Abstract
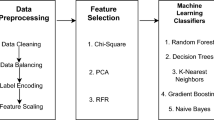
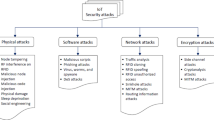
Security infrastructure for Internet of Things (IoT) networks is still a major concern today, as they are constantly violated by cyber attacks. Machine Learning (ML)can efficiently scale to identify abnormal activity in large volumes of IoT traffic. The proposed Smart Secured IoT Framework (SSIF) is used to improve the security of smart IoT networks with the assist of the Bot-IoT dataset. The framework begins with data preprocessing to ensure high-quality input, followed by Cluster F1–MI feature engineering, which uses correlation-based F1–MI to select the most informative attributes and produce a robust, compact feature set. Cluster-based feature validation groups features that are related to cluster the features that are correlated with each other so that a representative feature is selected from the cluster and the correlation is removed to improve efficiency. Our framework uses a variety of ML classifiers, such as SVM, Random Forest, Gradient Boosting, XGBoost, and Neural Networks, for threat classification that is adaptable and accurate. The effectiveness of the classifiers can be tested using metrics like Accuracy, Precision, Recall, F1 Score, and AUC-PR. The random forest can classify attack types with accuracy of more than 0.97. The system also generates an email notification to the admin and activates the alarm when an anomaly is detected. The proposed SSIF proves to be an effective, cheap, and easy solution to secure smart IoT environments from Bot-IoT.
Similar content being viewed by others
Data availability
The corresponding author, Vidhya Nagavel, can provide access to the data upon reasonable request.
References
Koroniotis, N., Sitnikova, E. & NourMoustafa, and A new network forensic framework based on deep learning for internet of things networks: A particle deep framework. Future Generation Comput. Syst. 110, 91–106 (2020).
Illy, P. Georges Kaddoum, KuljeetKaur, and SahilGarg. ML-based IDPS enhancement with complementary features for home IoT networks. IEEE Trans. Netw. Serv. Manage. 19 (2), 772–783 (2022).
Nawir, M. Amiza Amir, NaimahYaakob, and Ong Bi Lynn. Effective and efficient network anomaly detection system using MLalgorithm. Bull. Electr. Eng. Inf. 8 (1), 46–51 (2019).
Hu, Y. et al. Graph-based semi-supervised learning for activity labeling in health smart home. IEEE Access. 8, 193655–193664 (2020).
Ramesh, P. et al. Detection of commercial crop weeds using machine learning algorithms. Sci. Rep. 15 (1), 38791 (2025).
Zhang, Y., MeikangQiu, C. W. & Tsai Mohammad mehedi Hassan, and AtifAlamri. Health-CPS: healthcare cyber-physical system assisted by cloud and big data. IEEE Syst. J. 11 (1), 88–95 (2015).
Wu, Y. et al. Masinet: network intrusion detection for Iot security based on meta-learning framework. IEEE Internet Things J. 11 (14), 25136–25146 (2024).
El-Sofany, H. & El-Seoud, S. A. Karam, and BelgacemBouallegue. Using MLalgorithms to enhance IoT system security. Sci. Rep. 14 (1), 12077 (2024).
Hossain, M. A. Deep learning-based intrusion detection for IoT networks: a scalable and efficient approach. EURASIP Journal on Information Security no. 1 (2025): 28. (2025).
Kerrakchou, I., Hassan, A. A. E., Chadli, S. & Emharraf, M. Selection of efficient MLalgorithm on Bot-IoT dataset for intrusion detection in internet of things networks. Indones. J. Electr. Eng. Comput. Sci. 31 (3), 1784–1793 (2023).
Elayan, H. Digital twin for intelligent context-aware IoT healthcare systems. IEEE Internet Things J. 8 (23), 16749–16757 (2021).
Kaur, B. et al. Ghorbani. Internet of things (IoT) security dataset evolution: challenges and future directions. Internet Things. 22, 100780 (2023).
Qi, K. Advancing hospital healthcare: achieving IoT-based secure health monitoring through multilayer machine learning. J. Big Data. 12 (1), 1 (2025).
Ali, M., Ahmed & Salah Alawi Hussein Al-Sharafi. Intrusion detection in IoT networks using MLand deep learning approaches for MitM attack mitigation. Discover Internet Things. 5 (1), 1–13 (2025).
Otoum, Y., Liu, D. & AmiyaNayak DL-IDS: a deep learning–based intrusion detection framework for Securing IoT. Trans. Emerg. Telecommunications Technol. 33 (3), e3803 (2022).
Gajewski, M., JordiMongayBatalla, G., Mastorakis & Constandinos, X. Mavromoustakis. Anomaly traffic detection and correlation in smart home automation IoT systems. Trans. Emerg. Telecommunications Technol. 33 (6), e4053 (2022).
