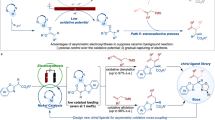
Abstract
Carboxylic ester motifs are prevalent in biological, chemical and materials sciences, and the asymmetric α-functionalization of simple esters plays a crucial role in the field of organic synthesis. Here we present a versatile electricity-driven asymmetric Lewis base catalysis strategy for the oxidative radical cross-coupling of simple esters with silyl enol ethers. This approach integrates the electrochemical anodic oxidation process with chiral isothiourea catalysis, enabling a polarity inversion at the nucleophilic carbon of the enolate to trigger the formation of a chiral isothiourea-bound α-carbonyl radical species from a C1-ammonium enolate. The combination of asymmetric Lewis base catalysis and electrochemistry unlocks mild oxidative radical coupling reactions, achieving up to 98% enantiomeric excess and demonstrating broad substrate compatibility. This work underscores the synthetic potential of the approach and provides a platform for advancing asymmetric electrosynthesis.

This is a preview of subscription content, access via your institution
Access options
Access Nature and 54 other Nature Portfolio journals
Get Nature+, our best-value online-access subscription
$32.99 / 30 days
cancel any time
Subscribe to this journal
Receive 12 digital issues and online access to articles
$119.00 per year
only $9.92 per issue
Buy this article
- Purchase on SpringerLink
- Instant access to the full article PDF.
USD 39.95
Prices may be subject to local taxes which are calculated during checkout







Similar content being viewed by others
Data availability
Crystallographic data for the structure reported in this Article have been deposited at the Cambridge Crystallographic Data Centre (CCDC) under deposition number CCDC 2378242 (3ad). Copies of the data can be obtained free of charge via https://www.ccdc.cam.ac.uk/structures/. The atomic coordinates from DFT calculations are provided in the Supplementary Data. All other data supporting the findings of this study, including experimental procedures, compound characterization, NMR and HPLC, are available within the Article and its Supplementary Information or from the authors.
References
Denmark, S. E. & Beutner, G. L. Lewis base catalysis in organic synthesis. Angew. Chem. Int. Ed. 47, 1560–1638 (2008).
Merad, J., Pons, J.-M., Chuzel, O. & Bressy, C. Enantioselective catalysis by chiral isothioureas. Eur. J. Org. Chem. 2016, 5589–5610 (2016).
Birman, V. B. Amidine based catalysts (ABCs): design, development, and applications. Aldrichimica Acta 49, 23–33 (2016).
McLaughlin, C. & Smith, A. D. Generation and reactivity of C(1)-ammonium enolates by using isothiourea catalysis. Chem. Eur. J. 27, 1533–1555 (2021).
West, T. H., Daniels, D. S. B., Slawin, A. M. Z. & Smith, A. D. An isothiourea-catalyzed asymmetric [2,3]-rearrangement of allylic ammonium ylides. J. Am. Chem. Soc. 136, 4476–4479 (2014).
Arokianathar, J. N., Frost, A. B., Slawin, A. M. Z., Stead, D. & Smith, A. D. Isothiourea-catalyzed enantioselective addition of 4-nitrophenyl esters to iminium ions. ACS Catal. 8, 1153–1160 (2018).
Zhao, F. et al. Enantioselective synthesis of α-aryl-β2-amino-esters by cooperative isothiourea and Brønsted acid catalysis. Angew. Chem. Int. Ed. 60, 11892–11900 (2021).
Schwarz, K. J., Amos, J. L., Klein, J. C., Do, D. T. & Snaddon, T. N. Uniting C1-ammonium enolates and transition metal electrophiles via cooperative catalysis: the direct asymmetric α-allylation of aryl acetic acid esters. J. Am. Chem. Soc. 138, 5214–5217 (2016).
Schwarz, K. J., Yang, C., Fyfe, J. W. B. & Snaddon, T. N. Enantioselective α-benzylation of acyclic esters using π-extended electrophiles. Angew. Chem. Int. Ed. 57, 12102–12105 (2018).
Jiang, X., Beiger, J. J. & Hartwig, J. F. Stereodivergent allylic substitutions with aryl acetic acid esters by synergistic iridium and Lewis base catalysis. J. Am. Chem. Soc. 139, 87–90 (2017).
Zhu, M., Wang, P., Zhang, Q., Tang, W. & Zi, W. Diastereodivergent Aldol-type coupling of alkoxyallenes with pentafluorophenyl esters enabled by synergistic palladium/chiral Lewis base catalysis. Angew. Chem. Int. Ed. 61, e202207621 (2022).
