Abstract
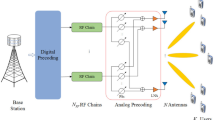
Analog and digital precoding are used in distributed massive multiple-input multiple-output (MIMO) at millimeter wave (mmWave) frequencies to efficiently manage data transfer across several antennas and base stations (BSs) situated at different locations. This method enhances spectral efficiency(SE) in spite of having a smaller amount complexity and cost compared fully digital systems. This paper presents a fully connected hybrid precoding design for a downlink mmWave dispensed or distributed massive multi-user MIMO. The objective function for the optimization problem is the SE of the proposed system, subject to constraints on analog radio frequency (RF) precoding and power budget. The main aim is to maximize SE. Due to the nonconvex nature of the problem, a two-stage iterative algorithm is proposed to conclude the optimal analog and digital beamforming matrices and sum rate. The 1st stage obtains the optimal digital matrix assuming the analog RF precoder matrix is known, followed by acquiring the optimal analog RF precoder matrix in the next step. The Karush–Kuhn–Tucker (KKT) condition for each maximization problem are compute and examine to derive the solving algorithms for each stage. The simulation results display that the proposed design outperforms current methods in sum rate and approaches the performance of fully digital systems with reduced complexity compared to other alternatives.
Similar content being viewed by others
Data availability
The datasets used and/or analyzed during the current study are available from the corresponding author upon reasonable request.
References
Marzetta, T. L. Noncooperative cellular wireless with unlimited numbers of base station antennas. IEEE Trans. Wireless Commun. 9 (11), 3590–3600 (2010).
Björnson, E., Sanguinetti, L. & MariosKountouris Deploying dense networks for maximal energy efficiency: small cells Meet massive MIMO. IEEE J. Sel. Areas Commun. 34 (4), 832–847 (2016).
Wei, Z., Ng, D. W. K., Yuan, J. & Hui-Ming, W. Optimal resource allocation for power-efficient MC-NOMA with imperfect channel state information. IEEE Trans. Commun. 65 (9), 3944–3961 (2017).
Rappaport, T. S. et al. Mathew Samimi, and Felix Gutierrez. Millimeter wave mobile communications for 5G cellular: it will work! IEEE access 1, 335–349. (2013).
Alkhateeb, A., Leus, G. & Robert, W. Heath. Limited feedback hybrid precoding for multi-user millimeter wave systems. IEEE transactions on wireless communications, 14(11), 6481–6494. (2015).
Heath, R. W., Gonzalez-Prelcic, N. & WonilRoh, S. R. Sayeed. An overview of signal processing techniques for millimeter wave MIMO systems. IEEE J. Selec. Topics Signal Process. 10 (3), 436–453 (2016).
Chen, C. M., Blandino, S., Gaber, A. & Desset, C. André Bourdoux, Liesbet Van der Perre, and SofiePollin. Distributed massive MIMO: A diversity combining method for TDD reciprocity calibration. In GLOBECOM 2017–2017 IEEE Global Communications Conference, 1–7. IEEE, (2017).
Ngo, H. Q., Larsson, E. G. & Marzetta, T. L. Energy and spectral efficiency of very large multiuser MIMO systems. IEEE Trans. Commun. 61 (4), 1436–1449 (2013).
Li, N., Wei, Z., Yang, H., Zhang, X. & Yang, D. Hybrid precoding for MmWave massive MIMO systems with partially connected structure. IEEE Access. 5, 15142–15151 (2017).
Huang, H., Song, Y., Yang, J., Gui, G. & Adachi, F. Deep-learning-based millimeter-wave massive MIMO for hybrid precoding. IEEE Trans. Veh. Technol. 68 (3), 3027–3032 (2019).
Yu, X., Shen, J. C., Zhang, J. & Khaled, B. Letaief. Alternating minimization algorithms for hybrid precoding in millimeter wave MIMO systems. IEEE J. Selec. Topics Signal Process. 10 (3), 485–500 (2016).
Liang, L. & Xu, W. Low-complexity hybrid precoding in massive multiuser MIMO systems. IEEE Wirel. Commun. Lett. 3 (6), 653–656 (2014).
Sohrabi, F. Hybrid digital and analog beamforming design for large-scale antenna arrays. IEEE J. Selec. Topics Signal Process. 10 (3), 501–513 (2016).
