Abstract
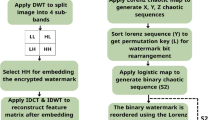
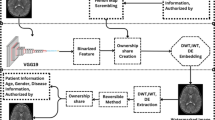
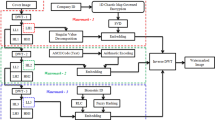
Zero-watermarking (ZW) presents a promising approach for safeguarding image copyright, as it does not alter the original image, a crucial feature for preserving the integrity of medical and high-fidelity visual data. Nevertheless, numerous existing ZW techniques are susceptible to geometric distortions and signal-processing attacks, thereby offering limited protection for ownership and licensing information. This paper proposes a robust and secure zero-watermarking scheme for medical and natural color images that jointly supports ownership authentication and license verification. The method combines entropy- and SIFT-based sub-region selection, DWT-DCT feature extraction, and XOR fusion between robust features and an Arnold-scrambled logo, followed by an ElGamal-style signcryption of the resulting share. Multiple local zero-watermarks are registered in a Certification Authority (CA), enabling global watermark reconstruction without altering the original image. Experimental results show that the normalized correlation (NC) between the recovered and watermark remains above 0.99 under various geometric and non-geometric attacks, confirming the robustness of the scheme. In addition, the signcryption module incurs low computational overhead, with both the encryption and joint decryption–verification processes requiring approximately 8.5 milliseconds. This overhead is small compared with the transform-based processing time and yields a favorable trade-off between enhanced cryptographic protection of ownership/license records and the computational efficiency required for practical medical imaging and large-scale copyright management systems.
Similar content being viewed by others
Data availability
The medical images used in this study were randomly selected from the publicly available The Cancer Imaging Archive (TCIA) repository and can be accessed at: [https://nbia.cancerimagingarchive.net/nbia-search/](https:/nbia.cancerimagingarchive.net/nbia-search) . In addition, three standard color images were obtained from the widely used USC-SIPI image database, available at: [http://sipi.usc.edu/database/](http:/sipi.usc.edu/database) . All datasets analysed during the current study are publicly available from the above repositories and were used in accordance with their respective terms of use.No additional permission or informed consent is required to publish or reuse the images used in this study. The medical images were obtained from The Cancer Imaging Archive (TCIA), which provides publicly available datasets that have been fully de-identified in accordance with applicable ethical and legal standards, including HIPAA. Therefore, the images do not contain any personally identifiable information. The color images were taken from the USC-SIPI standard image database, which is a publicly available benchmark dataset widely used for research and reproducibility purposes. Consequently, all images used in this study can be safely employed for reproducibility without ethical or consent-related restrictions.
Code availability
The core implementation of the proposed zero-watermarking framework is publicly available at: https://github.com/hungpt-mta/zero-watermarking-core. The provided code is sufficient to run the benchmarking procedures described in this paper. The experimental datasets are not redistributed within the code repository, but are publicly available from The Cancer Imaging Archive (TCIA) and the USC-SIPI image database, and can be obtained directly from their respective sources.
References
Nha, P. T., Thanh, T. M. & Phong, N. T. Consideration of a robust watermarking algorithm for color images using improved QR decomposition. Soft. Comput. 26(11), 5069–5093. https://doi.org/10.1007/s00500-022-06975-3 (2022).
Iwakiri, M. & Thanh, T. M. Incomplete cryptography method using invariant Huffman code length for digital rights management. In Proc. IEEE Int. Conf. Advanced Information Networking and Applications (AINA), 763–770. https://doi.org/10.1109/AINA.2012.112 (2012).
Gaur, S. & Barthwal, V. An extensive analysis of digital image watermarking techniques. Int. J. Intell. Syst. Appl. Eng. 12(1), 121–145 (2023).
Rana, M. S., Hasan, M. M. & Shuva, S. K. S. Digital image watermarking using discrete wavelet transform and discrete cosine transform with noise identification. In Proc. 2nd Int. Conf. Intelligent Technologies (CONIT), 1–4. https://doi.org/10.1109/CONIT55038.2022.9847745 (2022).
Thanh, T. M. & Tanaka, K. A novel q-DWT for blind and robust image watermarking. In Proc. IEEE Int. Symp. Personal, Indoor and Mobile Radio Communications (PIMRC), 2061–2065. https://doi.org/10.1109/PIMRC.2014.7136511 (2014).
