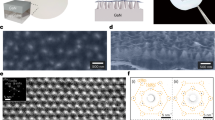
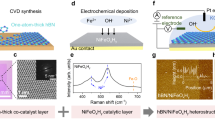
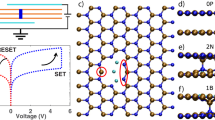
Abstract
Atomically thin hexagonal boron nitride (hBN) interlayers control interactions between electronic states of interfacing materials by modulating their separation at the atomic scale. These interlayers regulate interactions, whose strengths vary with distance. Here, we review how hBN is employed to enhance electronic and optoelectronic performance by mitigating disadvantageous interactions while preserving advantageous ones. Recent advances in hBN growth and integration are highlighted, and challenges that hinder widespread application are discussed.
Similar content being viewed by others
Data availability
No datasets were generated or analysed during the current study.
References
Geim, A. K. & Grigorieva, I. V. Van der Waals heterostructures. Nature 499, 419–425 (2013).
Liu, X. & Hersam, M. C. Interface Characterization and Control of 2D Materials and Heterostructures. Adv. Mater. 30, 1801586 (2018).
Harfah, H., Wicaksono, Y., Sunnardianto, G. K., Majidi, M. A. & Kusakabe, K. High magnetoresistance of a hexagonal boron nitride–graphene heterostructure-based MTJ through excited-electron transmission. Nanoscale Adv. 4, 117–124 (2022).
Jang, J. et al. Reduced dopant-induced scattering in remote charge-transfer-doped MoS2 field-effect transistors. Sci. Adv. 8, eabn3181 (2022).
Britnell, L. et al. Electron tunneling through ultrathin boron nitride crystalline barriers. Nano Lett. 12, 1707–1710 (2012).
Li, J. F. et al. Shell-isolated nanoparticle-enhanced Raman spectroscopy. Nature 464, 392–395 (2010).
Lee, D. et al. Remote modulation doping in van der Waals heterostructure transistors. Nat. Electron. 4, 664–670 (2021).
Cai, Q. et al. Boron nitride nanosheets improve sensitivity and reusability of surface-enhanced Raman spectroscopy. Angew. Chem. 128, 8545–8549 (2016).
Lee, M.-H. et al. Two-dimensional materials inserted at the metal/semiconductor interface: attractive candidates for semiconductor device contacts. Nano Lett. 18, 4878–4884 (2018).
Park, J.-H., Yang, S.-J., Choi, C.-W., Choi, S.-Y. & Kim, C.-J. Pristine graphene insertion at the metal/semiconductor interface to minimize metal-induced gap states. ACS Appl. Mater. Interfaces 13, 22828–22835 (2021).
Wang, J. I. et al. Hexagonal boron nitride as a low-loss dielectric for superconducting quantum circuits and qubits. Nat. Mater. 21, 398–403 (2022).
Mishchenko, A. et al. Twist-controlled resonant tunnelling in graphene/boron nitride/graphene heterostructures. Nat. Nanotechnol. 9, 808–813 (2014).
Ma, L. et al. Strongly correlated excitonic insulator in atomic double layers. Nature 598, 585–589 (2021).
Ma, K. Y., Kim, M. & Shin, H. S. Large-area hexagonal boron nitride layers by chemical vapor deposition: growth and applications for substrates, encapsulation, and membranes. Acc. Mater. Res. 3, 748–760 (2022).
Chernikov, A. et al. Exciton binding energy and nonhydrogenic rydberg series in monolayer WS2. Phys. Rev. Lett. 113, 076802 (2014).
Raja, A. et al. Dielectric disorder in two-dimensional materials. Nat. Nanotechnol. 14, 832–837 (2019).
Laturia, A., Van de Put, M. L. & Vandenberghe, W. G. Dielectric properties of hexagonal boron nitride and transition metal dichalcogenides: from monolayer to bulk. npj 2D. Mater. Appl. 2, 6 (2018).
Keldysh, L. V. Coulomb interaction in thin semiconductor and semimetal films. JETP Lett. 29, 716 (1979).
Berkelbach, T. C., Hybertsen, M. S. & Reichman, D. R. Theory of neutral and charged excitons in monolayer transition metal dichalcogenides. Phys. Rev. B. 88, 045318 (2013).
Utama, M. I. B. et al. A dielectric-defined lateral heterojunction in a monolayer semiconductor. Nat. Electron. 2, 60–65 (2019).
Bai, Y. et al. Ultrafast chemical imaging by widefield photothermal sensing of infrared absorption. Sci. Adv. 5, eaav7127 (2019).
