Abstract
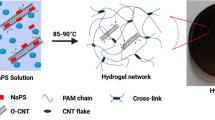
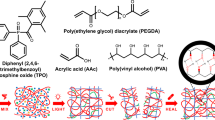
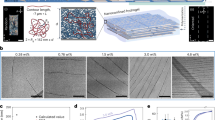
Self-healing hydrogels are advanced materials that can restore their original functionality and properties after mechanical damage, either through intrinsic mechanisms or via external stimuli. However, their widespread application is often limited by challenges such as insufficient mechanical strength, low thermal stability, and inadequate self-healing efficiency. In this study, we developed a novel self-healing hydrogel based on salep. This natural polysaccharide was modified through free radical polymerization using two distinct polymers: polyacrylamide (PAM) and poly)diallyldimethylammonium( chloride (PDADMAC). Additionally, Fe3O4 magnetic nanoparticles (MNPs) were synthesized and incorporated into the hydrogel matrix, imparting magnetic responsiveness. The resulting semi-interpenetrating (semi-IPN) hydrogel network exhibited robust self-healing properties, attributed to dynamic, reversible hydrogen bonds within the polymer chains. The inclusion of Fe3O4 MNPs further facilitated the mobility of polymer chains under an external magnetic field, significantly improving the efficiency and rate of self-repair. The PAM-modified nanocomposite hydrogel achieved an equilibrium swelling ratio of ~ 2300%, while the PDADMAC-based composite reached ~ 1875% at pH = 7. Notably, the semi-IPN structure endowed the hydrogel with self-healing, enabling it to recover its original mechanical integrity within 35 min at room temperature. Combining a natural salep matrix with synthetic polymer networks and Fe3O4 MNPs produced a self-healing hydrogel with markedly improved strength, stability, and functionality. The dynamic hydrogen-bonded network ensures rapid, autonomous repair, while the magnetic component provides tunable responsiveness under external fields. These features, together with High tensile properties and antimicrobial efficacy, suggest broad applicability in biomedical, agricultural, and environmental technologies.
Similar content being viewed by others
Data availability
All data generated or analyzed during this study are included in this published article.
References
Park, J., Kim, M., Choi, S. & Sun, J. Y. Self-healable soft shield for γ-ray radiation based on polyacrylamide hydrogel composites. Sci. Rep. 10, 21689 (2020).
Vivek, B., Kumar, P. & Prasad, E. Induction and tunability of self-healing property of dendron based hydrogel using clay nanocomposite. J. Phys. Chem. B. 120, 5262–5271 (2016).
Lou, J. et al. Amylopectin-phytic acid-based hyperstretchable hydrogel with 30-minute self-healing and high adhesion for human motion monitoring. Int. J. Biol. Macromol. 328, 147670 (2025).
Shu, Q. et al. Injectable hydrogels for bioelectronics: A viable alternative to traditional hydrogels. Chem. Eng. J. 495, 153391 (2024).
Kurt, A. Salep glucomannan: properties and applications. In Polysaccharides: Properties and Applications (eds (eds Inamuddin, Ahamed, M. I., Boddula, R. & Altalhi, T.) 177–203 (Wiley, doi:https://doi.org/10.1002/9781119711414.ch9. (2021).
Dannert, C., Stokke, B. T. & Dias, R. S. Nanoparticle-hydrogel composites: from molecular interactions to macroscopic behavior. Polymers 11, 275 (2019).
Mohanty, S., Swarup, J., Priya, S., Jain, R. & Singhvi, G. Exploring the potential of polysaccharide-based hybrid hydrogel systems for their biomedical and therapeutic applications: A review. Int. J. Biol. Macromol. 256, 128348 (2024).
Sahoo, S. D., Vasudha, T. K., Muthuvijayan, V. & Prasad, E. Chitosan-based self-healable and adhesive hydrogels for flexible strain sensor application. ACS Appl. Polym. Mater. 4, 9176–9185 (2022).
Rial-Hermida, M. I. et al. Recent progress on polysaccharide-based hydrogels for controlled delivery of therapeutic biomolecules. ACS Biomater. Sci. Eng. 7, 4102–4127 (2021).
Sahoo, S. D. & Prasad, E. 2D and 3D printable self-healing hydrogels based on polyacrylic and Tricarballylic acids through a double network strategy. ACS Appl. Polym. Mater. 6, 10393–10400 (2024).
Zanbili, F., Gozali Balkanloo, P. & Poursattar Marjani, A. Semi-IPN polysaccharide-based hydrogels for effective removal of heavy metal ions and dyes from wastewater: A comprehensive investigation of performance and adsorption mechanism. Rev. Environ. Health 40, 296–318 (2025).