Thanh, T. M. & Thanh, N. T. Extended DCT domain for improving the quality of watermarked images. In Proc. Int. Conf. Knowledge and Systems Engineering (KSE), 336–339. https://doi.org/10.1109/KSE.2015.70 (2015).
Iwakiri, M. & Thanh, T. M. Fundamental incomplete cryptography method for digital rights management based on JPEG lossy compression. In Proc. IEEE Int. Conf. Advanced Information Networking and Applications (AINA), 755–762. https://doi.org/10.1109/AINA.2012.111 (2012).
Xia, Y. et al. An adaptive blind color watermarking scheme based on Hadamard transform and information mapping system. Circuits Syst. Signal. Process. 44(5), 3432–3465. https://doi.org/10.1007/s00034-024-02971-0 (2025).
Beggari, A. S., Wali, A., Khaldi, A., Kafi, M. R. & Sahu, A. K. Secure and imperceptible medical image watermarking via multiscale QR embedding and attention-based optimization. Eng. Sci. Technol. Int. J. 73, 102250. https://doi.org/10.1016/j.jestch.2025.102250 (2026).
Sahu, A. K. & Mishra, S. (eds) Fortressing Pixels: Information Security for Images, Videos, Audio and Beyond https://doi.org/10.1049/PBSE030E (IET, 2024).
Sayah, M. M., Zermi, N., Khaldi, A. & Kafi, M. R. ECG signal protection using redundant discrete wavelet transform-based data hiding. In Fortressing Pixels: Information Security for Images, Videos, Audio and Beyond (eds Deb, S. et al.) ch. 2, https://doi.org/10.1049/PBSE030E_ch2 (The Institution of Engineering and Technology (IET), 2025).
Bekkari, F., Kafi, M. & Khaldi, A. Hybrid deep semantic query expansion using multi-objective fireworks-transformer optimization: a reinforcement learning approach. Evol. Intel. 18, 122. https://doi.org/10.1007/s12065-025-01109-8 (2025).
Beggari, A. S., Wali, A., Khaldi, A., Kafi, M. R. & Sahu, A. K. Robust medical image watermarking based on ridgelet transform and ant colony optimization for telemedicine security. Syst. Soft Comput. 7, 200390. https://doi.org/10.1016/j.sasc.2025.200390 (2025).
Beggari, A. S., Wali, A., Khaldi, A., Kafi, M. R. & Sahu, A. K. Robust and imperceptible medical image watermarking for telemedicine applications based on transform-domain and neural clustering techniques. J. Franklin Inst. 362(15), 108039. https://doi.org/10.1016/j.jfranklin.2025.108039 (2025).
Beggari, A. S., Wali, A., Khaldi, A., Kafi, M. R. & Sahu, A. K. FDCT-based watermarking for robust and imperceptible medical image protection. Intelligence-Based Med. 12, 100280. https://doi.org/10.1016/j.ibmed.2025.100280 (2025).
Sahu, A. K. & Sahu, M. Hybrid fragile image watermarking for tamper detection, localization and dual self-recovery. Eng. Sci. Technol. Int. J. 73, 102266. https://doi.org/10.1016/j.jestch.2025.102266 (2026).
Fang, Y. et al. Robust zero-watermarking algorithm for medical images based on SIFT and bandelet-DCT. Multimedia Tools Appl. 81(12), 16863–16879. https://doi.org/10.1007/s11042-022-12592-x (2022).
Su, Q., Liu, D. & Sun, Y. A robust adaptive blind color image watermarking scheme for resisting geometric attacks. Inf. Sci. 606, 194–212. https://doi.org/10.1016/j.ins.2022.05.046 (2022).
Hu, H. T. & Lee, T. T. Robust complementary dual image watermarking in subbands derived from the laplacian pyramid, discrete wavelet transform, and directional filter bank. Circuits Syst. Signal. Process. 41(7), 4090–4116. https://doi.org/10.1007/s00034-022-01975-y (2022).
Yuan, Y. et al. Robust zero-watermarking algorithm based on discrete wavelet transform and Daisy descriptors for encrypted medical images. CAAI Trans. Intell. Technol. 9(1), 40–53. https://doi.org/10.1049/cit2.12282 (2024).
Yuan, X. C. & Li, M. Local multi-watermarking method based on robust and adaptive feature extraction. Sig. Process. 149, 103–117. https://doi.org/10.1016/j.sigpro.2018.03.007 (2018).
Thanh, T. M. et al. Robust semi-blind video watermarking based on frame-patch matching. AEU – Int. J. Electron. Commun. 68(10), 1007–1015. https://doi.org/10.1016/j.aeue.2014.05.004 (2014).
