Abstract
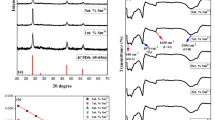
The extensive use of synthetic dyes in industry has raised environmental concerns due to their high toxicity and persistence in water. In this study, a Z-scheme g-C3N4/SnS2 heterostructure was synthesized via a facile one-pot thermal decomposition method with varying SnS₂ loading. The nanocomposites were thoroughly characterized using XRD, FT-IR, DRS, PL, Raman, XPS, FE-SEM, and TEM to confirm their structural, optical, and morphological structures. The photocatalytic performance was evaluated for indigo carmine degradation under natural sunlight. The nanocomposite GS5 sample (5% SnS₂) showed the highest efficiency, achieving 100% dye removal and 74.1% mineralization (TOC) of 10 ppm dye within 30 min at 1 mg/mL catalyst dosage, and 88.67% removal at 50 ppm dye concentration. The photocatalytic performance of the g-C3N4/SnS2 nanocomposites was evaluated by varying key parameters such as pH, catalyst dosage, dye concentration, and regeneration cycles. Structural and optical analyses confirmed the formation of a well-coupled Z-scheme heterojunction, promoting charge separation and reactive oxygen species generation. The degradation mechanism, supported by GC-MS and scavenger studies, highlighted the dominant role of superoxide radicals. Machine learning models, including Random Forest, ANN, SVM, and XGBoost, successfully predicted photocatalytic efficiency, with Random Forest showing the highest accuracy (R² = 0.9734, error = 6.24). This study highlights the importance of light-driven photocatalysis, efficient Z-scheme heterostructures for improved charge separation, and the limited reports using machine learning with g-C3N4/SnS2. It demonstrates the potential of g-C3N4/SnS2 as a solar-driven photocatalyst for degrading recalcitrant dyes and the role of machine learning in predicting real-world performance.
Similar content being viewed by others
Data availability
The data will be made available on request.
References
Hasanpour, M. & Hatami, M. Photocatalytic performance of aerogels for organic dyes removal from wastewaters: review study. J. Mol. Liq. 309, 113094 (2020).
Zhuang, H. et al. Construction of one dimensional ZnWO4@ SnWO4 core-shell heterostructure for boosted photocatalytic performance. J. Mater. Sci. Technol. 35 (10), 2312–2318 (2019).
Haounati, R. et al. Advanced contaminant removal through synergistic interactions of montmorillonite, CoFe2O4 nanoparticles, and surfactants: combining theoretical and experimental approaches. J. Mol. Liq. 428, 127490 (2025).
Kobylewski, S., Jacobson & M.F. and Toxicology of food dyes. Int. J. Occup. Environ. Health. 18 (3), 220–246 (2012).
Jiang, C. et al. Construction of magnetic lignin-based adsorbent and its adsorption properties for dyes. J. Hazard. Mater. 369, 50–61 (2019).
Grzechulska-Damszel, J., Tomaszewska, M. & Morawski, A. Integration of photocatalysis with membrane processes for purification of water contaminated with organic dyes. Desalination 241 (1–3), 118–126 (2009).
Rafiq, A. et al. Photocatalytic degradation of dyes using semiconductor photocatalysts to clean industrial water pollution. J. Ind. Eng. Chem. 97, 111–128 (2021).
Haounati, R., Moutanassim, L. & Hankari, S. E. Tandem incorporation and encapsulation of ag2S nanoparticles onto a nickel metal-organic framework decorated with ag NPs heterojunction for efficient photoreduction of cr (VI). Inorg. Chem. Commun. 182, 115573 (2025).
Hsini, A. et al. 1,2,4,5-Benzene Tetracarboxylic Acid-Doped Polyaniline/Protonated carbon nitride nanostructures for Cr(VI) adsorption in water. ACS Appl. Nano Mater. 7 (11), 13050–13061 (2024).
Kumar, R. et al. Unlocking the non-covalent electrostatic engineering of photocatalysts: from molecular interactions to multifield tuning strategies toward enhanced charge dynamics. Adv. Powder Mater. 4 (6), 100338 (2025).
Kumar, R. et al. Designing tandem S-scheme photo-catalytic systems: mechanistic insights, characterization techniques, and applications. Acta Phys. Chim. Sin. 41 (11), 100150 (2025).