Raja, A. et al. Coulomb engineering of the bandgap and excitons in two-dimensional materials. Nat. Commun. 8, 15251 (2017).
Lu, J. M. et al. Evidence for two-dimensional Ising superconductivity in gated MoS2. Science 350, 1353–1357 (2015).
Lu, X. et al. Superconductors, orbital magnets and correlated states in magic-angle bilayer graphene. Nature 574, 653–657 (2019).
van Loon, E. G. C. P. et al. Coulomb engineering of two-dimensional Mott materials. npj 2D Mater. Appl. 7, 47 (2023).
Cao, Y. et al. Correlated insulator behaviour at half-filling in magic-angle graphene superlattices. Nature 556, 80–84 (2018).
Florian, M. et al. The dielectric impact of layer distances on exciton and trion binding energies in van der Waals heterostructures. Nano Lett. 18, 2725–2732 (2018).
He, K. et al. Tightly bound excitons in monolayer WSe2. Phys. Rev. Lett. 113, 026803 (2014).
Ghosh, A. et al. Advancing excited-state properties of two-dimensional materials using a dielectric-dependent hybrid functional. Phys. Rev. B. 112, 045128 (2025).
Lin, Y. et al. Dielectric screening of excitons and trions in single-layer MoS2. Nano Lett. 14, 5569–5576 (2014).
Ross, J. S. et al. Electrically tunable excitonic light-emitting diodes based on monolayer WSe2 p–n junctions. Nat. Nanotechnol. 9, 268–272 (2014).
Ciarrocchi, A., Tagarelli, F., Avsar, A. & Kis, A. Excitonic devices with van der Waals heterostructures: valleytronics meets twistronics. Nat. Rev. Mater. 7, 449–464 (2022).
Rhodes, D., Chae, S. H., Ribeiro-Palau, R. & Hone, J. Disorder in van der Waals heterostructures of 2D materials. Nat. Mater. 18, 541–549 (2019).
Li, L. H. et al. Dielectric screening in atomically thin boron nitride nanosheets. Nano Lett. 15, 218–223 (2015).
Zastrow, M. Meet the crystal growers who sparked a revolution in graphene electronics. Nature 572, 429–433 (2019).
Dreher, P. et al. Proximity effects on the charge density wave order and superconductivity in single-layer NbSe2. ACS Nano 15, 19430–19438 (2021).
Veyrat, L. et al. Helical quantum Hall phase in graphene on SrTiO3. Science 367, 781–786 (2020).
Zollner, K., Gmitra, M., Frank, T. & Fabian, J. Theory of proximity-induced exchange coupling in graphene on hBN/(Co, Ni). Phys. Rev. B. 94, 155441 (2016).
Jafarpisheh, S. et al. Proximity-induced spin-orbit coupling in graphene/Bi1.5Sb0.5Te1.7Se1.3 heterostructures. Phys. Rev. B. 98, 241402 (2018).
Cohnitz, L., De Martino, A., Häusler, W. & Egger, R. Proximity-induced superconductivity in Landau-quantized graphene monolayers. Phys. Rev. B. 96, 140506 (2017).
Island, J. O. et al. Spin–orbit-driven band inversion in bilayer graphene by the van der Waals proximity effect. Nature 571, 85–89 (2019).
Lin, J.-X. et al. Spin-orbit–driven ferromagnetism at half moiré filling in magic-angle twisted bilayer graphene. Science 375, 437–441 (2022).
Fan, S. et al. Quantum tunneling in two-dimensional van der Waals heterostructures and devices. Sci. China Mater. 64, 2359–2387 (2021).
Yang, S.-J. et al. Wafer-scale programmed assembly of one-atom-thick crystals. Nano Lett. 22, 1518–1524 (2022).
Ko, K. et al. Competition between bipolar conduction modes in extrinsically p-doped MoS2: interaction with gate dielectric matters. ACS Nano 19, 1630–1641 (2025).
Liu, X., Choi, M. S., Hwang, E., Yoo, W. J. & Sun, J. Fermi level pinning dependent 2D semiconductor devices: challenges and prospects. Adv. Mater. 34, 2108425 (2022).
Liu, Y. et al. Approaching the Schottky–Mott limit in van der Waals metal–semiconductor junctions. Nature 557, 696–700 (2018).
Kim, C. et al. Fermi level pinning at electrical metal contacts of monolayer molybdenum dichalcogenides. ACS Nano 11, 1588–1596 (2017).