Vasile, C., Pamfil, D., Stoleru, E. & Baican, M. New developments in medical applications of hybrid hydrogels containing natural polymers. Molecules 25, 1539 (2020).
Chang, L., Xu, L., Liu, Y. & Qiu, D. Superabsorbent polymers used for agricultural water retention. Polym. Test. 94, 107021 (2021).
Biery, A. R. & Knauss, D. M. Recent advances in the synthesis of Diallylammonium polymers. Mater. Today Chem. 26, 101251 (2022).
Sahoo, S. D. & Prasad, E. Self-healing stable polymer hydrogel for pH regulated selective adsorption of dye and slow release of graphene quantum Dots. Soft Matter. 16, 2075–2085 (2020).
Bharathan Jeneena, K. & Vivek, B. Peripherally modified poly(amido amine) nanocomposite hydrogel with stimuli-responsive self‐healing, high tensile strength, and selective superadsorption poperties. ChemistrySelect 8, e202303066 (2023).
Vivek, B. & Prasad, E. Self-assembly-directed aerogel and membrane formation from a magnetic composite: an approach to developing multifunctional materials. ACS Appl. Mater. Interfaces. 9, 7619–7628 (2017).
Hawkins, A. M., Bottom, C. E., Liang, Z., Puleo, D. A. & Hilt, J. Z. Magnetic nanocomposite sol–gel systems for remote controlled drug release. Adv. Healthc. Mater. 1, 96–100 (2012).
Hu, X. et al. Adhesive tough magnetic hydrogels with high Fe3O4 content. ACS Appl. Mater. Interfaces. 11, 10292–10300 (2019).
Xue, L. et al. Self-healing hydrogels: mechanisms and biomedical applications. MedComm 6, e70181 (2025).
Vivek, B. & Jeneena, K. B. Under water adhesive smart hydrogels with ph-responsive self‐healing ability, enhanced mechanical strength, and selective perchlorate adsorption. ChemistrySelect 10, e02010 (2025).
Nadim, E., Major, I., Devine, D. & Paraskar, P. Biobased self-healing functional composites and their applications. J. Mater. Sci. : Compos. 6, 3 (2025).
Duarte, J., Mascarenhas-Melo, F., Pires, P. C., Veiga, F. & Paiva-Santos, A. C. Multifunctional hydrogels-based therapies for chronic diabetic wound healing. Eur. Polym. J. 211, 113026 (2024).
Bardajee, G. R., Sharifi, M., Karimi, M. A. & Rezanejad, H. Application of a nanocomposite based on modified salep glucomannan for monitoring controlled release of Tetracycline as a model drug. J. Polym. Res. 29, 184 (2022).
Zohreh, N. et al. Natural Salep/PEGylated Chitosan double layer toward a more sustainable pH-responsive magnetite nanocarrier for targeted delivery of DOX and hyperthermia application. ACS Appl. Nano Mater. 2, 853–866 (2019).
Wang, Q., Zhang, Y., Ma, Y., Wang, M. & Pan, G. Nano-crosslinked dynamic hydrogels for biomedical applications. Mater. Today Bio. 20, 100640 (2023).
Jiang, Y., Krishnan, N., Heo, J., Fang, R. H. & Zhang, L. Nanoparticle–hydrogel superstructures for biomedical applications. J. Control Release. 324, 505–521 (2020).
Nugraha, A. D. et al. One-pot synthesis and surface modification of Fe3O4 nanoparticles using Polyvinyl alcohol by coprecipitation and ultrasonication methods. IOP Conf. Ser. : Mater. Sci. Eng. 299, 012066 (2018).
Zhang, K., Feng, W. & Jin, C. Protocol efficiently measuring the swelling rate of hydrogels. MethodsX 7, 100779 (2020).
Banerjee, P., Dinda, P., Kar, M., Uchman, M. & Mandal, T. K. Ionic liquid Cross-Linked High-Absorbent polymer hydrogels: kinetics of swelling and dye adsorption. Langmuir 39, 9757–9772 (2023).
Kumar, S., Yadav, H. & Shivakumar, H. G. In Vitro and In Vivo evaluation of pH-sensitive hydrogels of carboxymethyl chitosan for intestinal delivery of theophylline. ISRN Pharm. 2012, 763127 (2012).
Ninciuleanu, C. M. et al. The effects of monomer, crosslinking agent, and filler concentrations on the viscoelastic and swelling properties of poly(methacrylic acid) hydrogels: A comparison. Mater. (Basel). 14, 2305 (2021).