Chauhan, A. et al. Novel hydrogen-bonded organic framework (HOF) for highly efficient photocatalysis: from structural designs to multifunctional applications. Coord. Chem. Rev. 535, 216634 (2025).
Huang, T. Y. et al. Synthesis, characterization, enhanced sunlight photocatalytic properties, and stability of Ag/Ag 3 PO 4 nanostructure-sensitized BiPO 4. RSC Adv. 5 (54), 43854–43862 (2015).
Bora, L. V. & Mewada, R. K. Visible/solar light active photocatalysts for organic effluent treatment: Fundamentals, mechanisms and parametric review. Renew. Sustain. Energy Rev. 76, 1393–1421 (2017).
Ng, Y. H. et al. A perspective on fabricating carbon-based nanomaterials by photocatalysis and their applications. Energy Environ. Sci. 5 (11), 9307–9318 (2012).
Hong, Y. et al. A facile and scalable route for synthesizing ultrathin carbon nitride nanosheets with efficient solar hydrogen evolution. Carbon 136, 160–167 (2018).
Jiang, L. et al. Doping of graphitic carbon nitride for photocatalysis: A review. Appl. Catal. B. 217, 388–406 (2017).
Hu, C. et al. Phosphorus and sulfur codoped g-C3N4 as an efficient metal-free photocatalyst. Carbon 127, 374–383 (2018).
Yang, Y. et al. In-situ growth of Zn–AgIn5S8 quantum Dots on g-C3N4 towards 0D/2D heterostructured photocatalysts with enhanced hydrogen production. Int. J. Hydrog. Energy. 44 (30), 15882–15891 (2019).
Tang, M. et al. Facile synthesis of dual Z-scheme g-C3N4/Ag3PO4/AgI composite photocatalysts with enhanced performance for the degradation of a typical neonicotinoid pesticide. Appl. Catal. B. 268, 118395 (2020).
Bagheri, N. et al. Synthesis of g-C3N4@ CuMOFs nanocomposite with superior peroxidase mimetic activity for the fluorometric measurement of glucose. Spectrochim. Acta Part A Mol. Biomol. Spectrosc. 213, 28–36 (2019).
Li, P. et al. Ultrathin porous g-C3N4 nanosheets modified with AuCu alloy nanoparticles and CC coupling photothermal catalytic reduction of CO2 to ethanol. Appl. Catal. B. 266, 118618 (2020).
Wang, X. et al. Metal-containing carbon nitride compounds: a new functional organic–metal hybrid material. Adv. Mater. 21 (16), 1609–1612 (2009).
Pan, C. et al. Dramatic activity of C3N4/BiPO4 photocatalyst with core/shell structure formed by self-assembly. Adv. Funct. Mater. 22 (7), 1518–1524 (2012).
Liu, E. et al. Fabrication of 2D SnS2/g-C3N4 heterojunction with enhanced H2 evolution during photocatalytic water splitting. J. Colloid Interface Sci. 524, 313–324 (2018).
Xu, Q. et al. S-scheme heterojunction photocatalyst. Chem 6 (7), 1543–1559 (2020).
Xiang, Q., Yu, J. & Jaroniec, M. Preparation and enhanced visible-light photocatalytic H2-production activity of graphene/C3N4 composites. J. Phys. Chem. C. 115 (15), 7355–7363 (2011).
Li, X. et al. Synthesis and photoactivity of nanostructured CdS–TiO2 composite catalysts. Catal. Today. 225, 64–73 (2014).
Haounati, R. et al. Z-Scheme g-C3N4/Fe3O4/Ag3PO4 @Sep magnetic nanocomposites as heterojunction photocatalysts for green malachite degradation and dynamic molecular studies. Colloids Surf., A. 671, 131509 (2023).
Sudhaik, A. et al. Structural design of dual Z-scheme GCN/CdO/CaFe2O4 ternary heterojunction with high visible light activity: photocatalytic performance and mechanism in the degradation of congo red dye. Inorg. Chem. Commun. 172, 113697 (2025).
Chauhan, A. et al. Recent updates on Ag2WO4-based S-scheme heterojunction photocatalytic materials for environmental remediation. Inorg. Chem. Commun. 170, 113370 (2024).
Sharma, S. et al. Recent updates on a Cs3Bi2Br9-based heterojunction photocatalyst for selective CO2 conversion into (CO/CH4) products. J. Ind. Eng. Chem. 148, 724–741 (2025).
