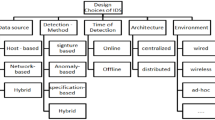
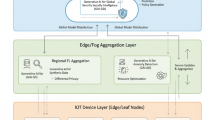
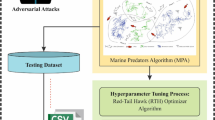
Abstract
The internet of medical things (IoMT) ecosystem is highly vulnerable to malware attacks due to the vast number of connected devices and their continuous collection, transmission, and processing of sensitive data. Inadequate device management often makes each device a potential entry point, enabling malware to spread rapidly across networks with minimal detection. Given the resource constraints, privacy concerns, and distributed nature of IoT devices, there is a pressing need for lightweight and adaptive intrusion detection models. This paper proposes a federated learning (FL) based framework enhanced with TinyGAN, where the generator produces synthetic data to improve malware detection. The federated approach enables continuous, decentralized learning, allowing the model to adapt to emerging threats without requiring centralized retraining, thereby preserving privacy and reducing computational overhead. Experimental evaluations demonstrate significant improvements in both detection accuracy and efficiency compared to conventional centralized techniques. After 20 training rounds, the proposed model achieved a precision of 99.30%, a recall of 100%, and an F1-score of 99.52%. These results highlight the scalability, privacy-preserving nature, and effectiveness of the framework, offering a practical advancement in securing IoT environments against malware attacks. An experimental analysis of the IoT-23 dataset reveals that FL with TinyGAN consistently outperforms traditional models, such as MLP and FNN/LSTM, in terms of accuracy, convergence rate, and resource consumption, thereby establishing its effectiveness for practical IoT malware detection.
Similar content being viewed by others
Data availability
The dataset analysed during the current study is publicly available in the Kaggle repository, [https://www.kaggle.com/datasets/engraqeel/iot23preprocesseddata].
References
Rehman, A., Cengiz, K., Ali, S. & Awan, K. A. H-SecNet: Lightweight and adaptable security framework for IoT-integrated consumer electronics. IEEE Trans. Consumer Electron. 99, 1–1 (2025).
Rehman, A. et al. LEMS: Optimized large model framework for edge-AI in consumer internet of things devices. IEEE Trans. Consumer Electron. 99, 1–1 (2025).
Rehman, A. et al. Optimized federated learning for trustworthy edge decision-making in IoT consumer electronics. IEEE Trans. Consumer Electron. 99, 1–1 (2025).
Sorkhpour, M., Yazdinejad, A. & Dehghantanha, A. Auto-CIDS: An autonomous intrusion detection system for vehicular networks. In Proceedings of the Workshop on Autonomous Cybersecurity 45–55 (2023).
Mohammed, B. H., Sallehudin, H., Satar, N. S. M., Murhg, H. D., Mohamed, S. A., Alaba, F. A. & Bianchi, I. (2025). Anomaly detection of distributed denial of service (DDoS) in IoT network using machine learning. In Digital Technologies and Transformation in Business, Industry and Organizations: Volume 3 pp. 41–64. (Springer Nature Switzerland, Cham).
Kirubavathi, G., Sumathi, I. R., Mahalakshmi, J. & Srivastava, D. Detection and mitigation of TCP-based DDoS attacks in cloud environments using a self-attention and intersample attention transformer model. J. Supercomput. 81(3), 474 (2025).
Durga, S., Daniel, E., Seetha, S., Reshma, V. K. & Sachnev, V. FLEM-XAI: Federated learning based real time ensemble model with explainable AI framework for an efficient diagnosis of lung diseases. Front. Comput. Sci. 7, 1633916. https://doi.org/10.3389/fcomp.2025.1633916 (2025).
Durga, S., Deepakanmani, S. & Daniel, E. 2D convolution neural network-based efficient model for brain tumor detection using 5G edge cloud. Adv. Comput. 139, 433–450 (2025).
Riaz, S. et al. Malware detection in internet of things (IoT) devices using deep learning. Sensors 22(23), 9305 (2022).