Lin, T., Cong, J., Zhu, Y., Zhang, J. & Khaled Ben, L. Hybrid beamforming for millimeter wave systems using the MMSE criterion. IEEE Trans. Commun. 67 (5), 3693–3708 (2019).
Zhao, L., JiajiaGuo, Z. & Wei Derrick Wing Kwan Ng, and Jinhong Yuan. A distributed multi-RF chain hybrid mmWave scheme for small-cell systems. In ICC 2019–2019 IEEE International Conference on Communications (ICC), pp. 1–7. IEEE, (2019).
Zhang, Y., Du, J., Chen, Y. & Li, X. Rabie, and RupakKharel. Near-optimal design for hybrid beamforming in MmWave massive multi-user MIMO systems. IEEE Access. 8, 129153–129168 (2020).
Zhao, X., Lin, T., Zhu, Y. & Zhang, J. Partially-connected hybrid beamforming for spectral efficiency maximization via a weighted MMSE equivalence. IEEE Trans. Wireless Commun. 20 (12), 8218–8232 (2021).
Chary, M., Kanaka, C. H. V., Krishna & Rama Krishna, D. Accurate channel Estimation and hybrid beamforming using artificial intelligence for massive MIMO 5G systems. AEU-International J. Electron. Commun. 173, 154971 (2024).
Senthilkumar, S. et al. Design of microstrip antenna using high frequency structure simulator for 5G applications at 29 ghz resonant frequency. Int. J. Adv. Technol. Eng. Explor. (IJATEE). 9 (92), 996–1008. https://doi.org/10.19101/IJATEE.2021.875500 (July 2022).
Singh, J., Mehrotra, A., Srivastava, S. & Jagannatham, A. K. Lajos Hanzo.Spectral efficiency maximization for MmWave MIMO-Aided integrated sensing and communication under practical constraints. IEEE Trans. Veh. Technol., https://doi.org/10.1109/TVT.2025.3577955
Singh, J., Naveen, B. & Srivastava, S. Jagannatham Pareto-Optimal hybrid beamforming for Finite-Blocklength millimeter wave systems. IEEE Trans. Veh. Technol. 74, 9910–9915. https://doi.org/10.1109/TVT.2025.3534021 (June 2025).
Jitendra Singh, I., Suraj, C. & Srivastava, A. K. NCC Jagannatham,Hybrid transceiver design and optimal power allocation in downlink MmWave hybrid MIMO cognitive radio systems, (2022). https://doi.org/10.1109/NCC55593.2022.9806757
Acknowledgements
Princess Nourah bint Abdulrahman University Researchers Supporting Project number (PNURSP2026R161), Princess Nourah bint Abdulrahman University, Riyadh, Saudi Arabia. Research Supporting Project number (RSPD2026R608), King Saud University, Riyadh, Saudi Arabia.
Author information
Authors and Affiliations
Contributions
R. Rajaganapathy – Developed mathematical equations, conduct the research work and draft the first copy of the manuscript. S. Senthilkumar, Eatedal Alabdulkreem, Nuha Alruwais – Supported in the literature review based on the existing research works and support to final drafting of this paper.
Corresponding author
Ethics declarations
Competing interests
The authors declare no competing interests.
Additional information
Publisher’s note
Springer Nature remains neutral with regard to jurisdictional claims in published maps and institutional affiliations.
Rights and permissions
Open Access This article is licensed under a Creative Commons Attribution-NonCommercial-NoDerivatives 4.0 International License, which permits any non-commercial use, sharing, distribution and reproduction in any medium or format, as long as you give appropriate credit to the original author(s) and the source, provide a link to the Creative Commons licence, and indicate if you modified the licensed material. You do not have permission under this licence to share adapted material derived from this article or parts of it. The images or other third party material in this article are included in the article’s Creative Commons licence, unless indicated otherwise in a credit line to the material. If material is not included in the article’s Creative Commons licence and your intended use is not permitted by statutory regulation or exceeds the permitted use, you will need to obtain permission directly from the copyright holder. To view a copy of this licence, visit http://creativecommons.org/licenses/by-nc-nd/4.0/.
About this article
Cite this article
Rajaganapathi, R., Senthilkumar, S., Alabdulkreem, E. et al. Improving spectral efficiency in distributed massive MIMO in multi-user downlink millimeter wave. Sci Rep (2026). https://doi.org/10.1038/s41598-026-37016-w
Received:
Accepted:
Published:
DOI: https://doi.org/10.1038/s41598-026-37016-w