Abstract
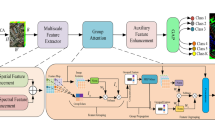
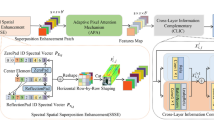
Hyperspectral image (HSI) classification faces challenges in diverse scenarios due to spectral-spatial complexity and class imbalance. Existing methods lack generalizability. This paper presents a novel Graph-Convolutional Networks with Adaptive Region Ensembles (GCN-ARE) framework. It integrates graph spectral learning, dynamic region subdivision, and classifier fusion. The key contributions are as follows: First, a normalized graph Laplacian operator ensures graph spectral stability, bounding the eigenvalue spectrum to stabilize feature propagation and address gradient issues in irregular terrains. Second, recursive K-means clustering under empirical risk bounds achieves adaptive region optimality, dynamically partitioning complex regions for enhanced local discriminability. Third, theoretical guarantees based on Hoeffding’s inequality enable dynamic ensemble consistency, facilitating optimal classifier selection under spatial-spectral uncertainty. Experiments on four HSI datasets (Botswana, Houston, Indian Pines, WHU-Hi-LongKou) show that GCN-ARE outperforms benchmarks like ViT and GAT, with average OA improvements of 1.5–5.7%. Ablation studies confirm the importance of adaptive subdivision and ensemble modules, and parameter sensitivity analyses reveal its robustness. The framework sets a new standard for robust HSI classification with its theoretical rigor and practical efficacy.
Similar content being viewed by others
Data availability
The datasets analyzed in this study are publicly available: the **Botswana** dataset from NASA’s EO-1 Hyperion mission (IEEE GRSS Data Fusion Contest), the **Houston** dataset from the IEEE GRSS 2013 Data Fusion Contest, the **Indian Pines** dataset from Purdue University’s MultiSpec, and the **WHU-Hi-LongKou** dataset released by Wuhan University. All datasets can be freely accessed for research purposes. Processed data and codes supporting the findings of this study are available from the corresponding author upon reasonable request.
References
Ahmad, M. et al. Hyperspectral image classification—Traditional to deep models: A survey for future prospects. IEEE J. Sel. Top. Appl. Earth Observ Remote Sens. 15, 968–999 (2021).
Vaidya, R. & Nalavade, D. Kale. Hyperspectral imagery for crop yield Estimation in precision agriculture using machine learning approaches: a review. Int. J. Creat Res. Thoughts. 9, a777–a789 (2022).
Himeur, Y. et al. Using artificial intelligence and data fusion for environmental monitoring: A review and future perspectives. Inf. Fusion. 86, 44–75 (2022).
Jiang, X. et al. Efficient two-phase multiobjective sparse unmixing approach for hyperspectral data. IEEE J. Sel. Top. Appl. Earth Observ Remote Sens. 14, 2418–2431 (2021).
Paoletti, M. E. et al. A comprehensive survey of imbalance correction techniques for hyperspectral data classification. IEEE J. Sel. Top. Appl. Earth Observ Remote Sens. 16, 5297–5314 (2023).
Li, K., Wan, Y., Ma, A. & Zhong, Y. A lightweight multiscale and multiattention hyperspectral image classification network based on multistage search. IEEE Trans. Geosci. Remote Sens. 63, 1–18 (2025).
Fu, H. et al. HyperDehazing: A hyperspectral image dehazing benchmark dataset and a deep learning model for haze removal. ISPRS J. Photogramm Remote Sens. 218, 663–677 (2024).
Xue, Z. & Xu, Q. Zhang. Local transformer with Spatial partition restore for hyperspectral image classification. IEEE J. Sel. Top. Appl. Earth Observ Remote Sens. 15, 4307–4325 (2022).
Chen, Y. S., Lin, Z. H., Zhao, X. & Wang, G. Gu. Deep learning-based classification of hyperspectral data. IEEE J. Sel. Top. Appl. Earth Observ Remote Sens. 7, 2094–2107 (2014).
Li, S., Luo, X. Y., Wang, Q. X. & Li, L. & J. H. Yin. H2AN: hierarchical homogeneity-attention network for hyperspectral image classification. IEEE Trans. Geosci. Remote Sens. 60, 1–16 (2022).
Farmonov, N. et al. Crop type classification by DESIS hyperspectral imagery and machine learning algorithms. IEEE J. Sel. Top. Appl. Earth Observ Remote Sens. 16, 1576–1588 (2023).
Guo, Y. et al. Comparison of different machine learning algorithms for predicting maize grain yield using UAV-based hyperspectral images. Int. J. Appl. Earth Observ Geoinf. 124, 103528 (2023).
Duan, Y., Huang, H. & Wang, T. Semisupervised feature extraction of hyperspectral image using nonlinear geodesic sparse hypergraphs. IEEE Trans. Geosci. Remote Sens. 60, 1–15 (2021).
Datta, D. et al. Hyperspectral image classification: Potentials, challenges, and future directions. Comput. Intell. Neurosci. 2022, 3854635 (2022).
Li, Y. et al. Multidimensional local binary pattern for hyperspectral image classification. IEEE Trans. Geosci. Remote Sens. 60, 1–13 (2021).
Paoletti, M. E. et al. Ghostnet for hyperspectral image classification. IEEE Trans. Geosci. Remote Sens. 59, 10378–10393 (2021).
Xu, X. et al. Multimodal Remote Sensing Land Cover Data Augmentation and Classification Based on Diffusion Model. 2024 14th Workshop on Hyperspectral Imaging and Signal Processing: Evolution in Remote Sensing (WHISPERS), 1–5 (2024).
