Abstract
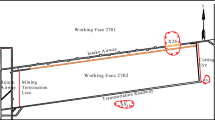
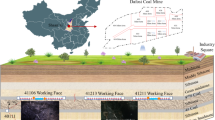
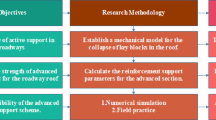
The installation quality and long-term stability of roadway roof bolts/cables are critical to the safety of deep coal mines, yet conventional manual inspections are time-consuming, subjective, and difficult to perform frequently. This paper presents a mobile laser scanning (MLS)–based method for automatic recognition and parameter extraction of roof bolts/cables from 3D point clouds. A SLAM-based MLS system is first used to obtain a continuous 3D model of the roadway. The roof is then globally aligned and separated from surrounding objects using a cloth simulation filter (CSF), which yields candidate roof points. Instance-level clusters are extracted by density-based clustering combined with geometric constraints, and principal component analysis (PCA) is applied to derive key geometric parameters for each bolt/cable, including exposed length, inclination, and row/column spacing. Field experiments were carried out on five consecutive segments of a return airway in a deep coal mine, with 127 manually labeled bolts/cables. The proposed method correctly identified 118 of them, achieving a precision of 96.72% and a recall of 92.91%, while also providing an automatically generated parameter database for engineering evaluation. The results indicate that the method can effectively support intelligent assessment of roadway support quality, although its performance remains dependent on MLS data quality and the visibility of exposed bolts/cables, highlighting the need for further validation in additional mines and under more extreme monitoring conditions.
Similar content being viewed by others
Data availability
The data that support the findings of this study are available from the corresponding author(yrf@hpu.edu.cn) on reasonable request.
References
Gao, F. & Liu, W. A non-destructive method for measuring rock bolt loads based on 3D laser scanning and deep learning. J. China Coal Soc. https://doi.org/10.13225/j.cnki.jccs.2025.0245 (2025).
Wang, G. et al. Research and application practice of digital intelligent technology and complete set of equipment for efficient coal mining. J. China Coal Soc. 50, 43–64. https://doi.org/10.13225/j.cnki.jccs.2024.1402 (2025).
Zang, C. et al. Research on the failure process and stability control technology in a deep roadway: numerical simulation and field test. Energy Sci. Eng. 8, 2297–2310. https://doi.org/10.1002/ese3.664 (2020).
Cheng, P. et al. Mechanical analysis of combined bearing action of surrounding rock and prestressed anchor support and optimization of support parameters. Chin. J. Rock. Mech. Eng. 44, 134–142 (2025).
Kang, H., Wang, J. & Lin, J. Study and applications of roadway support techniques for coal mines. J. China Coal Soc. 35, 1809–1814. https://doi.org/10.13225/j.cnki.jccs.2010.11.008 (2010).
Ma, Z. et al. Identification and application of key parameters of bolt support for roadways with extra-thick mudstone roof. China Saf. Sci. J. 27, 121–126. https://doi.org/10.16265/j.cnki.issn1003-3033.2017.07.022 (2017).
Kang, H. et al. Key technology and equipment analysis and research strategies of rapid and intelligent driving in complex roadways of coal mines. J. China Univ. Min. Technol. 54, 237–257. https://doi.org/10.13247/j.cnki.jcumt.20240116 (2025).
Zhou, K. Development of dynamic monitoring system for underground support based on wireless sensor network. Thesis, Northeastern University (2020).
Wang, K. et al. Evaluation method of bolt anchorage quality based on convolutional neural network. Tunn. Constr. 40, 202–208 (2020).
Qi, J. et al. Design of a tunnel anchor monitoring system based on long Short-Term Memory–Autoregressive integrated moving average prediction. Electronics 13, 2840. https://doi.org/10.3390/electronics13142840 (2024).
Song, X. et al. Apollocar3d: A large 3D car instance understanding benchmark for autonomous driving. In Proc. IEEE/CVF Conf. Comput. Vis. Pattern Recognit. (CVPR) 5452–5462 (2019).
Ren, Z. et al. Review and prospects of 3D laser scanning technology in underground mining. J. Henan Polytech. Univ. (Nat Sci). 44, 89–100. https://doi.org/10.16186/j.cnki.1673-9787.2024070014 (2025).