Diwan, T. D., Siddartha Choubey, H. S., Hota, S. B. & Goyal Sajjad Shaukat Jamal, Piyush Kumar Shukla, and Basant Tiwari. Feature entropy estimation (FEE) for malicious IoT traffic and detection using machine learning. Mob. Inf. Syst. 2021 (1), 8091363. (2021).
Badawy, M., Ramadan, N. & Hesham Ahmed Hefny. Healthcare predictive analytics using MLand deep learning techniques: a survey. J. Electr. Syst. Inform. Technol. 10 (1), 40 (2023).
Khan, M., Mahsal & Alkhathami, M. Anomaly detection in IoT-based healthcare: MLfor enhanced security. Sci. Rep. 14 (1), 5872 (2024).
Makkar, A., SahilGarg, N., Kumar, M. & ShamimHossain Ahmed Ghoneim, and Mubarak Alrashoud. An efficient spam detection technique for IoT devices using machine learning. IEEE Trans. Industr. Inf. 17 (2), 903–912 (2020).
Shafiq, M., ZhihongTian, Y., Sun, X. D. & Guizani, M. Selection of effective MLalgorithms and Bot-IoT attacks traffic identification for internet of things in smart cities. Future Generation Comput. Syst. 107, 433–442 (2020).
Shareena, J., AiswaryaRamdas & Haripriya, A. P. Intrusion detection system for Iot botnet attacks using deep learning. SN Comput. Sci. 2 (3), 1–8 (2021).
Cvitić, I., DraganPerakovic, B. B. & Gupta Boosting-based DDoS detection in internet of things systems. IEEE Internet Things J. 9 (3), 2109–2123 (2021).
Bhatti, M., Ahmed, R. R. & Shokat, S. S. R. S. Farina Riaz, and se Jin Kwon. Outlier detection in indoor localization and internet of things (IoT) using machine learning. J. Commun. Netw. 22 (3), 236–243 (2020).
Manzano, C., Meneses, C. & Fukuda, H. Paul Leger, and An empirical evaluation of supervised learning methods for network malware identification based on feature selection. Complexity 2022 (2022).
Kostas, K., Just, M. & Lones, M. A. IoTDevID: A behaviour-based device identification method for the IoT. IEEE Internet Things J. 9 (23), 23741–23749 (2022).
Ghaffari, A., NasimJelodari, S. & Pouralish NahideDerakhshanfard, and BahmanArasteh. Securing internet of things using machine and deep learning methods: a survey. Cluster Comput. 27 (7), 9065–9089 (2024).
Koroniotis, N., NourMoustafa, E. & Sitnikova and Benjamin Turnbull. Towards the development of realistic botnet dataset in the internet of things for network forensic analytics: Bot-iot dataset.Fut. Gener. Comput. Syst. 100 779–796. (2019).
Doghramachi, D. F., Siddeeq, Y. & Ameen Internet of things (IoT) security enhancement using XGboostMLTechniques. Computers. Mater. Continua. 77, 1 (2023).
Lal, Bechoo, S., Ravichandran, R., Kavin, N., Anil Kumar & DibyahashBordoloi Ganesh Kumar. IOT-BASED cyber security identification model through MLtechnique. Measurement: Sens. 27, 100791 (2023).
Bhayo, J. et al. Towards a machine learning-based framework for DDOS attack detection in software-defined IoT (SD-IoT) networks. Eng. Appl. Artif. Intell. 123, 106432 (2023).
Zakariyya, I., HarshaKalutarage & Omar Al-Kadri, M. Towards a robust, effective and resource efficient MLtechnique for IoT security monitoring. Computers Secur. 133, 103388 (2023).
Vidhya, N. and P. T. V. Bhuvaneswari. ADBIS: anomaly detection to bolster IoT security using machine learning. 2023 IEEE 3rd International Conference on Applied Electromagnetics, Signal Processing, & Communication (AESPC). (IEEE, 2023).
Shafiq, M., ZhihongTian, A. K., Bashir, X., Du & Guizani, M. CorrAUC: A malicious bot-IoT traffic detection method in IoT network using machine-learning techniques. IEEE Internet Things J. 8 (5), 3242–3254 (2020).
García, J., Entrena, J. & Alesanco Álvaro Empirical evaluation of feature selection methods for ML based intrusion detection in IoT scenarios. Internet Things 28 101367. (2024).
Hazman, C., AzidineGuezzaz, S., Benkirane & MouradeAzrour lIDS-SIoEL: intrusion detection framework for IoT-based smart environments security using ensemble learning. Cluster Comput. 26 (6), 4069–4083 (2023).
Douiba, M. & Benkirane, S. AzidineGuezzaz, and MouradeAzrour. An improved anomaly detection model for IoT security using decision tree and gradient boosting. J. Supercomputing. 79 (3), 3392–3411 (2023).
Habeeb, M. & Sayeeduddin Coarse and fine feature selection for network intrusion detection systems (IDS) in IoT networks. Trans. Emerg. Telecommunications Technol. 35 (4), e4961 (2024).