Kim, B., Kim, Y. & Lee, S. Y. Stereodivergent carbon–carbon bond formation between iminium and enolate intermediates by synergistic organocatalysis. J. Am. Chem. Soc. 143, 73–79 (2021).
Li, C.-J. Cross-dehydrogenative coupling (CDC): exploring C–C bond formations beyond functional group transformations. Acc. Chem. Res. 42, 335–344 (2009).
Girard, S. A., Knauber, T. & Li, C.-J. The cross-dehydrogenative coupling of Csp3—H bonds: a versatile strategy for C—C bond formations. Angew. Chem. Int. Ed. 53, 74–100 (2014).
Song, J., Zhang, Z.-J., Chen, S.-S., Fan, T. & Gong, L.-Z. Lewis base/copper cooperatively catalyzed asymmetric α-amination of esters with diaziridinone. J. Am. Chem. Soc. 140, 3177–3180 (2018).
Hartley, W. C., Schiel, F., Ermini, E. & Melchiorre, P. Lewis base-catalysed enantioselective radical conjugate addition for the synthesis of enantioenriched pyrrolidinones. Angew. Chem. Int. Ed. 61, e202204735 (2022).
del Río-Rodríguez, R. et al. Isothiourea-catalysed enantioselective radical conjugate addition under batch and flow conditions. Chem. Commun. 58, 7277–7280 (2022).
Yoshida, J., Kataoka, K., Horcajada, R. & Nagaki, A. Modern strategies in electroorganic synthesis. Chem. Rev. 108, 2265–2299 (2008).
Francke, R. & Little, R. D. Redox catalysis in organic electrosynthesis: basic principles and recent developments. Chem. Soc. Rev. 43, 2492–2521 (2014).
Yan, M., Kawamata, Y. & Baran, P. S. Synthetic organic electrochemical methods since 2000: on the verge of a renaissance. Chem. Rev. 117, 13230–13319 (2017).
Nutting, J. E., Rafiee, M. & Stahl, S. S. Tetramethylpiperidine N-oxyl (TEMPO), phthalimide N-oxyl (PINO), and related N-oxyl species: electrochemical properties and their use in electrocatalytic reactions. Chem. Rev. 118, 4834–4885 (2018).
Tang, S., Liu, Y. & Lei, A. Electrochemical oxidative cross-coupling with hydrogen evolution: a green and sustainable way for bond formation. Chem 4, 27–45 (2018).
Xiong, P. & Xu, H.-C. Chemistry with electrochemically generated N-centered radicals. Acc. Chem. Res. 52, 3339–3350 (2019).
Meyer, T., Choi, I., Tian, C. & Ackermann, L. Powering the future: how can electrochemistry make a difference in organic synthesis? Chem 6, 2484–2496 (2020).
Huang, X., Zhang, Q., Lin, J., Harms, K. & Meggers, E. Electricity-driven asymmetric Lewis acid catalysis. Nat. Catal. 2, 34–40 (2019).
Zhang, Q., Chang, X., Peng, L. & Guo, C. Asymmetric Lewis acid catalyzed electrochemical alkylation. Angew. Chem. Int. Ed. 58, 6999–7003 (2019).
Xiong, P., Hemming, M., Ivlev, S. I. & Meggers, E. Electrochemical enantioselective nucleophilic α-C(sp3)–H alkenylation of 2-acyl imidazoles. J. Am. Chem. Soc. 144, 6964–6971 (2022).
Liang, K., Zhang, Q. & Guo, C. Nickel-catalyzed switchable asymmetric electrochemical functionalization of alkenes. Sci. Adv. 8, eadd7134 (2022).
Zhang, Q., Liang, K. & Guo, C. Enantioselective nickel-catalyzed electrochemical radical allylation. Angew. Chem. Int. Ed. 61, e202210632 (2022).
Liang, K., Zhang, Q. & Guo, C. Enantioselective nickel-catalysed electrochemical cross-dehydrogenative amination. Nat. Synth. 2, 1184–1193 (2023).
Zhang, Q., Zhang, J., Zhu, W., Lu, R. & Guo, C. Enantioselective nickel-catalyzed anodic oxidative dienylation and allylation reactions. Nat. Commun. 15, 4477 (2024).
Zhang, J., Zhu, W., Chen, Z., Zhang, Q. & Guo, C. Dual-catalyzed stereodivergent electrooxidative homocoupling of benzoxazolyl acetate. J. Am. Chem. Soc. 146, 1522–1531 (2024).
Mazzarella, D. et al. Electrochemical asymmetric radical functionalization of aldehydes enabled by a redox shuttle. Angew. Chem. Int. Ed. 63, e202401361 (2024).
