Abstract
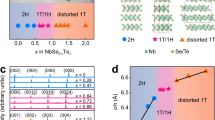
Polytypism in transition metal dichalcogenides (TMDs) introduces an additional degree of freedom for tailoring the electronic properties of layered van der Waals materials. Polytypes with larger unit cells, spanning four or six layers, can be viewed as natural homostructures, since their atomic composition remains identical across the layers. The resultant crystalline environments can potentially give rise to exotic electronic states, earning these materials recent attention. In this study, we examine structural and charge transport properties of metallic and superconducting 4Ha-NbSe2. We find that the compound has a highly disordered stacking of layers, which impedes interlayer coherence, as demonstrated by detailed out-of-plane resistivity measurements, and effectively tunes the bulk system towards an atomically thin limit. The disordered structure largely accounts for the enhanced resistivity anisotropy and superconducting upper critical field, when compared to 2Ha-NbSe2. This phenomenon can be exploited to promote quasi-two-dimensional physics in bulk crystals, and our study also underscores the importance of thorough structural characterization when investigating large-unit-cell polytypes of TMDs.
Similar content being viewed by others
Data availability
Data supporting the results of this paper can be provided by K.S. upon a reasonable request.
Code availability
Code used for processing the data in this work can be provided by K.S. upon a reasonable request.
References
Song, J. C. W. & Gabor, N. M. Electron quantum metamaterials in van der Waals heterostructures. Nat. Nanotechnol. 13, 986–993 (2018).
Katzke, H., Tolédano, P. & Depmeier, W. Phase transitions between polytypes and intralayer superstructures in transition metal dichalcogenides. Phys. Rev. B 69, 134111 (2004).
Witteveen, C. et al. Polytypism and superconductivity in the NbS2 system. Dalton Trans. 50, 3216–3223 (2021).
Ribak, A. et al. Chiral superconductivity in the alternate stacking compound 4Hb-TaS2. Sci. Adv. 6, eaax9480 (2020).
Silber, I. et al. Two-component nematic superconductivity in 4Hb-TaS2. Nat. Commun. 15, 824 (2024).
Leroux, M. et al. Traces of charge density waves in NbS2. Phys. Rev. B 97, 195140 (2018).
Martino, E. et al. Unidirectional Kondo scattering in layered NbS2. npj 2D Mater. Appl. 5, 86 (2021).
Kadijk, F. & Jellinek, F. On the polymorphism of niobium diselenide. J. Less. Common Met. 23, 437–441 (1971).
Xi, X. et al. Ising pairing in superconducting NbSe2 atomic layers. Nat. Phys. 12, 139–143 (2015).
Toyota, N. et al. Temperature and angular dependences of upper critical fields for the layer structure superconductor 2H-NbSe2. J. Low Temp. Phys. 25, 485–499 (1976).
Naik, I. & Rastogi, A. K. Charge density wave and superconductivity in 2H- and 4H-NbSe2: a revisit. Pramana 76, 957–963 (2011).
Meerschaut, A. & Deudon, C. Crystal structure studies of the 3R-Nb(1.09)S2 and the 2H-NbSe2 compounds: correlation between nonstoichiometry and stacking type (= polytypism). Mater. Res. Bull. 36, 1721–1727 (2011).
Zhou, M. et al. Structures, charge density wave, and superconductivity of noncentrosymmetric 4Ha-NbSe2. Phys. Rev. B 108, 224518 (2023).
Martino, E. et al. Preferential out-of-plane conduction and quasi-one-dimensional electronic states in layered 1T-TaS2. npj 2D Mater. Appl. 4, 7 (2020).
Moll, P. J. W. Focused ion beam microstructuring of quantum matter. Annu. Rev. Condens. Matter Phys. 9, 147–162 (2018).
Xi, X. et al. Strongly enhanced charge-density-wave order in monolayer NbSe2. Nat. Nanotechnol. 10, 765–769 (2015).
Calandra, M., Mazin, I. I. & Mauri, F. Effect of dimensionality on the charge-density wave in few-layer 2H-NbSe2. Phys. Rev. B 80, 241108 (2009).
He, R. et al. Interlayer breathing and shear modes in NbSe2 atomic layers. 2D Mater. 3, 031008 (2016).
Eremenko, V. et al. Heat capacity, thermal expansion and pressure derivative of critical temperature at the superconducting and charge density wave (CDW) transitions in NbSe2. Phys. C Supercond. 469, 259–264 (2009).