Li, J. et al. Contrastive MLP network based on adjacent coordinates for Cross-Domain Zero-Shot hyperspectral image classification. IEEE Trans. Circuits Syst. Video Technol. 35, 8377–8390 (2025).
Zheng, H., Su, H., Wu, Z. & Paoletti, M. E. Du. Graph convolutional network with relaxed collaborative representation for hyperspectral image classification. IEEE Trans. Geosci. Remote Sens. 62, 1–13 (2024).
Qin, B. et al. FDGNet: frequency disentanglement and data geometry for domain generalization in cross-scene hyperspectral image classification. IEEE Trans. Neural Netw. Learn. Syst. 36, 10297–10310 (2024).
Hong, D., Gao, L., Yao, J., Zhang, B. & Plaza, A. Chanussot. Graph convolutional networks for hyperspectral image classification. IEEE Trans. Geosci. Remote Sens. 59, 5966–5978 (2021).
Yang, Y. et al. Semi-supervised multiscale dynamic graph Convolution network for hyperspectral image classification. IEEE Trans. Neural Netw. Learn. Syst. 35, 6806–6820 (2022).
Ghaderizadeh, S. et al. Hyperspectral image classification using a hybrid 3D-2D convolutional neural networks. IEEE J. Sel. Top. Appl. Earth Observ Remote Sens. 14, 7570–7588 (2021).
Zhao, Z., Xu, X., Li, S. & Plaza, A. Hyperspectral image classification using groupwise separable convolutional vision transformer network. IEEE Trans. Geosci. Remote Sens. 62, 1–17 (2024).
Ma, Q. et al. Learning a 3D-CNN and transformer prior for hyperspectral image super-resolution. Inf. Fusion. 100, 101907 (2023).
Zhang, X. et al. A lightweight transformer network for hyperspectral image classification. IEEE Trans. Geosci. Remote Sens. 61, 1–17 (2023).
Ding, Y. et al. Unsupervised self-correlated learning smoothy enhanced locality preserving graph Convolution embedding clustering for hyperspectral images. IEEE Trans. Geosci. Remote Sens. 60, 1–16 (2022).
Ding, Y. et al. Semi-supervised locality preserving dense graph neural network with ARMA filters and context-aware learning for hyperspectral image classification. IEEE Trans. Geosci. Remote Sens. 60, 1–12 (2022).
Ding, Y. et al. SLCGC: A lightweight self-supervised low-pass contrastive graph clustering network for hyperspectral images. IEEE Trans. Multimedia. 27, 8251–8262 (2025).
Ding, Y. et al. Adaptive homophily clustering: structure homophily graph learning with adaptive filter for hyperspectral image. IEEE Trans. Geosci. Remote Sens. 63, 1–15 (2025).
Ding, Y. et al. AF2GNN: graph Convolution with adaptive filters and aggregator fusion for hyperspectral image classification. Inf. Sci. 602, 201–219 (2022).
Ding, Y. et al. Deep hybrid: Multi-graph neural network collaboration for hyperspectral image classification. Def. Technol. 19 (5), 1339–1354 (2023).
Ding, Y. et al. Multi-scale receptive fields: graph attention neural network for hyperspectral image classification. Expert Syst. Appl. 223, 119858 (2023).
Zhang, Z. et al. Multireceptive field: an adaptive path aggregation graph neural framework for hyperspectral image classification. Expert Syst. Appl. 223, 119508 (2023).
Acknowledgements
This was supported in by Natural Science Research Funds of Education Department of Anhui Province under Grant 2025AHGXZK40086, Spatial Information Acquisition and Application Joint Laboratory of Anhui Province, NO. 2024tlxykjxx03 and Talent Research Initiation Fund Project of Tongling University under Grant 2024tlxyrc039.
Author information
Authors and Affiliations
Contributions
Yutian Chen: Conceived the core idea of the GCN-ARE framework; implemented the algorithm design; conducted experiments on multiple hyperspectral datasets; analyzed the experimental results; drafted the initial manuscript; Hongliang Lu: Supervised the research; provided theoretical guidance on graph spectral stability, adaptive region subdivision, and ensemble learning; revised and refined the manuscript; secured project funding and coordinated collaboration among institutions; Xianglin Huang: Contributed to the validation experiments and comparative analysis; assisted in interpreting results; provided constructive feedback on the manuscript and contributed to improving its clarity and technical depth.
Corresponding author
Ethics declarations
Competing interests
The authors declare no competing interests.
Additional information
Publisher’s note
Springer Nature remains neutral with regard to jurisdictional claims in published maps and institutional affiliations.
Rights and permissions
Open Access This article is licensed under a Creative Commons Attribution 4.0 International License, which permits use, sharing, adaptation, distribution and reproduction in any medium or format, as long as you give appropriate credit to the original author(s) and the source, provide a link to the Creative Commons licence, and indicate if changes were made. The images or other third party material in this article are included in the article's Creative Commons licence, unless indicated otherwise in a credit line to the material. If material is not included in the article's Creative Commons licence and your intended use is not permitted by statutory regulation or exceeds the permitted use, you will need to obtain permission directly from the copyright holder. To view a copy of this licence, visit http://creativecommons.org/licenses/by/4.0/.
About this article
Cite this article
Chen, Y., Lu, H. & Huang, X. Collaborative representation and confidence-driven semi-supervised learning for hyperspectral image classification. Sci Rep (2026). https://doi.org/10.1038/s41598-026-36806-6
Received:
Accepted:
Published:
DOI: https://doi.org/10.1038/s41598-026-36806-6