Ghosh, M., Shinde, V. S. & Rueping, M. A review of asymmetric synthetic organic electrochemistry and electrocatalysis: concepts, applications, recent developments and future directions. Beilstein J. Org. Chem. 15, 2710–2746 (2019).
Lin, Q., Li, L. & Luo, S. Asymmetric electrochemical catalysis. Chem. Eur. J. 25, 10033–10044 (2019).
Chang, X., Zhang, Q. & Guo, C. Asymmetric electrochemical transformations. Angew. Chem. Int. Ed. 59, 12612–12622 (2020).
Fu, N., Li, L., Yang, Q. & Luo, S. Catalytic asymmetric electrochemical oxidative coupling of tertiary amines with simple ketones. Org. Lett. 19, 2122–2125 (2017).
DeLano, T. J. & Reisman, S. E. Enantioselective electroreductive coupling of alkenyl and benzyl halides via nickel catalysis. ACS Catal. 9, 6751–6754 (2019).
Fu, N. et al. New bisoxazoline ligands enable enantioselective electrocatalytic cyanofunctionalization of vinylarenes. J. Am. Chem. Soc. 141, 14480–14485 (2019).
Dhawa, U. et al. Enantioselective pallada-electrocatalyzed C–H activation by transient directing groups: expedient access to helicenes. Angew. Chem. Int. Ed. 59, 13451–13457 (2020).
Li, L., Li, Y., Fu, N., Zhang, L. & Luo, S. Catalytic asymmetric electrochemical α-arylation of cyclic β-ketocarbonyls with anodic benzyne intermediates. Angew. Chem. Int. Ed. 59, 14347–14351 (2020).
Gao, P.-S. et al. CuII/TEMPO-catalyzed enantioselective C(sp3)–H alkynylation of tertiary cyclic amines through Shono-type oxidation. Angew. Chem. Int. Ed. 59, 15254–15259 (2020).
Song, L. et al. Dual electrocatalysis enables enantioselective hydrocyanation of conjugated alkenes. Nat. Chem. 12, 747–754 (2020).
Wang, Z.-H. et al. TEMPO-enabled electrochemical enantioselective oxidative coupling of secondary acyclic amines with ketones. J. Am. Chem. Soc. 143, 15599–15605 (2021).
Zhou, P., Li, W., Lan, J. & Zhu, T. Electroredox carbene organocatalysis with iodide as promoter. Nat. Commun. 13, 3827 (2022).
Ding, W., Li, M., Fan, J. & Cheng, X. Palladium-catalyzed asymmetric allylic 4-pyridinylation via electroreductive substitution reaction. Nat. Commun. 13, 5642 (2022).
Tan, X., Wang, Q. & Sun, J. Electricity-driven asymmetric bromocyclization enabled by chiral phosphate anion phase-transfer catalysis. Nat. Commun. 14, 357 (2023).
Gao, S., Wang, C., Yang, J. & Zhang, J. Cobalt-catalyzed enantioselective intramolecular reductive cyclization via electrochemistry. Nat. Commun. 14, 1301 (2023).
von Münchow, T., Dana, S., Xu, Y., Yuan, B. & Ackermann, L. Enantioselective electrochemical cobalt-catalyzed aryl C–H activation reactions. Science 379, 1036–1042 (2023).
Hu, X., Cheng-Sánchez, I., Cuesta-Galisteo, S. & Nevado, C. Nickel-catalyzed enantioselective electrochemical reductive cross-coupling of aryl aziridines with alkenyl bromides. J. Am. Chem. Soc. 145, 6270–6279 (2023).
Gao, Y., Zhang, B., He, J. & Baran, P. S. Ni-electrocatalytic enantioselective doubly decarboxylative C(sp3)–C(sp3) cross coupling. J. Am. Chem. Soc. 145, 11518–11523 (2023).
Yao, Q.-J., Huang, F.-R., Chen, J.-H., Zhong, M.-Y. & Shi, B.-F. Enantio- and regioselective electrooxidative cobalt-catalyzed C–H/N–H annulation with alkenes. Angew. Chem. Int. Ed. 62, e202218533 (2023).
Sibi, M. P. & Porter, N. A. Enantioselective free radical reactions. Acc. Chem. Res. 32, 163–171 (1999).
Mondal, S. et al. Enantioselective radical reactions using chiral catalysts. Chem. Rev. 122, 5842–5976 (2022).
