Abstract
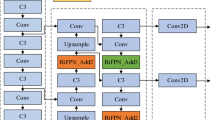
In high-risk industrial environments such as tunnel construction, reliable safety helmet detection is critical for preventing head injuries. However, severe illumination inhomogeneity and multi-scale object appearances pose significant challenges to existing detectors due to static anchor designs and the absence of illumination-aware feature learning. This paper proposes AE-LFOG-YOLO, an end-to-end framework that enhances YOLOv8 through dual physics-informed optimizations. The approach integrates an Illumination-Invariant Module (IIM) that employs a dual-path feature decoupling strategy to suppress lighting artifacts within the network backbone. Concurrently, the Adaptive Evolutionary - Light Field Optimized Generation (AE-LFOG) algorithm replaces static anchors with a dynamic evolutionary process guided by local illumination gradients and thin-lens imaging principles, enabling continuous optimization of anchor parameters during training. Evaluated on a real-world tunnel dataset, the method achieves 94.83% mAP@0.5 and significantly improves robustness under challenging illumination variations, as evidenced by a 35.7% extension in effective operating range. These results demonstrate the effectiveness of integrating physical imaging priors into deep learning for robust visual perception in complex industrial scenarios.
Similar content being viewed by others
Data availability
The data used in this paper is public that named as Safety Helmet Detection and has been deposited at https://tianchi.aliyun.com/dataset/94696. And dataset named as VOC2028 has been deposited at https://aistudio.baidu.com/datasetdetail/43757. The datasets used and analysed during the current study available from the corresponding author on reason able request.
References
Newaz, M. T., Jefferies, M. & Ershadi, M. A critical analysis of construction incident trends and strategic interventions for enhancing safety. Saf. Sci. 187, 106865 (2025).
Rasouli, S., Alipouri, Y. & Chamanzad, S. Smart personal protective equipment (PPE) for construction safety: A literature review. Saf. Sci. 170, 106368 (2024).
Wang, J. et al. Correction of uneven illumination in color microscopic image based on fully convolutional network. Opt. Express. 29 (18), 28503–28520 (2021).
Wang, H. et al. Multi-Scale retinex unfolding network for Low-Light image enhancement. IEEE Trans. Multimedia. 27, 5709–5721 (2025).
Du, Q. et al. A hybrid zero-reference and dehazing network for joint low-light underground image enhancement. Sci. Rep. 15, 10135 (2025).
Wang, B., Zhang, B., Sheng, J. & SRLFormer Single-Retinex-based and low-light image guidance transformer for low-light image enhancement. Comput. Ind. 170, 104314 (2025).
Zhang, T. et al. Cross-modal guided and refinement-enhanced retinex network for robust low-light image enhancement. Inform. Fusion. 124, 103380 (2025).
Zhang, Z. et al. RetinexD-Net: A retinex-densenet fusion architecture for low-light image enhancementin drill pipe detection. Optics & Laser Technology 192, 113547 (2025).
Shi, Y., Zhang, Y. & Dai, S. Chunying Xu. Footsteps detection and identification based on distributed optical fiber sensor and double-YOLO model. Opt. Express. 31 (25), 41391–41405 (2023).
Simon, R. et al. You only thermoelastically deform once: point absorber detection in LIGO test masses with YOLO. Opt. Express. 33, 17601–17616 (2025).
Zhang, Y. et al. Detection of helmet use among construction workers via helmet-head region matching and state tracking. Autom. Constr. 171, 105987 (2025).
Liu, D., Zhao, X. & Fan, W. A small object detection algorithm for mine environment. Eng. Appl. Artif. Intell. 153, 110936 (2025).
Chen, X., Jiao, Z. & Liu, Y. Improved YOLOv8n based helmet wearing inspection method. Sci. Rep. 15, 1945 (2025).
Chen, X. et al. YOLO-GL for efficient multi-target detection in large FOV via hierarchical feature fusion. Sci. Rep. 15, 30774 (2025).
Li, C. et al. Edge Real-Time object detection and DPU-Based hardware implementation for optical remote sensing images. REMOTE Sens. 15 (16), 3975 (2023).