Lan, H.-Y., Tripathi, R., Appenzeller, J. & Chen, Z. Near-ideal subthreshold swing in scaled 2D transistors: the critical role of monolayer hBN passivation. IEEE Electron Dev. Lett. 45, 1337–1340 (2024).
Wang, J. et al. High Mobility MoS2 transistor with low Schottky barrier contact by using atomic thick h-BN as a tunneling layer. Adv. Mater. 28, 8302–8308 (2016).
Kim, Y. H. et al. Boltzmann switching MoS2 metal–semiconductor field-effect transistors enabled by monolithic-oxide-gapped metal gates at the schottky–mott limit. Adv. Mater. 36, 2314274 (2024).
Karpan, V. M., Khomyakov, P. A., Giovannetti, G., Starikov, A. A. & Kelly, P. J. Ni (111)|graphene|h-BN junctions as ideal spin injectors. Phys. Rev. B. 84, 153406 (2011).
Lee, M.-J. et al. Measurement of exciton and trion energies in multistacked hBN/WS2 coupled quantum wells for resonant tunneling diodes. ACS Nano 14, 16114–16121 (2020).
Xie, J. et al. On-chip direct synthesis of boron nitride memristors. Nat. Nanotechnol. 20, 1596–1604 (2025).
Asshoff, P. U. et al. Magnetoresistance in Co-hBN-NiFe tunnel junctions enhanced by resonant tunneling through single defects in ultrathin hBN barriers. Nano Lett. 18, 6954–6960 (2018).
Tian, J. et al. A Josephson junction with h-BN tunnel barrier: observation of low critical current noise. J. Phys. Condens. Matter 33, 495301 (2021).
Withers, F. et al. WSe2 light-emitting tunneling transistors with enhanced brightness at room temperature. Nano Lett. 15, 8223–8228 (2015).
Lorchat, E. et al. Filtering the photoluminescence spectra of atomically thin semiconductors with graphene. Nat. Nanotechnol. 15, 283–288 (2020).
Kim, G. et al. Hexagonal boron nitride/Au substrate for manipulating surface plasmon and enhancing capability of surface-enhanced Raman spectroscopy. ACS Nano 10, 11156–11162 (2016).
Guselnikova, O. et al. New trends in nanoarchitectured SERS substrates: nanospaces, 2D materials, and organic heterostructures. Small 18, 2107182 (2022).
Cai, Q. et al. Boron nitride nanosheet-veiled gold nanoparticles for surface-enhanced Raman scattering. ACS Appl. Mater. Interfaces 8, 15630–15636 (2016).
Caldwell, J. D. et al. Photonics with hexagonal boron nitride. Nat. Rev. Mater. 4, 552–567 (2019).
Splendiani, A. et al. Emerging photoluminescence in monolayer MoS2. Nano Lett. 10, 1271–1275 (2010).
Wang, C. et al. Monolayer atomic crystal molecular superlattices. Nature 555, 231–236 (2018).
Zhou, J. et al. Layered intercalation materials. Adv. Mater. 33, 2004557 (2021).
Xu, Z. et al. Synergistic effects of charge transfer, energy transfer and cavity interference on the exciton emission in WS2/hBN/WS2 heterostructures. Nanoscale 17, 18889–18899 (2025).
Kumar, P. et al. Light–matter coupling in large-area van der Waals superlattices. Nat. Nanotechnol. 17, 182–189 (2022).
Zhou, H. et al. Controlling exciton and valley dynamics in two-dimensional heterostructures with atomically precise interlayer proximity. ACS Nano 14, 4618–4625 (2020).
Fang, H. et al. Strong interlayer coupling in van der Waals heterostructures built from single-layer chalcogenides. Proc. Natl. Acad. Sci. USA 111, 6198–6202 (2014).
Vu, Q. A. et al. Tuning carrier tunneling in van der waals heterostructures for ultrahigh detectivity. Nano Lett. 17, 453–459 (2017).
Islam, M. S. et al. Growth mechanisms of monolayer hexagonal boron nitride (h-BN) on metal surfaces: theoretical perspectives. Nanoscale Adv. 5, 4041–4064 (2023).
Page, R. et al. Rotationally aligned hexagonal boron nitride on sapphire by high-temperature molecular beam epitaxy. Phys. Rev. Mater. 3, 064001 (2019).
Cho, Y.-J. et al. Hexagonal boron nitride tunnel barriers grown on graphite by high temperature molecular beam epitaxy. Sci. Rep. 6, 34474 (2016).
Moon, S. et al. Metal-organic chemical vapor deposition of hexagonal boron nitride: from high-quality growth to functional engineering. 2D Mater. 12, 042006 (2025).