Sankaran, K., Sakthidasan, T. H., Kim & Renjith, P. N. An improved ai-based secure m-trust privacy protocol for medical internet of things in smart healthcare system. IEEE Internet Things J. 10 (21), 18477–18485 (2023).
Dash, P. B., JanmenjoyNayak, B. N., Hafizul Islam, S. K. & EtuariOram, and Model based IoT security framework using multiclass adaptive boosting with SMOTE. Secur. Priv. 3 (5), e112 (2020).
Abdeen, M. A. R., Ahmed, M. H., Seliem, H., TarekRahilSheltami & Turki, M. Alghamdi. Smart health systems components, challenges, and opportunities. IEEE Can. J. Electr. Comput. Eng. 45 (4), 436–441 (2022).
Foley, J. & Naghmeh Moradpoor and Henry Ochenyi. Employing a ML approach to detect combined internet of things attacks against two objective functions using a novel dataset. Secur. Commun. Netw. (1), 2804291. (2020).
Saranya, S. S. & Sabiyath Fatima, N. IoT-based patient health data using improved context-aware data fusion and enhanced recursive feature elimination model. IEEE Access 10 128318–128335. (2022).
Zonayed, M., Rumana Tasnim, S. S., Jhara, M. & Akter Mimona Molla Rashied Hussein, Md Hosne Mobarak, and Umme Salma. ML and IoT in healthcare: recent advancements, challenges & future direction. Adv. Biomark. Sci. Technol.(2025).
Din, I. U., Almogren, A., Guizani, M. & Zuair, M. A decade of internet of things: analysis in the light of healthcare applications. Ieee Access. 7, 89967–89979 (2019).
Saheed, Y. & Kayode and Joshua Ebere Chukwuere. CPS-IIoT-P2Attention: explainable privacy-preserving with scaled dot-product attention in cyber physical system-industrial IoT network. IEEE Access (2025).
Saheed, Y. K. A binary firefly algorithm based feature selection method on high dimensional intrusion detection data. In Illumination of Artificial Intelligence in Cybersecurity and Forensics, 273–288. Cham: Springer International Publishing, (2022).
Adeyiola, A., Qudus, Y. K., Saheed, S., Misra & Sabarathinam Chockalingam. Metaheuristic firefly and C5.0 algorithms based intrusion detection for critical infrastructures. In 2023 3rd International Conference on Applied Artificial Intelligence (ICAPAI) 1–7. (IEEE, 2023).
Gurubaran, K. et al. Machine learning approach for soil nutrient prediction. 2023 IEEE Silchar Subsection Conference (SILCON). (IEEE, 2023).
Saheed, Y. K. Xaiensembletl-iov: A new explainable artificial intelligence ensemble transfer learning for zero-day botnet attack detection in the internet of vehicles. Results Eng. 24, 103171 (2024).
Saheed, Y., Kayode, O. H., Abdulganiyu & Taha Ait Tchakoucht A novel hybrid ensemble learning for anomaly detection in industrial sensor networks and SCADA systems for smart City infrastructures. J. King Saud University-Computer Inform. Sci. 35 (5), 101532 (2023).
Saheed, Y., Kayode, S., Misra & Chockalingam, S. Autoencoder via DCNN and LSTM models for intrusion detection in industrial control systems of critical infrastructures. In 2023 IEEE/ACM 4th International Workshop on Engineering and Cybersecurity of Critical Systems (EnCyCriS) 9–16. (IEEE, 2023).
Author information
Authors and Affiliations
Contributions
Vidhya Nagavel wrote the literature survey, investigation, methodology part and experimental analysis. Parameswaran Ramesh has reviewed the original draft. Bhuvaneswari PTV supervised the research work.
Corresponding author
Ethics declarations
Competing interests
The authors declare no competing interests.
Additional information
Publisher’s note
Springer Nature remains neutral with regard to jurisdictional claims in published maps and institutional affiliations.
Rights and permissions
Open Access This article is licensed under a Creative Commons Attribution-NonCommercial-NoDerivatives 4.0 International License, which permits any non-commercial use, sharing, distribution and reproduction in any medium or format, as long as you give appropriate credit to the original author(s) and the source, provide a link to the Creative Commons licence, and indicate if you modified the licensed material. You do not have permission under this licence to share adapted material derived from this article or parts of it. The images or other third party material in this article are included in the article’s Creative Commons licence, unless indicated otherwise in a credit line to the material. If material is not included in the article’s Creative Commons licence and your intended use is not permitted by statutory regulation or exceeds the permitted use, you will need to obtain permission directly from the copyright holder. To view a copy of this licence, visit http://creativecommons.org/licenses/by-nc-nd/4.0/.
About this article
Cite this article
Nagavel, V., Bhuvaneswari, P.T.V. & Ramesh, P. Smart IoT applications of multi attack detection using cluster F1MI approach. Sci Rep (2026). https://doi.org/10.1038/s41598-026-37695-5
Received:
Accepted:
Published:
DOI: https://doi.org/10.1038/s41598-026-37695-5