Abstract
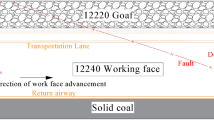
Coal is an important energy and industrial resource. Coal mining-resulted goafs and subsequently developed caving zones exhibit strong heterogeneity and instability, which can severely restricts the exploration and development of deep coal seams. Focusing on a coal mine in eastern China, this study relied on 2D migrated seismic profiles, and seismic simulating and imaging on a model to systematically investigate the seismic reflection characteristics and its genesis of goafs, caving zones, and their underlying strata. The results indicate that the bottom of goafs presents strong seismic reflections, caving zones generate intense seismic scattering, and reflections from the underlying coal seams exhibit three diagnostic features: namely energy attenuation, phase anomalies, and reduced continuity. Energy attenuation stems from the superimposed effects of strong reflection at the goaf bottom and intense scattering in caving zones. Phase anomalies are dominated by the low-velocity property of goafs and caving zones. Poor continuity is mainly controlled by the scattering in caving zones. The proposed correlation between the attributes of goaf-caving zones and the reflection responses of underlying strata can be used to evaluate the occurrence state of goafs and provide support for the exploration and development of deep coal resources.
Similar content being viewed by others
Data availability
The datasets generated and/or analyzed during the current study are not publicly available due to confidentiality restrictions.
References
Lei, C. et al. L. A lithofacies modeling method based on τ-model algorithm and its application. Reserv. Evaluation Dev. 13(2), 206–214 (2023).
Liu, Y. M. et al. Application of artificial intelligence lithofacies prediction in carbonate rock petrophysical modeling. Oil Geophys. Prospect. 58(S1), 125–131 (2023).
Yuan, Y., Gao, Y., Bai, L. & Liu, Z. Prestack Kirchhoff time migration of 3D coal seismic data from mining zones. Geophys. Prospect. 59, 455–463 (2011).
Yuan, H., Liu, J. & Yuan, Y. Using 4-D seismic data for detecting gob areas of coal mines: A case study from the Zhangji coal mine. IEEE Trans. Geosci. Remote Sens. 60, 5917810 (2022).
Jia, N. Study on seismic wave propagation and permeability characteristics of strata damaged by mining [PhD thesis]. Liaoning Technical University, (2024).
Wang, A., Fu, C., Li, G., Wang, H. F. & Chen, T. J. Comparative study on locating Goaf boundaries by seismic attributes. Coal Technol. 42(10), 31–35 (2023).
Cao, X. S. Seismic response characteristics of Goaf and its lower coal seam. Coal Chem. Ind. 46(1), 35–38 (2023).
Cao, X. S., Shen, Y. X., Guo, P. P. & Zhang, Z. Application of 3D seismic in exploration of lower coal seam under double-layer Goaf. Coal Chem. Ind. 46(2), 38–41 (2023).
Liang, J. M. Study on surface movement and deformation law of goaf under fault influence [PhD thesis]. China University of Mining and Technology (2024).
Zhang, Z. Z. Stability analysis of coal pillars in strip goaf and study on surface deformation law in Daizhuang Coal Mine [PhD thesis]. China Coal Research Institute (2024).
Guo, Y. H. Study on surface prevention and control of coal mining subsidence range in Huaibei Plain mining area [PhD thesis]. Anhui Jianzhu University (2025).
Deng, H. W., Wang, Y. & Xu, Y. H. Study on the Spatial structural evolution law of large complex Goaf. J. Disaster Prev. Mitigation Eng. 38(3), 401–408 (2018).
Sun, S. W. et al. Mechanism of slope failure induced by subsidence of underground Goaf in coal mines. Chin. J. Rock Mechan. Eng. 44(6), 1405–1419 (2025).
Li, X. Study on forward modeling of seismic wavefield and full waveform inversion method in undulating surface [PhD thesis]. China University of Petroleum (Beijing) (2022).
Funding
This research was financially supported by the Science and Technology Innovation Fund of China Coal Technology & Engineering Group Ecological and Environmental Technology Co., Ltd. (Grant No. 0206KGST0030), and by the Science and Technology Innovation Fund of China Coal Technology & Engineering Group Xi’an Research Institute Co., Ltd. (Grant No. 2025XAYJS02).
Author information
Authors and Affiliations
Contributions
S.N. and C.Z. wrote the main manuscript text, and Z. collected the seismic data. All authors reviewed and approved the final manuscript.
Corresponding author
Ethics declarations
Competing interests
The authors declare no competing interests.
Additional information
Publisher’s note
Springer Nature remains neutral with regard to jurisdictional claims in published maps and institutional affiliations.
Rights and permissions
Open Access This article is licensed under a Creative Commons Attribution 4.0 International License, which permits use, sharing, adaptation, distribution and reproduction in any medium or format, as long as you give appropriate credit to the original author(s) and the source, provide a link to the Creative Commons licence, and indicate if changes were made. The images or other third party material in this article are included in the article’s Creative Commons licence, unless indicated otherwise in a credit line to the material. If material is not included in the article’s Creative Commons licence and your intended use is not permitted by statutory regulation or exceeds the permitted use, you will need to obtain permission directly from the copyright holder. To view a copy of this licence, visit http://creativecommons.org/licenses/by/4.0/.
About this article
Cite this article
Shan, R., Nie, A., Cao, X. et al. Seismic reflection characteristics and genesis of goafs and underlying coal seams. Sci Rep (2026). https://doi.org/10.1038/s41598-026-37861-9
Received:
Accepted:
Published:
DOI: https://doi.org/10.1038/s41598-026-37861-9