Kobayashi, Y., Kumakura, K., Akasaka, T. & Makimoto, T. Layered boron nitride as a release layer for mechanical transfer of GaN-based devices. Nature 484, 223–227 (2012).
Sharma, S. et al. The influence of carbon on polytype and growth stability of epitaxial hexagonal boron nitride films. Adv. Mater. Interfaces 11, 2400091 (2024).
Ma, K. Y. et al. Epitaxial single-crystal hexagonal boron nitride multilayers on Ni (111). Nature 606, 88–93 (2022).
Kim, S. M. et al. Synthesis of large-area multilayer hexagonal boron nitride for high material performance. Nat. Commun. 6, 8662 (2015).
Shi, Z. et al. Vapor–liquid–solid growth of large-area multilayer hexagonal boron nitride on dielectric substrates. Nat. Commun. 11, 849 (2020).
Zhang, L., Kong, X., Dong, J. & Ding, F. A mechanism for thickness-controllable single crystalline 2D materials growth. Sci. Bull. 68, 2936–2944 (2023).
Jung, J. H. et al. Step-directed epitaxy of unidirectional hexagonal boron nitride on vicinal Ge (110). Small Struct. 5, 2400297 (2024).
Liu, Y., Huang, Y. & Duan, X. Van der Waals integration before and beyond two-dimensional materials. Nature 567, 323–333 (2019).
Pham, P. V. et al. Transfer of 2D films: from imperfection to perfection. ACS Nano 18, 14841–14876 (2024).
Kim, H. et al. Remote epitaxy. Nat. Rev. Methods Prim. 2, 40 (2022).
Kong, W. et al. Polarity governs atomic interaction through two-dimensional materials. Nat. Mater. 17, 999–1004 (2018).
Kim, H. et al. High-throughput manufacturing of epitaxial membranes from a single wafer by 2D materials-based layer transfer process. Nat. Nanotechnol. 18, 464–470 (2023).
Farmanbar, M. & Brocks, G. Ohmic contacts to 2D semiconductors through van der Waals bonding. Adv. Electron. Mater. 2, 1500405 (2016).
Farmanbar, M. & Brocks, G. Controlling the Schottky barrier at MoS2/metal contacts by inserting a BN monolayer. Phys. Rev. B. 91, 161304 (2015).
Wang, G., Yang, P., Moody, N. A. & Batista, E. R. Overcoming the quantum efficiency-lifetime tradeoff of photocathodes by coating with atomically thin two-dimensional nanomaterials. npj 2D Mater. Appl. 2, 17 (2018).
Park, J.-H. et al. Reduction of hole carriers by van der waals contact for enhanced photoluminescence quantum yield in two-dimensional tin halide perovskite. ACS Energy Lett. 8, 3536–3544 (2023).
Nguyen, V. L. et al. Layer-controlled single-crystalline graphene film with stacking order via Cu–Si alloy formation. Nat. Nanotechnol. 15, 861–867 (2020).
Zhao, C., Shan, L., Sun, R., Wang, X. & Ding, F. Wrinkle formation in synthesized graphene and 2D materials. Mater. Today 81, 104–117 (2024).
Wang, Y. et al. Ultraflat single-crystal hexagonal boron nitride for wafer-scale integration of a 2D-compatible high-κ metal gate. Nat. Mater. 23, 1495–1501 (2024).
Yuan, G. et al. Proton-assisted growth of ultra-flat graphene films. Nature 577, 204–208 (2020).
Hu, S. et al. Proton transport through one-atom-thick crystals. Nature 516, 227–230 (2014).
Yuan, Y. et al. On the quality of commercial chemical vapour deposited hexagonal boron nitride. Nat. Commun. 15, 4518 (2024).
Knobloch, T. et al. The performance limits of hexagonal boron nitride as an insulator for scaled CMOS devices based on two-dimensional materials. Nat. Electron. 4, 98–108 (2021).
Chubarov, M. et al. Wafer-scale epitaxial growth of unidirectional WS2 monolayers on sapphire. ACS Nano 15, 2532–2541 (2021).
Suenaga, K., Kobayashi, H. & Koshino, M. Core-level spectroscopy of point defects in single layer h-BN. Phys. Rev. Lett. 108, 075501 (2012).
Qiu, Z. et al. Atomic and electronic structure of defects in hBN: enhancing single-defect functionalities. ACS Nano 18, 24035–24043 (2024).
Tang, T. W. et al. Structured-defect engineering of hexagonal boron nitride for identified visible single-photon emitters. ACS Nano 19, 8509–8519 (2025).