Van, K. N. et al. Facile construction of S-scheme SnO2/g-C3N4 photocatalyst for improved photoactivity. Chemosphere 289, 133120 (2022).
Tahir, M. et al. Enhanced photocatalytic hydrogen energy production of g-C3N4‐WO3 composites under visible light irradiation. Int. J. Energy Res. 42 (15), 4667–4673 (2018).
MuthuKathija, M. et al. A novel biogenic method to synthesis a ternary (ZnO-Ag)/g-C3N4 nanocomposite with an enhanced photocatalytic and antibacterial activities. Inorg. Chem. Commun. 154, 110877 (2023).
Tahir, M. B. et al. Activated carbon doped WO3 for photocatalytic degradation of rhodamine-B. Appl. Nanosci. 10 (3), 869–877 (2020).
Kumar, R. et al. Photocatalysis and adsorption coupling in S-scheme K and P doped g-C3N4/GO/MgFe2O4 photocatalyst for enhanced degradation of congo red dye. Nano Express 6 (1) (2025).
Rana, A. et al. Tailoring dual S-Scheme based g-C3N4/ZnO/TiO2 ternary photocatalytic system immobilized on floating Cork for environmental remediation. J. Taiwan Inst. Chem. Eng. 168, 105914 (2025).
Sudhaik, A. et al. Manipulating the charge transfer pathway in a dual Z-scheme BiOBr/g-C3N4/V2O5-Al2O3 heterojunction toward efficient degradation of textile dyes. J. Taiwan Inst. Chem. Eng. 178, 106373 (2026).
Chauhan, A. et al. Fabrication of a dual Z-scheme Ag3PO4/g-C3N4/Bi2MoO6 ternary nanocomposite for effective degradation of methylene blue dye. J. Solgel Sci. Technol. 112 (3), 688–702 (2024).
Zhang, Z. et al. Ultrathin hexagonal SnS2 nanosheets coupled with g-C3N4 nanosheets as 2D/2D heterojunction photocatalysts toward high photocatalytic activity. Appl. Catal. B. 163, 298–305 (2015).
Xiang, Q., Yu, J. & Jaroniec, M. Synergetic effect of MoS2 and graphene as cocatalysts for enhanced photocatalytic H2 production activity of TiO2 nanoparticles. J. Am. Chem. Soc. 134 (15), 6575–6578 (2012).
Cheng, Y., He, J. & Yang, P. Construction of layered SnS2 and g-C3N4 nanoarchitectonics towards pollution degradation and H2 generation. Colloids Surf., A. 680, 132678 (2024).
Parmar, M. et al. Synthesis of eco-friendly polyaniline-zeolite nanocomposite for pollutant remediation: empowered by robust machine learning algorithm. J. Clean. Prod. 470, 143339 (2024).
Meng, K. et al. Application of machine learning based high-throughput analysis for predicting the degradation performance of TiO2 doped photocatalysts in air pollutants. Mater. Today Commun. 42, 111163 (2025).
Gnanaprakasam, A., Thirumarimurugan, M. & Shanmathi, N. Machine learning, a powerful tool for the prediction of BiVO4 nanoparticles efficiency in photocatalytic degradation of organic dyes. J. Environ. Sci. Health A. 59 (1), 15–24 (2024).
Ahmed, Y. et al. Optimizing photocatalytic dye degradation: A machine learning and metaheuristic approach for predicting methylene blue in contaminated water. Results Eng. 25, 103538 (2025).
Ansari, S. A. & Cho, M. H. Growth of three-dimensional flower-like SnS2 on g-C3N4 sheets as an efficient visible-light photocatalyst, photoelectrode, and electrochemical supercapacitance material. Sustainable Energy Fuels. 1 (3), 510–519 (2017).
Li, M. et al. Facet, junction and electric field engineering of bismuth-based materials for photocatalysis. ChemCatChem 10 (20), 4477–4496 (2018).
Goclon, J. & Winkler, K. Computational insight into the mechanism of O2 to H2O2 reduction on amino-groups-containing g-C3N4. Appl. Surf. Sci. 462, 134–141 (2018).
AbouSeada, N., Ahmed, M. A. & Elmahgary, M. G. Synthesis and characterization of novel magnetic nanoparticles for photocatalytic degradation of Indigo Carmine dye. Mater. Sci. Energy Technol. 5, 116–124 (2022).
