Abstract
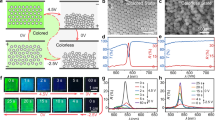
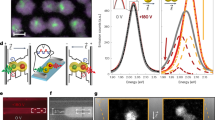
Three-color electrophoretic display (EPD) makes up for the limitation of traditional EPDs in color representation. However, when displaying red color, there are issues such as long response time and low red saturation. In order to improve these defects, a simulation model was constructed using COMSOL finite element simulation method to explore the movement of electro-phoretic particles. Leveraging the principles of three-color EPDs and electrophoresis theory, a novel driving scheme was proposed. This scheme employed high-frequency voltage and low-voltage differential oscillation, aiming to expedite the response time of red particles and enhance the red saturation. The final experimental results showed that the response time of the red particles was 1.76 s, a decrease of 2.42 s, the number of flickers was 1, a decrease of 8, and the maximum red saturation rose to 0.53, an increase of 0.08. The proposed driving scheme effectively improved the red display performance of three-color EPDs.
Similar content being viewed by others
Data availability
Data is contained within the article.
References
Bert, T. & De Smet, H. The microscopic physics of electronic paper revealed. Displays 24, 103–110 (2003).
Cao, J. et al. A convolutional neural network for ghost image recognition and waveform design of electrophoretic displays. IEEE Trans. Consum. Electron. 66, 356–365 (2020).
Duan, F. et al. An adaptive generation method for electrophoretic display driving waveform design. J. Soc. Inform. Display. 24, 676–685 (2016).
Gu, C., Jia, A., Zhang, Y. & Zhang, S. X. A. Emerging electrochromic materials and devices for future displays. Chem. Rev. 122, 14679–14721 (2022).
He, W. et al. Driving waveform design of electrophoretic display based on optimized particle activation for a rapid response speed. Micromachines 11, 498 (2020).
Heikenfeld, J., Drzaic, P., Yeo, J. S. & Koch, T. A critical review of the present and future prospects for electronic paper. J. Soc. Inform. Display. 19, 129–156 (2011).
Jin, M., Shen, S., Yi, Z., Zhou, G. & Shui, L. Optofluid-based reflective displays. Micromachines 9, 159 (2018).
Johnson, M. T. et al. High-quality images on electrophoretic displays. J. Soc. Inform. Display. 14, 175–180 (2006).
Kao, W. C., Chen, H. Y., Liu, Y. H. & Liou, S. C. Hardware engine for supporting gray-tone paintbrush function on electrophoretic papers. J. Disp. Technol. 10, 138–145 (2013).
Kao, W. C. & Tsai, J. C. Driving method of three-particle electrophoretic displays. IEEE Trans. Electron. Devices. 65, 1023–1028 (2018).
Kao, W. C., Ye, J. A., Lin, F., Cheng, P. & Sprague, R. Configurable timing controller design for active matrix electrophoretic display. IEEE Trans. Consum. Electron. 55, 1–5 (2009).
Kim, M. K., Lim, Y. J., Bhattacharyya, S. S., Lee, M. H. & Lee, S. H. Control of motion of fullerene colloidals by dielectrophoretic force for electronic paper-like display. Curr. Appl. Phys. 11, 1192–1196 (2011).
Kim, Y. C. An analysis of reflectivity and response time by Charge-to-Mass of charged particles in an electrophoretic display. Trans. Electr. Electron. Mater. 17, 212–216 (2016).
Lee, J. K., Kim, S. S., Park, Y. I., Kim, C. D. & Hwang, Y. K. In-cell adaptive touch technology for a flexible e-paper display. Solid State Electron. 56, 159–162 (2011).
Li, W. et al. Driving waveform design with rising gradient and Sawtooth wave of electrowetting displays for ultra-low power consumption. Micromachines 11, 145 (2020).
Liu, Y. et al. Active matrix driven electrophoretic display with in-plane switching layout and driving waveform for reflective and transparent modes. Opt. Express. 31, 40102–40112 (2023).
Lu, C. M. & Wey, C. L. A controller design for high-quality images on microcapsule active-matrix electrophoretic displays. J. Inform. Disp. 13, 21–30 (2012).
Qin, Z. et al. Digital halftoning method with simultaneously optimized perceptual image quality and drive current for multi-tonal electrophoretic displays. Appl. Opt. 59, 201–209 (2020).