Wu, N. et al. Investigation on the structure and mechanical properties of highly tunable elastomeric silk fibroin hydrogels cross-linked by γ-ray radiation. ACS Appl. Bio Mater. 3, 721–734 (2020).
Hossain, T. J. Methods for screening and evaluation of antimicrobial activity: A review of protocols, advantages, and limitations. Eur. J. Microbiol. Immunol. 14, 97–115 (2024).
Mahmoudian, M. & Zanbili, F. Fabrication of modified fibrous filters by electrospinning and investigating their application as improved face masks. Chin. J. Polym. Sci. 42, 1738–1748 (2024).
Antarnusa, G., Jayanti, P. D., Denny, Y. R. & Suherman, A. Utilization of co-precipitation method on synthesis of Fe3O4/PEG with different concentrations of PEG for biosensor applications. Materialia 25, 101525 (2022).
Soleyman, R., Pourjavadi, A., Monfared, A. & Khorasani, Z. Novel salep-based chelating hydrogel for heavy metal removal from aqueous solutions: novel salep-based chelating hydrogel. Polym. Adv. Technol. 27, 999–1005 (2016).
Sun, W., Liu, W. & Hu, Y. FTIR analysis of adsorption of Poly diallyl-dimethyl-ammonium chloride on kaolinite. J. Cent. South. Univ. Technol. 15, 373–377 (2008).
Mahdavi, M. et al. Synthesis, surface modification and characterisation of biocompatible magnetic iron oxide nanoparticles for biomedical applications. Molecules 18, 7533–7548 (2013).
Sungoradee, T. & Srikulkit, K. Preparation and characterizations of PSS/PDADMAC polyelectrolyte complex hydrogel. Polymers 14, 1699 (2022).
Ba-Abbad, M. M., Benamour, A., Ewis, D., Mohammad, A. W. & Mahmoudi, E. Synthesis of Fe3O4 nanoparticles with different shapes through a co-precipitation method and their application. J. Min. Met. Mater. Soci. 74, 3531–3539 (2022).
Lotfi, S., Ghaderi, F., Bahari, A. & Mahjoub, S. Preparation and characterization of magnetite–chitosan nanoparticles and evaluation of their cytotoxicity effects on MCF7 and fibroblast cells. J. Supercond Nov Magn. 30, 3431–3438 (2017).
Cao, Z. et al. Preparation and properties of polyacrylamide/sodium alginate hydrogel and the effect of Fe adsorption on its mechanical performance. J. Renew. Mater. 9, 1447–1462 (2021).
Mohamed Alshangiti, D., El-damhougy, K., Zaher, T., Madani, A., Ghobashy, M. M. & M. & Revolutionizing biomedicine: Advancements, applications, and prospects of nanocomposite macromolecular carbohydrate-based hydrogel biomaterials: a review. RSC Adv. 13, 35251–35291 (2023).
Feng, W. & Wang, Z. Tailoring the swelling-shrinkable behavior of hydrogels for biomedical applications. Adv. Sci. 10, 2303326 (2023).
Kollár, J., Mrlík, M., Moravčíková, D., Iván, B. & Mosnáček, J. Effect of monomer content and external stimuli on properties of renewable Tulipalin A-based superabsorbent hydrogels. Eur. Polym. J. 115, 99–106 (2019).
Batys, P., Zhang, Y., Lutkenhaus, J. L. & Sammalkorpi, M. Hydration and temperature response of water mobility in poly(diallyldimethylammonium)–poly(sodium 4-styrenesulfonate) complexes. Macromolecules 51, 8268–8277 (2018).
Wang, Y. et al. Novel biological hydrogel: swelling behaviors study in salt solutions with different ionic Valence number. Polym. (Basel). 10, 112 (2018).
Trivedi, J. & Chourasia, A. Sodium salt of partially carboxymethylated sodium alginate-graft-poly(acrylonitrile): II Superabsorbency, salt sensitivity and swelling kinetics of hydrogel, H-Na-PCMSA-g-PAN. Gels 9, 407 (2023).
Cao, C. et al. Effects of sodium chloride on the physical and oxidative stability of filled hydrogel particles fabricated with phase separation behavior. Foods 10, 1027 (2021).
Gupta, N. V. & Shivakumar, H. G. Investigation of swelling behavior and mechanical properties of a ph-sensitive superporous hydrogel composite. Iran. J. Pharm. Res. 11, 481–493 (2012).
Xuan, X. et al. Three-dimensional printable magnetic hydrogels with adjustable stiffness and adhesion for magnetic actuation and magnetic hyperthermia applications. Gels 11, 67 (2025).