Li, S. et al. Study on key technology of patrol robots for fully-mechanized mining face. Coal Sci. Technol. 48, 218–225. https://doi.org/10.13199/j.cnki.cst.2020.07.022 (2020).
Singh, S. K., Banerjee, B. P. & Raval, S. A review of laser scanning for geological and geotechnical applications in underground mining. Int. J. Min. Sci. Technol. 33, 133–154. https://doi.org/10.1016/j.ijmst.2022.09.022 (2023).
Zhang, W. et al. An easy-to-use airborne lidar data filtering method based on cloth simulation. Remote Sens. 8, 501. https://doi.org/10.3390/rs8060501 (2016).
Guo, Y. et al. Rotational projection statistics for 3D local surface description and object recognition. Int. J. Comput. Vis. 105, 63–86. https://doi.org/10.1007/s11263-013-0627-y (2013).
Liu, J. & Bai, D. 3D point cloud registration algorithm based on feature matching. Acta Opt. Sin. 38, 1215005. https://doi.org/10.3788/AOS201838.1215005 (2018).
Patwardhan, A. & Karim, R. Health monitoring of ground support system through point-cloud processing: rockbolts extraction phase. Int. J. Syst. Assur. Eng. Manag. 1–13. https://doi.org/10.1007/s13198-025-02758-9 (2025).
Singh, S. K., Raval, S. & Banerjee, B. Roof bolt identification in underground coal mines from 3D point cloud data using local point descriptors and artificial neural network. Int. J. Remote Sens. 42, 367–377. https://doi.org/10.1080/2150704X.2020.1809734 (2021).
Weidner, L. & Walton, G. Generalized extraction of bolts, mesh, and rock in tunnel point clouds: A critical comparison of geometric feature-based methods using random forest and neural networks. Remote Sens. 16, 4466. https://doi.org/10.3390/rs16234466 (2024).
Li, S. et al. A geometric-feature-based method for automatic extraction of anchor rod points from dense point cloud. Sensors 22, 9289. https://doi.org/10.3390/s22239289 (2022).
Gallwey, J., Eyre, M. & Coggan, J. A machine learning approach for the detection of supporting rock bolts from laser scan data in an underground mine. Tunn. Undergr. Space Technol. 107, 103656. https://doi.org/10.1016/j.tust.2020.103656 (2021).
Brodu, N. & Lague, D. 3D terrestrial lidar data classification of complex natural scenes using a multi-scale dimensionality criterion: applications in geomorphology. ISPRS J. Photogramm Remote Sens. 68, 121–134. https://doi.org/10.1016/j.isprsjprs.2012.01.006 (2012).
Weinmann, M., Jutzi, B. & Mallet, C. Feature relevance assessment for the semantic interpretation of 3D point cloud data. ISPRS Ann. Photogramm. Remote Sens. Spat. Inf. Sci. 2, 313–318. https://doi.org/10.5194/isprsannals-II-5-W2-313-2013 (2013).
Qi, C. R. et al. PointNet: Deep learning on point sets for 3D classification and segmentation. In Proc. IEEE Conf. Comput. Vis. Pattern Recognit. (CVPR) 652–660. (2017). https://doi.org/10.1109/CVPR.2017.76
Qi, C. R. et al. PointNet++: deep hierarchical feature learning on point sets in a metric space. Adv. Neural Inf. Process. Syst. 30, 5099–5108 (2017).
Hu, Q. et al. RandLA-Net: Efficient semantic segmentation of large-scale point clouds. In Proc. IEEE/CVF Conf. Comput. Vis. Pattern Recognit. (CVPR) 11108–11117 (2020). https://doi.org/10.1109/CVPR42600.2020.01112
Saydam, S. et al. A coarse-to-fine approach for rock bolt detection from 3D point clouds. IEEE Access. 9, 148873–148883. https://doi.org/10.1109/ACCESS.2021.3120207 (2021).
Singh, S. K., Raval, S. & Banerjee, B. A robust approach to identify roof bolts in 3D point cloud data captured from a mobile laser scanner. Int. J. Min. Sci. Technol. 31, 303–312. https://doi.org/10.1016/j.ijmst.2021.01.001 (2021).
