Abstract
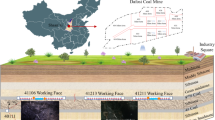
This article takes the transportation channel of the 2507 working face as the engineering background to carry out the analysis of the surrounding rock failure mechanism of the roadside filling in gob-side entry retaining of large mining height panel, and summarizes three common forms of instability failure of the filling wall. The method and idea of using a combination of “strengthened support + roof cutting pressure relief” to control the surrounding rock of gob-side entry retaining of roadside filling is determined. In theory, the optimal range of roof cutting height and roof cutting angle was obtained, and an innovative introduction of deviatoric stress analysis index was made. Numerical simulation research was conducted on the distribution characteristics of deviatoric stress in the surrounding rock of the gob-side entry retaining under different roof cutting heights, roof cutting angles, and wall width conditions. The optimal parameters for roof cutting and pressure relief of the gob-side entry retaining of roadside filling in the high mining face were obtained. The on-site engineering practice shows that after adopting the joint control technology of “strengthening support + roof cutting pressure relief”, the displacement of the surrounding rock of the retained roadway, the force of the anchor cable, and the bearing capacity of the flexible formwork wall are all within the normal range, ensuring that the retained roadway can continue to be used by the next working face.
Similar content being viewed by others
Data availability
All the data can be obtained with corresponding author by the Email 489698551@qq.com.
References
Li, C. et al. Surrounding rock stabilization and deformation evolution of gob-side entry retaining in deep colliery with mega-height coal seam extracted[J]. Chin. J. Undergr. Space Eng. 17 (3), 897–908 (2021).
Guotao, F. et al. Research on floor heave mechanism and control technology of mining roadways in deeply buried large mining height fully mechanized mining faces[J]. Min. Res. Dev. 42 (05), 95–100 (2022).
Zhu, H. et al. Key technology of gob-side entry retained by roof cutting without coal pillar for hard main roof: A typical case study[J]. J. Cent. South. Univ. 30 (12), 4097–4121 (2023).
Zhang, J. & Lu, S. Study on gob-side entry retaining of flexible formwork concrete in large mining height working face of Chengzhuang coal mine[J]. Coal Technol. 42 (10), 16–21 (2023).
Tang, J. et al. Gob side entry protection technology of small coal pillar in steeply inclined three-soft Thick coal seam[J]. Chin. J. Undergr. Space Eng. 18 (4), 1392–1400 (2022).
Zhongyi Wen. Practice of Non pillar mining in large and medium Thick coal seam in Yongcheng mining area[J]. Chin. J. Undergr. Space Eng. 15 (S1), 256–259 (2019).
Cao, Q. et al. Study on Support Technology of gob-side Entry Retaining in Isolated Island Coal Pillar Working Face in the Deep well[J]. 50(3), 56–61 (Mining Safety & Environmental Protection, 2023).
Wang, L., Jiang, Q. & Wang, Y. Numerical simulation on mechanical characteristics of surrounding rock of gob-side entry retaining[J]. Chin. J. Undergr. Space Eng. 11 (6), 1564–1571 (2015).
Jiankang Jiao. Roadway side rigid-flexible combined support technology of the gob-side entry retaining with roof cutting[J]. Coal Eng. 55 (06), 45–49 (2023).
Zhang, Z. et al. Dynamic loading mechanism and stability control of gob-side entry retaining with Thick and hard roof: insights from numerical simulation and field test[J]. Min. Metall. Explor. 40 (2), 703–717 (2023).
Chen, D. et al. Study on stability mechanism and control techniques of surrounding rock in gob-side entry retaining with flexible formwork concrete wall[J]. J. Cent. South. Univ. 30 (9), 2966–2982 (2023).
Man Sun, K. et al. Research on surrounding rock deformation and mining field stress distribution during gob-side entry retaining by roof cutting and pressure releasing in the inclined Thick coal seam[J]. Adv. Civil Eng. 2024 (1), 4553594 (2024).
Yinwei Wang, Z. et al. Deformation Mechanism and Control Technology of gob-side Entry Retaining with Roadside Backfilling: a Numerical Analysis and Field investigation[J]. 10(1), 175 (Geomechanics and Geophysics for Geo-Energy and Geo-Resources, 2024).
Shuai Wu. Study on deformation mechanism and construction technology of surrounding rock of gob side entry retaining with flexible formwork wall[J]. Coal Sci. Technol. 50 (S2), 127–135 (2022).
Guo, Y. et al. Study on Air Leakage Law of Goaf Under One Inlet and Two Return Ventilation in gob-side Entry Retaining Working face[J]. 49(06), 46–51 (Mining Safety & Environmental Protection, 2022).
Gong, P. et al. Structural evolution mechanism of surrounding rock of gob side entry retaining in backfilling mining face[J]. J. Min. Saf. Eng. 40 (4), 764–773 (2023).
Zhu, Y. et al. Stability control of gob-side entry retention under the condition of inclined Thick layer and hard roof[J]. J. Cent. South. University(Science Technology). 54 (3), 956–966 (2023).
Shaowei Liu, X. et al. Mechanism of roof-cutting by densely drilled holes in gob‐side entry retaining and its main influencing factors[J]. Energy Sci. Eng. 13 (10), 4794–4809 (2025).
Zhang, D. et al. Theory and simulation investigations on stability control of gob-side entry retaining with coal pillar-backfill body system[J]. Int. J. Min. Sci. Technol. 35 (8), 1399–1417 (2025).