Shen, S. et al. Improving electrophoretic particle motion control in electrophoretic displays by eliminating the fringing effect via driving waveform design. Micromachines 9, 143 (2018).
Wang, L., Yi, Z., Peng, B. & Zhou, G. In AOPC : Advanced Display Technology; and Micro/Nano Optical Imaging Technologies and Applications, (SPIE: 2015), pp 14–22. (2015).
Xu, W. et al. High-Performance Multi-Level grayscale conversion by driving waveform optimization in electrowetting displays. Micromachines 15, 137 (2024).
Yang, S. H. et al. In SID Symposium Digest of Technical Papers, (Wiley Online Library: pp 1361–1364. (2012).
Yi, Z., Bai, P., Wang, L., Zhang, X. & Zhou, G. An electrophoretic display driving waveform based on improvement of activation pattern. J. Cent. south. Univ. 21, 3133–3137 (2014).
Yi, Z., Feng, H., Zhou, X. & Shui, L. Design of an open electrowetting on dielectric device based on printed circuit board by using a parafilm m. Front. Phys. 8, 193 (2020).
Yi, Z. et al. A novel driver for active matrix electrowetting displays. Displays 37, 86–93 (2015).
Yi, Z. et al. Design of driving waveform based on a damping Oscillation for optimizing red saturation in three-color electrophoretic displays. Micromachines 12, 162 (2021).
Yu, D. et al. Preparation and characterization of acrylic-based electronic inks by in situ emulsifier-free emulsion polymerization for electrophoretic displays. Chem. Mater. 16, 4693–4698 (2004).
Zeng, W. et al. Design of driving waveform based on overdriving voltage for shortening response time in electrowetting displays. Front. Phys. 9, 642682 (2021).
Zeng, W. et al. Design of driving waveform for shortening red particles response time in three-color electrophoretic displays. Micromachines 12, 578 (2021).
Zhang, H. et al. Design of driving waveform for shortening response time of black particles and white particles in Three-Color electrophoretic displays. Micromachines 12, 1306 (2021).
Zhang, Y. et al. Fast-response and monodisperse silica nanoparticles modified with ionic liquid towards electrophoretic displays. Dyes Pigm. 148, 270–275 (2018).
Zhang, Y. et al. Low density and fast response silica coated with ionic liquid polymer nanoparticles towards electrophoretic displays. Mater. Lett. 211, 17–20 (2018).
Funding
This work was supported by the National Natural Science Foundation of China (no. 62575059), the Key Laboratory of Regular Universities in Guangdong Province (no. 2023KSYS011).
Author information
Authors and Affiliations
Contributions
M.J. designed this project and conducted most experiments and data analysis. Z.Y. performed part of the experiments and helped with discussions during manuscript preparation. L.L. and F.C. revised the paper. J.W., W.X. and Z.L. gave suggestions on project management. L.W. and G.Z. provided helpful discussions on the experimental results. All authors have read and agreed to the published version of the manuscript.
Corresponding author
Ethics declarations
Competing interests
The authors declare no competing interests.
Additional information
Publisher’s note
Springer Nature remains neutral with regard to jurisdictional claims in published maps and institutional affiliations.
Rights and permissions
Open Access This article is licensed under a Creative Commons Attribution-NonCommercial-NoDerivatives 4.0 International License, which permits any non-commercial use, sharing, distribution and reproduction in any medium or format, as long as you give appropriate credit to the original author(s) and the source, provide a link to the Creative Commons licence, and indicate if you modified the licensed material. You do not have permission under this licence to share adapted material derived from this article or parts of it. The images or other third party material in this article are included in the article’s Creative Commons licence, unless indicated otherwise in a credit line to the material. If material is not included in the article’s Creative Commons licence and your intended use is not permitted by statutory regulation or exceeds the permitted use, you will need to obtain permission directly from the copyright holder. To view a copy of this licence, visit http://creativecommons.org/licenses/by-nc-nd/4.0/.
About this article
Cite this article
Jiang, M., Yi, Z., Wang, J. et al. Enhancing red color performance in three-color electrophoretic displays using high-frequency voltage and low-voltage differential oscillation. Sci Rep (2026). https://doi.org/10.1038/s41598-026-37368-3
Received:
Accepted:
Published:
DOI: https://doi.org/10.1038/s41598-026-37368-3