropriate credit to the original author(s) and the source, provide a link to the Creative Commons licence, and indicate if you modified the licensed material. You do not have permission under this licence to share adapted material derived from this article or parts of it. The images or other third party material in this article are included in the article’s Creative Commons licence, unless indicated otherwise in a credit line to the material. If material is not included in the article’s Creative Commons licence and your intended use is not permitted by statutory regulation or exceeds the permitted use, you will need to obtain permission directly from the copyright holder. To view a copy of this licence, visit http://creativecommons.org/licenses/by-nc-nd/4.0/.
About this article
Cite this article
Bahramgour, M., Niaei, A., Asghari, E. et al. Enhancing structural and optical properties of hybrid perovskite layers with polymer modification. Sci Rep (2026). https://doi.org/10.1038/s41598-026-36719-4
Received:
Accepted:
Published:
DOI: https://doi.org/10.1038/s41598-026-36719-4