Breve, B., Cimino, G. & Deufemia, V. Identifying security and privacy violation rules in trigger-action IoT platforms with NLP models. IEEE Internet Things J. 10(6), 5607–5622 (2022).
Aminu, M., Akinsanya, A., Dako, D. A. & Oyedokun, O. Enhancing cyber threat detection through real-time threat intelligence and adaptive defense mechanisms. Int. J. Comput. Appl. Technol. Res. 13(8), 11–27 (2024).
Lin, T. & Lin, R. Efficient ransomware detection in resource-constrained environments using optimized multi-layer perceptron networks. IEEE Access. 99, 1–1 (2025).
Mofidi, F., Hounsinou, S. G. & Bloom, G. L-IDS: A multi-layered approach to ransomware detection in IoT. In 2024 IEEE 14th Annual Computing and Communication Workshop and Conference (CCWC) 0387–0396 (IEEE, 2024).
Ahmad, I., Wan, Z., Ahmad, A. & Ullah, S. S. A hybrid optimization model for efficient detection and classification of Malware in the internet of things. Mathematics 12(10), 1437 (2024).
Baker del Aguila, R., Contreras Pérez, C. D., Silva-Trujillo, A. G., Cuevas-Tello, J. C. & Nunez-Varela, J. Static malware analysis using low-parameter machine learning models. Computers 13(3), 59 (2024).
Ijaz, A. et al. Innovative machine learning techniques for malware detection. J. Comput. Biomed. Inf. 7(01), 403–424 (2024).
Taşcı, B. Deep-learning-based approach for IoT attack and malware detection. Appl. Sci. (2076–3417) 14(18), 8505 (2024).
Nobakht, M., Javidan, R. & Pourebrahimi, A. SIM-FED: Secure IoT malware detection model with federated learning. Comput. Electr. Eng. 116, 109139 (2024).
Nandanwar, H. & Katarya, R. Secure and privacy-preserving data sharing in 6g-enabled blockchain IoT healthcare systems. Secur. Privacy 8(6), e70105 (2025).
Nandanwar, H. & Katarya, R. A hybrid blockchain-based framework for securing intrusion detection systems in internet of things. Clust. Comput. 28(7), 471 (2025).
Nandanwar, H. & Katarya, R. Optimized intrusion detection and secure data management in IoT networks using GAO-Xgboost and ECC-integrated blockchain framework. Knowl. Inf. Syst. 67, 9531–9586 (2025).
Nandanwar, H. & Katarya, R. Deep learning enabled intrusion detection system for Industrial IOT environment. Expert Syst. Appl. 249, 123808 (2024).
Nandanwar, H. & Katarya, R. TL-BILSTM IoT: Transfer learning model for prediction of intrusion detection system in IoT environment. Int. J. Inf. Secur. 23(2), 1251–1277 (2024).
Nandanwar, H. & Katarya, R. A secure and privacy-preserving ids for IoT networks using hybrid blockchain and federated learning. In International Conference on Next-Generation Communication and Computing 207–219 (Springer Nature Singapore, Singapore, 2024).
Nyabuto, M. G. M., Mony, V. & Mbugua, S. Architectural review of client-server models. Int. J. Sci. Res. Eng. Trends 10(1), 139–143 (2024).
Beltrán, E. T. M. et al. Decentralized federated learning: Fundamentals, state of the art, frameworks, trends, and challenges. IEEE Commun. Surveys Tutor. 25(4), 2983–3013 (2023).
Pei, J., Liu, W., Li, J., Wang, L. & Liu, C. A review of federated learning methods in heterogeneous scenarios. IEEE Trans. Consumer Electron. 70(3), 5983–5999 (2024).
Lim, W., Yong, K. S. C., Lau, B. T. & Tan, C. C. L. Future of generative adversarial networks (GAN) for anomaly detection in network security: A review. Comput. Secur. 139, 103733 (2024).
