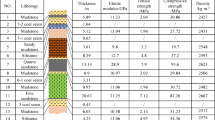
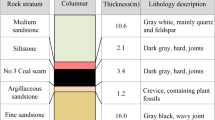
Abstract
To investigate the catastrophic instability mechanisms of roadway roof and sidewall rock masses under deep-hole roof blasting in coal mines, this study establishes potential energy functions and instability criteria models for layered roof and sidewall strata based on cusp catastrophe theory. First, the layered roof is idealized as a simply supported beam. Considering the coupling effects of deep-hole blasting loads, rock mechanical properties, and support resistance, a total potential energy equation for the system is derived, and the cusp catastrophe equation along with sufficient and necessary conditions for instability are obtained. Second, for the roadway sidewall, a tensile-shear coupled sliding failure mechanical model is proposed to analyze the influence of blasting loads on sidewall stability, and a corresponding catastrophe instability criterion is developed. Through theoretical derivation, the critical maximum explosive charge for both the layered roof and sidewall rock masses is formulated, along with a mechanical criterion for instability judgment. Finally, taking the lower roadway of the 2205 working face in Songshan Coal Mine as the engineering background, theoretical calculations indicate that the maximum critical explosive charge for the roadway is 93.3 kg. Field monitoring shows that, within 1 day after blasting, the roof subsidence increased by 5 mm and the convergence of the two sidewalls increased by 11 mm, indicating that the roadway was only slightly affected by roof deep-hole blasting.This work provides a theoretical basis and engineering guidance for the prediction and control of roadway rock instability under deep-hole roof blasting conditions.
Similar content being viewed by others
Data availability
The partial or all data generated or used during the research process can be provided by the corresponding author upon request.
References
Gao, R. et al. Investigation on the ground pressure induced by hard roof fracturing at different layers during extra thick coal seam mining. Geofluids 2020, 1–15 (2020).
Wang B, et al. Study on the Mechanism and Prevention of Frequent Mine Seismic Events in Goaf Mining under a Multi-Layer Thick Hard Roof: A Case Study. Minerals 13(7), (2023
Hu C, et al. Research on the Key Technology of Gob-Side Entry Retaining by Roof Cutting for Thick and Hard Sandstone Roofs. Sustainability 14(16), (2022)
Wang J. Research on the control technology of heavy layer hard roof blasting.” IOP Conference Series: Earth and Environmental Science 358(4) (2019).
Xiang Z, et al. “Cooperative Control Mechanism of Long Flexible Bolts and Blasting Pressure Relief in Hard Roof Roadways of Extra-Thick Coal Seams: A Case Study. Applied Sciences 11(9), (2021)
Dang J, et al. Research on the bearing characteristics of brackets in thick hard roof mining sites and the effect of blasting on roof control. Geomechanics and Geophysics for Geo-Energy and Geo-Resources 10(1), (2024)
Yang, X. et al. Research on the deformation mechanism and directional blasting roof cutting control measures of a deep buried high-stress roadway. Shock. Vib. 2020, 1–14 (2020).
Shan, R. et al. Research on the zoning of blasting for ultra-deep hole cylindrical charges based on thick-walled cylinder theory. Mech. Adv. Mater. Struct. 31(29), 12305–12319 (2024).
Xia H-b, et al. (2013). Study on Seismic Wave Propagation Characteristic of Deep-Hole Loose Blasting in Coal Mine. Paper presented at the 2013 Fourth International Conference on Digital Manufacturing & Automation.
Wu, K. et al. Insight and effectiveness of working-face deep-hole blasting for prevention of strong seismicity induced by deep coal mining. Rock Mech. Rock Eng. 56(12), 8693–8709 (2023).
Li, X. et al. Numerical simulation of blast vibration and crack forming effect of rock-anchored beam excavation in deep underground caverns. Shock. Vib. 2017, 1–13 (2017).
Wang W, et al. (2019) Plastic limit bearing calculation of blasting-roof in deep hole mining and its applications. Royal Society Open Science 6(7).
Xu, J. et al. Dynamic characteristics and safety criterion of deep rock mine opening under blast loading. Int. J. Rock Mech. Min. Sci. 119, 156–167 (2019).
Jing H-d, et al. ) Study on the Deformation Mechanism of Soft Rock Roadway under Blasting Disturbance in Baoguo Iron Mine. Shock and Vibration 2018(1).