Shinde, S. G. et al. Multi-doped ZnO photocatalyst for solar induced degradation of Indigo Carmine dye and as an antimicrobial agent. J. Inorg. Organomet. Polym Mater. 30 (4), 1141–1152 (2020).
Ray, S. K., Dhakal, D. & Lee, S. W. Visible light driven Ni–BaMo3O10 photocatalyst for Indigo Carmine degradation: mechanism and pathways. Mater. Sci. Semiconduct. Process. 105, 104697 (2020).
Bhapkar, A. R. et al. Aluminium doped ZnO nanostructures for efficient photodegradation of Indigo Carmine and Azo Carmine G in solar irradiation. Appl. Nanosci. 13 (8), 5777–5793 (2023).
Kumar, R. et al. Visible light assisted surface plasmon resonance triggered Ag/ZnO nanocomposites: synthesis and performance towards degradation of Indigo Carmine dye. Environ. Sci. Pollut. Res. 30 (44), 98619–98631 (2023).
Matsudo, A. et al. Eco-Friendly photocatalytic solutions: synthesized TiO2 nanoparticles in cellulose membranes for enhanced degradation of Indigo Carmine dye. ACS Omega. 9 (43), 43395–43405 (2024).
Malomane, N., Moutloali, R. M. & Managa, M. Enhanced visible light degradation of Indigo Carmine dye using conventional and green synthesized TiO2 conjugates with porphyrin. J. Mol. Struct. 1336, 142063 (2025).
Chuan, Z. et al. Enhanced photocatalytic degradation of Indigo Carmine dye by biomass carbon supported beta-Bi2O3 doping with ag ions. J. Alloys Compd. 1024, 180163 (2025).
de Graaf, M. E. et al. Mechanistic insights into the photocatalytic Indigo Carmine dye decolorization by Co3O4/TiO2. ChemPhysChem 26 (8), e202400688 (2025).
Sukhadeve, G. K. et al. Visible light assisted photocatalytic degradation of Indigo Carmine dye and NO2 removal by Fe doped TiO2 nanoparticles. Ceram. Int. 48 (19, Part B), 29121–29135 (2022).
Lianmawii, L. & Singh, N. M. Luminescence and photocatalytic degradation of Indigo Carmine in the presence of Sm3 + doped ZnS nanoparticles. Sci. Rep. 13 (1), 22450 (2023).
Abdel-Aziz, R., Ahmed, M. A. & Abdel-Messih, M. F. A novel UV and visible light driven photocatalyst AgIO4/ZnO nanoparticles with highly enhanced photocatalytic performance for removal of Rhodamine B and Indigo Carmine dyes. J. Photochem. Photobiol., A. 389, 112245 (2020).
Channei, D. et al. Synthesis and characterization of WO3/CeO2 heterostructured nanoparticles for photodegradation of Indigo Carmine dye. ACS Omega. 6 (30), 19771–19777 (2021).
Ali, H. A. et al. Photo catalytic degradation of Indigo Carmine in aqueous media using nano crystalline zirconia by solid state method: synthesis and characterization. Eurasian J. Phys. Chem. Math. 12, 55–64 (2022).
Darwish, A. S., Sayed, M. A. & Shebl, A. Cuttlefish bone stabilized Ag3VO4 nanocomposite and its Y2O3-decorated form: Waste-to-value development of efficiently ecofriendly visible-light-photoactive and biocidal agents for dyeing, bacterial and larvae depollution of egypt’s wastewater. J. Photochem. Photobiol., A. 401, 112749 (2020).
Janbandhu, S. Y. et al. CdS/TiO2 heterojunction in glass matrix: Synthesis, characterization, and application as an improved photocatalyst. Appl. Surf. Sci. 497, 143758 (2019).
Lubis, S., Sheilatina, Wardani, D. & Sitompul Photocatalytic degradation of indigo carmine dye using α-Fe2O3/bentonite nanocomposite prepared by mechanochemical synthesis. IOP Conference Series: Materials Science and Engineering, 509(1): p. 012142. (2019).
Divya Lakshmi, K. V. et al. Visible Light Driven Mesoporous Mn and S co-doped TiO2 Nano Material: Characterization and Applications in Photocatalytic Degradation of Indigocarmine Dye and Antibacterial Activity Vol. 10, p. 494–504 (Environmental Nanotechnology, Monitoring & Management, 2018).