Yu, L., Zhou, R., Chen, R. & Lai, K. K. Missing data preprocessing in credit classification: One-hot encoding or imputation?. Emerg. Mark. Financ. Trade 58(2), 472–482 (2022).
Al Saaidah, A. et al. Enhancing malware detection performance: Leveraging K-nearest neighbors with firefly optimization algorithm. Multimed. Tools Appl. 84(12), 10071–10094 (2024).
Mehta, S. & Aneja, A. Securing data privacy in machine learning: The FedAvg of federated learning approach. In 2024 4th Asian Conference on Innovation in Technology (ASIANCON) 1–5 (IEEE, 2024).
Dhakal, R., Raza, W., Tummala, V. & Kandel, L. N. Enhancing intrusion detection in iot networks through federated learning. IEEE Access. 12, 167168–167182 (2024).
Yazdinejad, A., Mohammadabadi, Z. D., Dehghantanha, A. & Srivastava, G. An explainable and privacy-preserving federated learning model for threat detection in cyber-physical-social systems. IEEE Trans. Comput. Soc. Syst.. 99, 1–13 (2025).
Yazdinejad, A., Dehghantanha, A., Karimipour, H., Srivastava, G. & Parizi, R. M. A robust privacy-preserving federated learning model against model poisoning attacks. IEEE Trans. Inf. Forensics Secur. 19, 6693–6708 (2024).
Yazdinejad, A., Dehghantanha, A., Srivastava, G., Karimipour, H. & Parizi, R. M. Hybrid privacy preserving federated learning against irregular users in next-generation Internet of Things. J. Syst. Architect. 148, 103088 (2024).
Ganapathiyappan, K. & Yadav, A. Optimized deep learning technique for the effective detection of windows PE malware. In International Conference on Cyber Warfare, Security and Space Computing 359–370. (Springer Nature Switzerland, Cham, 2024).
Rajesh Kanna, P. & Santhi, P. Exploring the landscape of network security: A comparative analysis of attack detection strategies. J. Ambient. Intell. Humaniz. Comput. 15(8), 3211–3228 (2024).
Ganapathy, V., Ramachandran, R. & Ohtsuki, T. Deep LEarning methods for secure IoT SWIPT Networks. IEEE Internet Things J. 11(11), 19657–19677 (2024).
Funding
Open access funding provided by Amrita Vishwa Vidyapeetham. No funding was received for conducting this research.
Author information
Authors and Affiliations
Contributions
Durga S and Gobi Shankar M conceived the study and designed the methodology. Durga S and Gobi Shankar M performed the experiments and analyzed the data. Durga S and Esther Daniel contributed to writing the manuscript. Bright Gee Varghese analyzed the results. All authors read and approved the final manuscript.
Corresponding author
Ethics declarations
Competing interests
The authors declare no competing interests.
Additional information
Publisher’s note
Springer Nature remains neutral with regard to jurisdictional claims in published maps and institutional affiliations.
Rights and permissions
Open Access This article is licensed under a Creative Commons Attribution-NonCommercial-NoDerivatives 4.0 International License, which permits any non-commercial use, sharing, distribution and reproduction in any medium or format, as long as you give appropriate credit to the original author(s) and the source, provide a link to the Creative Commons licence, and indicate if you modified the licensed material. You do not have permission under this licence to share adapted material derived from this article or parts of it. The images or other third party material in this article are included in the article’s Creative Commons licence, unless indicated otherwise in a credit line to the material. If material is not included in the article’s Creative Commons licence and your intended use is not permitted by statutory regulation or exceeds the permitted use, you will need to obtain permission directly from the copyright holder. To view a copy of this licence, visit http://creativecommons.org/licenses/by-nc-nd/4.0/.
About this article
Cite this article
S, D., Shankar, M.G., Daniel, E. et al. Enhancing security in IoMT using federated TinyGAN for lightweight and accurate malware detection. Sci Rep (2026). https://doi.org/10.1038/s41598-026-37830-2
Received:
Accepted:
Published:
DOI: https://doi.org/10.1038/s41598-026-37830-2