Abstract
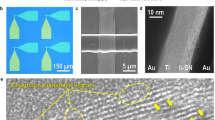
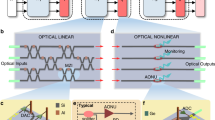
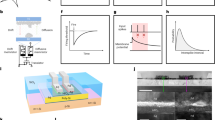
The continuing development of artificial intelligence requires more powerful computing architectures. However, the large footprint of complementary-metal–oxide–semiconductor-based neurons and constraints on electric routing hinder the scaling of conventional artificial neurons and their synaptic connectivity. Here we show that memristive blinking neurons can be used to build scalable photonically linked three-dimensional neural networks. Our artificial neuron is based on a silver/poly(methyl methacrylate)/silver metal–insulator–metal memristive switching in-plane junction. Its resistive switching relies on atomic-scale filamentary dynamics and the device emits photon pulses on integrating a critical number of incoming electrical spikes, which eliminates the need for bulky peripheral circuit read-out and electrical wiring for transmitting signals. We use the memristive blinking neuron, which has a footprint of 170 nm × 240 nm, to build a photonically linked three-dimensional spiking neural network. We show that the network can perform a four-class classification task within the Google Speech dataset with an accuracy of 91.51%. We also create a high-density artificial neuron array with a pitch of 1 μm and show that it can perform an MNIST classification task with an accuracy of 92.27%.
This is a preview of subscription content, access via your institution
Access options
Access Nature and 54 other Nature Portfolio journals
Get Nature+, our best-value online-access subscription
$32.99 / 30 days
cancel any time
Subscribe to this journal
Receive 12 digital issues and online access to articles
$119.00 per year
only $9.92 per issue
Buy this article
- Purchase on SpringerLink
- Instant access to the full article PDF.
USD 39.95
Prices may be subject to local taxes which are calculated during checkout





Similar content being viewed by others
Data availability
The data that support the plots and findings in this paper are available from the corresponding author upon request.
Code availability
The code for the SNN is publicly available via GitHub at https://github.com/Neuromorphic-Electronics-Photonics-Lab/Photonic-Linked-3D-Spiking-NN.
References
LeCun, Y., Bengio, Y. & Hinton, G. Deep learning. Nature 521, 436–444 (2015).
Reuther, A. et al. AI accelerator survey and trends. In 2022 IEEE High Performance Extreme Computing Conference (HPEC) https://doi.org/10.1109/HPEC49654.2021.9622867 (IEEE, 2022).
Dhar, P. The carbon impact of artificial intelligence. Nat. Mach. Intell. 2, 423–425 (2020).
Baldo, M. Introduction to Nanoelectronics (MIT OpenCourseWare, 2011).
International Roadmap for Devices and Systems (IRDS). 2020 edn (IEEE, 2020); https://irds.ieee.org/editions/2020
Samsi, S. et al. From words to watts: benchmarking the energy costs of large language model inference. In 2023 IEEE High Performance Extreme Computing Conference (HPEC) https://doi.org/10.1109/HPEC58863.2023.10363447 (IEEE, 2023).
Taylor, M. B. A landscape of the new dark silicon design regime. IEEE Micro 33, 8–19 (2013).
Kim, J. et al. A novel dimensionally-decomposed router for on-chip communication in 3D architectures. In Proc. 34th Annual International Symposium on Computer Architecture 138–149 (Association for Computing Machinery, 2007).
Esmaeilzadeh, H., Blem, E., St. Amant, R., Sankaralingam, K. & Burger, D. Dark silicon and the end of multicore scaling. In Proc. 38th Annual International Symposium on Computer Architecture 365–376 (IEEE, 2012).
Young, N., Collins, C. & Kaas, J. Cell and neuron densities in the primary motor cortex of primates. Front. Neural Circuits 7, 30 (2013).
Christensen, D. V. et al. 2022 roadmap on neuromorphic computing and engineering. Neuromorph. Comput. Eng. 2, 022501 (2022).
Choi, S., Yang, J. & Wang, G. Emerging memristive artificial synapses and neurons for energy-efficient neuromorphic computing. Adv. Mater. 32, 2004659 (2020).
Gökgöz, B., Gül, F. & Aydın, T. An overview memristor based hardware accelerators for deep neural network. Concurr. Comput.: Pract. Exp. 36, e7997 (2024).
Goossens, A. S. et al. Memristive memory enhancement by device miniaturization for neuromorphic computing. Adv. Electron. Mater. 9, 2201111 (2023).
