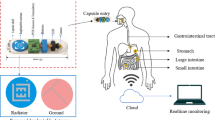
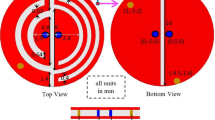
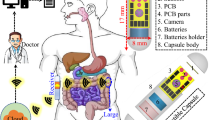
Abstract
This paper presents a highly compact linearly polarized planar dual annular ring antenna designed for wireless capsule endoscopy. The focus of this work on the small intestine is motivated by clinical practice in capsule endoscopy. Most capsule endoscopy systems are specifically designed to examine the small intestines, which are difficult to access with conventional wired endoscopes and are the primary region of interest for many gastrointestinal pathologists. The antenna is derived from a conventional annular ring structure and supports dual-band operation, covering both Wi-Fi frequencies at 2.45 GHz and 5.8 GHz. With a radius of only 4.7 mm, the planar geometry occupies minimal space inside the capsule, leaving more room for essential electronics and the battery. The antenna achieves bandwidths of 20.8% at the lower band and 6.7% at the upper band. A key feature of the design is the capability for electronic switching of the higher band, which enables efficient power management. This allows continuous transmission of critical data, such as control signals, over the lower band, while high-volume data, such as images and video, can be transmitted on demand over the upper band through microcontroller-controlled switching. This mechanism ensures battery conservation as well as reduced time average SAR levels for higher safety. In-vitro testing of the prototypes was conducted, and the measured gains of -17.3 dBi and -18 dBi at the lower and upper bands have been achieved. Furthermore, the antenna exhibits specific absorption rate (SAR) values of 21.5 W/kg and 24.7 W/kg for the two operating bands. To ensure safe operation in compliance with IEEE and ECC standards, maximum transmit powers of 93 mW and 81 mW can be utilized, respectively, while maintaining reliable link quality and extended communication coverage. The link margin remains at 21.1 dB and 12.3 dB at 2.45 GHz and 5.8 GHz, respectively, ensuring an excellent link reliability at a distance of 4 m.
Similar content being viewed by others
Data availability
The datasets used and/or analyzed during the current study are available from the corresponding author on reasonable request.
References
Gogosh, N., Khalid, S., Malik, B. T. & Koziel, S. Artificial magnetic conductor backed dual-mode sectoral cylindrical DRA for off-body biomedical telemetry. Sci. Rep. 15 (1), 31870 (2025).
Yang, X. et al. A substrate integrated adaptable wearable antenna for enhancing IOT communication. IEEE Trans. Compon. Packaging Manuf. Technology 15(10) 2083–2096, (2025).
Baudh, R. K., Sahu, S., Parihar, M. S. & Kumar, V. D. A novel proximity coupled fed high gain circularly polarized wearable antenna for on body IoT-based defense applications. IEEE Internet Things Journal, 12(23), 51372–51380 (2025).
Rajagopalan, H. & Rahmat-Samii, Y. Wireless medical telemetry characterization for ingestible capsule antenna designs. IEEE Antennas. Wirel. Propag. Lett. 11, 1679–1682 (2013).
Fontana, S. et al. State of the Art on advancements in wireless capsule endoscopy telemetry: A systematic approach. IEEE Open. J. Antennas Propag. 5 (5), 1282–1294 (2024).
Iddan, G., Meron, G., Glukhovsky, A. & Swain, P. Wireless capsule endoscopy. Nature 405 (6785), 417–417 (2000).
Zhu, X. Q., Guo, Y. X. & Wu, W. Miniaturized dual-band and dual-polarized antenna for MBAN applications. IEEE Trans. Antennas Propag. 64 (7), 2805–2814 (2016).
Mosavinejad, S. S., Rezaei, P., Khazaei, A. A. & Shirazi, J. A triple-band spiral-shaped antenna for high data rate fully passive implantable devices. AEU-International J. Electron. Commun. 159, 154474 (2023).
Govindan, T. et al. Design and analysis of a conformal MIMO ingestible bolus sensor antenna for wireless capsule endoscopy for animal husbandry. IEEE Sens. J. 23 (22), 28150–28158 (2023).
Bao, Z., Guo, Y. X. & Mittra, R. Conformal capsule antenna with reconfigurable radiation pattern for robust communications. IEEE Trans. Antennas Propag. 66 (7), 3354–3365 (2018).
Wang, J. et al. An implantable and conformal antenna for wireless capsule endoscopy. IEEE Antennas. Wirel. Propag. Lett. 17 (7), 1153–1157 (2018).
Gao, R., Sun, H., Ren, R. & Zhang, H. Design of a biomedical antenna system for wireless communication of ingestible capsule endoscope. IEEE Antennas Wirel. Propag. Letters, 23(12), 4243–4247(2024).
Nikolayev, D., Skrivervik, A. K., Ho, J. S., Zhadobov, M. & Sauleau, R. Reconfigurable dual-band capsule-conformal antenna array for in-body bioelectronics. IEEE Trans. Antennas Propag. 70 (5), 3749–3761 (2021).
Das, R. & Yoo, H. A wideband circularly polarized conformal endoscopic antenna system for high-speed data transfer. IEEE Trans. Antennas Propag. 65 (6), 2816–2826 (2017).
Mohan, A. & Kumar, N. Compact wideband implantable antenna for wireless capsule endoscopy application in the 2.45 ghz ISM band. Sci. Rep. 15 (1), 30644 (2025).
Hayat, S., Shah, S. A. A. & Yoo, H. Miniaturized dual-band circularly polarized implantable antenna for capsule endoscopic system. IEEE Trans. Antennas Propag. 69 (4), 1885–1895 (2020).