Sibi, M. P., Ji, J., Wu, J. H., Gürtler, S. & Porter, N. A. Chiral Lewis acid catalysis in radical reactions: enantioselective conjugate radical additions. J. Am. Chem. Soc. 118, 9200–9201 (1996).
Sibi, M. P., Ji, J., Sausker, J. B. & Jasperse, C. P. Free radical-mediated intermolecular conjugate additions. Effect of the Lewis acid, chiral auxiliary, and additives on diastereoselectivity. J. Am. Chem. Soc. 121, 7517–7526 (1999).
Sibi, M. P. & Chen, J. Enantioselective tandem radical reactions: vicinal difunctionalization in acyclic systems with control over relative and absolute stereochemistry. J. Am. Chem. Soc. 123, 9472–9473 (2001).
Sibi, M. P., Zimmerman, J. & Rheault, T. Enantioselective conjugate radical addition to β-acyloxy acrylate acceptors: an approach to acetate Aldol-type products. Angew. Chem. Int. Ed. 42, 4521–4523 (2003).
Sibi, M. P., Petrovic, G. & Zimmerman, J. Enantioselective radical addition/trapping reactions with α,β-disubstituted unsaturated imides. Synthesis of anti-propionate aldols. J. Am. Chem. Soc. 127, 2390–2391 (2005).
Beeson, T. D., Mastracchio, A., Hong, J.-B., Ashton, K. & MacMillan, D. W. C. Enantioselective organocatalysis using SOMO activation. Science 316, 582–585 (2007).
Sibi, M. P. & Hasegawa, M. Organocatalysis in radical chemistry. Enantioselective α-oxyamination of aldehydes. J. Am. Chem. Soc. 129, 4124–4125 (2007).
Mastracchio, A., Warkentin, A. A., Walji, A. M. & MacMillan, D. W. C. Direct and enantioselective α-allylation of ketones via singly occupied molecular orbital (SOMO) catalysis. Proc. Natl Acad. Sci. USA 107, 20648–20651 (2010).
Zhao, F. et al. Enantioselective aza-ene-type reactions of enamides with gold carbenes generated from α-diazoesters. Angew. Chem. Int. Ed. 56, 3247–3251 (2017).
Birman, V. B., Li, X. & Han, Z. Nonaromatic amidine derivatives as acylation catalysts. Org. Lett. 9, 37–40 (2007).
Liu, P., Yang, X., Birman, V. B. & Houk, K. N. Origin of enantioselectivity in benzotetramisole-catalyzed dynamic kinetic resolution of azlactones. Org. Lett. 14, 3288–3291 (2012).
Greenhalgh, M. D. et al. A C=O···isothiouronium interaction dictates enantiodiscrimination in acylative kinetic resolutions of tertiary heterocyclic alcohols. Angew. Chem. Int. Ed. 57, 3200–3206 (2018).
Young, C. M. et al. The importance of 1,5-oxygen···chalcogen interactions in enantioselective isochalcogenourea catalysis. Angew. Chem. Int. Ed. 59, 3705–3710 (2020).
Acknowledgements
We acknowledge financial support from the National Natural Science Foundation of China (22071229 and 22471002) and the Anhui Provincial Natural Science Foundation (2308085Y12).
Author information
Authors and Affiliations
Contributions
J.S. conceived the project. N.L. performed the experiments and analysed the data. X.Y. and Y.L. synthesized some of the substrates and catalysts. All authors discussed the results and prepared the paper.
Corresponding author
Ethics declarations
Competing interests
The authors declare no competing interests.
Peer review
Peer review information
Nature Catalysis thanks the anonymous reviewers for their contribution to the peer review of this work.
Additional information
Publisher’s note Springer Nature remains neutral with regard to jurisdictional claims in published maps and institutional affiliations.
Supplementary information
Supplementary Information
Supplementary Figs. 1–15 and Tables 1–8.
Supplementary Data 1
The atomic coordinates of the optimized computational models studied in this paper.
Supplementary Data 2
CIF of compound 3ad.
Rights and permissions
Springer Nature or its licensor (e.g. a society or other partner) holds exclusive rights to this article under a publishing agreement with the author(s) or other rightsholder(s); author self-archiving of the accepted manuscript version of this article is solely governed by the terms of such publishing agreement and applicable law.
About this article
Cite this article
Li, N., Ye, X., Liu, Y. et al. Enantioselective radical α-enolation of esters via electrochemical chiral isothiourea catalysis. Nat Catal 8, 957–967 (2025). https://doi.org/10.1038/s41929-025-01408-4
Received:
Accepted:
Published:
Version of record:
Issue date:
DOI: https://doi.org/10.1038/s41929-025-01408-4