Gu, L. J. et al. Flame Detection using YOLOv5 with K-means Optimized Anchor Boxes. in International Conference on Orange Technology (ICOT), Tainan, Taiwan, (2024).
Gupta, C. et al. An optimized YOLO NAS based framework for realtime object detection. Sci. Rep. 15, 32903 (2025).
Wu, S. et al. Shadow hunter: Low-Illumination Object-Detection algorithm. Appl. Sci. 13 (16), 9261 (2023).
Wang, Z. et al. S-YOLO: an enhanced small object detection method based on adaptive gating strategy and dynamic multi-scale focus module. Neural Netw. 191, 107782 (2025).
Sadima, E., Alkharijah, U. & Hamid, Y. EgoVision a YOLO-ViT hybrid for robust egocentric object recognition. Sci. Rep. 15, 34723 (2025).
Chen, W., Li, C. & Guo, H. A lightweight face-assisted object detection model for welding helmet use. Expert Syst. Appl. 221, 119764 (2023).
Baoju, L. et al. Safety helmet detection methods in heavy machinery factory. Sci. Rep. 15, 18565 (2025).
Du, Q., Zhang, S. & Yang, S. BLP-YOLOv10: efficient safety helmet detection for low-light mining. J. Real-Time Image Proc. 22, 10 (2025).
Han, D. et al. YOLOv8s-SNC: An Improved Safety-Helmet-Wearing Detection Algorithm Based on YOLOv8. Buildings 14(2), 3883 (2024).
Wang, S. et al. Safety helmet monitoring on construction sites using YOLOv10 and advanced transformer architectures with surveillance and Body-Worn cameras. J. Constr. Eng. Manag. 151 (11), 18 (2025).
Hu, L. & Ren, J. YOLO-LHD: an enhanced lightweight approach for helmet wearing detection in industrial environments. Front. Built Environ. 9, 1288445 (2023).
Song, C. & Li, Y. A. YOLOv8 algorithm for safety helmet wearing detection in complex environment. Sci. Rep. 15, 24236 (2025).
Yi, H. et al. Small object detection algorithm based on improved YOLOv8 for remote sensing. IEEE J. Sel. Top. Appl. Earth Observations Remote Sens. 17, 1734–1747 (2024).
Acknowledgements
The authors wish to thank the anonymous reviewers for their valuable suggestions.
Funding
National Natural Science Foundation of China(62275178). Major Science and Technology Program of Sichuan Provincial (2023ZDZX00299).
Author information
Authors and Affiliations
Contributions
Suimei Liu designed the study and wrote the main manuscript text and prepared all figures. Jun Wang supervised the research. All authors reviewed the manuscript.
Corresponding author
Ethics declarations
Competing interests
The authors declare no competing interests.
Additional information
Publisher’s note
Springer Nature remains neutral with regard to jurisdictional claims in published maps and institutional affiliations.
Rights and permissions
Open Access This article is licensed under a Creative Commons Attribution-NonCommercial-NoDerivatives 4.0 International License, which permits any non-commercial use, sharing, distribution and reproduction in any medium or format, as long as you give appropriate credit to the original author(s) and the source, provide a link to the Creative Commons licence, and indicate if you modified the licensed material. You do not have permission under this licence to share adapted material derived from this article or parts of it. The images or other third party material in this article are included in the article’s Creative Commons licence, unless indicated otherwise in a credit line to the material. If material is not included in the article’s Creative Commons licence and your intended use is not permitted by statutory regulation or exceeds the permitted use, you will need to obtain permission directly from the copyright holder. To view a copy of this licence, visit http://creativecommons.org/licenses/by-nc-nd/4.0/.
About this article
Cite this article
Liu, S., Wang, J. AE-LFOG-YOLO: robust safety helmet detection via adaptive anchors and illumination invariant learning. Sci Rep (2026). https://doi.org/10.1038/s41598-026-37326-z
Received:
Accepted:
Published:
DOI: https://doi.org/10.1038/s41598-026-37326-z