Pan W, et al. (2024) Roadway rock burst prediction based on catastrophe theory. Scientific Reports 14(1).
Chen, F., et al. (2025). "Analysis of slab buckling rockburst of surrounding rock under dynamic and static combined disturbance." Tunnelling and Underground Space Technology 158.
Yuan, C., et al. (2025). "Calculation Method and Treatment Scheme for Critical Safety Rock Pillar Thickness Based on Catastrophe Theory." Applied Sciences 15(17).
Xu, X., et al. (2021). "Research on Deformation and Failure Evolution of Deep Rock Burst Drivage Roadway Surrounding Rock under Dynamic Disturbance." Shock and Vibration 2021(1).
Zhang, D. et al. Investigation on instability mechanism and control of abandoned roadways in coal pillars recovery face: A case study. Underground Space 20, 119–139 (2025).
Zhao H, et al. (2025) Static Blasting Roof Cutting Surrounding Rock Control Technology for Narrow Coal Pillar Gob-Side Entry Driving in Thick Coal Seams. International Journal of Geomechanics 25(6).
Wang X, et al. (2021) Instability Mechanism of Pillar Burst in Asymmetric Mining Based on Cusp Catastrophe Model. Rock Mechanics and Rock Engineering 54(3): 1463–1479. d
Cao, Z. et al. Disaster-causing mechanism of spalling rock burst based on folding catastrophe model in coal mine. Rock Mech. Rock Eng. 58(7), 7591–7604 (2025).
Yuan Y, et al. (2019) The Catastrophe Criterion for Instability of Deep Roadway based on Malignant Expansion of Plastic Zone. IOP Conference Series: Earth and Environmental Science 218.
Jixun, Z. et al. Study on rock mass stability criterion based on catastrophe theory. Math. Probl. Eng. 2015, 1–7 (2015).
Xue Y, et al. (2019) Destabilization and energy characteristics of coal pillar in roadway driving along gob based on rockburst risk assessment. Royal Society Open Science 6(7).
Qin, S. et al. Instability leading to coal bumps and nonlinear evolutionary mechanisms for a coal-pillar-and-roof system. Int. J. Solids Struct. 43(25–26), 7407–7423 (2006).
Zhang, P.-f et al. Combined roof interstory shear energy storage model and analysis of influencing factors. J. Theor. Appl. Mech. 63(1), 37–50 (2024).
Wang, J. C. & Sun, S. W. Open-pit Mine Slope Engineering (Science Press, China, 2016).
Bao M, et al. (2022) Fractional Catastrophe Model considering the Rheological Properties of Slope Faults. Lithosphere 2021(Special 7).
Acknowledgements
This work was financially supported by the National Natural Science Foundation of China (Grant no. 51974315).
Author information
Authors and Affiliations
Contributions
G.D.M. : supervision, writing-review and editing. C.J. : data curation, methodology, writing-original draft. W.H.K. : supervision, writing-review and editing. W.Z.H. : conceptualization, project administration, supervision. G.Q.L. : conceptualization, writing-original draft. All the authors reviewed the manuscript.
Corresponding author
Ethics declarations
Competing interests
The authors declare no competing interests.
Additional information
Publisher’s note
Springer Nature remains neutral with regard to jurisdictional claims in published maps and institutional affiliations.
Rights and permissions
Open Access This article is licensed under a Creative Commons Attribution 4.0 International License, which permits use, sharing, adaptation, distribution and reproduction in any medium or format, as long as you give appropriate credit to the original author(s) and the source, provide a link to the Creative Commons licence, and indicate if changes were made. The images or other third party material in this article are included in the article’s Creative Commons licence, unless indicated otherwise in a credit line to the material. If material is not included in the article’s Creative Commons licence and your intended use is not permitted by statutory regulation or exceeds the permitted use, you will need to obtain permission directly from the copyright holder. To view a copy of this licence, visit http://creativecommons.org/licenses/by/4.0/.
About this article
Cite this article
Guo, D., Chen, J., Wang, H. et al. Catastrophic instability criterion for roadway roof and sidewall rock mass under deep-hole roof blasting in Songshan coal mine. Sci Rep (2026). https://doi.org/10.1038/s41598-026-36794-7
Received:
Accepted:
Published:
DOI: https://doi.org/10.1038/s41598-026-36794-7