Sowbhagya & Ananda, S. Synthesis and characterization of Se-doped ZnO nanoparticles by electrochemical method: photodegradation kinetics of Indigo Carmine dye and study of Antimicrobial, antimitotic activities of Se-doped ZnO nanoparticles. Chem. Sci. Int. J. 4 (5), 616–637 (2014).
Rakesh et al. Synthesis of Niobium doped ZnO nanoparticles by electrochemical method: Characterization, photodegradation of Indigo Carmine dye and antibacterial study. Adv. Nanopart. 03No.04, 15 (2014).
Mai Tho, N. T. et al. A novel n–p heterojunction Bi2S3/ZnCo2O4 photocatalyst for boosting visible-light-driven photocatalytic performance toward Indigo Carmine. RSC Adv. 13 (24), 16248–16259 (2023).
Sayed, M. A. et al. Hydrothermal synthesis and structural optimization of Bi2O3/Bi2WO6 nanocomposites for synergistic photodegradation of Indigo Carmine dye. Sci. Rep. 15 (1), 17260 (2025).
Ajibade, P. A. & Nnadozie, E. C. Synthesis and structural studies of manganese ferrite and zinc ferrite nanocomposites and their use as photoadsorbents for Indigo Carmine and methylene blue dyes. ACS Omega. 5 (50), 32386–32394 (2020).
Kurt, B. Z., Durmus, Z. & Durmus, A. Preparation and characterization of platinum (Pt) and palladium (Pd) nanoparticle decorated graphene sheets and their utilization for the elimination of basic Fuchsin and Indigo Carmine dyes. Solid State Sci. 51, 51–58 (2016).
Dabhade, G. et al. Optical CuAl2O4 used as photocatalyst for IC dye degradation. Water Pract. Technol. 19 (5), 2032–2044 (2024).
Acknowledgements
The authors would like to thank the Department of Chemistry (PDEU), Dr. Uttam Kumar Bhui, School of Petroleum Engineering, PDEU (PL analysis), Solar Research and Development Centre (SRDC), PDEU (FE-SEM analysis) and PDEU for support in characterization and analysis facilities. The authors acknowledge the support and guidance of Dr. Abhishek Gor for Rietveld analysis.
Funding
This work was supported by the Deanship of Scientific Research, Vice Presidency for Graduate Studies and Scientific Research at King Faisal University, Saudi Arabia (Grant No. KFU253313).
Author information
Authors and Affiliations
Contributions
HP, PM, JP: data collection, analysis and interpretation of results draft manuscript preparation, GP & RG: software modelling, manuscript preparation, IT, NT, MAM SM & SS: Resources and investigation, manuscript preparation, RG: Supervision, Review and revision of the manuscript, Conceptualization. All authors reviewed the results and approved the final version of the manuscript.
Corresponding authors
Ethics declarations
Competing interests
The authors declare no competing interests.
Additional information
Publisher’s note
Springer Nature remains neutral with regard to jurisdictional claims in published maps and institutional affiliations.
Supplementary Information
Below is the link to the electronic supplementary material.
Rights and permissions
Open Access This article is licensed under a Creative Commons Attribution-NonCommercial-NoDerivatives 4.0 International License, which permits any non-commercial use, sharing, distribution and reproduction in any medium or format, as long as you give appropriate credit to the original author(s) and the source, provide a link to the Creative Commons licence, and indicate if you modified the licensed material. You do not have permission under this licence to share adapted material derived from this article or parts of it. The images or other third party material in this article are included in the article’s Creative Commons licence, unless indicated otherwise in a credit line to the material. If material is not included in the article’s Creative Commons licence and your intended use is not permitted by statutory regulation or exceeds the permitted use, you will need to obtain permission directly from the copyright holder. To view a copy of this licence, visit http://creativecommons.org/licenses/by-nc-nd/4.0/.
About this article
Cite this article
Gaur, R., Parmar, H., Patel, J. et al. Machine learning-driven performance prediction of Z-scheme g-C3N4/SnS2 heterostructure photocatalyst for complete mineralization of indigo carmine and elucidation of degradation pathways. Sci Rep (2026). https://doi.org/10.1038/s41598-026-37528-5
Received:
Accepted:
Published:
DOI: https://doi.org/10.1038/s41598-026-37528-5