Terabe, K., Hasegawa, T., Nakayama, T. & Aono, M. Quantized conductance atomic switch. Nature 433, 47–50 (2005).
Valov, I. et al. Nanobatteries in redox-based resistive switches require extension of memristor theory. Nat. Commun. 4, 1771 (2013).
Akinaga, H. & Shima, H. Resistive random access memory (ReRAM) based on metal oxides. Proc. IEEE 98, 2237–2251 (2010).
Jo, S. H. et al. Nanoscale memristor device as synapse in neuromorphic systems. Nano Lett. 10, 1297–1301 (2010).
Le Gallo, M. et al. A 64-core mixed-signal in-memory compute chip based on phase-change memory for deep neural network inference. Nat. Electron. 6, 680–693 (2023).
Wang, Z. et al. Fully memristive neural networks for pattern classification with unsupervised learning. Nat. Electron. 1, 137–145 (2018).
Aamir, S. A., Müller, P., Hartel, A., Schemmel, J. & Meier, K. A highly tunable 65-nm CMOS LIF neuron for a large scale neuromorphic system. In ESSCIRC Conference 2016: 42nd European Solid-State Circuits Conference 71–74 (IEEE, 2016).
Qiao, N. et al. A reconfigurable on-line learning spiking neuromorphic processor comprising 256 neurons and 128 K synapses. Front. Neurosci. 9, 141 (2015).
Sun, W. et al. Understanding memristive switching via in situ characterization and device modeling. Nat. Commun. 10, 3453 (2019).
Yang, R., Huang, H.-M. & Guo, X. Memristive synapses and neurons for bioinspired computing. Adv. Electron. Mater. 5, 1900287 (2019).
Corinto, F. & Forti, M. Memristor circuits: flux—charge analysis method. IEEE Trans. Circuits Syst. I, Reg. Papers 63, 1997–2009 (2016).
Amirsoleimani, A. et al. In-memory vector-matrix multiplication in monolithic complementary metal–oxide–semiconductor-memristor integrated circuits: design choices, challenges, and perspectives. Adv. Intell. Syst. 2, 2000115 (2020).
Güngördü, A. D., Dündar, G. & Yelten, M. B. A high performance TIA design in 40 nm CMOS. In Proc. 2020 IEEE International Symposium on Circuits and Systems (ISCAS) 1–5 (IEEE, 2020).
Aguirre, F. et al. Hardware implementation of memristor-based artificial neural networks. Nat. Commun. 15, 1974 (2024).
Zhou, Z. et al. Prospects and applications of on-chip lasers. eLight 3, 1 (2023).
Shastri, B. J. et al. Photonics for artificial intelligence and neuromorphic computing. Nat. Photon. 15, 102–114 (2021).
Lindenmann, N. et al. Photonic wire bonding: a novel concept for chip-scale interconnects. Opt. Express 20, 17667–17677 (2012).
Hamerly, R., Bernstein, L., Sludds, A., Soljačić, M. & Englund, D. Large-scale optical neural networks based on photoelectric multiplication. Phys. Rev. X 9, 021032 (2019).
Zhou, T. et al. Large-scale neuromorphic optoelectronic computing with a reconfigurable diffractive processing unit. Nat. Photonics 15, 367–373 (2021).
Ai, C. Y. et al. 0.56 μm-pitch CMOS image sensor for high resolution application. In Proc. International Image Sensor Workshop (IISW) 22–25 (IISW, 2023).
Uchiyama, M. et al. A 40/22 nm 200 MP stacked CMOS image sensor with 0.61 μm pixel. In Proc. International Image Sensor Workshop (IISW) 1–3 (IISW, 2021).
Hughes, R. W. & Warner, M. LEDs driven by a.c. without transformers or rectifiers. Sci. Rep. 11, 963 (2021).
Żak, M. et al. Bidirectional light-emitting diode as a visible light source driven by alternating current. Nat. Commun. 14, 7562 (2023).
Li, X. et al. Bright semiconductor single-photon sources pumped by heterogeneously integrated micropillar lasers with electrical injections. Light: Sci. Appl. 12, 65 (2023).
Qian, H. et al. Efficient light generation from enhanced inelastic electron tunnelling. Nat. Photon. 12, 485–488 (2018).
Cheng, B. et al. Atomic scale memristive photon source. Light: Sci. Appl. 11, 78 (2022).
Malchow, K. et al. Self-induced light emission in solid-state memristors replicates neuronal biophotons. ACS Nano 18, 24004–24011 (2024).
Cao, R. et al. Compact artificial neuron based on anti-ferroelectric transistor. Nat. Commun. 13, 7018 (2022).
