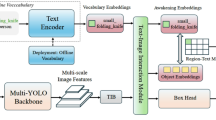
Abstract
Open-vocabulary detection (OVD) aims to detect and classify objects from an unrestricted set of categories, including those unseen during training. Existing open-vocabulary detectors often suffer from visual-textual misalignment and long-tailed category imbalance, leading to poor performance when handling objects described by complex, long-tailed textual queries. To overcome these challenges, we propose Multimodal Question Answering Detection (MQADet), a universal plug-and-play paradigm that enhances existing open-vocabulary detectors by leveraging the cross-modal reasoning capabilities of multimodal large language models (MLLMs). MQADet can be seamlessly integrated with pre-trained object detectors without requiring additional training or fine-tuning. Specifically, we design a novel three-stage Multimodal Question Answering (MQA) pipeline that guides MLLMs to accurately localize objects described by complex textual queries while refining the focus of existing detectors toward semantically relevant regions. To evaluate our approach, we construct a comprehensive benchmark across four challenging open-vocabulary datasets and integrate three state-of-the-art detectors as baselines. Extensive experiments demonstrate that MQADet consistently improves detection accuracy, particularly for unseen and linguistically complex categories, across diverse and challenging scenarios. To support further research, we will publicly release our code.
Similar content being viewed by others
Data availability
The datasets used and/or analysed during the current study are available from the corresponding author on reasonable request.
References
Cheng, G. & Han, J. A survey on object detection in optical remote sensing images. ISPRS journal of photogrammetry and remote sensing. 117, 11–28 (2016).
Xu, G., Khan, A. S., Moshayedi, A. J., Zhang, X. & Shuxin, Y. The object detection, perspective and obstacles in robotic: a review. EAI Endorsed Transactions on AI and Robotics. 1(1) (2022).
Huang, W.-J., Lu, Y.-L., Lin, S.-Y., Xie, Y. & Lin, Y.-Y. Aqt: Adversarial query transformers for domain adaptive object detection. In: IJCAI, pp. 972–979 (2022).
Ren, S., He, K., Girshick, R. & Sun, J. Faster r-cnn: Towards real-time object detection with region proposal networks. IEEE transactions on pattern analysis and machine intelligence 39(6), 1137–1149 (2016).
Chen, S., Sun, P., Song, Y. & Luo, P. Diffusiondet: Diffusion model for object detection. In: Proceedings of the IEEE/CVF International Conference on Computer Vision, pp. 19830–19843 (2023).
Zhao, Y. et al. Detrs beat yolos on real-time object detection. In: Proceedings of the IEEE/CVF Conference on Computer Vision and Pattern Recognition, pp. 16965–16974 (2024).
Lin, T.-Y. et al. Microsoft coco: Common objects in context. In: Computer Vision–ECCV 2014: 13th European Conference, Zurich, Switzerland, September 6-12, 2014, Proceedings, Part V 13, pp. 740–755. Springer (2014).
Li, B. et al. Seed-bench: Benchmarking multimodal large language models. In: Proceedings of the IEEE/CVF Conference on Computer Vision and Pattern Recognition, pp. 13299–13308 (2024).
Cui, C. et al. A survey on multimodal large language models for autonomous driving. In: Proceedings of the IEEE/CVF Winter Conference on Applications of Computer Vision, pp. 958–979 (2024).
Liu, S. et al. Grounding dino: Marrying dino with grounded pre-training for open-set object detection. In: European Conference on Computer Vision, pp. 38–55 (2025). Springer
Cheng, T. et al. Yolo-world: Real-time open-vocabulary object detection. In: Proceedings of the IEEE/CVF Conference on Computer Vision and Pattern Recognition, pp. 16901–16911 (2024).
Zhao, T., Liu, P., He, X., Zhang, L. & Lee, K. Real-time transformer-based open-vocabulary detection with efficient fusion head. arXiv:2403.06892 (2024).
Radford, A. et al. Learning transferable visual models from natural language supervision. In: Meila, M. & Zhang, T. (eds.) Proceedings of the 38th International Conference on Machine Learning. Proceedings of Machine Learning Research, vol. 139, pp. 8748–8763. PMLR, (2021). https://proceedings.mlr.press/v139/radford21a.html
Zhong, Y. et al. Regionclip: Region-based language-image pretraining. In: Proceedings of the IEEE/CVF Conference on Computer Vision and Pattern Recognition, pp. 16793–16803 (2022).
Zhang, H. et al. Dino: Detr with improved denoising anchor boxes for end-to-end object detection. arXiv:2203.03605 (2022).
Chen, P. et al. Open vocabulary object detection with proposal mining and prediction equalization. arXiv:2206.11134 (2022).
Zhao, S. et al. Exploiting unlabeled data with vision and language models for object detection. In: European Conference on Computer Vision, pp. 159–175 (2022). Springer
Zhou, K., Yang, J., Loy, C. C. & Liu, Z. Learning to prompt for vision-language models. International Journal of Computer Vision 130(9), 2337–2348 (2022).