Alcantarilla, P. F. et al. KAZE features, in Computer Vision – ECCV 2012, (eds Fitzgibbon, A.) 214–227 (Springer, 2012).
Pham, V. Q. et al. Geometrically invariant object-based watermarking using SIFT features. In Proc. IEEE Int. Conf. Image Processing (ICIP), Vol. 5, 473–476. https://doi.org/10.1109/ICIP.2007.4379868 (2007).
Hung, P. T. & Thanh, T. M. A strategy to select feature points for robust zero-watermarking algorithms. In Proc. RIVF Int. Conf. Computing and Communication Technologies, 63–67. https://doi.org/10.1109/RIVF64335.2024.11009088 (2024).
Tsai, H. H., Lai, Y. S. & Lo, S. C. A zero-watermark scheme with geometrical invariants using SVM and PSO against geometric attacks. J. Syst. Softw. 86(2), 335–348. https://doi.org/10.1016/j.jss.2012.08.040 (2013).
Nawaz, S. A. et al. Medical image zero-watermarking algorithm based on dual-tree complex wavelet transform, AlexNet, and discrete cosine transform. Appl. Soft Comput. 169, 112556. https://doi.org/10.1016/j.asoc.2024.112556 (2025).
Lowe, D. G. Distinctive image features from scale-invariant keypoints. Int. J. Comput. Vis. 60(2), 91–110 (2004).
Shannon, C. E. A mathematical theory of communication. Bell Syst. Tech. J. 27(3), 379–423, 27(4), 623–656 (1948).
Mallat, S. A theory for multiresolution signal decomposition: the wavelet representation. IEEE Trans. Pattern Anal. Mach. Intell. 11(7), 674–693 (1989).
Ahmed, N., Natarajan, T. & Rao, K. R. Discrete cosine transform. IEEE Trans. Computers. C-23(1), 90–93 (1974).
Arnold, V. I. & Avez, A. Ergodic Problems of Classical Mechanics(Benjamin, 1968).
Liao, X., Wong, K. & Chen, S. A novel image encryption algorithm based on chaotic maps. Chaos Solitons Fractals. 36(2), 432–444 (2008).
Thanh, N. K. et al. A public-key encryption–authentication scheme based on the elgamal cryptographic algorithm. J. Sci. Technique – Inform. Communication Technol. https://doi.org/10.56651/lqdtu.jst.v12.n1.658.ict (2023).
Zheng, Y. Digital signcryption or how to achieve cost (signature & encryption) ≪ cost (signature) + cost (encryption). In Advances in Cryptology – CRYPTO’97, LNCS, Vol. 1294, 165–179 (Springer, 1997).
National Institute of Standards and Technology. Digital Signature Standard (DSS), FIPS PUB 186 (U.S. Department of Commerce, 1994).
Funding
This research is funded by Vietnam National Foundation for Science and Technology Development (NAFOSTED) under grant number 04/2025/TN.
Author information
Authors and Affiliations
Contributions
Ta Minh Thanh: Supervision, Investigation, Conceptualization, Methodology. Pham Thai Hung: Code, Data curation, Visualization, Investigation, Software.
Corresponding author
Ethics declarations
Competing interests
The authors declare no competing interests.
Additional information
Publisher’s note
Springer Nature remains neutral with regard to jurisdictional claims in published maps and institutional affiliations.
Rights and permissions
Open Access This article is licensed under a Creative Commons Attribution-NonCommercial-NoDerivatives 4.0 International License, which permits any non-commercial use, sharing, distribution and reproduction in any medium or format, as long as you give appropriate credit to the original author(s) and the source, provide a link to the Creative Commons licence, and indicate if you modified the licensed material. You do not have permission under this licence to share adapted material derived from this article or parts of it. The images or other third party material in this article are included in the article’s Creative Commons licence, unless indicated otherwise in a credit line to the material. If material is not included in the article’s Creative Commons licence and your intended use is not permitted by statutory regulation or exceeds the permitted use, you will need to obtain permission directly from the copyright holder. To view a copy of this licence, visit http://creativecommons.org/licenses/by-nc-nd/4.0/.
About this article
Cite this article
Hung, P.T., Thanh, T.M. A robust zero-watermarking and signcryption scheme for image copyright protection and license verification. Sci Rep (2026). https://doi.org/10.1038/s41598-026-38991-w
Received:
Accepted:
Published:
DOI: https://doi.org/10.1038/s41598-026-38991-w