Seok Jeong, D., Kim, I., Ziegler, M. & Kohlstedt, H. Towards artificial neurons and synapses: a materials point of view. RSC Adv. 3, 3169–3183 (2013).
Atluri, P. P. & Regehr, W. G. Determinants of the time course of facilitation at the granule cell to Purkinje cell synapse. J. Neurosci. 16, 5661 (1996).
Eshraghian, J. K., Wang, X. & Lu, W. D. Memristor-based binarized spiking neural networks: challenges and applications. IEEE Nanotechnol. Mag. 16, 14–23 (2022).
Li, X., Zhang, G., Huang, H. H., Wang, Z. & Zheng, W. Performance analysis of GPU-based convolutional neural networks. In Proc. 2016 45th International Conference on Parallel Processing (ICPP) 67–76 (IEEE, 2016).
Wong, C. Cubic millimetre of brain mapped in spectacular detail. Nature 629, 739–740 (2024).
Besrour, M. et al. Analog spiking neuron in 28 nm CMOS. In Proc. 2022 20th IEEE Interregional NEWCAS Conference (NEWCAS) 148–152 (IEEE, 2022).
Moradi, S., Bhave, S. A. & Manohar, R. Energy-efficient hybrid CMOS–NEMS LIF neuron circuit in 28 nm CMOS process. In Proc. 2017 IEEE Symposium Series on Computational Intelligence (SSCI) 1–5 (IEEE, 2017).
Feldmann, J., Youngblood, N., Wright, C. D., Bhaskaran, H. & Pernice, W. H. P. All-optical spiking neurosynaptic networks with self-learning capabilities. Nature 569, 208–214 (2019).
Wang, T. et al. Image sensing with multilayer nonlinear optical neural networks. Nat. Photon. 17, 408–415 (2023).
Chen, Y. et al. All-analog photoelectronic chip for high-speed vision tasks. Nature 623, 48–57 (2023).
Ashtiani, F., Geers, A. J. & Aflatouni, F. An on-chip photonic deep neural network for image classification. Nature 606, 501–506 (2022).
Acknowledgements
This work has been funded by the Young Scientists Fund of the National Natural Science Foundation of China (grant numbers 62305278 (to B.C.) and 62405255 (to R.X.)), the Werner Siemens Foundation (to J.L.) and the French Agence Nationale de la Recherche (ANR-17-EURE-0002 to A.B.). All experiments in this study are performed at Novel IC Exploration Facility (NICE), Guangzhou, China, and Laboratoire Interdisciplinaire Carnot de Bourgogne (ICB), Dijon, France. We thank the operations team of NICE and ICB for their help and support in the experiment setup. All samples in this study are fabricated at the cleanroom facilities of the Binnig and Rohrer Nanotechnology Center (BRNC), Ruschlikon, Switzerland. We thank the cleanroom operations team of the BRNC for their help and support in sample fabrication.
Author information
Authors and Affiliations
Contributions
B.C., A.B. and J.L. conceived the concept and supervised the project. R.G. fabricated the samples. Y.Z. carried out the measurements. Y.F. and H.R. designed and trained the network. H.F., Z.M. and Y.Z. optimized the experimental setup. Y.Z., Y.H., R.X. and B.C. analysed the data. Y.Z. performed the FEM simulation. Y.Z., Y.F., R.G., A.B., J.L. and B.C. wrote the manuscript. All authors discussed and commented on the manuscript.
Corresponding author
Ethics declarations
Competing interests
The authors declare no competing interests.
Peer review
Peer review information
Nature Electronics thanks Qionghai Dai, Ilia Valov and the other, anonymous, reviewer(s) for their contribution to the peer review of this work.
Additional information
Publisher’s note Springer Nature remains neutral with regard to jurisdictional claims in published maps and institutional affiliations.
Supplementary information
Supplementary Information
Supplementary Sections I–XI and Figs. 1–16.
Rights and permissions
Springer Nature or its licensor (e.g. a society or other partner) holds exclusive rights to this article under a publishing agreement with the author(s) or other rightsholder(s); author self-archiving of the accepted manuscript version of this article is solely governed by the terms of such publishing agreement and applicable law.
About this article
Cite this article
Zhou, Y., Fang, Y., Gisler, R. et al. Photonically linked three-dimensional neural networks based on memristive blinking neurons. Nat Electron (2026). https://doi.org/10.1038/s41928-025-01529-5
Received:
Accepted:
Published:
Version of record:
DOI: https://doi.org/10.1038/s41928-025-01529-5
This article is cited by
-
A photonically linked memristive neural network
Nature Electronics (2026)