Volavka, D. et al. Ising superconductivity in noncentrosymmetric bulk NbSe2. Phys. Rev. Lett. https://doi.org/10.1103/qxb4-sf28 (2025).
Weber, F. et al. Three-dimensional Fermi surface of 2H−NbSe2: Implications for the mechanism of charge density waves. Phys. Rev. B 97, 235122 (2018).
Dordevic, S. V. et al. Optical properties of the quasi-two-dimensional dichalcogenides 2H-TaSe2 and 2H-NbSe2. Eur. Phys. J. B 33, 15–23 (2003).
Dvir, T. et al. Spectroscopy of bulk and few-layer superconducting NbSe2 with van der Waals tunnel junctions. Nat. Commun. 9, 598 (2018).
Kiss, T. et al. Charge-order-maximized momentum-dependent superconductivity. Nat. Phys. 3, 720–725 (2007).
Noat, Y. et al. Quasiparticle spectra of 2H-NbSe2: two-band superconductivity and the role of tunneling selectivity. Phys. Rev. B 92, 134510 (2015).
Martin, S. et al. Transport properties of Al65Cu15Co20 and Al70Ni15Co15 decagonal quasicrystals. Phys. Rev. Lett. 67, 719–722 (1991).
Korn, D., Mürer, W. & Zibold, G. C. Amorphous metallic systems.temperature dependence of the electrical resistivity of amorphous Ge, Sn And Bi alloys and its relation to superconductivity. J. Phys. Colloq. 35, C4-257–C4-260 (1974).
Forro, L. Out-of-plane resistivity of Bi2Sr2CaCu2O8+x high temperature superconductor. Phys. Lett. A 179, 140–144 (1993).
Forro, L. et al. Out-of-plane conductivity of YBa2Cu3O7−δ. Phys. Rev. B 46, 6626–6629 (1992).
Devarakonda, A. et al. Clean 2D superconductivity in a bulk van der Waals superlattice. Science 370, 231–236 (2020).
Sun, F. et al. Clean-limit 2D superconductivity in a thick exfoliated kagome film. Adv. Funct. Mater. e11314, online version at https://doi.org/10.1002/adfm.202511314 (2025).
Dyadkin, V. et al. A new multipurpose diffractometer PILATUS@SNBL. J. Synchrotron Radiat. 23, 825–829 (2016).
Petříček, V., Dušek, M. & Palatinus, L. Crystallographic computing system JANA2006:general features. Z. Kristallogr. 229, 345–352 (2014).
Foner, S. & McNiff, E. J. Upper critical fields of layered superconducting NbSe₂ at low temperature. Phys. Lett. A 45, 429–430 (1973).
Acknowledgements
E.M., K.S., and L.F. disclose the support of this work by the Swiss National Science Foundation through its SINERGIA network MPBH and grants No. 200021_175836 and PP00P2_170544.
Funding
Open Access funding enabled and organized by Projekt DEAL.
Author information
Authors and Affiliations
Contributions
E.M. and A.A. conducted the X-ray measurements. A.A. and Y.P. analyzed and interpreted the crystallographic data. H.B. produced the crystals of 2Ha-NbSe2 and 4Ha-NbSe2. E.M. and M.K. prepared the samples for resistivity measurements, which were conducted by E.M. and K.S., who also analyzed the data. E.M., L.F., and K.S. wrote the manuscript. The project was directed by L.F. and K.S.
Corresponding author
Ethics declarations
Competing interests
The authors declare no competing interests.
Additional information
Publisher’s note Springer Nature remains neutral with regard to jurisdictional claims in published maps and institutional affiliations.
Supplementary information
Rights and permissions
Open Access This article is licensed under a Creative Commons Attribution 4.0 International License, which permits use, sharing, adaptation, distribution and reproduction in any medium or format, as long as you give appropriate credit to the original author(s) and the source, provide a link to the Creative Commons licence, and indicate if changes were made. The images or other third party material in this article are included in the article’s Creative Commons licence, unless indicated otherwise in a credit line to the material. If material is not included in the article’s Creative Commons licence and your intended use is not permitted by statutory regulation or exceeds the permitted use, you will need to obtain permission directly from the copyright holder. To view a copy of this licence, visit http://creativecommons.org/licenses/by/4.0/.
About this article
Cite this article
Martino, E., Arakcheeva, A., Berger, H. et al. Towards atomically-thin regime in bulk 4H-NbSe2 with interlayer disorder. npj 2D Mater Appl (2026). https://doi.org/10.1038/s41699-025-00659-w
Received:
Accepted:
Published:
DOI: https://doi.org/10.1038/s41699-025-00659-w