Hongzhi Yang, W. et al. The relative movement deformation mechanism and control technique of gob-side entry retaining in top-coal caving mining[J]. J. Min. Saf. Eng. 40 (02), 224–231 (2023).
Li Zhang, J. et al. An innovative approach for gob-side entry retaining by roof cutting in steeply pitching seam Longwall mining with hard roof: a case study[J]. Min. Metall. Explor. 37 (4), 1079–1091 (2020).
Ming, C. et al. Control technology of surrounding rock stability based on compensation theory in gob-side entry retaining with composite hard roof[J]. J. Mt. Sci. 22 (3), 1029–1047 (2025).
Fu, Q. et al. Research on location optimization and application of the gob-side entry retaining by roof cutting in close-distance coal seams[J]. Sci. Rep. 15 (1), 42661 (2025).
Chao Feng, S. et al. Study on the bearing characteristics and reasonable width of the backfilling body for gob-side entry in fully-mechanized top-coal caving face under the roof cutting condition[J]. J. Min. Saf. Eng. 40 (2), 232–242 (2023).
Zhizeng Huang, X. et al. Stress distribution of cutting roof with deep borehole blasting for gob-side entry retaining technology[J]. Coal Sci. Technol. 50 (S2), 88–96 (2022).
Wang, K. et al. Deformation and failure characteristics of gob-side entry retaining in soft and thick coal seam and the control technology[J]. Rock and Soil Mechanics, 43(7): 1913–1924, 1960. (2022).
En Wang, D. et al. Study on deviatoric stress distribution and control technology of surrounding rock at gob-side entry retaining with dual-roadways[J]. J. Min. Saf. Eng. 39 (3), 557–566 (2022).
Fangtian Wang, J. et al. Surrounding rock structural characteristics and anchor-cable strengthened support technology of the gob-side entry retaining with roof cutting and pressure releasing[J]. Chin. J. Rock Mechan. Eng. 40 (11), 2296–2305 (2021).
Zhao, M. et al. Research on roof structure and support resistance of gob-side entry retaining with roof cutting and non-pillar mining[J]. J. China Coal Soc. 46 (S1), 84–93 (2021).
Nannan Li. Study on roof management technology of composite roof large mining height face[J]. Coal Sci. Technol. 50 (S2), 33–37 (2022).
LiXin Zhang, Y. et al. Evolutionary law and regulatory technology of roof migration on gob-side entry retaining[J]. Sci. Rep. 14 (1), 5581 (2024).
Guorui Feng, Y. et al. Stress distribution and deformation characteristics of roadside backfill body for gob-side entry of fully-mechanized caving in Thick coal seam[J]. J. Min. Saf. Eng. 36 (06), 1109–1119 (2019).
Chen, Y. & Yang, Y. Study on reinforcement mechanism of filling body in gob-side entry retaining[J]. J. Min. Saf. Eng. 35 (6), 1129–1134 (2018).
Liu, D. et al. Study on key parameters of hard roof cutting and pressure release and roadway retaining in medium Thick coal seam[J]. Saf. Coal Mines. 51 (12), 237–243 (2020).
Funding
This work was supported financially by the Key Research and Development of Lvliang City (Project No.2025GY20) and Research Fund of State and Local Joint Engineering Laboratory for Gas Drainage & Ground Control of Deep Mines (Henan Polytechnic University) (SJF202503), Fundamental Research Funds for Universities in Xinjiang Uygur Autonomous Region (Project No. XJEDU2025J141), Fundamental Research Program of Shanxi Province (202303021222249) and Key R&D Program for the Introduction of High-level Scientific and Technological Talents in Lüliang City (2023RC19).
Author information
Authors and Affiliations
Contributions
Weiyong Lu: Writing–review & editing, Resources, Project administration, Funding acquisition, Methodology, Formal analysis, Data curation, Conceptualization.Shengjun LI: Writing–review & editing, Writing–original draft, Visualization, Validation, Software, Conceptualization.Yaohui Sun: Writing–review & editing, Validation, Investigation.Tao Gao: Investigation, Data curation.Wansheng Mi: Supervision, Resources, Project administration, Conceptualization.Xiaowu Zhang: Investigation, Data curation.
Corresponding author
Ethics declarations
Competing interests
The authors declare no competing interests.
Additional information
Publisher’s note
Springer Nature remains neutral with regard to jurisdictional claims in published maps and institutional affiliations.
Rights and permissions
Open Access This article is licensed under a Creative Commons Attribution-NonCommercial-NoDerivatives 4.0 International License, which permits any non-commercial use, sharing, distribution and reproduction in any medium or format, as long as you give appropriate credit to the original author(s) and the source, provide a link to the Creative Commons licence, and indicate if you modified the licensed material. You do not have permission under this licence to share adapted material derived from this article or parts of it. The images or other third party material in this article are included in the article’s Creative Commons licence, unless indicated otherwise in a credit line to the material. If material is not included in the article’s Creative Commons licence and your intended use is not permitted by statutory regulation or exceeds the permitted use, you will need to obtain permission directly from the copyright holder. To view a copy of this licence, visit http://creativecommons.org/licenses/by-nc-nd/4.0/.
About this article
Cite this article
Weiyong, L., Shengjun, L., Yaohui, S. et al. Research on surrounding rock control technology of roof cutting and pressure relieving for roadside filling in gob-side entry retaining of large mining height panel. Sci Rep (2026). https://doi.org/10.1038/s41598-026-37916-x
Received:
Accepted:
Published:
DOI: https://doi.org/10.1038/s41598-026-37916-x