Cui, W. et al. Design of wideband implantable antenna for wireless capsule endoscope system. IEEE Antennas. Wirel. Propag. Lett. 18 (12), 2706–2710 (2019).
Huang, L., Li, H., Ding, X., Shao, W. & Xiao, S. A compact wideband omnidirectional circularly polarized implantable antenna for capsule endoscopy system. IEEE Antennas Wirel. Propag. Letters, 24(4), 818–822, (2024).
Alshammari, A., Iqbal, A., Basir, A., Simorangkir, R. B. & Mabrouk, I. B. Ultraminiaturized dual-band implantable antenna for wireless capsule endoscopy. IEEE Sens. J. 24 (9), 15210–15218 (2024).
Toktas, A. et al. A novel and simple expression to accurately calculate the resonant frequency of annular-ring microstrip antennas. Int. J. Microw. Wirel. Technol. 7 (6), 727–733 (2015).
Lee, K. & Dahele, J. Theory and experiment on the annular-ring microstrip antenna, in Annales Des télécommunications, 40(9): Springer, 508–515. (1985).
Balanis, C. A. Antenna Theory: Analysis and Design (Wiley, 2016).
Fluoroproducts, D. Teflon PTFE fluoropolymer resin: properties handbook, DuPont Fluoroproducts: Wilmington, NC, USA, (1996).
Foundation, I. I. Tissue Properties Database V5.0 [Online] Available: https://itis.swiss/s/news-events/news/virtual-population/tissue-db-5-0
IEEE. Standard for Safety Levels with Respect to Human Exposure to Radio Frequency Electromagnetic Fields, 3 kHz to 300 GHz, I. S. C.-R. o. I. S. C95.1-1991), (2006).
IEEE Standard for Safety Levels With Respect to Human Exposure to Radio Frequency Electromagnetic, C95.1-2019, I. S. C95.1-2019, (2019).
Trabelsi, S. Variation of the dielectric properties of chicken meat with frequency and temperature. J. Food Meas. Charact. 9 (3), 299–304 (2015).
Miah, M. S., Khan, A. N., Icheln, C., Haneda, K. & Takizawa, K. I. Antenna system design for improved wireless capsule endoscope links at 433 MHz. IEEE Trans. Antennas Propag. 67 (4), 2687–2699 (2019).
Song, Z., Xu, X., Shi, Y. & Wang, L. Design of a compact circularly polarized implantable antenna for capsule endoscopy systems, Sensors, vol. 24, no. 12, p. 3960, (2024).
Pozar, D. M. Microwave and RF Design of Wireless Systems (Wiley, 2000).
Rappaport, T. S. Wireless communications: Principles and practice, 2/E. Pearson Education India, (2010).
Wang, Y., Huang, B., Yan, S., Dual-Polarized, A. & Meandered Ring-Slot antenna for wireless capsule endoscope systems. IEEE Antennas. Wirel. Propag. Lett. 23 (6), 1804–1808 (2024).
Wang, G., Xuan, X., Jiang, D., Li, K. & Wang, W. A miniaturized implantable antenna sensor for wireless capsule endoscopy system. AEU-International J. Electron. Commun. 143, 154022 (2022).
Alshammari, A. et al. Compact in-band full-duplex implantable antenna for wireless capsule endoscopy. IEEE Trans. Antennas Propagation, 73(2), 897–905 (2024).
Acknowledgements
The authors thank Dassault Systemes, France, for making CST Microwave Studio available. This work is partially supported by the Icelandic Centre for Research (RANNIS) Grant 2410297 and by National Science Centre of Poland Grant 2025/57/B/ST7/00738.
Author information
Authors and Affiliations
Contributions
Conceptualization, N.G. (Nayab Gogosh) and S.Kh. (Sohail Khalid); methodology, N.G. and S.Kh.; data generation, N.G. and B.T.M (Bilal Tariq Malik).; investigation, N.G. and S.Kh.; prototyping and testing N.G. and M. Farhan Shafique (M.F.S) writing original draft preparation, N.G., and B.T.M.; writing review and editing, S.K. (Slawomir Koziel) and Stanislaw Szczepanski (S.S); visualization, B.T.M and S.K.; supervision, S.K. and S.Kh.; project administration, S.K and S.S.
Corresponding author
Ethics declarations
Competing interests
The authors declare that they have no known competing financial interests or personal relationships that could have appeared to influence the work reported in this paper.
Additional information
Publisher’s Note
Springer Nature remains neutral with regard to jurisdictional claims in published maps and institutional affiliations.
Rights and permissions
Open Access This article is licensed under a Creative Commons Attribution-NonCommercial-NoDerivatives 4.0 International License, which permits any non-commercial use, sharing, distribution and reproduction in any medium or format, as long as you give appropriate credit to the original author(s) and the source, provide a link to the Creative Commons licence, and indicate if you modified the licensed material. You do not have permission under this licence to share adapted material derived from this article or parts of it. The images or other third party material in this article are included in the article’s Creative Commons licence, unless indicated otherwise in a credit line to the material. If material is not included in the article’s Creative Commons licence and your intended use is not permitted by statutory regulation or exceeds the permitted use, you will need to obtain permission directly from the copyright holder. To view a copy of this licence, visit http://creativecommons.org/licenses/by-nc-nd/4.0/.
About this article
Cite this article
Gogosh, N., Khalid, S., Malik, B.T. et al. Electronically switchable dual-band capsule antenna for wireless endoscopic applications. Sci Rep (2026). https://doi.org/10.1038/s41598-026-37736-z
Received:
Accepted:
Published:
DOI: https://doi.org/10.1038/s41598-026-37736-z