Liu, W. et al. A novel method for estimating axial force of rock bolt through 3D laser scanning and deep learning. Rock. Mech. Rock. Eng. 57, 1437–1450. https://doi.org/10.1007/s00603-023-03638-z (2024).
Liu, W. et al. An enhanced segmentation method for 3D point cloud of tunnel support system using PointNet + + and coverage-voted strategy algorithms. J. Rock. Mech. Geotech. Eng. https://doi.org/10.1016/j.jrmge.2025.03.039 (2025).
Patra, D. et al. A deep learning approach to identify rock bolts in complex 3D point clouds of underground mines captured using mobile laser scanners. Remote Sens. 17, 2701. https://doi.org/10.3390/rs17152701 (2025).
Han, Z. et al. A physics-guided hierarchical deep learning framework for underground rock reinforcement compliance check based on 4D point cloud data. Tunn. Undergr. Space Technol. 164, 106829. https://doi.org/10.1016/j.tust.2025.106829 (2025).
Ren, Z., Wang, L., Bi, L. & Robust GICP-based 3D lidar SLAM for underground mining environment. Sensors 19, 2915. https://doi.org/10.3390/s19132915 (2019).
Ren, Z. et al. Two-stage denoising method for complex underground tunnel scene three-dimensional point clouds. Coal Sci. Technol. 53, 327–337 (2025).
Xu, Y. et al. Generation of ground truth datasets for the analysis of 3D point clouds in urban scenes acquired via different sensors. Int. Arch. Photogramm Remote Sens. Spat. Inf. Sci. 42, 2009–2015. https://doi.org/10.5194/isprs-archives-XLII-3-2009-2018 (2018).
Fontana, S. et al. A benchmark for point clouds registration algorithms. Robot Auton. Syst. 140, 103734. https://doi.org/10.1016/j.robot.2021.103734 (2021).
Acknowledgements
The authors would like to thank the National Natural Science Foundation of China (Project No. 52204168), the Henan Province Key Research and Development and Promotion Special Project (Science and Technology Research) (Project No. 252102321101), and the Fundamental Research Funds for the Universities of Henan Province (NSFRF2502065) ,The 77th Batch of General Financial Support from the China Postdoctoral Science Foundation (2025M771793) for their financial support.
Funding
The National Natural Science Foundation of China (Project No. 52204168); the Henan Province Key Research and Development and Promotion Special Project (Science and Technology Research) (Project No. 252102321101); the Fundamental Research Funds for the Universities of Henan Province (NSFRF2502065); The 77th Batch of General Financial Support from the China Postdoctoral Science Foundation (2025M771793).
Author information
Authors and Affiliations
Contributions
Zhuli Ren: Conceptualization, Methodology, Investigation, Resources, Writing-review & editing, Supervision; Hongyang Zhu: Conceptualization, Methodology, Data curation, Writing-original draft, Writing-review & editing; Lei Zhao: Conceptualization, Writing-original draft, Writing review & editing; Ruifu Yuan: Methodology, Writing-review & editing.
Corresponding author
Ethics declarations
Competing interests
The authors declare no competing interests.
Additional information
Publisher’s note
Springer Nature remains neutral with regard to jurisdictional claims in published maps and institutional affiliations.
Rights and permissions
Open Access This article is licensed under a Creative Commons Attribution-NonCommercial-NoDerivatives 4.0 International License, which permits any non-commercial use, sharing, distribution and reproduction in any medium or format, as long as you give appropriate credit to the original author(s) and the source, provide a link to the Creative Commons licence, and indicate if you modified the licensed material. You do not have permission under this licence to share adapted material derived from this article or parts of it. The images or other third party material in this article are included in the article’s Creative Commons licence, unless indicated otherwise in a credit line to the material. If material is not included in the article’s Creative Commons licence and your intended use is not permitted by statutory regulation or exceeds the permitted use, you will need to obtain permission directly from the copyright holder. To view a copy of this licence, visit http://creativecommons.org/licenses/by-nc-nd/4.0/.
About this article
Cite this article
Ren, Z., Zhu, H., Zhao, L. et al. MLS-based recognition and parameter extraction of roadway roof bolts/cables from 3D point clouds. Sci Rep (2026). https://doi.org/10.1038/s41598-026-37689-3
Received:
Accepted:
Published:
DOI: https://doi.org/10.1038/s41598-026-37689-3