Sankar, S. et al. Optical properties of low-defect large-area hexagonal boron nitride for quantum applications. Phys. Status Solidi RRL 18, 2400034 (2024).
Okonai, T. et al. Anomalous Raman signals in multilayer hexagonal boron nitride grown by chemical vapour deposition on metal foil catalysts. Nanoscale Adv. 7, 7538–7546 (2025).
Lyu, B. et al. Phonon polariton-assisted infrared nanoimaging of local strain in hexagonal boron nitride. Nano Lett. 19, 1982–1989 (2019).
Yang, Y. et al. Atomic defect quantification by lateral force microscopy. ACS Nano 18, 6887–6895 (2024).
Ismach, A. et al. Carbon-assisted chemical vapor deposition of hexagonal boron nitride. 2D Mater. 4, 025117 (2017).
Chen, M. et al. Ultrawide-bandwidth boron nitride photonic memristors. Nat. Nanotechnol. 20, 1633–1640 (2025).
Lee, G.-H. et al. Electron tunneling through atomically flat and ultrathin hexagonal boron nitride. Appl. Phys. Lett. 99, 243114 (2011).
Kaushik, N. et al. Reversible hysteresis inversion in MoS2 field effect transistors. npj 2D Mater. Appl. 1, 34 (2017).
Hwang, S. et al. A facile approach towards Wrinkle-Free transfer of 2D-MoS2 films via hydrophilic Si3N4 substrate. Appl. Surf. Sci. 604, 154523 (2022).
Zhao, P. et al. Understanding the impact of annealing on interface and border traps in the Cr/HfO2/Al2O3/MoS2 system. ACS Appl. Electron. Mater. 1, 1372–1377 (2019).
Qian, Q. et al. Improved gate dielectric deposition and enhanced electrical stability for single-layer MoS2 MOSFET with an AlN interfacial layer. Sci. Rep. 6, 27676 (2016).
McDonnell, S. et al. HfO2 on MoS2 by atomic layer deposition: adsorption mechanisms and thickness scalability. ACS Nano 7, 10354–10361 (2013).
Yan, H. et al. A clean van der Waals interface between the high-k dielectric zirconium oxide and two-dimensional molybdenum disulfide. Nat. Electron. 8, 906–912 (2025).
Xu, W. et al. Determining the optimized interlayer separation distance in vertical stacked 2D WS2:hBN:MoS2 heterostructures for exciton energy transfer. Small 14, 1703727 (2018).
Xu, W. et al. Controlling photoluminescence enhancement and energy transfer in WS2:hBN:WS2 vertical stacks by precise interlayer distances. Small 16, 1905985 (2020).
Park, H. et al. Atomically precise control of carbon insertion into hBN monolayer point vacancies using a focused electron beam guide. Small 17, 2100693 (2021).
Acknowledgements
This work was supported by the National R&D Program through the National Research Foundation of Korea (NRF) funded by the Ministry of Science and ICT (2023R1A2C2005427, RS-2023-00234622), and by the Institute for Basic Science (IBS-R034-D1).
Author information
Authors and Affiliations
Contributions
J.-H. J. and C.-J. K. conceived the outline of the review and wrote the manuscript. All authors have read and approved the final manuscript.
Corresponding author
Ethics declarations
Competing interests
The authors declare no competing interests.
Additional information
Publisher’s note Springer Nature remains neutral with regard to jurisdictional claims in published maps and institutional affiliations.
Rights and permissions
Open Access This article is licensed under a Creative Commons Attribution-NonCommercial-NoDerivatives 4.0 International License, which permits any non-commercial use, sharing, distribution and reproduction in any medium or format, as long as you give appropriate credit to the original author(s) and the source, provide a link to the Creative Commons licence, and indicate if you modified the licensed material. You do not have permission under this licence to share adapted material derived from this article or parts of it. The images or other third party material in this article are included in the article’s Creative Commons licence, unless indicated otherwise in a credit line to the material. If material is not included in the article’s Creative Commons licence and your intended use is not permitted by statutory regulation or exceeds the permitted use, you will need to obtain permission directly from the copyright holder. To view a copy of this licence, visit http://creativecommons.org/licenses/by-nc-nd/4.0/.
About this article
Cite this article
Jung, JH., Kim, CJ. Hexagonal boron nitride: interlayer with atomic scale precision for interface engineering in functional materials and devices. npj 2D Mater Appl (2026). https://doi.org/10.1038/s41699-026-00664-7
Received:
Accepted:
Published:
DOI: https://doi.org/10.1038/s41699-026-00664-7