Li, K. et al. In the process of polysaccharide gel formation: A review of the role of competitive relationship between water and alcohol molecules. Int. J. Biol. Macromol. 281, 136398 (2024).
Li, S. & Mohseni, M. Development of poly(diallyldimethylammonium) chloride-modified activated carbon for efficient adsorption of Methyl red in aqueous systems. Clean. Technol. 7, 61 (2025).
Suhail, M. et al. Magnetically responsive hydrogel systems: fundamental features, emerging applications, and future horizons. Coord. Chem. Rev. 543, 216916 (2025).
Zhou, S. et al. Recent progress in intrinsic self-healing polymer materials: Mechanisms, challenges and potential applications in oil and gas development. Chem. Eng. J. 511, 161906 (2025).
Cerdan, K., Moya, C., Van Puyvelde, P., Bruylants, G. & Brancart, J. Magnetic self-healing composites: synthesis and applications. Molecules 27, 3796 (2022).
Bercea, M. Self-healing behavior of polymer/protein hybrid hydrogels. Polymers 14, 130 (2021).
Zhao, L. et al. Natural polymer-based hydrogels: from polymer to biomedical applications. Pharmaceutics 15, 2514 (2023).
Bustamante-Torres, M., Romero-Fierro, D., Arcentales-Vera, B., Pardo, S. & Bucio, E. Interaction between filler and polymeric matrix in nanocomposites: magnetic approach and applications. Polymers 13, 2998 (2021).
Chang, A., Babhadiashar, N., Barrett-Catton, E. & Asuri, P. Role of nanoparticle–polymer interactions on the development of double-network hydrogel nanocomposites with high mechanical strength. Polym. (Basel). 12, 470 (2020).
Zhao, L. et al. PAM-Flexible genome editing with an engineered chimeric Cas. Nat. Commun. 14, 6175 (2023).
Tang, Y. et al. Advances in Preparation and application of antibacterial hydrogels. J. Nanobiotechnol. 21, 300 (2023).
Prabhu, Y. T., Rao, K. V., Kumari, B. S., Kumar, V. S. S. & Pavani, T. Synthesis of Fe3O4 nanoparticles and its antibacterial application. Int. Nano Lett. 5, 85–92 (2015).
Yang, Y. et al. Injectable chitosan-based self-healing supramolecular hydrogels with temperature and pH dual-responsiveness. Int. J. Biol. Macromol. 227, 1038–1047 (2023).
Wei, Z. et al. Autonomous self-healing of poly(acrylic acid) hydrogels induced by the migration of ferric ions. Polym. Chem. 4, 4601 (2013).
Wang, Z., Zhai, X., Fan, M., Tan, H. & Chen, Y. Thermal-reversible and self-healing hydrogel containing magnetic microspheres derived from natural polysaccharides for drug delivery. Eur. Polym. J. 157, 110644 (2021).
Acknowledgements
The authors are grateful to Urmia University for supporting this research.
Author information
Authors and Affiliations
Contributions
F.Z. wrote the original draft and was responsible for data curation, investigation, methodology, and visualization. A.P.M. and M.M. contributed to the investigation, supervision, and writing – review and editing. All authors reviewed the manuscript.
Corresponding authors
Ethics declarations
Competing interests
The authors declare no competing interests.
Additional information
Publisher’s note
Springer Nature remains neutral with regard to jurisdictional claims in published maps and institutional affiliations.
Supplementary Information
Below is the link to the electronic supplementary material.
Rights and permissions
Open Access This article is licensed under a Creative Commons Attribution-NonCommercial-NoDerivatives 4.0 International License, which permits any non-commercial use, sharing, distribution and reproduction in any medium or format, as long as you give appropriate credit to the original author(s) and the source, provide a link to the Creative Commons licence, and indicate if you modified the licensed material. You do not have permission under this licence to share adapted material derived from this article or parts of it. The images or other third party material in this article are included in the article’s Creative Commons licence, unless indicated otherwise in a credit line to the material. If material is not included in the article’s Creative Commons licence and your intended use is not permitted by statutory regulation or exceeds the permitted use, you will need to obtain permission directly from the copyright holder. To view a copy of this licence, visit http://creativecommons.org/licenses/by-nc-nd/4.0/.
About this article
Cite this article
Zanbili, F., Poursattar Marjani, A. & Mahmoudian, M. Multi-responsive, room-temperature self-healing salep-based nanocomposite hydrogels with enhanced mechanical performance as smart biomaterial. Sci Rep (2026). https://doi.org/10.1038/s41598-026-38127-0
Received:
Accepted:
Published:
DOI: https://doi.org/10.1038/s41598-026-38127-0