Du, Y. et al. Learning to prompt for open-vocabulary object detection with vision-language model. In: Proceedings of the IEEE/CVF Conference on Computer Vision and Pattern Recognition, pp. 14084–14093 (2022).
Chen, H. et al. Taskclip: Extend large vision-language model for task oriented object detection. arXiv:2403.08108 (2024).
Bui, D. C., Le, T. V., Ngo, B. H. & Choi, T. J. Clear: Cross-transformers with pre-trained language model for person attribute recognition and retrieval. Pattern Recognition 164, 111486 (2025).
Bui, D.C., Le, T.V. & Ngo, B.H. C2t-net: Channel-aware cross-fused transformer-style networks for pedestrian attribute recognition. In: Proceedings of the IEEE/CVF Winter Conference on Applications of Computer Vision, pp. 351–358 (2024).
Sun, Y., Zhang, K. & Su, Y. Multimodal question answering for unified information extraction. arXiv:2310.03017 (2023).
Yu, L., Poirson, P., Yang, S., Berg, A.C. & Berg, T.L. Modeling context in referring expressions. In: Computer Vision–ECCV 2016: 14th European Conference, Amsterdam, The Netherlands, October 11-14, 2016, Proceedings, Part II 14, pp. 69–85 (2016). Springer
Nagaraja, V.K., Morariu, V.I. & Davis, L.S. Modeling context between objects for referring expression understanding. In: Computer Vision–ECCV 2016: 14th European Conference, Amsterdam, The Netherlands, October 11–14, 2016, Proceedings, Part IV 14, pp. 792–807 (2016). Springer
Chen, J. et al. Revisiting referring expression comprehension evaluation in the era of large multimodal models. arXiv:2406.16866 (2024)
Peng, Z. et al. Kosmos-2: Grounding multimodal large language models to the world. arXiv:2306.14824 (2023).
Zhan, Y. et al. Griffon: Spelling out all object locations at any granularity with large language models. In: European Conference on Computer Vision, pp. 405–422 (2025). Springer
Chen, K. et al. Shikra: Unleashing multimodal llm’s referential dialogue magic. arXiv:2306.15195 (2023).
Zhang, A. et al. Next-chat: An lmm for chat, detection and segmentation. arXiv:2311.04498 (2023).
Liu, H., Li, C., Wu, Q. & Lee, Y. J. Visual instruction tuning. Advances in neural information processing systems 36 (2024).
Liu, H., Li, C., Li, Y. & Lee, Y.J. Improved baselines with visual instruction tuning. In: Proceedings of the IEEE/CVF Conference on Computer Vision and Pattern Recognition, pp. 26296–26306 (2024).
Liu, H., Li, C., Li, Y. & Lee, Y.J. Improved baselines with visual instruction tuning. In: Proceedings of the IEEE/CVF Conference on Computer Vision and Pattern Recognition, pp. 26296–26306 (2024).
Wu, Z. et al. Deepseek-vl2: Mixture-of-experts vision-language models for advanced multimodal understanding. arXiv:2412.10302 (2024).
Wang, P. et al. Qwen2-vl: Enhancing vision-language model’s perception of the world at any resolution. arXiv:2409.12191 (2024).
Comanici, G. et al. Gemini 2.5: Pushing the frontier with advanced reasoning, multimodality, long context, and next generation agentic capabilities. arXiv:2507.06261 (2025).
Funding
This study was funded by the Natural Science Foundation of Qinghai Province under Grant 2023-QLGKLYCZX-017.
Author information
Authors and Affiliations
Contributions
Caixiong Li: Methodology, Software, Writing–original draft preparation, Writing–review and editing. Xiongwei Zhao: Methodology, Writing–original draft preparation, Writing–review and editing. Jinhang Zhang: Data curation, Investigation, Formal analysis. Xing Zhang: Resources, funding acquisition. Qihao Sun: Visualization, Project administration. Zhou Wu: Visualization, Validation.
Corresponding author
Ethics declarations
Competing interests
The authors declare no competing interests.
Additional information
Publisher’s note
Springer Nature remains neutral with regard to jurisdictional claims in published maps and institutional affiliations.
Rights and permissions
Open Access This article is licensed under a Creative Commons Attribution 4.0 International License, which permits use, sharing, adaptation, distribution and reproduction in any medium or format, as long as you give appropriate credit to the original author(s) and the source, provide a link to the Creative Commons licence, and indicate if changes were made. The images or other third party material in this article are included in the article’s Creative Commons licence, unless indicated otherwise in a credit line to the material. If material is not included in the article’s Creative Commons licence and your intended use is not permitted by statutory regulation or exceeds the permitted use, you will need to obtain permission directly from the copyright holder. To view a copy of this licence, visit http://creativecommons.org/licenses/by/4.0/.
About this article
Cite this article
Li, C., Zhao, X., Zhang, J. et al. MQADet: a plug-and-play paradigm for enhancing open-vocabulary object detection via multimodal question answering. Sci Rep (2026). https://doi.org/10.1038/s41598-026-36936-x
Received:
Accepted:
Published:
DOI: https://doi.org/10.1038/s41598-026-36936-x